Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Skin Structure
Skin Structure
Uploaded by
Mm Noona0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesOriginal Title
skin structure
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesSkin Structure
Skin Structure
Uploaded by
Mm NoonaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Jaravata, Jhuliana Marie
BSN-1H
Functions of Skin Structure on the Body
The skin serves several important functions in maintaining the body's overall
health and well-being. Some of the key functions of skin structures include:
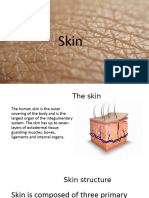
1. Protection: The skin acts as a barrier that protects the body from physical injury,
harmful microorganisms, and UV radiation. The outermost layer of the skin, called
the epidermis, provides a protective shield against external threats.
2. Regulation of body temperature: The skin plays a crucial role in
thermoregulation by helping to maintain a stable internal body temperature. This is
achieved through processes such as sweating to cool the body and shivering to
generate heat.
3. Sensation: The skin contains a network of sensory receptors that allow us to
detect touch, pressure, temperature, and pain. These sensations are essential for
interacting with the external environment and avoiding potential harm.
4. Immune function: Skin structures, including specialized immune cells,
contribute to the body's immune defenses by identifying and combating pathogens
that come into contact with the skin.
5. Vitamin D synthesis: The skin is involved in the production of vitamin D when
it is exposed to sunlight. Vitamin D is essential for maintaining healthy bones and
overall immune function.
Overall, the skin structures play a vital role in protecting the body, regulating
internal processes, and facilitating sensory experiences.
You might also like
- Integumentary System-GRADE 6 MARCOSDocument41 pagesIntegumentary System-GRADE 6 MARCOSCRISTILE ANN GESMAN100% (1)
- Integumentary SystemDocument24 pagesIntegumentary SystemlloydNo ratings yet
- Yoga 4 Immune SystemDocument33 pagesYoga 4 Immune Systemsukunath100% (1)
- SkinDocument5 pagesSkinRodrigo Cantú ValdezNo ratings yet
- SkinDocument1 pageSkinal christfy catongNo ratings yet
- Jeab 101Document23 pagesJeab 101Dharmveer KumarNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System Lab Report: Structure and Function of The SkinDocument4 pagesIntegumentary System Lab Report: Structure and Function of The Skinapi-296683192No ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument2 pagesIntegumentary SystemKrystle GopaulNo ratings yet
- SkinDocument36 pagesSkinNatukunda DianahNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Group 2 Abm 11 C FinalDocument18 pagesCase Study of Group 2 Abm 11 C FinalRonaldo GonzalesNo ratings yet
- MTRT MagazineDocument77 pagesMTRT Magazinedainty pearl juezanNo ratings yet
- Limson - Human AnatomyDocument20 pagesLimson - Human AnatomyFaye RabulanNo ratings yet
- Functions of Each Part of The Intergumentary System.1Document61 pagesFunctions of Each Part of The Intergumentary System.1Jane Ilagan VizcoNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument2 pagesIntegumentary SystemErica RosislifeNo ratings yet
- PhysiologyDocument6 pagesPhysiologyFidiya NasirNo ratings yet
- Vincent VargasDocument3 pagesVincent Vargasapi-296590370No ratings yet
- Integumentary System: Prepared By: Lyra May C. Languido Judith Capoy Alexander Kenn P. CabudlanDocument24 pagesIntegumentary System: Prepared By: Lyra May C. Languido Judith Capoy Alexander Kenn P. CabudlanLyra May LanguidoNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument6 pagesIntegumentary SystemNhecel PascuaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument10 pagesIntegumentary SystemJohn Roi PeñafloridaNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary System Is Made Up of Several Organs and Structures Including The SkinDocument3 pagesThe Integumentary System Is Made Up of Several Organs and Structures Including The SkinAxel NeoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory: Session 13 Lesson ReviewDocument2 pagesLaboratory: Session 13 Lesson ReviewzimoneNo ratings yet
- Human Body System and CellsDocument101 pagesHuman Body System and CellsahmedNo ratings yet
- Analec Reaction PaperDocument1 pageAnalec Reaction Paperyuri dominxNo ratings yet
- Immune System: Nama Kelompok: 1. Anis Dwika Indriyani 2. Erma Nor Hidayah 3. Nanda Nur LatifaDocument8 pagesImmune System: Nama Kelompok: 1. Anis Dwika Indriyani 2. Erma Nor Hidayah 3. Nanda Nur LatifaNia Ayu RNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On Wound Care - With CommentsDocument7 pagesLesson Plan On Wound Care - With CommentsJoyJoy Tabada CalunsagNo ratings yet
- Anatomy OshDocument3 pagesAnatomy Oshpewpavithren19No ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument4 pagesIntegumentary Systemlmn4126No ratings yet
- General Science Unit 4-5 PDFDocument90 pagesGeneral Science Unit 4-5 PDFwildwolfNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument6 pagesIntegumentary Systemrosalyn gaboniNo ratings yet
- Review Human BodyDocument2 pagesReview Human BodyNicole GarcíaNo ratings yet
- How To Increase The Immune BodyDocument11 pagesHow To Increase The Immune BodyMuhammad Brahmana PutraNo ratings yet
- Science 6 - Q2 - L2 - Parts and Functions of The Integumentary SystemDocument31 pagesScience 6 - Q2 - L2 - Parts and Functions of The Integumentary SystemSonny MatiasNo ratings yet
- What To Know About The Integumentary SystemDocument2 pagesWhat To Know About The Integumentary Systemrosalyn gaboniNo ratings yet
- Intergumentary System: Skin Hair Nails ExocrineDocument2 pagesIntergumentary System: Skin Hair Nails ExocrineDennis VolanteNo ratings yet
- Informe de InglesDocument9 pagesInforme de InglesGabriela Ochoa CornejoNo ratings yet
- Ibd IntegumenDocument12 pagesIbd IntegumenIfanNo ratings yet
- IntegumentaryDocument6 pagesIntegumentarytrisha anne uberasNo ratings yet
- Paper Integument System: Group 6 Name: Rosita Rahmayani Rian Indrasuari NopinahDocument11 pagesPaper Integument System: Group 6 Name: Rosita Rahmayani Rian Indrasuari NopinahAzkil AzkiyaNo ratings yet
- Muscular and Integumentary System NotesDocument2 pagesMuscular and Integumentary System Notesraff estradaNo ratings yet
- XI Notes Immune System-2Document26 pagesXI Notes Immune System-2ramsha.wahid29No ratings yet
- Skin Disorder - ENDocument1 pageSkin Disorder - ENluismanguneaeNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2: Quarter 4: Week 4 - Module 1D PDocument25 pagesGeneral Biology 2: Quarter 4: Week 4 - Module 1D PSyrine Myles Sullivan100% (1)
- The Integumentary System NotesDocument3 pagesThe Integumentary System NotesJose Enrico SumayaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Activity 4 - Step 2 and Step 3 - MorenoDocument2 pagesLesson 1 - Activity 4 - Step 2 and Step 3 - MorenoAiza SaripNo ratings yet
- The Immune System NotesDocument2 pagesThe Immune System Notesapi-265180883No ratings yet
- By Cody Guidry: Integumentary System Lab ReportDocument2 pagesBy Cody Guidry: Integumentary System Lab Reportapi-296590119No ratings yet
- Mpe 5Document20 pagesMpe 5JC SabasNo ratings yet
- Module 2: The Organ SystemsDocument6 pagesModule 2: The Organ SystemsJayNo ratings yet
- Idioma Moderno Act 1Document2 pagesIdioma Moderno Act 1Rania SenhajiNo ratings yet
- The SkinDocument5 pagesThe SkinMigvelito219No ratings yet
- Skin - Integumentary System: Make Sentences Using The Following Words, in The Context of SkinDocument5 pagesSkin - Integumentary System: Make Sentences Using The Following Words, in The Context of SkinAsdNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument13 pagesEarth and Life ScienceShareah Faith BalanguiNo ratings yet
- Gs Grade 4Document119 pagesGs Grade 4Mekonnen AssefaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument17 pagesIntegumentary SystemDannica Trisha CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- What Is The Integumentary KeahDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Integumentary KeahJanine GuillermoNo ratings yet
- The Skin PDFDocument3 pagesThe Skin PDFThomas KurtzNo ratings yet
- THE INTEGUMENT ORGAN: The Integument As An Organ and Is An Alternative Name ForDocument16 pagesTHE INTEGUMENT ORGAN: The Integument As An Organ and Is An Alternative Name ForPdianghunNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 3 AnaphysDocument5 pagesACTIVITY 3 Anaphys리아No ratings yet
- The SkinDocument12 pagesThe Skinnikakalmaxelidze155No ratings yet
- Immune System And Function, A Simple Guide And Related ConditionsFrom EverandImmune System And Function, A Simple Guide And Related ConditionsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- LET Answer Sheets LongDocument1 pageLET Answer Sheets LongMm NoonaNo ratings yet
- Twinkl Receipt 22159846 27527117Document1 pageTwinkl Receipt 22159846 27527117Mm NoonaNo ratings yet
- Science Final DemoDocument8 pagesScience Final DemoMm NoonaNo ratings yet
- Reading A Thermometer: Answer KeyDocument2 pagesReading A Thermometer: Answer KeyMm NoonaNo ratings yet
- Utang KagawadDocument2 pagesUtang KagawadMm NoonaNo ratings yet
- Colorful Illustration Study Habits PresentationDocument2 pagesColorful Illustration Study Habits PresentationMm NoonaNo ratings yet
- Pdf&rendition 1Document17 pagesPdf&rendition 1Mm NoonaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document15 pagesLesson 2Mm NoonaNo ratings yet
- Q4 Summative 1 MathematicsDocument2 pagesQ4 Summative 1 MathematicsMm NoonaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Working Out Grid PaperDocument1 pageMathematics Working Out Grid PaperMm NoonaNo ratings yet
- Mystery Box Volume of CylinderDocument40 pagesMystery Box Volume of CylinderMm NoonaNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH4Q4MODULE2Document13 pagesENGLISH4Q4MODULE2Mm NoonaNo ratings yet
- Educ 107 - MidexamDocument4 pagesEduc 107 - MidexamMm NoonaNo ratings yet
- WEEK 3 DateDocument2 pagesWEEK 3 DateMm NoonaNo ratings yet
- Why Should You As An Individual Respect and Value People Who Are Different From YouDocument1 pageWhy Should You As An Individual Respect and Value People Who Are Different From YouMm NoonaNo ratings yet
- Banera Joanna Marie S. Bsed 2 Math Lesson Plan ActivityDocument3 pagesBanera Joanna Marie S. Bsed 2 Math Lesson Plan ActivityMm NoonaNo ratings yet
- EGED 111 Module 2Document43 pagesEGED 111 Module 2Mm NoonaNo ratings yet
- Enc Encoded K 5 VRH FTND Uuq 7 O4 C 8 Morz 2 X8 C 7 NWZ XLKLON3 HWQ GZ Wykb QP EEced YAn JS6 Oyi N2 MS67 JZNJ TDocument11 pagesEnc Encoded K 5 VRH FTND Uuq 7 O4 C 8 Morz 2 X8 C 7 NWZ XLKLON3 HWQ GZ Wykb QP EEced YAn JS6 Oyi N2 MS67 JZNJ TMm NoonaNo ratings yet
- Free Higher Education Application Form: TH TH ND TH RD STDocument2 pagesFree Higher Education Application Form: TH TH ND TH RD STMm NoonaNo ratings yet
- Jose Rizal and Philippine Nationalism: Ba Yan/ andDocument10 pagesJose Rizal and Philippine Nationalism: Ba Yan/ andMm NoonaNo ratings yet
- Module2 Eged 113 PDFDocument3 pagesModule2 Eged 113 PDFMm NoonaNo ratings yet
- Geec 111 Module 1 Lesson 1Document11 pagesGeec 111 Module 1 Lesson 1Mm NoonaNo ratings yet
- Gecc 101 Module 5 Lesson 1Document5 pagesGecc 101 Module 5 Lesson 1Mm NoonaNo ratings yet
- Gecc 101 Module 1 Lesson 2Document15 pagesGecc 101 Module 1 Lesson 2Mm NoonaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: Jose Rizal and Philippine Nationalism: National SymbolDocument9 pagesLesson 2: Jose Rizal and Philippine Nationalism: National SymbolMm NoonaNo ratings yet
- Gecc 101 Module 4 Lesson 2Document11 pagesGecc 101 Module 4 Lesson 2Mm NoonaNo ratings yet
- Gecc 101 Module 4 Lesson 1Document6 pagesGecc 101 Module 4 Lesson 1Mm Noona100% (1)