Professional Documents
Culture Documents
l-27 Metals and Non-Metals
Uploaded by
Mostafa ElngarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
l-27 Metals and Non-Metals
Uploaded by
Mostafa ElngarCopyright:
Available Formats
27.
Metals and Non-metals
z Elements are broadly classified as metals non- z Metallurgy is the branch of science which
metals. deals with extraction of metals from its ores.
z Metals can be distinguished from non-metal z Some of the non-metals are also found in free
on the basis of their physical properties like state in nature for example sulphur and carbon
malleability ductility, lusture etc. (as coal, graphite, diamond).
z Metals have tendency to lose electrons whereas z Chemical properties of metals and non-metal
non-metal have tendency to gain electrons. are different. Metal and non-metal both react
Thus metals show electropositive character with oxygen (air), water and acids.
whereas non-metals show electronegative
character. z Certain oxides of metals show both the
properties acidic as well as basic e.g. ZnO and
z An ore is a mineral from which a metal can be Al2O3.
profitably extracted from it.
Learner Guide
Build Your Understanding
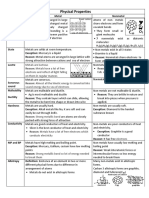
Physical Properties of metals and non-metals
Physical Properties Metals Non-Metals
Malleability and Metals are malleable. They can be Non-metals are neither
Ductilily beaten into thin sheets. They are malleable nor ductile. For e.g.
also ductile and can be drawn into coal, (carbon) and sulphur
wire
Metallic Lusture show metallic lusture. Do not show any metallic
lusture except I2.
Hardness Hard except Hg, Na Soft except diamond
Physical state solid and liquid states Solid, liquid and gas
Sonorous Sonorous (produce sound) Non-sonorous
Density High Low
Electrical conductivity Good conductor Bad conductor
Chemical Properties of Metals 2. Reaction with acids: Generally metals react
1. Reaction with Oxygen: Form oxides which with acids to form salts and evolved H2
are basic in nature Mg + 2HCl ⎯→ MgCl2 + H2
Oxides of aluminium (Al2O3), zinc (ZnO), tin 3. Reaction with water to form base
(SnO) and iron (Fe2O3) are amphoteric. React
with acids as well as with bases. 2Na + 2H2O ⎯⎯→ 2NaOH + H2
73
Al or Fe react with steam to form oxides Uses of Metals
z To make utensils (iron, aluminium)
3Fe + 4H2O ⎯⎯→ Fe3O4 + 4H2
z To make electrical wire (copper, aluminium)
4. Reaction with bases z to make machines
z uses in cells and batteries
Al, Sn and Zn react with common base
z to make Jewellery
Sn + 2NaOH + H2O ⎯→ Na2SnO3 + 2H2 z To make sheets Al and iron are used to make
Corrosion: Oxygen reacts with metals to form sheet due to malleable nature (Malleability)
oxides. Oxidation of metals is known corrosion
Uses of Non-metals
for example rusting of iron.
z For the manufacture of fertilizer
4Fe + xH2O + O2 ⎯⎯→ 2Fe2O3.xH2O
z Silicon is used for making transistor, chips etc
Presence of moisture and oxygen is necessary for z White phosphorous is used in match industry
corrosion. Corrosion can be prevented by (i)
z Sulphur is used to control fungus pests. It is
Painting (ii) oiling and greasing (iii) Galvanization
also used for the manufacture of H2SO4 and
(iv) Alloying gun powder.
Learner Guide
Stretch Yourself ? Test Yourself
1. Why is it better to use copper than carbon in 1. Metals are good conductor of electricity but
electrical wires. non-metal are not why?
2. Aluminium metals is used as utensils in houses 2. What are the main conditions for the corrosion?
why? How will you prevent it?
3. Left copper coin in open air and observed. 3. How will you prove that metal oxides are
After one month a green layer is developed on basic but non-metal oxides are acidic in nature?
the coin. Why it is so? 4. Sn is soluble in excess NaOH why? Explain
with equation.
74
You might also like
- Ncert Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials Metals and Non Metals PDFDocument4 pagesNcert Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials Metals and Non Metals PDFAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Science Test BookDocument3 pagesScience Test Bookayush sonar100% (1)
- Metals and Non-MetalsDocument20 pagesMetals and Non-MetalsDevyansh MishraNo ratings yet
- Study Material Class 10 Chapter 3 2017 PDFDocument10 pagesStudy Material Class 10 Chapter 3 2017 PDFKaran Pratap67% (3)
- Metals and Non Metals Notes For Class 8Document8 pagesMetals and Non Metals Notes For Class 8Vikash SharmaNo ratings yet
- CDI 6 Fire Behavior and Arson InvestigationDocument54 pagesCDI 6 Fire Behavior and Arson InvestigationJames Dela Cruz100% (4)
- Metals & Non-Metals: Topics in The ChapterDocument7 pagesMetals & Non-Metals: Topics in The ChapterManya SinghviNo ratings yet
- Element Classification of Elements: Class-X Chapter - 3 Metals and Non-MetalsDocument11 pagesElement Classification of Elements: Class-X Chapter - 3 Metals and Non-MetalsInsha Hasan 10DNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals - NotesDocument8 pagesMetals and Non Metals - NotesMohita RastogiNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals N 1Document8 pagesMetals and Non Metals N 1rincyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes-Metals and Non MetalsDocument15 pagesChemistry Notes-Metals and Non MetalsKISHORE ADITYA DHINESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- 3 NOV Class 10 Metals and Non-Metals ChemDocument40 pages3 NOV Class 10 Metals and Non-Metals Chemgourav kaliaNo ratings yet
- Materials Metals and Non-MetalsDocument5 pagesMaterials Metals and Non-Metalssidhantm823No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document16 pagesChapter 4Bhavya JangidNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non MetalsDocument22 pagesMetals and Non MetalsPranati SharmaNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes On Materials Metals and Non-MetalsDocument9 pagesRevision Notes On Materials Metals and Non-MetalsHoang HaNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals Notes Class 10 2022-23Document37 pagesMetals and Non Metals Notes Class 10 2022-23ramkumarsingh12406100% (1)
- Chapter - 3 Metals - and - Non - Metals NewDocument14 pagesChapter - 3 Metals - and - Non - Metals NewRahul IngleNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-Metals: Module - 6Document19 pagesMetals and Non-Metals: Module - 6Brandeice BarrettNo ratings yet
- Learn PracticallyDocument79 pagesLearn Practicallyprincethakan9No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 3 2Document8 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 3 2Maithili PanwarNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument31 pagesChemistryvisheshsingla411No ratings yet
- Non MetalsDocument14 pagesNon MetalsankitrathoreagentNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-Metals - PpsDocument41 pagesMetals and Non-Metals - Ppswagner.garciaNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-Metals NotesDocument18 pagesMetals and Non-Metals NotesMustafa Khan100% (1)
- Arvind Academy: Properties of MetalDocument11 pagesArvind Academy: Properties of MetalGhantaNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-Metals Notes - RemovedDocument15 pagesMetals and Non-Metals Notes - RemovedCyber Atharv100% (1)
- Metals and Non-Metals NotesDocument18 pagesMetals and Non-Metals NotesAzeem IqbalNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Subject Science Chapter 4Document3 pagesClass 8 Subject Science Chapter 4Geetank PugliaNo ratings yet
- Metals & Non MetalsDocument24 pagesMetals & Non Metalsbharath vNo ratings yet
- Metal and Non-Metal PDFDocument29 pagesMetal and Non-Metal PDFSukomal Dey SarkarNo ratings yet
- Metals and Nonmetals NotesDocument8 pagesMetals and Nonmetals NotesManthan KheraNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non MetalsDocument9 pagesMetals and Non Metalsbhumika motiyaniNo ratings yet
- MetalsDocument7 pagesMetalsritesh kavuruNo ratings yet
- By:-Utsah Sharma - at Crazy ScienceDocument21 pagesBy:-Utsah Sharma - at Crazy ScienceUtsah SharmaNo ratings yet
- Metal and NonmetalDocument26 pagesMetal and NonmetalSudhanshu Sekhar PandaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 Metals and Non - MetalsDocument4 pagesChapter - 3 Metals and Non - MetalsJohnny MurrayNo ratings yet
- Class 8 - Science - CH - 3 - Metals - Non Metals - NotesDocument4 pagesClass 8 - Science - CH - 3 - Metals - Non Metals - Notes8eanjanimaitreyNo ratings yet
- 3 NOV Class 10 Metals and Non-Metals ChemDocument40 pages3 NOV Class 10 Metals and Non-Metals Chemgourav kaliaNo ratings yet
- M&NM-TABLE - Phy and Chem PropDocument3 pagesM&NM-TABLE - Phy and Chem PropanjanaNo ratings yet
- Exp SC 8 - Chapter 04Document19 pagesExp SC 8 - Chapter 04megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- Metal and NonDocument18 pagesMetal and NonMIN. Dr. Tanaji sawant officeNo ratings yet
- Notes On Materials Metals and Non MetalsDocument6 pagesNotes On Materials Metals and Non Metalsmatho logyNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument4 pagesNotesYASHVI MODINo ratings yet
- St. John'S School Greater Noida WestDocument5 pagesSt. John'S School Greater Noida WestIndia Tech with AstitvaNo ratings yet
- Shiksha Group Education: Chemical Properties of MetalsDocument18 pagesShiksha Group Education: Chemical Properties of MetalsHarshit RajputNo ratings yet
- 9 Science Metals NonmetalsDocument7 pages9 Science Metals NonmetalsAjay AnandNo ratings yet
- Metaullargy NotesDocument14 pagesMetaullargy Noteswama ojhaNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals Class 10Document8 pagesMetals and Non Metals Class 10Gowtham LNo ratings yet
- Metal and Non Metal Class 8Document23 pagesMetal and Non Metal Class 8Ripu Daman SinghNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non MetalsDocument72 pagesMetals and Non MetalssimoneNo ratings yet
- METALS NON METALS TheoryDocument23 pagesMETALS NON METALS TheoryweyiNo ratings yet
- Materials-Metals and Non-MetalsDocument3 pagesMaterials-Metals and Non-Metalsaadithya.v.5502.sssmscNo ratings yet
- Uydz Uw WV USKa N61 MM JC 4Document6 pagesUydz Uw WV USKa N61 MM JC 4varshatagade126No ratings yet
- Metals, Non Metals, and MetallurgyDocument13 pagesMetals, Non Metals, and MetallurgyM. Amebari NongsiejNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-Metals Notes Provided by TeacherDocument7 pagesMetals and Non-Metals Notes Provided by TeacherAdeeba Raheel QureshiNo ratings yet
- Caie Checkpoint Science Chemistry v4Document19 pagesCaie Checkpoint Science Chemistry v4Shame BopeNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Metals and Non Metals NotesDocument12 pagesClass 10 Metals and Non Metals NotesShreyash VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- CLASS VIII QUESTION BANK - 4. Metals and Non-MetalsDocument7 pagesCLASS VIII QUESTION BANK - 4. Metals and Non-MetalsSurbhi NayarNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionFrom EverandInorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionNo ratings yet
- Ass2 ScienceDocument36 pagesAss2 ScienceMostafa ElngarNo ratings yet
- Technical Report NEWDocument62 pagesTechnical Report NEWMostafa ElngarNo ratings yet
- Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT)Document4 pagesInsulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT)Mostafa ElngarNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Analog SignalDocument4 pagesCharacteristics of Analog SignalMostafa ElngarNo ratings yet
- Instant Download Ebook PDF Exploring Chemical Analysis 5th Edition by Daniel C Harris PDF ScribdDocument41 pagesInstant Download Ebook PDF Exploring Chemical Analysis 5th Edition by Daniel C Harris PDF Scribdida.clemmons523100% (33)
- The Waste Management of TextileDocument10 pagesThe Waste Management of TextiledaabgchiNo ratings yet
- ManghiDocument2 pagesManghiJomelyn DawiNo ratings yet
- Thesis On Soap MakingDocument7 pagesThesis On Soap Makingdwrxjhgr100% (1)
- ENPREP 114E - TDS US EnglishDocument4 pagesENPREP 114E - TDS US EnglishPhanuwit ThavalNo ratings yet
- Fly Ash Based Light Weight Geopolymer ConcreteDocument7 pagesFly Ash Based Light Weight Geopolymer Concretegowtham svNo ratings yet
- Experiment 20Document4 pagesExperiment 20Beenu SinghNo ratings yet
- The MineralsDocument44 pagesThe MineralsWilly ApryantoNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Aromatic CompoundsDocument57 pagesHaloalkanes and Aromatic CompoundsShabir Ahmad BhatNo ratings yet
- Manganese Removal in Base Metal Hydrometallurgical ProcessesDocument17 pagesManganese Removal in Base Metal Hydrometallurgical ProcessesJeromeNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes by Ahsan KhanDocument22 pagesBiology Notes by Ahsan KhanAhsan khanNo ratings yet
- Cie A2 - 12Document18 pagesCie A2 - 12S Ms.No ratings yet
- Export Pesticide Residue CurrentMRLDocument24 pagesExport Pesticide Residue CurrentMRLHuy HảiNo ratings yet
- Pha612 Lab Expt 6 Reactions and Analysis of The Ammonium Sulfide Group PDFDocument4 pagesPha612 Lab Expt 6 Reactions and Analysis of The Ammonium Sulfide Group PDFAmmonium ChlorideNo ratings yet
- Astm E104 Humedad RelativaDocument5 pagesAstm E104 Humedad RelativaAlbertoNo ratings yet
- Triton InvoiceDocument3 pagesTriton InvoiceKishnsNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument4 pagesChemistry NotesSean HungNo ratings yet
- Surface Chemistry Revision 2022Document2 pagesSurface Chemistry Revision 2022Dêêpák Sîñgh ÑîtwálNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 StereochemistryDocument39 pagesCHAPTER 3 StereochemistrysyamimiafrinaNo ratings yet
- Sheet - 01Document22 pagesSheet - 01Sanchayan ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Halo Alkanes & HaloarenesDocument30 pagesHalo Alkanes & HaloarenesEarNo ratings yet
- W1W2 BTD1123 Chapter 1 Intro To Mat ScienceDocument39 pagesW1W2 BTD1123 Chapter 1 Intro To Mat ScienceHakim ShahmiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Syllabus of 1st YearDocument12 pagesChemistry Syllabus of 1st YearAbdul HakeemNo ratings yet
- Biology Class 12 Microbes in Human WelfareDocument30 pagesBiology Class 12 Microbes in Human Welfaresouravsinghrathore.2006No ratings yet
- Black MasterbatchDocument4 pagesBlack MasterbatchThao TonNo ratings yet
- Paper 171Document12 pagesPaper 171Natural CuresNo ratings yet
- Exercise Book - 03 - Bricks (Ddpanda)Document6 pagesExercise Book - 03 - Bricks (Ddpanda)Dipankar NathNo ratings yet
- Effect of Sugar Cane Bagasse Ash On The Physical Properties of Subgrade LayerDocument14 pagesEffect of Sugar Cane Bagasse Ash On The Physical Properties of Subgrade LayerIdham Nurul MahmudNo ratings yet
- Epicon DSP: Technical DatasheetDocument2 pagesEpicon DSP: Technical DatasheetBogdanBNo ratings yet