0% found this document useful (0 votes)
419 views33 pagesNovel Multilevel Inverter for Induction Motors
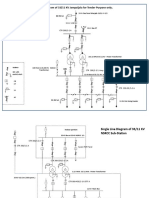
The document summarizes a simulation of a novel multilevel inverter topology for induction motor drive applications. It presents a new multilevel inverter topology that produces a 13-level output voltage using only 9 switches and a diode, compared to the conventional H-bridge topology that requires 12 switches. The proposed topology reduces the number of components needed to generate multilevel output voltages. Simulation results in MATLAB/Simulink show the output voltage waveform and total harmonic distortion for the proposed topology applied to an induction motor drive, demonstrating lower THD compared to conventional topologies.
Uploaded by
Prathap VuyyuruCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
Topics covered
- Induction Motor,
- Performance Comparison,
- Clamping Diodes,
- MATLAB/SIMULINK,
- Voltage Waveform,
- Multilevel Inverter,
- Balancing Capacitors,
- THD Analysis,
- PWM Techniques,
- Phase Disposition
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
419 views33 pagesNovel Multilevel Inverter for Induction Motors
The document summarizes a simulation of a novel multilevel inverter topology for induction motor drive applications. It presents a new multilevel inverter topology that produces a 13-level output voltage using only 9 switches and a diode, compared to the conventional H-bridge topology that requires 12 switches. The proposed topology reduces the number of components needed to generate multilevel output voltages. Simulation results in MATLAB/Simulink show the output voltage waveform and total harmonic distortion for the proposed topology applied to an induction motor drive, demonstrating lower THD compared to conventional topologies.
Uploaded by
Prathap VuyyuruCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
Topics covered
- Induction Motor,
- Performance Comparison,
- Clamping Diodes,
- MATLAB/SIMULINK,
- Voltage Waveform,
- Multilevel Inverter,
- Balancing Capacitors,
- THD Analysis,
- PWM Techniques,
- Phase Disposition