0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views13 pagesFormwork-Guy Wire
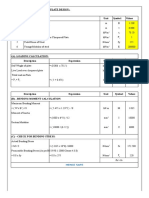
The document contains structural design calculations for the NLEX-SLEX Connector Road Section 2, focusing on column formwork supported by guy wires. It details the design criteria, wind load computations, and stability analysis to ensure the adequacy of the formwork against lateral forces. The calculations confirm that the design meets safety standards and structural integrity requirements based on various load conditions.
Uploaded by
iwwiw oplaksCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views13 pagesFormwork-Guy Wire
The document contains structural design calculations for the NLEX-SLEX Connector Road Section 2, focusing on column formwork supported by guy wires. It details the design criteria, wind load computations, and stability analysis to ensure the adequacy of the formwork against lateral forces. The calculations confirm that the design meets safety standards and structural integrity requirements based on various load conditions.
Uploaded by
iwwiw oplaksCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd