Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Crude Oil - Fuels - Plastics
Uploaded by
agentdog175Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Crude Oil - Fuels - Plastics
Uploaded by
agentdog175Copyright:
Available Formats
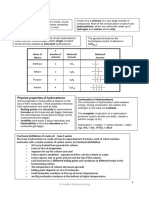
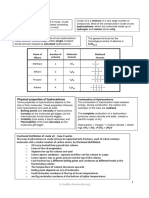
Production and uses of fuels
Crude oil (petroleum) Formed over millions of years from the remains of simple
marine organisms
Natural
Remains of simple Pressure gas(e.g. CH4)
marine organisms
Heat Sandstone containing oil
Millions of Years
There is a limit to coal, crude oil (petroleum) and natural gas life as they will run out over
time – they are finite – or non-renewable.
Crude oil is a mixture of hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons are compounds that contain the elements hydrogen and carbon only.
H H H H
Example of a H C C C C H
hydrocarbon H H H
H
Some other
substances are S
also present
Carbon has the ability to form bonds with other carbon atoms resulting in the formation
of carbon atom chains, e.g.
H H H H H H H H H H
H H H
H C C C C C C C C H H C C C H
H C C H
H H H H H H
H H H H H H H
Crude oil contains a mixture of different sized hydrocarbon chains
28 GCSE Science: Chemistry 1 www.bangor.ac.uk
Production and uses of fuels
Crude oil is separated into fractions The process is called Fractional Distillation
Fraction No. of Carbon Boiling point
atoms in chain range / ˚C
Gas 1–4 -160 to 25
petrol 4 – 12 40 to 100
Fractionating naphtha 7 – 14 100 to 150
column
paraffin/kerosine 11 – 15 150 to 250
diesel oil 15 – 19 250 to 350
20 – 30 over 350
Lubricating oil
Hot crude oil
Bitumen C30 – and above over 400
Fractions contain hydrocarbons with boiling points in the same range, e.g. the petrol
fraction has hydrocarbons with boiling points in the range 40-100 ˚C
Long chain hydrocarbons are at the bottom of the column as they do not boil until a
very high temperature
Some of the fractions are used as fuels (e.g. Kerosine – aeroplane fuel) others are further
processed by cracking. (see next page)
Problems with burning fossil fuels
CO2
SO2
Global Warming
Acid Rain
NO2
CO
Incomplete combustion
www.bangor.ac.uk GCSE Science: Chemistry 1 29
Cracking and Addition Polymerisation
Cracking
At high temperature long hydrocarbon chains are broken down into smaller, more
useful hydrocarbons.
Shorter Used to make the
more useful plastic polythene
This can create ethene.
Decane Octane + Ethene
Ethene is a small reactive molecule, a monomer
If many ethene molecules are linked together it is called polythene which is used to
make many plastics
Creating Plastics
When small reactive molecules such as ethene react together in a chemical
reaction a long chain molecule called a polymer is formed.
Monomer is the name given to small reactive organic molecule
Ethene has a double bond.
One of the bond breaks to
allow the molecule to join
with another
monomer
polymer
The process whereby monomers link to create a polymer is polymerisation.
The type of polymerisation that happen here is addition polymerisation as
there is only one product formed
30 GCSE Science: Chemistry 1 www.bangor.ac.uk
Properties of Plastics
There are many types of plastics, all made by polymerisation, e.g. polythene, PVC, PTFE
(Teflon) and polystyrene.
Electrical insulator / Thermal Transparent /
flexible insulator flexible
Strong /
Strong / low density
low density
Plastics versus traditional materials
Plastics are used widely in place of natural materials such as paper and iron
PVC plastic is used to make water pipes/guttering because they are light, do not rust like
iron, cheaper and last longer
Polythene is used to make plastic bags in place of paper as they are stronger, do not rip
and are waterproof
The disadvantages of plastics are that the do not rot i.e. the do not decompose (takes
hundreds of years) and fill landfill sites.
With heat some plastics melt easily
If plastics burn they form poisonous gases
Recycling waste plastic:
1. reduces the amount of waste but equally importantly
2. conserves crude oil reserves and
3. requires less energy than making new plastics
www.bangor.ac.uk GCSE Science: Chemistry 1 31
You might also like
- Organic Chemistry Notes PDFDocument58 pagesOrganic Chemistry Notes PDFAzadnikov94% (16)
- Stereochemistry QustionsDocument43 pagesStereochemistry QustionsSwaraj Paul100% (1)
- Chemistry Past 10 Year Papers 2002-2013Document106 pagesChemistry Past 10 Year Papers 2002-2013siddharth199650% (2)
- PPSC Physics Lecturer Test Past Papers SolvedDocument18 pagesPPSC Physics Lecturer Test Past Papers SolvedfatimaNo ratings yet
- NGS GrafoilEngineeringDesignManualDocument86 pagesNGS GrafoilEngineeringDesignManualHARSHANo ratings yet
- Chemical Engg Basic IndiabixDocument123 pagesChemical Engg Basic IndiabixRishikesh Awale100% (3)
- IGCSE Chemistry Section 5 Lesson 3Document43 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Section 5 Lesson 3Bhawana SinghNo ratings yet
- Exercise Chemistry Form 5 Carbon CompoundsDocument6 pagesExercise Chemistry Form 5 Carbon CompoundsWan ShuhaimiNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry For IGCSE ChemistryDocument4 pagesOrganic Chemistry For IGCSE Chemistrydanielmahsa100% (1)
- UNIT-2 Engg. Materials 2019 ModifiedDocument67 pagesUNIT-2 Engg. Materials 2019 ModifiedANABOINA SHIVRAJNo ratings yet
- 03 Hydrocarbon ChemistryDocument18 pages03 Hydrocarbon Chemistryfaraj100% (1)
- Project Lucy Extended Version 4Document40 pagesProject Lucy Extended Version 4Jim Lee ClimateViewerNo ratings yet
- Crude Petroleum analysis handbook: Crude oil Quality control, #1From EverandCrude Petroleum analysis handbook: Crude oil Quality control, #1Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Organic DADocument8 pagesOrganic DAagentdog175No ratings yet
- Fractional DistillationDocument6 pagesFractional Distillationagentdog175No ratings yet
- Notebook Work Coal & PetroleumDocument2 pagesNotebook Work Coal & PetroleumaryanshaindilyaNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument71 pages1 Introduction To Organic ChemistryAj MirandaNo ratings yet
- 4.7 Organic Chemistry: o o o o o oDocument2 pages4.7 Organic Chemistry: o o o o o oPedro Moreno de SouzaNo ratings yet
- (19th of 19 Chapters) Organic Chemistry Part 1 of 3 - GCE O Level Chemistry LectureDocument37 pages(19th of 19 Chapters) Organic Chemistry Part 1 of 3 - GCE O Level Chemistry LectureChengeto MatandaNo ratings yet
- 4 7 Organic ChemistryDocument6 pages4 7 Organic ChemistryJadyn Mc SweenNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - Petroleum/Crude OilDocument6 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Petroleum/Crude Oilanya de silvaNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument33 pagesOrganic ChemistryFari Sweet PumpkinNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1 The Fuel and Energy RelationshipDocument10 pages1.1.1 The Fuel and Energy RelationshipRomeo San GasparNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document17 pagesModule 5ABIGAIL OLAJUMOKE JOSEPHNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project: By: Ouail BalahDocument9 pagesChemistry Project: By: Ouail BalahOuail BalahNo ratings yet
- FEI CSEC Chemistry Handbook Section B - Organic Chemistry and Section CDocument134 pagesFEI CSEC Chemistry Handbook Section B - Organic Chemistry and Section CMarques GrantNo ratings yet
- Alkanes ClassDocument27 pagesAlkanes ClassRyan JamesNo ratings yet
- As Level - AlkanesDocument12 pagesAs Level - AlkanesRegine BalagtasNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes (Organic Chem)Document6 pagesChemistry Notes (Organic Chem)Teo Jia Ming NickolasNo ratings yet
- Fuels and CombustionDocument24 pagesFuels and Combustionmukirir47No ratings yet
- A8757657 A A&PolymersDocument84 pagesA8757657 A A&PolymersKushNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument10 pagesOrganic ChemistrySayeef MahdiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Chemistry Crude Oil and AmmoniaDocument40 pagesUnit 2 Chemistry Crude Oil and AmmoniaCrisa ChinaNo ratings yet
- Liquid FuelsDocument29 pagesLiquid FuelsMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Section 5 Lesson 3Document43 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Section 5 Lesson 3sanobarNo ratings yet
- MCB 410Document33 pagesMCB 410oluwaleye victorNo ratings yet
- HSC Production of Materials. BestnotesDocument24 pagesHSC Production of Materials. Bestnotes16choi.michaelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Carbon CompoundDocument38 pagesChapter 2 Carbon CompoundHING LEE NA MoeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document32 pagesChapter 2alicia sambaiNo ratings yet
- Crude Oil RefiningDocument28 pagesCrude Oil RefiningtswNo ratings yet
- Oil Refining AssignmentDocument19 pagesOil Refining AssignmentKiran ShahzadiNo ratings yet
- CombustionDocument35 pagesCombustionm_mukbel8752No ratings yet
- 4.C Alkanes ASDocument13 pages4.C Alkanes ASytshortsfromopus65No ratings yet
- Fuels and CombustionDocument12 pagesFuels and CombustionAbhishek PrasadNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry '13Document33 pagesOrganic Chemistry '13Princess KimNo ratings yet
- 6 +fuelsDocument15 pages6 +fuelsAustin LipnicaNo ratings yet
- 5 2018 04 12!07 56 06 PM PDFDocument19 pages5 2018 04 12!07 56 06 PM PDFzeonNo ratings yet
- Energy Chemistry NotesDocument11 pagesEnergy Chemistry NotesClayton Feng100% (1)
- Peet Material 1Document130 pagesPeet Material 1SaikrisdNo ratings yet
- Fuel Combustion RkrajputDocument34 pagesFuel Combustion Rkrajputsunita.storage01No ratings yet
- Petroleum and Alkanes Fractional Distillation Cracking CombustionDocument10 pagesPetroleum and Alkanes Fractional Distillation Cracking CombustionCarlton GrantNo ratings yet
- Origin/History of Fossil FuelsDocument8 pagesOrigin/History of Fossil FuelsVincent TanNo ratings yet
- Chapt 8 (Grade 10)Document15 pagesChapt 8 (Grade 10)Myint Myint HtweNo ratings yet
- Energy Engineering (18ME81) : Pradeep N B Asst. Professor Mechanical Dept., JNNCEDocument50 pagesEnergy Engineering (18ME81) : Pradeep N B Asst. Professor Mechanical Dept., JNNCEPradeep N BNo ratings yet
- Part 5 Fossil Fuels and Carbon CompoundsDocument66 pagesPart 5 Fossil Fuels and Carbon CompoundsMatthew Chu100% (1)
- Uses of HydrocarbonsDocument30 pagesUses of HydrocarbonscheetoNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Petroleum and AlkanesDocument10 pages1.6 Petroleum and Alkanesmaya 1DNo ratings yet
- CH 4 L 1 (Introduction To Polymers)Document50 pagesCH 4 L 1 (Introduction To Polymers)Ermyas DejeneNo ratings yet
- FuelsDocument19 pagesFuels22cs103No ratings yet
- L02 - w3 - 01 - Fuels Energy - RelationsDocument6 pagesL02 - w3 - 01 - Fuels Energy - RelationsJohn Rave Manuel GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Petrochemicals and PolymersDocument6 pagesPetrochemicals and PolymersM.zuhair asifNo ratings yet
- 8 ChemistryDocument5 pages8 ChemistryJakia Wahima Class:-6C Rollno.:-38No ratings yet
- Xperimen 2012 (Kimia) P1Document8 pagesXperimen 2012 (Kimia) P1Shafinaz SaadNo ratings yet
- Synthetic PolymersDocument40 pagesSynthetic Polymersproslimeplays1No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry (Main)Document67 pagesOrganic Chemistry (Main)Adil Yaqub - 74665/TCHR/CNTBNo ratings yet
- 2008 Chemistry NotesDocument20 pages2008 Chemistry NotesJohndoeNo ratings yet
- Week 4 PDFDocument16 pagesWeek 4 PDFNoor FatimaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Chap 06Document12 pagesOrganic Chemistry Chap 06Daniya Sohail Sohail HashimNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Sine Cosine RulesDocument15 pagesIGCSE Sine Cosine Rulesagentdog175No ratings yet
- IGCSE Standard Form Ratio ProportionDocument25 pagesIGCSE Standard Form Ratio Proportionagentdog175No ratings yet
- Separation Techniques Revision CardDocument1 pageSeparation Techniques Revision Cardagentdog175No ratings yet
- Gases in The AtmosphereDocument4 pagesGases in The Atmosphereagentdog175No ratings yet
- Chemistry MCQs 2nd Year. TESTDocument48 pagesChemistry MCQs 2nd Year. TESTPremier AcademyNo ratings yet
- June 2011 MS - Unit 1 Edexcel Chemistry A-LevelDocument24 pagesJune 2011 MS - Unit 1 Edexcel Chemistry A-LevelNabindra RuwaliNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/02Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/02Yu MayNo ratings yet
- Air Gasification of FuelDocument8 pagesAir Gasification of FuelB DASNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Question Bank For 10th STDDocument4 pagesChemistry Question Bank For 10th STDsameeraNo ratings yet
- 5070 s16 QP 11Document16 pages5070 s16 QP 11kameshNo ratings yet
- Chapter Practice QuestionsDocument12 pagesChapter Practice QuestionsNoranisza MahmudNo ratings yet
- Sydney Grammar 2014 Chemistry Prelim HY & SolutionsDocument52 pagesSydney Grammar 2014 Chemistry Prelim HY & SolutionsgihanbajitheNo ratings yet
- Plastic Waste To SyngasDocument10 pagesPlastic Waste To Syngaswaseemkhan49No ratings yet
- Advanced Nanomaterials PDFDocument270 pagesAdvanced Nanomaterials PDFMariela RguezNo ratings yet
- English: 1. 994 X 1006 Is Equal To: 2. As The Founder Satvahana Dynasty ?Document11 pagesEnglish: 1. 994 X 1006 Is Equal To: 2. As The Founder Satvahana Dynasty ?vivek vinod kastureNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Chemistry Unit 1 June 2010 GceDocument28 pagesEdexcel Chemistry Unit 1 June 2010 Gceaym3nNo ratings yet
- RiskWISE Import Template StorageTank 11-Aug-2018 145718412Document41 pagesRiskWISE Import Template StorageTank 11-Aug-2018 145718412irfanlarikhotmailcomNo ratings yet
- Assessing Ocean Alkalinity For Carbon Sequestration Renforth Et Al-2017-Reviews of GeophysicsDocument39 pagesAssessing Ocean Alkalinity For Carbon Sequestration Renforth Et Al-2017-Reviews of GeophysicsInés KallfvNo ratings yet
- Growth and Photodissociation of CR Complexes: - (Coronene)Document8 pagesGrowth and Photodissociation of CR Complexes: - (Coronene)Gustavo GuillénNo ratings yet
- Chang Chemistry Chapter 3 QuestionsDocument14 pagesChang Chemistry Chapter 3 QuestionsBlanche Dauz100% (1)
- Module 2 Petrochemical Precursor (Raw Material) Part 1Document23 pagesModule 2 Petrochemical Precursor (Raw Material) Part 1Muhammad AshmanNo ratings yet
- CHO33 Gravimetric Analysis Worksheet 1Document2 pagesCHO33 Gravimetric Analysis Worksheet 1benhawkins26No ratings yet
- Applications of Nanotechnology in Water Treatment PDFDocument16 pagesApplications of Nanotechnology in Water Treatment PDFSivamani SelvarajuNo ratings yet
- Science & Technology IndonesiaDocument6 pagesScience & Technology IndonesiaIndah Fitriany PurwaningtyasNo ratings yet
- ETEA Entry Test Guide, Information, Sample PaperDocument13 pagesETEA Entry Test Guide, Information, Sample PaperShawn Parker83% (6)
- jpcrd628 PDFDocument360 pagesjpcrd628 PDFShijumon KpNo ratings yet