Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pons Anatomy - Medicosis Perfectionalis Notes
Pons Anatomy - Medicosis Perfectionalis Notes
Uploaded by
hiba jasimCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pons Anatomy - Medicosis Perfectionalis Notes
Pons Anatomy - Medicosis Perfectionalis Notes
Uploaded by
hiba jasimCopyright:
Available Formats
Outline ♪ Motor nerve
A. Pons ♪ One of the nerve of Extra ocular muscles (3 4 6)
♪ Nucleus → abducens motor nucleus,
† wrapping abducens motor nucleus is fiber from
Video → Medicosis Perfectionalis
facial nerve nucleus.
Notes → Transcript of Medicosis Perfectionalis
† This wrap around of facial nerve form an
elevation → facial colliculus.
Pons † → facial colliculus caused by facial nerve
wrapping around nucleus of abducens.
– – Cranial nerve 7
– ♪ One of nerve of branchial apparatus ( 5 7 9 10)
– Peduncles ♪ One of the nerve of parasympathetic NS ( 3 7 910)
♪Recall → connection between midbrain and ♪ Mixed nerve
cerebrum → cerebral Peduncle ♪ Nucleus
♪ connection between brainstem and cerebellum →
† Sensory nucleus
cerebellar peduncle † motor nucleus → main
† Pons to cerebellum → middle cerebellar
† Superior Salivatory nucleus → Parasympathetic
peduncle Nucleus
† Middle cerebellar peduncle also called
Parasympathetic fibers to sublingual and
Intermediate fiber bundle. submandibular gland via submandibular
– back of pons ganglion.
♪ fourth ventricle → ventricle of hind brain.
† Note
† Half lies in pons
Sup Salivatory nucleus → CN 7
† Half lies in medulla
Inferior Salivatory Nucleus → CN 9
ϫ Cranial nerves from pons ž Mn → CN 7 superior to CN 9
♪ 5 6 7 8
Inferior Salivatory Nucleus fibers to parotid
– Cranial Nerve 5 gland via otic ganglion.
♪ One of the nerve of branchial apparatus (CN 5 7 9
† Note 2
10) Taste from anterior two-thirds → superior
♪ Mixed nerve
salivatory nucleus
♪ Nuclei
Taste from posterior tongue → inferior
† Motor nucleus
salivatory nucleus.
† Principal sensory nucleus aka main sensory
– CN 8 vestibulocochlear nerve
nucleus aka Principal pontine nucleus ♪ Nerve for hearing and balance
† principal sensory nucleus extends
♪ 2 nuclei
up in → midbrain – called mesencephalic part † Vestibular nucleus complex
of principal nucleus. † Cochlear nucleus
down in → medulla – called spinal part of ♪ Vestibular Nucleus complex
principal nucleus. † Location → ponto-medullary junction
– CN 6 abducens nerve
† Function → Information from vestibulocochlear red in image → pyramidal fibers → part of
nerve CN (VIII) for balance and equilibrium. pyramidal tract
† Part → 4 parts ž include corticospinal tract + corticobulbar
Superior component tract.
Inferior component ž corticospinal tract synapse in spinal nerves
Medial component ž corticobulbar tract synapse in cranial nerve
Lateral component nuclei.
♪ Cochlear nuclei † Pontine nuclei
† Two on each side corticopontine fibers from cerebral cortex to
Dorsal cochlear nuclei pons.
Ventral cochlear nuclei † Lemnisci
† Location → positioned dorsal and ventral to the Behind pontine nuclei is lemnisci.
inferior cerebellar peduncles Includes
† Function → receive auditory information from ž medial lemniscus
CN 8. ž trigeminal lemniscus
♪ ž spinal lemniscus
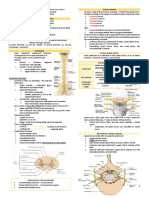
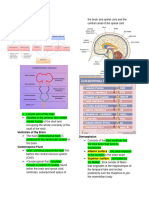
– External Anterior view of pons ž lateral lemniscus.
♪ Anterior part called → basilar part of pons lemniscus def →
♪ Basilar artery runs in a groove basilar groove. ž a tract that contains sensory fibers
♪ Horizontally on surface of pons run transverse ž leaving brainstem and heading upstairs to
streaks. thalamus
♪ cranial nerve 7 and 8 emerge from ponto-cerebellar ♪ Middle of Pons
angle at ponto-medullary junction. † nuclei of CN 5
– External Posterior view of Pons sensory nucleus
♪ Upper half of fourth ventricle lies in pons motor nucleus
♪ Sulcus in midline → median longitudinal sulcus. † Medial longitudinal fasciculus
♪ Superiorly lies → Superior medullary velum ♪ Anterior of Pons
♪ Facial colliculus caused by facial nerve wrapping † glimpse of superior cerebellar peduncle between
around abducens nucleus. midbrain and cerebellum.
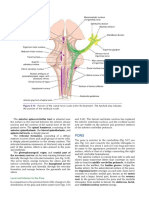
ϫ Transverse Section of Pons † 4th ventricle
– Cross section in upper / Rostral pons – Caudal / Lower Pons
♪ Anterior Pons→ ♪ Anterior Pons
† Basis pontis † Transverse fibers (same as in rostral pons)
Name of anterior part of pons is Basis Pontus † Longitudinal fibers (same as in rostral pons)
Basis pontis composed of transverse fibers of ♪ Middle Pons
pons † Trapezoid body
Called transverse fibers as in cross section † Medial lemniscus
they appear horizontal → mcq. † medial longitudinal fasciculus
Transverse fibers make middle cerebellar helps eye look medially towards your nose →
peduncles → mcq mcq
Transverse fibers of pons connect pons to ♪ Posterior Pons
cerebellar cortex → mcq Nuclei of CN 6, 7, 8
ž Mn → the nuclei of cerebellum are in ž Mn → 5 comes first → in superior pons
cerebellar cortex. ؞6 7 8 comes afterwards → in inferior
♪ Recall rule → anterior is motor and posterior is pons
sensory † facial colliculus → spherical elevation caused by
† Vertical / Longitudinal fibers facial nerve wrapping around abducens nucleus.
♪ Note → Because abducens nerve is purely somatic ϫ
motor, it leaves medially, but because facial nerve ϫ
is mixed, it's gonna leave more laterally ϫ
ϫ ϫ
ϫ ϫ
ϫ ϫ
ϫ Pearls ϫ
– CN 5 → anterolateral from pons ϫ
– CN 6 7 8 → from pontomedullary junction ♪
† H2O2 Catalase
→
O2 and H2O
ϫ
– Corticopontocerebellar Fibers
♪ Connect cerebral cortex to cerebellum.
♪ This connection is for Coordination of motor
activities between cerebrum & cerebellum
♪ Right Pontine nuclei connects to ipsilateral
cerebrum BUT contralateral cerebellum
† OR
♪ Right pontine nuclei + right cerebrum connect to
left cerebellum.
♪ A/c middle pons connect cerebrum to cerebellum
via middle cerebellar peduncle.
♪ These are classified afferent fibers from cerebral
cortex to cerebellum.
ϫ
ϫ
ϫ
ϫ
ϫ
ϫ
ϫ
ϫ
ϫ
ϫ
ϫ
ϫ
ϫ
You might also like
- Narcissistic Personality Disorder 2Document23 pagesNarcissistic Personality Disorder 2Dewi Alwi100% (2)
- 04 - Meninges - DR Najeeb NeuroanatomyDocument18 pages04 - Meninges - DR Najeeb Neuroanatomyhiba jasimNo ratings yet
- Neuro 1.27.22Document19 pagesNeuro 1.27.22Vhince PiscoNo ratings yet
- 01 - Introduction To Neuroanatomy - DR Najeeb VideosDocument6 pages01 - Introduction To Neuroanatomy - DR Najeeb Videoshiba jasimNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy Brainstem SummaryDocument11 pagesNeuroanatomy Brainstem SummaryStd Dlshsi100% (2)
- The Brainstem: Ot1024: NeuroscienceDocument6 pagesThe Brainstem: Ot1024: NeuroscienceReyna MedinaNo ratings yet
- Handouts MBBII ContinuedDocument18 pagesHandouts MBBII ContinuedLily KruegerNo ratings yet
- Disorder S: Corpuz, Rachella Nicole P. Spup Junior InternDocument53 pagesDisorder S: Corpuz, Rachella Nicole P. Spup Junior InternRachella Nicole CorpuzNo ratings yet
- 2023.neuroscience - Trans10.posterior Fossa Level Brainstem Cranial Nuclei and NervesDocument7 pages2023.neuroscience - Trans10.posterior Fossa Level Brainstem Cranial Nuclei and NervesstellaNo ratings yet
- Kenrick Cleveland - How Embedded Commands WorkDocument5 pagesKenrick Cleveland - How Embedded Commands WorkdikesmNo ratings yet
- Medulla Oblongata Anatomy: Abbas A. A. Shawka Medical Student 2nd GradeDocument40 pagesMedulla Oblongata Anatomy: Abbas A. A. Shawka Medical Student 2nd Gradetuhin100% (1)
- EDUC 5210 - Written Assignment 5Document3 pagesEDUC 5210 - Written Assignment 5Gilbert AyimanaNo ratings yet
- 07e - UMN & LMN Lesions - Ninja Nerd & DR NajeebDocument9 pages07e - UMN & LMN Lesions - Ninja Nerd & DR Najeebhiba jasimNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord and Its Lesions - Dr. Mattheus (2023)Document8 pagesSpinal Cord and Its Lesions - Dr. Mattheus (2023)Noreen Hannah GabrielNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Central Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesChapter 7 - Central Nervous SystemRishelle Mae Miñoza PilonesNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve AssessmentDocument42 pagesCranial Nerve AssessmentValeryn Quiman100% (8)
- Neurologic NursingDocument10 pagesNeurologic NursingAllisson Beckers100% (1)
- Wild and Isolated Children and The Critical Age Issue For Language Learning - Kelompok 4Document9 pagesWild and Isolated Children and The Critical Age Issue For Language Learning - Kelompok 4samiNo ratings yet
- Module 2 The Self Society and CultureDocument9 pagesModule 2 The Self Society and CultureMAILENE SALESNo ratings yet
- Progress in Neurodegeneration-The Role of MetalsDocument358 pagesProgress in Neurodegeneration-The Role of MetalsMaria Rosa100% (2)
- Psychology, Help) Conflict Resolution - Essential Skills For Couples and Their CounselorsDocument25 pagesPsychology, Help) Conflict Resolution - Essential Skills For Couples and Their Counselorsfabianp123100% (1)
- CNS PDFDocument412 pagesCNS PDFSami Juggy G100% (1)
- Neuro Part 1 NotesDocument3 pagesNeuro Part 1 NotesMarc JasminNo ratings yet
- Research Methods in PsychologyDocument2 pagesResearch Methods in PsychologyHillaryNo ratings yet
- TEACCH WorkshopDocument28 pagesTEACCH WorkshopCristina Penisoara100% (1)
- Sinelnikov Vol IIIDocument395 pagesSinelnikov Vol IIIFlorescu Diana NicoletaNo ratings yet
- PonsDocument61 pagesPonsAyberk ZorluNo ratings yet
- Neuroana 11 Brainstem Cranial NervesDocument4 pagesNeuroana 11 Brainstem Cranial Nervest4gjzhpfjcNo ratings yet
- 06a - Introduction To Spinal Cord - NeuroanatomyDocument9 pages06a - Introduction To Spinal Cord - Neuroanatomyhiba jasimNo ratings yet
- Brainstem and CerebellumDocument3 pagesBrainstem and CerebellumwifolNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument2 pagesCranial NervesJade ElevazoNo ratings yet
- Pons and MidbrainDocument11 pagesPons and MidbrainhusshamNo ratings yet
- 652ee54506eb96001861e88a - ## - Neural Control and Coordination Part 1 Short NotesDocument3 pages652ee54506eb96001861e88a - ## - Neural Control and Coordination Part 1 Short Notesjai maa Durga aadi parashakti100% (1)
- Pons and Midbrain Neuroanatomy: Abbas A. A. Shawka Medical Student 2nd GradeDocument47 pagesPons and Midbrain Neuroanatomy: Abbas A. A. Shawka Medical Student 2nd GradePlutokidNo ratings yet
- Di Encephalo NDocument6 pagesDi Encephalo NbolivarsefNo ratings yet
- PonsDocument18 pagesPonsDr.Saber - Ar - RaffiNo ratings yet
- Snell's Clinical Neuroanatomy Chapter PonsDocument6 pagesSnell's Clinical Neuroanatomy Chapter PonstsidazizyNo ratings yet
- B373 Unit 2 CNS W22Document60 pagesB373 Unit 2 CNS W22tamaraamhaNo ratings yet
- (REV) Neuroanatomy and NeurophysiologyDocument8 pages(REV) Neuroanatomy and NeurophysiologyReichelleNo ratings yet
- NEUR-B-S03-T04-Cranial Nerves VII-XIIDocument9 pagesNEUR-B-S03-T04-Cranial Nerves VII-XIIJohn Wilbern AlmeriaNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy: Chapter 5: Introduction To The BrainstemDocument4 pagesNeuroanatomy: Chapter 5: Introduction To The BrainstemANGELI SIAOTONGNo ratings yet
- Table of Tracts NCSDocument3 pagesTable of Tracts NCSLuis Manuel Vegas IsasiNo ratings yet
- NEURODocument10 pagesNEUROreooooNo ratings yet
- Lec 03 - Assessing of Neurological System and Special SensesDocument7 pagesLec 03 - Assessing of Neurological System and Special SensesIRISH MANIAGONo ratings yet
- The Peripheral Nervous System and Special SensesDocument10 pagesThe Peripheral Nervous System and Special SensesRODGIELYN MAE GEJONNo ratings yet
- Case Compilation 2 (Spina Bifida) by Navera, Aleksa Mikael EDocument10 pagesCase Compilation 2 (Spina Bifida) by Navera, Aleksa Mikael Ebtfd2ky4hhNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord & PNS - Dr. DoqueniaDocument42 pagesSpinal Cord & PNS - Dr. DoqueniaCRUZ Jill EraNo ratings yet
- NetterDocument2 pagesNetternclov.00No ratings yet
- My Encephalo NDocument2 pagesMy Encephalo NC1 - RAZALAN NICKA JOYNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Nervous Sytem of HumanDocument39 pagesAnatomy of Nervous Sytem of HumanKharisulNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord (3 of 5)Document24 pagesSpinal Cord (3 of 5)j53934762No ratings yet
- 23 Level 6 Introduction Neuroantomy MeningesDocument23 pages23 Level 6 Introduction Neuroantomy MeningesMustafa Kandil SolimanNo ratings yet
- Embryology NeuromuscularDocument6 pagesEmbryology NeuromuscularDEBORA RIADI ALIM SUPRAPTONo ratings yet
- The Brain: Telencephalon Diencephalon CerebellumDocument51 pagesThe Brain: Telencephalon Diencephalon Cerebellumprasun_vNo ratings yet
- 02-DEVELOPMENT OF THE CNS (DR. Jamila)Document32 pages02-DEVELOPMENT OF THE CNS (DR. Jamila)Ram LakshmanNo ratings yet
- 7 - Physiology of Brain StemDocument15 pages7 - Physiology of Brain StemkaputostanleyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesChapter 7 - Nervous SystemRishelle Mae Miñoza PilonesNo ratings yet
- 11-CNS & BrainDocument6 pages11-CNS & Brainapi-3757921No ratings yet
- Histology - MidtermDocument14 pagesHistology - MidtermMac-ris JandaNo ratings yet
- 0-Review File (FINAL)Document40 pages0-Review File (FINAL)kaputostanleyNo ratings yet
- Brainstem CN1-6Document31 pagesBrainstem CN1-6Dhanen Dran100% (1)
- Week 2 Musculo-Skeletal Notes The Structure of The Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesWeek 2 Musculo-Skeletal Notes The Structure of The Nervous SystemjhnnolanNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesNervous SystemJustGellaiNo ratings yet
- Abducent Nerve: DR. Nirmal Jayadev Final Year PG Student (MS Ophthalmology) MKCG Medical College Berhampur OdishaDocument58 pagesAbducent Nerve: DR. Nirmal Jayadev Final Year PG Student (MS Ophthalmology) MKCG Medical College Berhampur OdishaZeptalanNo ratings yet
- Brainstem: Midbrain and PonsDocument48 pagesBrainstem: Midbrain and PonsKiky Nur Asma RizkyNo ratings yet
- Neuro 3.05 Telencephalon Dra. TrinidadDocument11 pagesNeuro 3.05 Telencephalon Dra. TrinidadMarlon BauagNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument9 pagesReviewerbspsych.lajada.aNo ratings yet
- 3 TrigeminalwordDocument26 pages3 TrigeminalwordrajaniNo ratings yet
- Quantum PhysicsDocument6 pagesQuantum PhysicsshivanshuNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System: Dr. Rasha Alshali Assistant Prof. in Anatomy DepartmentDocument28 pagesThe Nervous System: Dr. Rasha Alshali Assistant Prof. in Anatomy DepartmentCaim ZNo ratings yet
- Tabl Cranial NervesDocument9 pagesTabl Cranial NervesRaya NadNo ratings yet
- Histophysiology of Synapses and Neurosecretion: International Series of Monographs on Pure and Applied Biology: Modern Trends in Physiological SciencesFrom EverandHistophysiology of Synapses and Neurosecretion: International Series of Monographs on Pure and Applied Biology: Modern Trends in Physiological SciencesNo ratings yet
- Echidnas: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied Biology: ZoologyFrom EverandEchidnas: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied Biology: ZoologyNo ratings yet
- Epithelium - Noted Anatomist - Location + MnemonicsDocument5 pagesEpithelium - Noted Anatomist - Location + Mnemonicshiba jasimNo ratings yet
- MidBrain Neuroanatomy - Medicosis PerfectionalisDocument4 pagesMidBrain Neuroanatomy - Medicosis Perfectionalishiba jasimNo ratings yet
- Bone Anatomy + Histology - Medicosis Perfectionalis NotesDocument11 pagesBone Anatomy + Histology - Medicosis Perfectionalis Noteshiba jasimNo ratings yet
- 01 - Bone Marrow & Hematopoiesis - Dr Najeeb HematologyDocument8 pages01 - Bone Marrow & Hematopoiesis - Dr Najeeb Hematologyhiba jasimNo ratings yet
- 07c - Spinal Cord - Descending Tracts - DR Najeeb VideosDocument19 pages07c - Spinal Cord - Descending Tracts - DR Najeeb Videoshiba jasimNo ratings yet
- Medulla Oblongata Neuroanatomy - Medicosis PerfectionalisDocument6 pagesMedulla Oblongata Neuroanatomy - Medicosis Perfectionalishiba jasimNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Neurophysiology - Medicosis Perfectionalis - All VideosDocument29 pagesAutonomic Neurophysiology - Medicosis Perfectionalis - All Videoshiba jasimNo ratings yet
- 07b - Spinal Cord - Ascending Tracts - DR Najeeb VideosDocument35 pages07b - Spinal Cord - Ascending Tracts - DR Najeeb Videoshiba jasimNo ratings yet
- 01 OogenesisDocument6 pages01 Oogenesishiba jasimNo ratings yet
- Gogh Case Study PDFDocument14 pagesGogh Case Study PDFzeelaf sirajNo ratings yet
- Life-Span Development Quizlet 2Document17 pagesLife-Span Development Quizlet 2Mik DeslateNo ratings yet
- U - Lesson 4 - Listening and Reading (Homework)Document7 pagesU - Lesson 4 - Listening and Reading (Homework)Tuấn Hợp VũNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER ONE Class XIIDocument16 pagesCHAPTER ONE Class XIILishika BellaniNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 1 - Introduction To Art AppreciationDocument34 pagesLECTURE 1 - Introduction To Art AppreciationAlyNo ratings yet
- Test of Memory Malingering (TOMM)Document11 pagesTest of Memory Malingering (TOMM)Helping OthersNo ratings yet
- Thought: NeuropsychologyDocument7 pagesThought: Neuropsychologypratyush1988No ratings yet
- Lobes Structures of The BrainDocument2 pagesLobes Structures of The BrainCognita CenterNo ratings yet
- Blue Brain TechnologyDocument15 pagesBlue Brain TechnologyGubbala SureshNo ratings yet
- HDEV 3rd Edition Rathus Test Bank 1Document25 pagesHDEV 3rd Edition Rathus Test Bank 1mark100% (48)
- Psychodynamics Part 1Document5 pagesPsychodynamics Part 1Nhicco Francis Abejuela100% (1)
- Faculty History: The Faculty of PsychologyDocument3 pagesFaculty History: The Faculty of Psychologyjaqueline kakuNo ratings yet
- Design and Explain A Daily Life Experiment According To Classical ConditioningDocument4 pagesDesign and Explain A Daily Life Experiment According To Classical ConditioningMuhammad Sohail MalikNo ratings yet
- The Importance of First Impressions in A Job Interview: Conference PaperDocument21 pagesThe Importance of First Impressions in A Job Interview: Conference PaperUngureanu DianaNo ratings yet
- WebbyDocument12 pagesWebbyapi-327832679No ratings yet
- 1 PreL Developmental Tasks of Normal AdolescenceDocument2 pages1 PreL Developmental Tasks of Normal AdolescenceCorazon AgramosNo ratings yet
- The Cognitive Perspective On Learning: Its Theoretical Underpinnings and Implications For Classroom PracticesDocument11 pagesThe Cognitive Perspective On Learning: Its Theoretical Underpinnings and Implications For Classroom PracticesPedro CalderonNo ratings yet
- Module 2 PPT The Nervous System 2022Document50 pagesModule 2 PPT The Nervous System 2022mazibukonokwanda146No ratings yet
- Trait & Type Theories of PersonalityDocument17 pagesTrait & Type Theories of Personalitykrishnavn82% (17)
- Response To Intervention Vs Discrepancy ModelDocument4 pagesResponse To Intervention Vs Discrepancy ModelshobaNo ratings yet