Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tune Hotel,: Hanoor Annisa Amir
Uploaded by
Hanoor AnnisaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tune Hotel,: Hanoor Annisa Amir
Uploaded by
Hanoor AnnisaCopyright:
Available Formats
Tune Hotel,
Hanoor Annisa Amir
Tune Hotel, Bali
Tunes hotel Bali, open in Legian
and Kuta Beach.
Tunes hotel star at room rate Rp.
98000 ($ 10.5)
The budget hotel follows closely
AirAsia's model by offering rooms
for accommodation at attractive
prices.
Balance Score Card
Vision
To be hotel chain that offer high
quality rooms with low price.
( 5 Star Sleeping experience with 1
Star price )
Mission
To provide hotel service resulting
long term satisfaction of our
stakeholders.
Tune Hotel Product
Limited Service
Low Price, Low Service
Omitting conventional full Service
Additional amenities and services like
toiletries, air-conditioning, TV and in-room
Wifi are offered as “pay as you use” extras.
Hotel space is also available for rent to
advertisers (indoors, outdoors as well as
whole floors) also on room walls, on room
keys, in hallways and in the lobby.
Major Brand that have advertisement =
Nestle, CIMB Bank, King Koil
Unit Selling Point
Tune Hotel design its hotels, rooms and business for guests who
are more likely to spend most of their time out and about during
the day time.
Its five unique selling propositions are:
5-star beds
Heated, high-pressure Power Showers
Central and strategic locations
Clean environment
Safe and secure environment with 24-hour security guards on
duty and extensive CCTV coverage
SWOT
Strength Opportunity
Low price in the market. High Tourism market in Bali.
High market in the Air Asia There is a lack of hotel that are
Customer. cheap and good quality rooms.
Weakness Threats
Low Quality Workers. Indonesia Economic and Political
Crisis
PESTEL
Risk of Political Instability, 2010 Country Rating1
Political = Australia 9.24
Singapore 8.78
Instability from
New Zealand 8.76
Germany 8.49
France 8.46
government
United States 8.16
Hong Kong SAR 7.49
Uncertainty of United Kingdom 7.41
China 7.12
government changing
India 7.08
Malaysia 6.90
Taiwan 6.42
Developing Taxation
Korea
Japan
5.72
5.40
Indonesia 4.94
Security Issues Philippines 3.50
Thailand 1.75
Footnotes:1: 0 = very high, 10 = very low
Economic
Instable Economic Policy
Global Financial Crisis
Increasing in hotel competitive in the hotel industry
PASTEL, cont
Social Technology
Low minimum income for labor
Challenges of Technology in
Low Level of Education Indonesia.
The high gap between low and medium to high
income.
High Consumerism Law and Regulation
UMR ( Minimum wages by
regulations )
Environment
800.000,0 ( $ 79 )
Natural Disaster
National Security Instable Regulations.
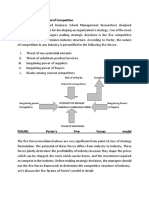
Porters 5 Forces Model
Threats of new Entrants Threat of Substitute
Capital Requirement, the start up There are number of low price
cost for making investment are hotel in this area.
better compare to other country.
Experience, Tune Hotel recruit
Indonesian employee and
shareholder.
Cost Competitive, Tunes hotel are
the cheapest hotel in the area.
Porters, cont
The bargaining power of buyers The Bargaining Power suppliers
Low degree of dependency High variations of distribution
channels
High buyer information
availability High substitutes but quality
questionable.
Unique of our hotel product.
Porters Generic Strategies
Tunes Hotel is Cost Leadership for Hospitality, not just
one specific market can be family, business etc
They have the lowest price in the hotel industry in Bali,
but they have profit from cost effective and efficiency.
COMMENTS
Good background
Identification of cost leadership strategy
The PEST should have come first giving more structure
Think of the S and its effect on E and the environment
and then link to business implications
SWOT identified and utlised, develop criticality
Use of P 5 Forces could have been more critical
Fair attempt.
Reference List
harp, Byron; Dawes, John (1996), "Is Differentiation Optional? A Critique of Porter's
Generic Strategy Typology," in Management, Marketing and the Competitive
Process, Peter Earl, Ed. London: Edward Elgar.
^ Speed, Richard J. (1989), "Oh Mr Porter! A Re-Appraisal of Competitive Stra
tegy," Marketing Intelligence and Planning, 7 (5/6), 8-11.
^ Yetton, Philip, Jane Craig, Jeremy Davis, and Fred Hilmer (1992), "Are Diam
onds a Country's Best Friend? A Critique of Porter's Theory of National Comp
etition as Applied to Canada, New Zealand and Australia," Australian Journal
of Management, 17 (No. 1, June), 89-120.
^ Allio, Robert J. (1990), "Flaws in Porter's Competitive Diamond?," Planning
Review, 18 (No. 5, September/October), 28-32
.
"Indonesia: Country Brief".
Indonesia:Key Development Data & Statistics. The World Bank. September 2006.^
"Historical Exchange Rates". OANDA. 7 January 2010. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
Indonesian Central Statistics Bureau (1 September 2006).
"Tingkat Kemiskinan di Indonesia Tahun 2005–2006" (in Indonesian) (PDF). Press r
elease. Archived from
the original on September 27, 2006. Retrieved 26 September 2006.
"Indonesia". InterKnowledge Corp.. Retrieved 6 October 2006.
You might also like
- Great Lakes Institute of Management, Chennai Class 3 Group 8Document5 pagesGreat Lakes Institute of Management, Chennai Class 3 Group 8Pratyuosh SrivastavNo ratings yet
- Tune - Power Point SlidesDocument42 pagesTune - Power Point SlidesYL HuiNo ratings yet
- Business EnvironmentDocument13 pagesBusiness EnvironmentArun SomanNo ratings yet
- Moonshot Applied: Sustaining Exceptional Innovation at ScaleFrom EverandMoonshot Applied: Sustaining Exceptional Innovation at ScaleNo ratings yet
- Competitive Analysis of Sleeping PodsDocument51 pagesCompetitive Analysis of Sleeping PodsRALPH JOSEPH SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management of ITC Hotel and SnapdealDocument22 pagesStrategic Management of ITC Hotel and SnapdealUtkarsh KumbhareNo ratings yet
- OYO Rooms - 5 Sep 2019Document18 pagesOYO Rooms - 5 Sep 2019Pk TripathiNo ratings yet
- Strategic Analysis of InfosysDocument44 pagesStrategic Analysis of InfosysGaurav AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Understanding REITDocument13 pagesUnderstanding REITHappyMan100% (1)
- Group 11 Presentation on 4 P's of MarketingDocument20 pagesGroup 11 Presentation on 4 P's of MarketingVinay VashisthNo ratings yet
- OYO Rooms Group AssignmentDocument13 pagesOYO Rooms Group AssignmentFaraz ShakirNo ratings yet
- Summer Internship Project ON Indian Hotels Company LimitedDocument13 pagesSummer Internship Project ON Indian Hotels Company LimitedLenovo K8noteNo ratings yet
- Tune Hotel 5 Forces ReportDocument2 pagesTune Hotel 5 Forces ReportYL Hui100% (1)
- Infosys AnalysisDocument17 pagesInfosys AnalysisSalil LavgankarNo ratings yet
- Lemon Tree Hotel Founder Patu Keswani's JourneyDocument5 pagesLemon Tree Hotel Founder Patu Keswani's JourneyskankashNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Group 4 Strategy ManagementDocument6 pagesFinal Exam Group 4 Strategy Managementaci liuNo ratings yet
- Oyo Case StudyDocument5 pagesOyo Case StudyKshitiz AgrawalNo ratings yet
- KPO IndustriesDocument22 pagesKPO IndustriesPathikaryNo ratings yet
- Green Purchasing: A Global Channel For Improving The Environmental Performance of Small EnterprisesDocument16 pagesGreen Purchasing: A Global Channel For Improving The Environmental Performance of Small EnterprisesBurt HamnerNo ratings yet
- Hotel MarketingDocument43 pagesHotel MarketingnboobeshkumarNo ratings yet
- Business Plan HellowDocument25 pagesBusiness Plan HellowHiraiNo ratings yet
- Report On Marketing Strategies of HotelDocument60 pagesReport On Marketing Strategies of Hotelrishi1110100% (1)
- Project 02: "Analysis of Business Environment of Viettel Telecom Corporation"Document34 pagesProject 02: "Analysis of Business Environment of Viettel Telecom Corporation"Quyên QuyênNo ratings yet
- Case Study 2 - ManikSirDocument8 pagesCase Study 2 - ManikSirVarunNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategies of OYO RoomsDocument84 pagesMarketing Strategies of OYO RoomsSami ZamaNo ratings yet
- End Term Exam DCP 2021Document4 pagesEnd Term Exam DCP 2021PuneetNo ratings yet
- Taj HotelDocument23 pagesTaj HotelNani NcNo ratings yet
- STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT OF HDFC LIFE INSURANCEDocument48 pagesSTRATEGIC MANAGEMENT OF HDFC LIFE INSURANCENitin GuravNo ratings yet
- Oyo Vacation HomesDocument15 pagesOyo Vacation Homesshreya bhandaryNo ratings yet
- Case Study On OYODocument8 pagesCase Study On OYOMd ShadabNo ratings yet
- International Business: The New Realities: Fourth EditionDocument39 pagesInternational Business: The New Realities: Fourth EditionLuciNo ratings yet
- Business Environment AnalysisDocument20 pagesBusiness Environment AnalysisAshi JainNo ratings yet
- BrochureDocument12 pagesBrochureAli_Mushtaq_223No ratings yet
- Hotel Industry Analysis - FINALDocument51 pagesHotel Industry Analysis - FINALHafeel MohamedNo ratings yet
- Hotel MarketingDocument35 pagesHotel MarketingHaritha Padmanabhan67% (3)
- SM Group Present TM BerhadDocument19 pagesSM Group Present TM BerhadLadiezApparelBiz50% (2)
- For You. AlwaysDocument45 pagesFor You. AlwaysNitin KumarNo ratings yet
- 2008 - Pyramid Research - VN Communication MarketDocument25 pages2008 - Pyramid Research - VN Communication MarketNam BuiNo ratings yet
- Global StrategyDocument16 pagesGlobal StrategytariqdurraniNo ratings yet
- Managing Rewards in AsiaDocument20 pagesManaging Rewards in Asiajim agustianNo ratings yet
- Marketing PlanDocument11 pagesMarketing PlanGemma Lou VargasNo ratings yet
- TAJ FinalDocument24 pagesTAJ Finalanish02No ratings yet
- Oyo VS MMTDocument11 pagesOyo VS MMTMadhusmita pattnaikNo ratings yet
- ED+ Factsheet JuneDocument1 pageED+ Factsheet JunejagsNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On Intel Corporation, 1992: Group-62 (B Section)Document33 pagesA Case Study On Intel Corporation, 1992: Group-62 (B Section)asifabdullah khanNo ratings yet
- Decoding Global Financial MarketsDocument9 pagesDecoding Global Financial MarketsAKANKSHA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting Assignment: OYO and BYJU's Lifecycle AnalysisDocument23 pagesManagement Accounting Assignment: OYO and BYJU's Lifecycle AnalysisPrakhar KapoorNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Manager AssessmentDocument16 pagesPortfolio Manager AssessmentDanny AljodiNo ratings yet
- Alliance Texas: - What It Takes To Be My PartnerDocument11 pagesAlliance Texas: - What It Takes To Be My PartnerAmr A. MohamedNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument12 pagesUntitledanju antonyNo ratings yet
- HOTEL INDUSTR by Sunil AnjanaDocument22 pagesHOTEL INDUSTR by Sunil Anjanasunil1312No ratings yet
- A Project Report On Ration Analysis of Hotel IndustryDocument20 pagesA Project Report On Ration Analysis of Hotel IndustrySuvayu ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Altimus Brands - Group 4Document13 pagesAltimus Brands - Group 4BHOOSHAN AGNIHOTRI75% (4)
- Huwaei 130716153405 Phpapp01Document22 pagesHuwaei 130716153405 Phpapp01AmR ZakiNo ratings yet
- Marriott PresentationDocument36 pagesMarriott PresentationMatthew Cua90% (10)
- Tourism IndustryDocument23 pagesTourism Industrykamdica100% (2)
- Hanoor Annissa Amir & Emmanuel Kretapradhana 14 December 2010Document16 pagesHanoor Annissa Amir & Emmanuel Kretapradhana 14 December 2010Hanoor AnnisaNo ratings yet
- Annisa Culture Terakhir MingguDocument5 pagesAnnisa Culture Terakhir MingguHanoor AnnisaNo ratings yet
- Annisa Culture 1Document2 pagesAnnisa Culture 1Hanoor AnnisaNo ratings yet
- Tune Hotel Essai-1Document2 pagesTune Hotel Essai-1Hanoor AnnisaNo ratings yet
- How Starbucks Became an $80B Business Through International ExpansionDocument2 pagesHow Starbucks Became an $80B Business Through International ExpansionhowellNo ratings yet
- Sample - Global Footwear Market (2020 - 2025) - Mordor IntelligenceDocument36 pagesSample - Global Footwear Market (2020 - 2025) - Mordor IntelligenceSajib Chandra RoyNo ratings yet
- Tesla Strategy AnalysisDocument10 pagesTesla Strategy AnalysisVlad TiforNo ratings yet
- Strategic Frameworks - Ready Reckoner PDFDocument20 pagesStrategic Frameworks - Ready Reckoner PDFShishir SalvatoreNo ratings yet
- Module 1 (Production and Operations Management)Document23 pagesModule 1 (Production and Operations Management)Marlyn DaguioNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Case StudiesDocument54 pagesIntroduction To Case StudieskaramNo ratings yet
- SM Tutorial Questions JAN 2024Document8 pagesSM Tutorial Questions JAN 2024jiayiwang0221No ratings yet
- Porter's Five ForcesDocument5 pagesPorter's Five ForcesKris Tina100% (1)
- Pharmaceuticals Industry Analysis - FinalDocument29 pagesPharmaceuticals Industry Analysis - FinalRishiraj Kashyap100% (1)
- Mkt760 - Mrketing StrategyDocument102 pagesMkt760 - Mrketing Strategyanon_800547339No ratings yet
- Burger KingDocument26 pagesBurger Kingbusinessdatabases100% (1)
- Group No. 3 Strama ResearchDocument11 pagesGroup No. 3 Strama ResearchJoshua Pangilinan SalinNo ratings yet
- Unilever 5ps WRKSHPDocument9 pagesUnilever 5ps WRKSHPAbhimita GaineNo ratings yet
- ch2 Service Strategy (No A)Document43 pagesch2 Service Strategy (No A)Jacky changNo ratings yet
- Industry, Customer, and Competitor Analysis of Waterproof Spray ProductDocument49 pagesIndustry, Customer, and Competitor Analysis of Waterproof Spray Productmohamad hafizNo ratings yet
- Lego Group 3 Section CDocument11 pagesLego Group 3 Section CAkhil SureshNo ratings yet
- Marketing Analysis of Fila: BUS 620: Marketing Management Section 4Document33 pagesMarketing Analysis of Fila: BUS 620: Marketing Management Section 4Binayak StoreNo ratings yet
- Boone Kurtz - Expanded PPT - Ch02Document36 pagesBoone Kurtz - Expanded PPT - Ch02VARGHESE JOSEPH NNo ratings yet
- Cloud - Professional - Services - Market 2022 PDFDocument230 pagesCloud - Professional - Services - Market 2022 PDFMichela RomanoNo ratings yet
- Micheal Porter 5 Force ModelDocument3 pagesMicheal Porter 5 Force ModelKasi BuvaneshNo ratings yet
- Global Action Camera Market, 2021-2027Document252 pagesGlobal Action Camera Market, 2021-2027Deviyani Gaur100% (1)
- Cae07 All Chapter PDFDocument108 pagesCae07 All Chapter PDFJocelyn Sta AnaNo ratings yet
- Stategic ManagementDocument28 pagesStategic ManagementNipuna Bandara WeerakoonNo ratings yet
- Porter in Non Profit OrganizationsDocument52 pagesPorter in Non Profit OrganizationsMafer RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Bring Internal & External Factors Together with SWOT AnalysisDocument5 pagesBring Internal & External Factors Together with SWOT AnalysisKARISHMA RAJNo ratings yet
- Porter's Five Forces ModelDocument5 pagesPorter's Five Forces ModelPrajakta GokhaleNo ratings yet
- Gamble7e C03 FinalDocument45 pagesGamble7e C03 Finalsouheilhamze16No ratings yet
- ResilienceDocument40 pagesResilienceakhilNo ratings yet
- Internship Manual KUSTDocument27 pagesInternship Manual KUSTSaif Bettani KustNo ratings yet
- Arvind LTDDocument60 pagesArvind LTDSushma AM100% (1)