Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 1 - The Characteristics of Cells
Uploaded by
Johny Cristian Mamani Contreras0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
222 views12 pagesssssssssssss
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentssssssssssss
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
222 views12 pagesLesson 1 - The Characteristics of Cells
Uploaded by
Johny Cristian Mamani Contrerasssssssssssss
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
Unit 1 Lesson 1 The Characteristics of Cells
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 1 The Characteristics of Cells
Cell-ebrate!
What is a cell?
• A cell is the smallest functional and structural unit
of all living organisms.
• An organism is any living thing that carries out
its own life processes.
• Robert Hooke was the first to describe cells. He
looked at the bark of a cork tree under a
microscope.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 1 The Characteristics of Cells
Why are most cells small?
• Cells are small because their size is limited by
their outer surface area.
• If cells get too large, they cannot take in enough
nutrients or get rid of enough wastes.
• The surface area-to-volume ratio of a cell is the
ratio of the outer surface to the cell’s volume. The
smaller the cell, the greater this ratio.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 1 The Characteristics of Cells
Cell Hall of Fame
What is the cell theory?
• The cell theory lists three basic characteristics of
all cells and organisms.
• All organisms are made up of one or more cells.
• The cell is the basic unit of all organisms.
• All cells come from existing cells.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 1 The Characteristics of Cells
What is the cell theory?
• Anton van Leeuwenhoek was the first to describe
living cells.
• Matthias Schleiden concluded that all plants are
made of cells.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 1 The Characteristics of Cells
What is the cell theory?
• Theodor Schwann determined that all animal
tissues are made of cells.
• Rudolf Virchow proposed that cells could form only
from the division of other cells.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 1 The Characteristics of Cells
What is the cell theory?
• Organisms made up of just one cell are called
unicellular organisms.
• The single cell must carry out all of the organism’s
life functions.
• Organisms made up of more than one cell are
called multicellular organisms.
• The cells of multicellular organisms have
specialized functions.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 1 The Characteristics of Cells
On the Cellular
What parts do all cells have in
common?
• All cells have some structures in common.
• A cell membrane is a protective layer that covers
a cell’s surface and controls materials moving into
and out of the cell.
• The cytoplasm is the region inside the cell that
includes the fluid and all the organelles except for
the nucleus.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 1 The Characteristics of Cells
What parts do all cells have in
common?
• An organelle is a small body in the cytoplasm
that is specialized to perform a specific function.
• The nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle that
contains DNA.
• DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is genetic material
that provides instructions for all cell processes.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 1 The Characteristics of Cells
What parts do all cells have in
common?
• How many parts of a cell can you name?
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 1 The Characteristics of Cells
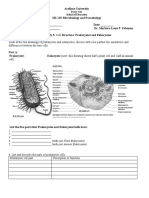
What are the two types of cells?
• Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms that do
not have a nucleus or membrane-bound
organelles.
• Prokaryotes’ DNA is in the cytoplasm. They have
organelles without cell membranes called
ribosomes.
• Some have hairlike structures called flagella that
help them move.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 1 The Characteristics of Cells
What are the two types of cells?
• Eukaryotes are organisms made up of cells that
contain DNA in a nucleus, membrane-bound
organelles, and ribosomes.
• Animals, plants, protists, and fungi are
eukaryotes.
• Most eukaryotes are multicellular but some are
unicellular.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
You might also like
- The Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandThe Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Cell - The Unit of Life - Mind Maps - Arjuna NEET 2024Document3 pagesCell - The Unit of Life - Mind Maps - Arjuna NEET 2024Wind Follower MusicNo ratings yet
- Are All Cells AlikeDocument5 pagesAre All Cells AlikebloodyvampirefangNo ratings yet
- 4 - Levels of Organization of Living ThingsDocument20 pages4 - Levels of Organization of Living ThingsFrancisco jezziel dominguez fernandezNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio1 q1 Module2 Wk2Document18 pagesGen Bio1 q1 Module2 Wk2Teacher Charlyn VlogNo ratings yet
- 6-8A - CNLAEPN693330 - U01L04 Levels of CellularDocument14 pages6-8A - CNLAEPN693330 - U01L04 Levels of CellularWafaaFaroukNo ratings yet
- نظري1 طب حياتيDocument7 pagesنظري1 طب حياتيrppuwwNo ratings yet
- 6-8A - CNLAEPN693330 - U01L03 Cell Strucure MdefiedDocument14 pages6-8A - CNLAEPN693330 - U01L03 Cell Strucure MdefiedWafaaFaroukNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Microbiology and ParasitologyDocument6 pagesModule 3 - Microbiology and Parasitologyarsdef tuanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document39 pagesLecture 1Mohammed SindiNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument16 pagesChapter - 5 The Fundamental Unit of Lifekarunadawar.11No ratings yet
- Gen BioDocument12 pagesGen BioBANGYAY, LAWRENCE ANTHONYNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Biology and Its ThemesDocument37 pagesLecture 1 Biology and Its Themesghazi113333No ratings yet
- CellDocument44 pagesCellIngridNo ratings yet
- Unit 6. The Eartha Planet Full of LifeDocument110 pagesUnit 6. The Eartha Planet Full of LifePika PiNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument11 pagesFundamental Unit of Lifeyogeshks1985No ratings yet
- CellDocument28 pagesCellرقية معتز محمودNo ratings yet
- RSL Cell TheoryDocument48 pagesRSL Cell TheoryReynald Legarda Jr.No ratings yet
- GB 1 - Quarter 3 Week 4-6Document115 pagesGB 1 - Quarter 3 Week 4-6cauilan.cameron11No ratings yet
- Animal Plant CellsDocument15 pagesAnimal Plant Cellsrain06021992No ratings yet
- Introduction To CellsDocument87 pagesIntroduction To CellsLovely Ann LoyogoyNo ratings yet
- Gen. BioDocument50 pagesGen. BioJohn Russel ValdezNo ratings yet
- Quipper 1 - Earth and Life Science - CellDocument17 pagesQuipper 1 - Earth and Life Science - CellPhil Christian MerinoNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure 1Document14 pagesCell Structure 1api-429724044No ratings yet
- 1&2. Basic Unit of Life - CellsDocument59 pages1&2. Basic Unit of Life - CellsRaffyChuaNo ratings yet
- 9.4. CellDocument88 pages9.4. CellTUĞRUL ERGÜLNo ratings yet
- Cells and StructureDocument17 pagesCells and StructurekayleenerikaNo ratings yet
- Classroom at Home: Department of Education HIGHSCHOOL DepartmentDocument33 pagesClassroom at Home: Department of Education HIGHSCHOOL DepartmentKrystin DiamosNo ratings yet
- 1 The CellDocument75 pages1 The CelllorenzegeneblaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure 1Document14 pagesCell Structure 1api-429724044No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document44 pagesChapter 3Altaf Hussain KhanNo ratings yet
- Module 1 2 Additional MaterialDocument7 pagesModule 1 2 Additional MaterialEli Joshua EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Cell ReviewerDocument6 pagesCell ReviewerEva Marie GaaNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument36 pagesCell StructureKate Clancy NugaoNo ratings yet
- GB L1Document34 pagesGB L1lamberto revecheNo ratings yet
- 1Q Reviewer General Biology 1Document9 pages1Q Reviewer General Biology 1Ruby May Regala100% (9)
- TOPIC 2 - CellDocument9 pagesTOPIC 2 - CellAl Johan Atienza100% (1)
- 3.1 Reinforcement: Key ConceptDocument1 page3.1 Reinforcement: Key ConceptEyad TalaatNo ratings yet
- Levels of OrganiztionDocument21 pagesLevels of OrganiztionSahar HassanNajadNo ratings yet
- Animal Plant CellsDocument15 pagesAnimal Plant CellsMarilou TagarinoNo ratings yet
- HSCI100 Lecture02 F2023Document56 pagesHSCI100 Lecture02 F2023niko.carson.9No ratings yet
- Se Mi N Nhóm 1Document87 pagesSe Mi N Nhóm 1Trịnh Bảo MinhNo ratings yet
- Bio g7Document66 pagesBio g744mnx692cbNo ratings yet
- Intro1 - The Cellular Basis of LifeDocument19 pagesIntro1 - The Cellular Basis of LifeCheryl MountainclearNo ratings yet
- Biology - Module 1Document6 pagesBiology - Module 1ASHLEY MONICA PLATANo ratings yet
- PRPLLLDocument19 pagesPRPLLLPraveen KolaganiNo ratings yet
- From Cells To Organisms: Learning ObjectivesDocument39 pagesFrom Cells To Organisms: Learning ObjectivesJoanneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction: Ten Themes in The Study of Life: 1. Each Level of Biological Organization Has Emergent PropertiesDocument77 pagesChapter 1 Introduction: Ten Themes in The Study of Life: 1. Each Level of Biological Organization Has Emergent Propertiestai3214No ratings yet
- 01 Living ThingsDocument32 pages01 Living Thingsapi-632307358No ratings yet
- HSTL Ch03Document99 pagesHSTL Ch03Patrick wasimNo ratings yet
- Bio MergedDocument366 pagesBio MergedReshab Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lower Secondary BIOLOGY NOTESDocument19 pagesLower Secondary BIOLOGY NOTESmamboian01No ratings yet
- Life Is: CellularDocument48 pagesLife Is: Cellularekapratista26No ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument60 pagesCell BiologyBhargavi SaravananNo ratings yet
- CellDocument27 pagesCellTom Anthony TonguiaNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument76 pagesCell BiologyDave Arthur Robledo100% (11)
- CellDocument15 pagesCellprakash kushwahaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Introduction To CellsDocument58 pages1.1 Introduction To CellsReeya WhabiNo ratings yet
- PHCG 201 CytologyDocument113 pagesPHCG 201 CytologyIbn HaarūnNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer MidtermDocument11 pagesScience Reviewer MidtermGenna CuencaNo ratings yet
- Ch05 Test File-CellsDocument37 pagesCh05 Test File-CellsRojan MirmohamadiNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic CellsDocument41 pagesProkaryotic vs. Eukaryotic CellsChennille Ann Bleu GundayaoNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles Functions Revised PowerPointDocument24 pagesCell Organelles Functions Revised PowerPointJanine Ginog FerrerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument18 pagesChapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeTownship TownshipNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document4 pagesModule 2Ivan PaulinoNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Earth & Life ScienceDocument16 pagesModule 3 Earth & Life ScienceNicole Mae SumaltaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Biochemistry A Short Course 4th Edition John Tymoczko Jeremy M Berg Gregory J Gatto JR Lubert StryerDocument11 pagesTest Bank For Biochemistry A Short Course 4th Edition John Tymoczko Jeremy M Berg Gregory J Gatto JR Lubert StryerJanice Linder100% (32)
- Cell Structure and Function For 1st Year MBBS Delivered by Miss Sumaira On 25 Jan 2010Document61 pagesCell Structure and Function For 1st Year MBBS Delivered by Miss Sumaira On 25 Jan 2010IMDCBiochem83% (6)
- Cell and Cell Organelles - Word Search PuzzleDocument2 pagesCell and Cell Organelles - Word Search Puzzleaubrianna.postellNo ratings yet
- Suggested Answers To Exercise, Reading To Learn and Cross-Topic ExerciseDocument23 pagesSuggested Answers To Exercise, Reading To Learn and Cross-Topic ExerciseBernard100% (1)
- Principles of Human Anatomy 13th Edition Tortora Test BankDocument35 pagesPrinciples of Human Anatomy 13th Edition Tortora Test Bankpithlessriverp4d6100% (32)
- Activity 14 - Cell Structure-PERALTADocument3 pagesActivity 14 - Cell Structure-PERALTACogie PeraltaNo ratings yet
- The Cell ActivitiesDocument3 pagesThe Cell Activitiestiareximena0308No ratings yet
- Science 7 Second Quarter - Module 2 Cells and Levels of Biological OrganizationDocument6 pagesScience 7 Second Quarter - Module 2 Cells and Levels of Biological OrganizationAriel angelioNo ratings yet
- Organelle Trading Card GameDocument1 pageOrganelle Trading Card Gamechabries100% (3)
- 2022 Cells Revision AnswersDocument11 pages2022 Cells Revision Answersdantimtam33No ratings yet
- NCERT BookDocument10 pagesNCERT Bookkaushikray06No ratings yet
- A Digital Escape Room: © Mary Neimeyer Heynow ScienceDocument6 pagesA Digital Escape Room: © Mary Neimeyer Heynow Sciencekendall knight0% (2)
- Bio - Cells - Amoeba Sisters Intro KEYDocument2 pagesBio - Cells - Amoeba Sisters Intro KEYMa.Janice GarciaNo ratings yet
- Biophysics: An Introduction IDocument31 pagesBiophysics: An Introduction IKusum SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cells - The Building Blocks of LifeDocument2 pagesCells - The Building Blocks of LifeMuhammad QasimNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 NCERT Book Science THE FUNDAMENTAL UNIT OF LIFE Chapter 5 PDFDocument11 pagesCBSE Class 9 NCERT Book Science THE FUNDAMENTAL UNIT OF LIFE Chapter 5 PDFRaghav AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Estenias Science Foundation School 2ND Half Examination in Science 7 S.Y. 2021-2022Document3 pagesEstenias Science Foundation School 2ND Half Examination in Science 7 S.Y. 2021-2022MJ HagosNo ratings yet
- Pond WaterDocument4 pagesPond Waterapi-264011999No ratings yet
- Interactive Textbook 1 2 PDFDocument7 pagesInteractive Textbook 1 2 PDFapi-240094705No ratings yet
- Cell SongDocument6 pagesCell SongAshlie Joy Mendez OpeñaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 (Cell and Enzymes) - 1Document3 pagesChapter-1 (Cell and Enzymes) - 1ToXicNo ratings yet
- A Cell Crossword PuzzleDocument2 pagesA Cell Crossword PuzzleRichelyn CheNo ratings yet
- Solutions For All Life Sciences Grade 11 Learners BookDocument73 pagesSolutions For All Life Sciences Grade 11 Learners BookJustinCase19910% (2)
- Activity 5 - Cell Structure - Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument8 pagesActivity 5 - Cell Structure - Prokaryotes and EukaryotesAdrian NenengNo ratings yet