Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Summary of Nervous System
Uploaded by
Elaf NaifCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Summary of Nervous System
Uploaded by
Elaf NaifCopyright:
Available Formats
Physiology Summary
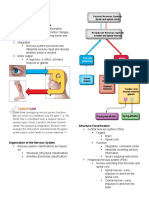
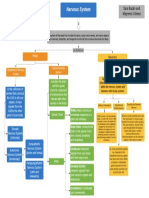
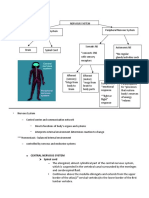
The Nervous System :
•Function : Master control , communication
• cells communicate by electrical , chemical singles -> rapid , speci c -> immediate responses .
• Function and division of the nervous system :
1- Sensory input: Sensory receptors monitor changes inside and outside the body. The gathered information is called sensory input.
2- Integration : Processing and interpretation of sensory input and decides what should be done at each moment .
3- Motor output : Activation of muscles and glands to cause a response.
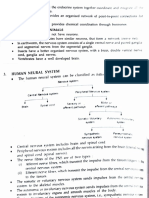
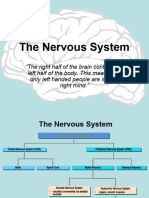
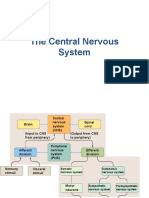
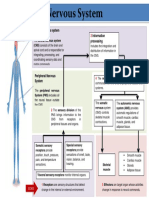
Nervous System
CNS PNS
— Consist of the brain , spinal cord — outside the CNS
— integrating and control center of the nervous system — Consist of the nerves (bundles of axons )
— interprets sensory input
— dictates motor output based on re exes, current Spinal carry impulses to and from the spinal cord
Cranial
conditions, and past experience. Nerve carry impulses to and from the brain Nerve
— These peripheral nerves serve as
communication lines that link all parts of the
body to the CNS.
Efferent [ Motor ] Afferent [ Sensory ]
Consist of nerve bres (axons ) that transmit impulses Consist of nerve bres (axons ) that convey impulses to the
from the CNS to effect organ ( muscles , glands ) CNS from sensory receptors located thought out the body
Visceral Sensory Somatic Sensory
Autonomic Nervous Somatic Nervous
bres bres
System System
Sympathetic 1- Involuntary Convey impulses from
1- Voluntary
Convey impulses from Skin - Skeletal muscles -
2- Visceral motor nerve bres 2- somatic motor nerve bres
Visceral organs Joint
Parasympathetic 3- CNS ⇾ Cardiac Muscle , 3- CNS ⇾ Skeletal Muscle
smooth muscles, glands
• Histology of the Nervous Tissue : The nervous system are densely packed and tightly intertwined. It is made up of two types of cells:
Neurons
Neuroglia
Nerve cells | excitable
Supporting cells | small | (responsive to stimuli) and
surround and wrap the transmit electrical signals
more delicate neurons
PNS CNS
Make up about half the mass of the brain
Satellite cells
Oligodendrocytes Ependymal Microglial Astrocytes
1- Surround neuron cell bodies
2- Similar to the astrocytes of 1- Fewer processes than 1- Squamous to columnar 1- Small , ovoid , long
CNS in function. - shaped like branching sea anemones .
astrocytes. shape , ciliated . processes ( thorny ) . - Their processes cling to neurons ,
Schwann cells 2- Function : Form the 2- Line the central cavities 2- Migrate towards the their synaptic endings, and cover nearby
myelin sheath ( brain , spinal cord ) injury neurone. capillaries
1- Surround nerve bers. ( insulating covering) , 3- Function : Form a 3- Function : - Function : support and anchor the
2- Form the myelin sheaths that line up along the barrier between CSF , - Protection —> due to the neurone | Making exchanges between
around the thicker nerve bers.
thick nerve bers and tissue uid . capillaries and neurons | Guide the
3- Similar to oligodendrocytes limited access of immune
warp their processes 4- Cilia helps to circulate migration of young neurons | formation
of the CNS in function . system to the CNS .
tightly . the CSF. of synapses (junctions) between
- Transform into a macrophage neurons | Control the chemical
—> phagocytizes the environment -> recycling released
microorganisms or neuronal neurotransmitters | Respond to nerve
debris impulses , released neurotransmitters |
Participate in information processing in
the brain .
You might also like
- Bioactivity study of modified curcumin loaded polymeric nanoparticlesFrom EverandBioactivity study of modified curcumin loaded polymeric nanoparticlesNo ratings yet
- Nervous System CompleteDocument20 pagesNervous System CompleteJoanna Marie TulioNo ratings yet
- Design Development and Analysis of a Nerve Conduction Study System An Auto Controlled Biofeedback ApproachFrom EverandDesign Development and Analysis of a Nerve Conduction Study System An Auto Controlled Biofeedback ApproachNo ratings yet
- Nervous System CompleteDocument21 pagesNervous System CompleteChris Deinielle Marcoleta SumaoangNo ratings yet
- Somatic Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesSomatic Nervous SystemanneNo ratings yet
- N - The Nervous System - 1 - 112 - 1Document79 pagesN - The Nervous System - 1 - 112 - 1st911035No ratings yet
- HAPL12M Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesHAPL12M Nervous SystemCarl Axel AzurNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy & Physiology: Fundamentals of The Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part ADocument46 pagesHuman Anatomy & Physiology: Fundamentals of The Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part AStephany Higueldo-CastroNo ratings yet
- Week 1: Fundamentals of The Nervous System and Nervous TissueDocument138 pagesWeek 1: Fundamentals of The Nervous System and Nervous TissueBhavik PatelNo ratings yet
- 1st SemDocument158 pages1st SemSana chaudharyNo ratings yet
- B.chapter 2 Nervous SystemDocument111 pagesB.chapter 2 Nervous SystemMynameis JarheadNo ratings yet
- NERVOUS AND ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Notes and ActivityDocument9 pagesNERVOUS AND ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Notes and ActivitySamantha SaavedraNo ratings yet
- AnaphyDocument8 pagesAnaphyCELLINA CLARISSE DE LEONNo ratings yet
- Functions of The NS (Midterms)Document4 pagesFunctions of The NS (Midterms)initaygracileshayneNo ratings yet
- 2) NeurophysiologyDocument81 pages2) NeurophysiologyyohdeforemostNo ratings yet
- 15) Central Nervous SystemDocument96 pages15) Central Nervous SystemyohdeforemostNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 THE NERVOUS SYSTEMDocument97 pagesTopic 2 THE NERVOUS SYSTEMIreneNo ratings yet
- Nervous System - Master Control and Communications System 3 Overlapping FunctionsDocument95 pagesNervous System - Master Control and Communications System 3 Overlapping FunctionsDioneSolonNo ratings yet
- 21.1 Nervous SystemDocument35 pages21.1 Nervous SystemNurul IzzatiNo ratings yet
- Impulses Which Are Rapid and Specific and CauseDocument9 pagesImpulses Which Are Rapid and Specific and CauseCellina De LeonNo ratings yet
- PChapter 12 Nerve Tissue PDFDocument3 pagesPChapter 12 Nerve Tissue PDFRuel MateoNo ratings yet
- 6.the Nervous SystemDocument31 pages6.the Nervous SystemElaine Victoria ElizanNo ratings yet
- Mapa ConceptualDocument1 pageMapa Conceptualsara bazanNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument49 pagesAutonomic Nervous SystemAzmi PlusNo ratings yet
- Organization, Neurons, Basic Functions of Synapses, and NeurotransmittersDocument3 pagesOrganization, Neurons, Basic Functions of Synapses, and Neurotransmitters22 - Fernandez, Lyza Mae D.No ratings yet
- The Physical Self: Brain and The Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesThe Physical Self: Brain and The Nervous System2022105340No ratings yet
- Nervsystem 1 VT 2017Document69 pagesNervsystem 1 VT 2017D ZamanNo ratings yet
- Nervous Tissues HandoutsDocument6 pagesNervous Tissues HandoutsKelly TrainorNo ratings yet
- Nervous System ExaminationDocument84 pagesNervous System ExaminationFelix FwsNo ratings yet
- Neural Control and Coordination NOTESDocument8 pagesNeural Control and Coordination NOTESYouTutor PSNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument37 pagesThe Nervous SystemNo NameNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Introduction To Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesLecture Notes Introduction To Nervous SystemKirstie Goc-ongNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of The Nervous SystemDocument16 pagesFundamentals of The Nervous SystemEthan Dreiz BaltazarNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy Lab Nervous NotesDocument7 pagesAnaPhy Lab Nervous NotesDING ANG BATONo ratings yet
- Unit III Nervous System and ElectromyographyDocument100 pagesUnit III Nervous System and ElectromyographymanasiNo ratings yet
- BHN Kuliah K22 Mekanisme Kontrol Motorik Somatik Dan RefleksDocument34 pagesBHN Kuliah K22 Mekanisme Kontrol Motorik Somatik Dan RefleksRhena Fitria KhairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Nervous Sys. 1 & 2Document3 pagesNervous Sys. 1 & 2Adolf Benedict Pardo SabanalNo ratings yet
- 21.1 Nervous SystemDocument35 pages21.1 Nervous SystemNazirah Arba'inNo ratings yet
- Chapter 28 Nerouvs System 2017Document35 pagesChapter 28 Nerouvs System 2017maryrose.oseoNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System For MBBSDocument20 pagesAutonomic Nervous System For MBBSjacobsNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint Presentation 6.5Document6 pagesPowerPoint Presentation 6.5Sıla DevrimNo ratings yet
- Nervous System PPT StudentsDocument43 pagesNervous System PPT StudentsAce Buenafe AdamosNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document7 pagesScience 10Jeryca Joy PascualNo ratings yet
- Nervous System CompleteDocument73 pagesNervous System CompleteRaven DoradoNo ratings yet
- Nervous System - Summary (Part 1)Document11 pagesNervous System - Summary (Part 1)s.tinaja.marieantonetteNo ratings yet
- Happ Chapter 8 TransesDocument13 pagesHapp Chapter 8 TransesFrencess Kaye SimonNo ratings yet
- (Oct 1) NERVOUS-SYSTEMDocument5 pages(Oct 1) NERVOUS-SYSTEMBea GualbertoNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Nervous SystemDocument41 pagesWeek 1 Nervous SystemKevinNo ratings yet
- Nervous System ReviewerDocument26 pagesNervous System ReviewerAllea Marie SabacNo ratings yet
- Psych ReviewerDocument20 pagesPsych ReviewerEllen Joyce P. CarnajeNo ratings yet
- Medicine 1 Neuro Lectures 2023 PDFDocument84 pagesMedicine 1 Neuro Lectures 2023 PDFnesinhle AunthiaNo ratings yet
- Neuro HandoutDocument13 pagesNeuro HandoutFatima Shaira PulahongNo ratings yet
- Science Third QuarterDocument8 pagesScience Third QuarterChelsea DizonNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument28 pagesNervous Systemphoebecruz636No ratings yet
- Anatomy Lecture On Nervous SystemDocument172 pagesAnatomy Lecture On Nervous SystemandreabreeNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Neuroanatomy: Muhammad Iqbal BasriDocument14 pagesIntroduction of Neuroanatomy: Muhammad Iqbal BasriUgaNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Nervous SystemDocument27 pagesAn Introduction To Nervous Systemprasun_v100% (2)
- The Central Nervous SystemDocument34 pagesThe Central Nervous SystemVincent TzaiNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument13 pagesNervous SystemanyaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument1 pageNervous SystemErica Faith MagapiNo ratings yet
- Unit 5-Nervous System Brain Retina QuestionsDocument70 pagesUnit 5-Nervous System Brain Retina Questionsareyouthere92No ratings yet
- Aunt Minnie Pediatric NeuroDocument15 pagesAunt Minnie Pediatric NeuroRommel OliverasNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Engineering Ktu Mod 3Document12 pagesBiomedical Engineering Ktu Mod 3Adheeb Shibu VattasserilNo ratings yet
- Clinical Neuroanatomy 29th EdDocument384 pagesClinical Neuroanatomy 29th Edarif 200667% (3)
- Nervous SystemDocument26 pagesNervous SystemAe-jay CacalNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System: Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument30 pagesThe Nervous System: Anatomy & PhysiologyDrAvinash NandanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Study GuideDocument4 pagesUnit 3 Study Guideapi-323808986No ratings yet
- Principles of Human Physiology 6th Edition Ebook PDFDocument61 pagesPrinciples of Human Physiology 6th Edition Ebook PDFbilly.sparks463100% (41)
- Anatomy of Spinal CordDocument41 pagesAnatomy of Spinal CordI Wayan Aryanta PutraNo ratings yet
- The Ventricular SystemDocument6 pagesThe Ventricular SystemM Arsalan TariqNo ratings yet
- Somatosensory System OkDocument47 pagesSomatosensory System OkIrayumastutiNo ratings yet
- Activity 10 The Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesActivity 10 The Nervous SystemAdrianNo ratings yet
- Extrapyramidal Disorders, OedemaDocument104 pagesExtrapyramidal Disorders, OedemaAyman RehmanNo ratings yet
- TDCS and Intense OrgasmDocument4 pagesTDCS and Intense Orgasmreadme50No ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy of The Zebrafish Brain - A Topological Atlas 1996Document141 pagesNeuroanatomy of The Zebrafish Brain - A Topological Atlas 1996Daniel RuizNo ratings yet
- Monteagudo 2007Document28 pagesMonteagudo 2007yngallo910No ratings yet
- The Neural Basis of Romantic LoveDocument6 pagesThe Neural Basis of Romantic LoveBooster CNo ratings yet
- Aportes NeuropsicologicosDocument7 pagesAportes NeuropsicologicosmagdalenaNo ratings yet
- Brain On The 3D Visual Art Through Virtual Reality Introducing Neuro-Art in A Case InvestigationDocument13 pagesBrain On The 3D Visual Art Through Virtual Reality Introducing Neuro-Art in A Case InvestigationSam JamNo ratings yet
- ANP1106B Syllabus 2020 ModifiedDocument5 pagesANP1106B Syllabus 2020 ModifiedphilofaltasNo ratings yet
- Summative TestDocument1 pageSummative TestJessa CalambaNo ratings yet
- Long Term Rel StudiesDocument15 pagesLong Term Rel StudiesLarn Nina RaymundoNo ratings yet
- Lab - Nerve ReflexesDocument6 pagesLab - Nerve Reflexesirfan100% (1)
- The Healy Programs Full List-0001Document15 pagesThe Healy Programs Full List-0001Vikram SharmaNo ratings yet
- Fernandez ED101 Module 2 PDFDocument28 pagesFernandez ED101 Module 2 PDFChristine ElnasNo ratings yet
- Review: Conscious Processing and The Global Neuronal Workspace HypothesisDocument23 pagesReview: Conscious Processing and The Global Neuronal Workspace HypothesisSebastian Gonzalez MazoNo ratings yet
- 2nd Year MBBS Syllabus Outline: Block - 4,5 and 6Document6 pages2nd Year MBBS Syllabus Outline: Block - 4,5 and 6Ambreen AyubNo ratings yet
- 1st LE Topics Week 1 5 Tables PsychiaDocument54 pages1st LE Topics Week 1 5 Tables PsychiaRobie Mae Sescon BandalanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document75 pagesChapter 03Tony DiPierryNo ratings yet
- Motor Skill in Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Subcortical ViewDocument43 pagesMotor Skill in Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Subcortical ViewDiego CampillayNo ratings yet