Professional Documents
Culture Documents
M32 9ThermalStress
Uploaded by
Ryan Jhay Yang0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views10 pagesThermal stress occurs due to temperature changes causing expansion and contraction of materials. For a homogeneous rod mounted between unyielding supports, thermal stress can be computed based on the modulus of elasticity, coefficient of thermal expansion, change in temperature, and length of the rod. As temperature increases, rods will be in compression, and as temperature decreases, rods will be in tension. Several example problems are provided to calculate thermal stress in steel rods and rails given temperature changes and material properties.
Original Description:
Original Title
M32-9ThermalStress
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThermal stress occurs due to temperature changes causing expansion and contraction of materials. For a homogeneous rod mounted between unyielding supports, thermal stress can be computed based on the modulus of elasticity, coefficient of thermal expansion, change in temperature, and length of the rod. As temperature increases, rods will be in compression, and as temperature decreases, rods will be in tension. Several example problems are provided to calculate thermal stress in steel rods and rails given temperature changes and material properties.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views10 pagesM32 9ThermalStress
Uploaded by
Ryan Jhay YangThermal stress occurs due to temperature changes causing expansion and contraction of materials. For a homogeneous rod mounted between unyielding supports, thermal stress can be computed based on the modulus of elasticity, coefficient of thermal expansion, change in temperature, and length of the rod. As temperature increases, rods will be in compression, and as temperature decreases, rods will be in tension. Several example problems are provided to calculate thermal stress in steel rods and rails given temperature changes and material properties.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
THERMAL STRESS
THERMAL STRESS
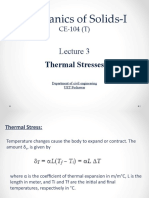
•Temperature changes cause the body to
expand or contract. The amount , is given
by
•where is the coefficient of thermal
expansion in m/m°C, is the length in meter,
and are the initial and final
temperatures, respectively in °C. For steel,
m/m°C.
THERMAL STRESS
•For a homogeneous rod mounted between
unyielding supports as shown, the thermal
stress is computed as:
•deformation due to temperature changes;
THERMAL STRESS
•deformation due to equivalent axial stress;
THERMAL STRESS
•where is the thermal stress in MPa, is the modulus of
elasticity of the rod in MPa.
•If the wall yields a distance of as shown, the following
calculations will be made:
THERMAL STRESS
•where represents the thermal stress.
•Take note that as the temperature rises
above the normal, the rod will be in
compression, and if the temperature drops
below the normal, the rod is in tension.
PROBLEMS
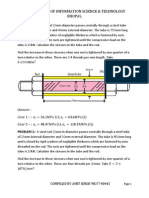
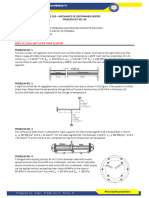
• 261. A steel rod with a cross-sectional area of
150mm2 is stretched between two fixed points.
The tensile load at 200C is 5000N. What will be
stress at –200C? At what temperature will the
stress be zero? Assume =11.7m/m0C and
E=200GPa.
PROBLEMS
• 262. A steel rod is stretched between two rigid
walls and carries a tensile load of 5000N at 200C.
If the allowable stress is not to exceed 130MPa at
–200C, what is the minimum diameter of the rod?
Assume =11.7m/m0C and E=200GPa.
PROBLEMS
• 263. Steel railroad rails 10m long are laid with a
clearance of 3mm at a temperature of 150C. At
what temperature will the rails just touch? What
stress would be included in the rails at that
temperature if there were no initial clearance?
Assume =11.7m/m0C and E=200GPa.
PROBLEMS
• 264. At a temperature of 900C, a steel tire 10mm
thick and 75mm wide that is to be shrunk onto a
locomotive driving wheel 1.8m in diameter just fits
over the wheel, which is at a temperature of 200C.
Determine the contact pressure between the tire
and wheel after the assembly cools to 200C.
Neglect the deformation of the wheel caused by
the pressure of the tire. Assume =11.7m/m0C
and E=200GPa.
You might also like
- Assignment Strength of MaterialsDocument11 pagesAssignment Strength of MaterialsVinay Korukonda0% (1)
- Thermal Stress: Mechanics of Deformable BodiesDocument10 pagesThermal Stress: Mechanics of Deformable BodiesPao CastillonNo ratings yet
- 1 SpringDocument69 pages1 SpringAJ Bantay100% (1)
- SOM Question Bank For RevisionDocument11 pagesSOM Question Bank For RevisiongoldencometNo ratings yet
- Set 6Document15 pagesSet 6Tare Er Kshitij60% (5)
- Strength of Materials Problem Set No.6Document9 pagesStrength of Materials Problem Set No.6Ashner NovillaNo ratings yet
- الاجهاد الحراريDocument3 pagesالاجهاد الحراريAmjed AL-KAHTEEBNo ratings yet
- Thermal Stress RumusDocument16 pagesThermal Stress RumusVakin Agung PermanaNo ratings yet
- Statically Indeterminate MembersDocument7 pagesStatically Indeterminate MembersKhan ToothNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids-I: Thermal StressesDocument16 pagesMechanics of Solids-I: Thermal StressesHammad AhmadNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument5 pagesQuestionsAli KasimNo ratings yet
- Es-103 PS4Document1 pageEs-103 PS4Frederick Perez IINo ratings yet
- Thermal Stress or Thermal Deformation Problems and SolutionDocument9 pagesThermal Stress or Thermal Deformation Problems and SolutionMiah EchavesNo ratings yet
- MOM Assignment IDocument3 pagesMOM Assignment IAll_regNo ratings yet
- Lec-4 Strength of MaterialsDocument18 pagesLec-4 Strength of MaterialsNathaniel Española Ovivir100% (1)
- Note Chapt IIDocument27 pagesNote Chapt IIRitesh KishoreNo ratings yet
- CE6302Document14 pagesCE6302Daniel MabengoNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids Ii Year/ Iv Semester Unit I Stress and Strain Part - ADocument14 pagesMechanics of Solids Ii Year/ Iv Semester Unit I Stress and Strain Part - AMohsin MullaNo ratings yet
- Simple Stress and StrainDocument3 pagesSimple Stress and StrainManish KumarNo ratings yet
- SOM Sheet - 3Document4 pagesSOM Sheet - 3Sonali VasisthaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1Sahil GaudeNo ratings yet
- CE 6306 / Strength of Materials Mechanical Engineering 2016-17Document6 pagesCE 6306 / Strength of Materials Mechanical Engineering 2016-17amdevaNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Simple Stresses and StrainsDocument54 pagesUnit-1 Simple Stresses and StrainsAmar Babu100% (1)
- Thermal ProblemsDocument2 pagesThermal Problemsحسين علي صبيحNo ratings yet
- 18ME404 Assignment 1Document2 pages18ME404 Assignment 1BharanitharanNo ratings yet
- 1-Thermal ADocument5 pages1-Thermal ABOITIZON, Julius C.No ratings yet
- MOM2Tutorial 10-1Document3 pagesMOM2Tutorial 10-1Ishola mujeebNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies: Engr. Ramir C. Del Mundo February 06, 2021Document51 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies: Engr. Ramir C. Del Mundo February 06, 2021Joshua DariaNo ratings yet
- Pre StressDocument9 pagesPre StressKevin John Ordoña EstilloreNo ratings yet
- Crane Rails and Changes in Temperature: Thermal ExpansionDocument3 pagesCrane Rails and Changes in Temperature: Thermal ExpansionPablo Hidalgo ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Thermal StressesDocument3 pagesThermal StressesYatharth KhicharNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Lecture 14 To 16Document7 pagesWeek 5 Lecture 14 To 16ChetanNo ratings yet
- Me2209 4Document28 pagesMe2209 4Anik hasan BadhonNo ratings yet
- Strema Act 2Document42 pagesStrema Act 2James Ryu ZagalaNo ratings yet
- Tarea 2do ParcialDocument3 pagesTarea 2do ParcialBrayan PopNo ratings yet
- Part 3Document20 pagesPart 3Loriel MendozaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 RamDocument3 pagesUnit 1 RamVENKATESHNo ratings yet
- Sample Questions - STRENGTHDocument4 pagesSample Questions - STRENGTHEvan Carniyan0% (1)
- Assignment 3Document3 pagesAssignment 3parmodrtkNo ratings yet
- B.Tech Assgn-1Document6 pagesB.Tech Assgn-1K Pushpendu PrashantNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument8 pagesLab ReportHenrique PradoNo ratings yet
- Ce6306 16Document3 pagesCe6306 16Arul JONo ratings yet
- Assignment No 1 MD-1..Document3 pagesAssignment No 1 MD-1..Yadnyesh TaNo ratings yet
- Statically Indeterminate Members & Thermal StressesDocument24 pagesStatically Indeterminate Members & Thermal StressesBuddy SinghNo ratings yet
- StrengthDocument27 pagesStrengthairaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Thermal Stress - For PresentationDocument13 pagesLesson 4 - Thermal Stress - For PresentationGabriel JavelonaNo ratings yet
- Week 1 TutorialsDocument5 pagesWeek 1 TutorialsViliameNo ratings yet
- Shearing DeformationDocument21 pagesShearing DeformationRyan Joseph Rabino100% (1)
- Steel Tutorial 2,3,4,5,6,7Document7 pagesSteel Tutorial 2,3,4,5,6,7Sankalp LamaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document1 pageTutorial 3SARVAYESWARAN L MX-llNo ratings yet
- SOM3601 Assignment 2Document3 pagesSOM3601 Assignment 2Elendu Emmanuel ChigozieNo ratings yet
- 05.1 Flanged Bolt Couplings Torsion in Thin Walled Tubes Helical SpringsDocument37 pages05.1 Flanged Bolt Couplings Torsion in Thin Walled Tubes Helical SpringsRoséyNo ratings yet
- Unit IIDocument67 pagesUnit IIonhaNo ratings yet
- Instructions on Modern American Bridge BuildingFrom EverandInstructions on Modern American Bridge BuildingNo ratings yet
- A Guide to Some of the Equations used in Constructing a Suspension BridgeFrom EverandA Guide to Some of the Equations used in Constructing a Suspension BridgeNo ratings yet