Professional Documents
Culture Documents
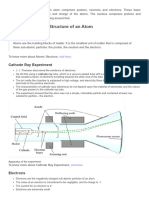
Understanding Radiation: Ionizing Radiation. Alpha, Beta or Gamma
Uploaded by
mohammed nawwab0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views30 pagesionising radiation presentation
Original Title
Ionising Radiation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentionising radiation presentation
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views30 pagesUnderstanding Radiation: Ionizing Radiation. Alpha, Beta or Gamma
Uploaded by
mohammed nawwabionising radiation presentation
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 30
Understanding Radiation
• A stable nucleus has the right
number of protons and
neutrons so that it does not
break apart.
• If this number changes the
nucleus becomes unstable and
breaks apart sending out
ionizing radiation.
• When this happens alpha,
beta or gamma radiation is
given out.
• Non-ionizing radiation comes
from the lower energy end of
the em spectrum
Before we discuss ionising
radiation we need to
understand a bit about
isotopes.
Does anybody know anything
about isotopes?
I have some
books here. I
would like you to
discuss in your
pairs the
meaning of
isotopes
Isotopes
• A particular element has a unique atomic
number.
• This means that the number of protons in the
nucleus of that element is fixed.
• For example oxygen will always have the
atomic number 8. In other words it will
always have 8 protons in its nucleus.
Isotopes
• However the number of neutrons can change.
• This means that an elements atomic mass can
change. (Remember Atomic mass = number of
protons + number of neutrons.)
• For instance Oxygen can have atomic masses
16, 17 or 18.
• Work out how many neutrons each isotope
has.
When an element has
too many neutrons
compared to the number
of protons it becomes
unstable. Lets explore
this a bit.
When the nucleus of
an element is
unstable it can emit
alpha, beta or
gamma rays
Radiation
The Helium Atom
• The Helium atom consists
of two protons, two
neutrons and 2 electrons.
• The protons and neutrons
are in the nucleus of the
atom.
• The electrons fly around
the nucleus
• Electrons are negatively
charged, protons are
positively charged.
The Alpha Particle
• The Alpha particle is the
same as a helium nucleus.
• The helium nucleus
consists of 2 protons and
2 neutrons.
• Because of the 2 protons
it has a charge of +2.
• A proton has a mass of 1
and so does a neutron.
The Alpha Particle Continued
• As we saw earlier the
helium nucleus consists of
2 protons and 2 neutrons.
• Because of this it has a
mass of 4
• We say the alpha particle
is heavy
• It moves with a speed of
1/10 the speed of light.
The Alpha Particle and Ionization
The Alpha Particle and Ionization
• The alpha particle is
large compared to an
electron.
• If the alpha particle hits
an electron on an atom
it will easily knock it off.
• When this happens the
atom becomes ionized
in other words it
becomes charged.
The Alpha Particle and Ionization
• It is for the reason
above that alpha
particles (α) are very
ionizing.
• However because α
particles are large and
heavy they cannot
penetrate material very
deeply.
The Alpha Particle and Ionization
• For instance our skin
protects humans from α
particles.
• If we get α particles
inside our body they
can do a lot of damage.
Let us look at the kind of
damage alpha particles
can do if ingested
Questions
• What is the charge on an α particle?
• What is the mass of an α particle?
• What does an α particle consist of?
• How fast does an α particle move?
• This is a challenge: Explain how an alpha
particle can cause ionization.
The Beta
Particle
All right then, lets talk
about the beta particle.
The beta
particle is
simply an How can
electron, but it that be sir?
comes from We all know
the nucleus of that there
an atom are only
protons and
neutrons in
the nucleus.
Let me ask you a question.
What is the charge on a
proton?
That’s right, it is positive?
We know both protons and
neutrons are in the nucleus and
they are the same mass.
Have you ever wondered why
neutrons do not have a charge?
We know that the proton has a
positive charge and has a mass
of 1.
If you squash an
electron into a proton,
what do you think the
charge would be?
The proton with its
positive charge and
the electron with its
negative charge add
up to 0.
The Neutron.
• A neutron is a proton with an electron
squashed into it.
• The electron neutralises the positive charge of
a proton.
• The electron adds no mass to the neutron.
• It is the electron that forms the neutron that
becomes a beta particle.
Questions
1. What is the charge on a proton?
2. What is the charge on a neutron?
3. What is the mass of a proton?
4. What is the mass of a neutron?
5. Explain how the neutron has no charge.
The Beta Particle
• A beta particle (β) is an electron.
• Because it is an electron it has a charge of -1.
• It is also very small. You need about 1700
electrons to equal the mass of 1 proton.
• A beta particle travels faster than the alpha
particle. The beta particle travels at 9/10 the
speed of light.
• Although it travels a lot faster than an α particle it
is a lot smaller and so has less ionization effects.
The Gamma Ray
• The gamma ray (ϒ) is a very high energy ray.
• It is part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
• It travels at the speed of light.
• It can only be stopped by thick concrete or
thick lead.
• Because it passes easily through most things it
does not ionize very greatly.
• It has no charge.
The Uses Of Ionizing Radiation
•Radioactive tracers
•Sterilising
•Thickness Control
•Checking welds
All can be found on page 352 of Keith
Johnson
•Alpha particles and fire alarms
Questions
• Where are protons and neutrons found?
• What is the charge on a proton?
• What is the charge on an electron?
• What is the mass of a proton?
• What is the mass of a neutron?
• What does an alpha particle consist of?
• What is the mass of an alpha particle?
• How fast does an alpha particle travel?
• What is the mass of an electron compared to a proton?
• Calculate how much smaller an electron is than an alpha particle?
• Explain why an alpha particle is a strong ioniser.
• What is a beta particle?
Questions
• What is the charge of a beta particle?
• How fast does it travel?
• Explain why it does not ionise very strongly.
• What is a gamma ray?
• What is the charge on a gamma ray?
• What is the speed of a gamma ray?
• What stops an alpha particle, a beta particle
and a gamma ray?
You might also like
- Monday: Chest and Triceps: Type Opener MainDocument3 pagesMonday: Chest and Triceps: Type Opener Mainmohammed nawwabNo ratings yet
- Atomic PhysicsDocument17 pagesAtomic PhysicsIbaad Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Atom and Molecule: Teaching Team in General ChemistryDocument43 pagesAtom and Molecule: Teaching Team in General ChemistryFarabi AlNo ratings yet
- Atom and Molecule: Teaching Team in General ChemistryDocument43 pagesAtom and Molecule: Teaching Team in General ChemistryAzizahNo ratings yet
- CH12 and CH15 Slides - AtomsDocument38 pagesCH12 and CH15 Slides - AtomskoalibrahimNo ratings yet
- The AtomDocument18 pagesThe Atomapi-276003030No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Materials and Cycles On EarthDocument218 pagesUnit 5 Materials and Cycles On EarthBlopNo ratings yet
- Periodic Trends CompleteDocument51 pagesPeriodic Trends CompleteZal Fildan DuomaNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity: Instructor: MR Toba Al-Kheir Islamic Girls' SeminaryDocument86 pagesRadioactivity: Instructor: MR Toba Al-Kheir Islamic Girls' SeminarySalehe TobaNo ratings yet
- Materials, Atoms, Bonding and Crystals: 3506FETQR Introductory Foundation PhysicsDocument70 pagesMaterials, Atoms, Bonding and Crystals: 3506FETQR Introductory Foundation Physicsalex tomsonNo ratings yet
- Dr.S.Balamurugan.,Bpharm, Pharmd Assistant Professor, Department of Pharmacy Practice, Kmch-CopDocument31 pagesDr.S.Balamurugan.,Bpharm, Pharmd Assistant Professor, Department of Pharmacy Practice, Kmch-CopbalamuruganNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Periodic TableDocument67 pagesAtomic Structure and Periodic Tablelsllsl9471No ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics CMDocument63 pagesNuclear Physics CMPeggyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17.1 Charging and DischargingDocument24 pagesChapter 17.1 Charging and Dischargingmostafa67No ratings yet
- 6B Atomic StructureDocument137 pages6B Atomic StructureOrane CassanovaNo ratings yet
- AtomsDocument6 pagesAtomsshreyaNo ratings yet
- Degay of ParticlesDocument19 pagesDegay of ParticlesbalamuruganNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 1 - Introduction To Electronics (The Atom)Document21 pagesLecture - 1 - Introduction To Electronics (The Atom)Yazeed AlharbiNo ratings yet
- Radioacitvity Lesson 1Document25 pagesRadioacitvity Lesson 1tanishknandal2009No ratings yet
- Structure of Atoms and IonsDocument34 pagesStructure of Atoms and IonsChristineNo ratings yet
- 6-8H Cnlaepn693408 U03l01Document16 pages6-8H Cnlaepn693408 U03l01Its ya BoiiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3. Nuclear Chemistry Part ONEDocument17 pagesChapter 3. Nuclear Chemistry Part ONEChengNo ratings yet
- MYP Atomic and Nuclear PhysicsDocument24 pagesMYP Atomic and Nuclear Physicszaidsarhan801No ratings yet
- Atomic Physics The Nuclear Atom and RadioactivityDocument44 pagesAtomic Physics The Nuclear Atom and RadioactivityAli Ahmad AliNo ratings yet
- Atom NotesDocument12 pagesAtom Notesapi-293263627No ratings yet
- AtomsDocument42 pagesAtomsapi-313808182No ratings yet
- Semiconductor BasicsDocument94 pagesSemiconductor BasicsArindam SenNo ratings yet
- The AtomDocument22 pagesThe Atomalbi veshiNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Elements and Molecules & Compounds and MixturesDocument32 pagesAtoms, Elements and Molecules & Compounds and MixturesTshanna RobertsNo ratings yet
- Nuclear TransformationDocument16 pagesNuclear TransformationAnsel MercadejasNo ratings yet
- Physics Art IntegratedDocument11 pagesPhysics Art IntegratedAnush DcostaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Number and Synthesis of New Elements, Nuclear ReactionDocument58 pagesAtomic Number and Synthesis of New Elements, Nuclear ReactionJesiah PascualNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document27 pagesChapter 1Imperial PlayzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Particle PhysicsDocument9 pagesChapter 11 Particle PhysicsLucas ShazNo ratings yet
- Atom Atom: Electron, The Proton and The NeutronDocument29 pagesAtom Atom: Electron, The Proton and The Neutronrehab ebraheemNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Fundamental ParticlesDocument7 pages1.1 Fundamental ParticlesAman ImranNo ratings yet
- Atom and Molecule: Teaching Team in General ChemistryDocument31 pagesAtom and Molecule: Teaching Team in General ChemistryRifqi AhmadNo ratings yet
- 1 - SCH3U 1.1 Nature of Atoms-2Document38 pages1 - SCH3U 1.1 Nature of Atoms-2Simon McCabeNo ratings yet
- C18-Radioactivity and Nuclear ReactionsDocument106 pagesC18-Radioactivity and Nuclear ReactionsAbhishek UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Radio Activity and ParticlesDocument34 pagesRadio Activity and ParticlesKiron SheiqNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Consituents of An Atom GSNDocument17 pagesLesson 1 Consituents of An Atom GSNhello3850No ratings yet
- 1 C Intro To Nuclear ChemistryDocument41 pages1 C Intro To Nuclear ChemistryNur Intan JunaediNo ratings yet
- Atomic PhysicsDocument41 pagesAtomic PhysicsFaiq IrfanNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Molecules: BIO 103-L2Document29 pagesThe Nature of Molecules: BIO 103-L2Nahid Sagar 1812889042No ratings yet
- Radioisotope TechniquesDocument57 pagesRadioisotope Techniquessamhossain1907No ratings yet
- Cie Igcse Physics Chapter 5 2023 OnwDocument12 pagesCie Igcse Physics Chapter 5 2023 OnwZeinab ElkholyNo ratings yet
- Periodic Trends: Elemental Properties and PatternsDocument42 pagesPeriodic Trends: Elemental Properties and PatternsreedskyNo ratings yet
- Atomic Physics.Document44 pagesAtomic Physics.Munashe MashiriNo ratings yet
- Periodic TrendsDocument10 pagesPeriodic TrendsyasiraeisigahroueiNo ratings yet
- TheatomwhatareatomsPDFNotesHandout 1Document25 pagesTheatomwhatareatomsPDFNotesHandout 1shanettes2000No ratings yet
- Introduction To The Structure of An Atom: AtomsDocument8 pagesIntroduction To The Structure of An Atom: Atomsshowmytv12No ratings yet
- The AtomDocument15 pagesThe AtomSeema ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics Atom and Its StructureDocument13 pagesModern Physics Atom and Its StructureRAHUL CHOUDHARYNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Unit 3 Atomic Theory (NXPowerLite) OppDocument35 pagesGrade 10 Unit 3 Atomic Theory (NXPowerLite) OppKrish CvNo ratings yet
- Structure of ElementsDocument20 pagesStructure of ElementsCJ MangasepNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules Revision NotesDocument45 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules Revision NotesOm KumarNo ratings yet
- RadioactivityDocument22 pagesRadioactivityChoudhry AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Chem ModuleDocument20 pagesChem Modulekeeno manzanoNo ratings yet
- Everything You Must Know about Radioactivity 6th Grade Chemistry | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandEverything You Must Know about Radioactivity 6th Grade Chemistry | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Studying A BTEC Degree Provided Me With Employability Skills Such As Cognitive and ProblemDocument1 pageStudying A BTEC Degree Provided Me With Employability Skills Such As Cognitive and Problemmohammed nawwabNo ratings yet
- Workplace Health Safety Business Productivity SustainabilityDocument49 pagesWorkplace Health Safety Business Productivity Sustainabilitymohammed nawwabNo ratings yet
- Packaging YourDocument2 pagesPackaging Yourmohammed nawwabNo ratings yet
- Presentation2 1Document5 pagesPresentation2 1mohammed nawwabNo ratings yet
- Legend of AestheticsDocument1 pageLegend of Aestheticsmohammed nawwabNo ratings yet
- Module 10 EcosystemDocument60 pagesModule 10 EcosystemDhvani DaxinaNo ratings yet
- 2021 SSG ProjectDocument3 pages2021 SSG ProjectAlbern Ray BaleanNo ratings yet
- NV Energy Files Settlement Agreement On GrandfatheringDocument40 pagesNV Energy Files Settlement Agreement On GrandfatheringAnonymous cBRIzagNo ratings yet
- Tiw PPT 06 FdtoolsDocument193 pagesTiw PPT 06 FdtoolsjovanivanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Lesson 1 What Are Some Plant Structures?Document16 pagesUnit 3: Lesson 1 What Are Some Plant Structures?Potato ManNo ratings yet
- Grade 9: Unit B: Matter and Chemical ChangeDocument7 pagesGrade 9: Unit B: Matter and Chemical Changeapi-253059746No ratings yet
- CSA Reforestation - C Estimates - AF MethodologyDocument2 pagesCSA Reforestation - C Estimates - AF MethodologySenator Cory BookerNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy For Passive House Heating Model of The Active Solar Heating SystemDocument13 pagesRenewable Energy For Passive House Heating Model of The Active Solar Heating SystemLuqmanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet-9 Work, K.E and P.EDocument3 pagesWorksheet-9 Work, K.E and P.EAndy MontesNo ratings yet
- CHM170L Exp2 DensityDocument6 pagesCHM170L Exp2 DensityKaiser SaltoNo ratings yet
- Power Factor Sizing GuideDocument6 pagesPower Factor Sizing GuideMatt SmithNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Headlands and BaysDocument3 pagesCharacteristics of Headlands and BaysRoshae SinclairNo ratings yet
- Una Interpretacion Fisica de La Constante de PlanckDocument11 pagesUna Interpretacion Fisica de La Constante de PlanckJuan Pablo Mejia GNo ratings yet
- Teske 2016 Global Outlook 2016 PDFDocument114 pagesTeske 2016 Global Outlook 2016 PDFaabbNo ratings yet
- Activity 6Document5 pagesActivity 6Sam MiraflorNo ratings yet
- 14.7 - Heat Capacity, Specific Heat, Molar Heat CapacityDocument24 pages14.7 - Heat Capacity, Specific Heat, Molar Heat Capacityadimegha100% (1)
- Report - Bridge PDFDocument21 pagesReport - Bridge PDFparas rahangdale100% (1)
- Rate of Reaction PPT 2Document11 pagesRate of Reaction PPT 2Aliyah HamiltonNo ratings yet
- DGT P Block ElementsDocument7 pagesDGT P Block ElementsFreelance WorkerNo ratings yet
- SLK Science Grade 7 Q4W3Document18 pagesSLK Science Grade 7 Q4W3JM RobleNo ratings yet
- The Low Carbon Menu: WhitepaperDocument34 pagesThe Low Carbon Menu: Whitepaperamitjain310No ratings yet
- DC Supply System, Batteries, UPSDocument59 pagesDC Supply System, Batteries, UPSNaresh RajuNo ratings yet
- Hooke's LawDocument29 pagesHooke's LawRene DescartesNo ratings yet
- Existing - Earthing - Layout For Bogra 230kV SubstationDocument1 pageExisting - Earthing - Layout For Bogra 230kV SubstationRashad SarwarNo ratings yet
- Pamphlet - System Earthing - English VersionDocument8 pagesPamphlet - System Earthing - English VersionDhanraj chavanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Periodic TableDocument4 pagesWorksheet Periodic TableMathilda AnisNo ratings yet
- 00b.types of MotionDocument4 pages00b.types of Motionaldy faleraNo ratings yet
- Trial Fizik K1 Melaka 2022Document22 pagesTrial Fizik K1 Melaka 2022GAN KHEK SEONG KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Planetary Geology: StratigraphyDocument2 pagesPlanetary Geology: StratigraphyJohn Kenneth BentirNo ratings yet
- (Oto-Hui - Com) en - Hydraulic CoursesDocument47 pages(Oto-Hui - Com) en - Hydraulic Courseseng_ebrahim_2000100% (1)