Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Trawler: - Many Modern Trawlers Are Equipped With Stern Ramp To Facilitate Easy
Uploaded by
joshigauta0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views6 pagesOriginal Title
Engine 3
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views6 pagesTrawler: - Many Modern Trawlers Are Equipped With Stern Ramp To Facilitate Easy
Uploaded by
joshigautaCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
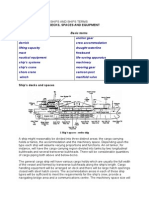
LAYOUT AND CHARACTERISTICS OF SELECTED
TYPES OF FISHING VESSELS
Trawler
The trawler is a fishing vessel which operates a trawl net. They range
from open boats powered by outboard engines to very large factory
trawlers. The layout varies depending on the type of trawler. The
general characteristics of stern trawler are as follows:
• Wide transom for more working space at the aft, with the engine in the
forward part.
• Large towing power required and hence a trawler is provided with
reasonable draft or displacement.
• The vessel should possess good buoyancy, stability & sea kindliness.
• Many large trawlers are provided with variable pitch propellers. Some
of them are provided with propeller nozzles also to give them more
towing power.
• The propeller speed is usually confined to less than 400 RPM at the
maximum engine speed; biggest possible diameter with
correspondingly low RPM, relatively low pitch resulting in maximum
thrust.
• Many modern trawlers are equipped with stern ramp to facilitate easy
handling of catch & gear, gantry for multiuse, gallows, winches, etc.
Drifter
Drifter is a gill netter operating drift gill nets. Depending on the
way in which the fishing gear is operated, these are designated
as bow pickers or stern pickers. The general characteristics of a
bow picker are as follows:
• The normal size usually ranges between 8-13 m length.
• A large cockpit is arranged forward where the nets and catch
can be stored.
• The engine is placed aft and fish hold in the forward.
• Power requirements are modest; maneuverability is important.
• Controllable pitch propeller is suggested for large vessels.
• Mizzen sail is often used in large drifters to keep the bow of
the vessel to the wind with the nets set out.
• Bow rudder is used in large drifters while drifting with the stern
ahead.
• These vessels may be equipped with a line hauler at the
forward on the starboard side for hauling the net, a net chute
on the port side for shooting the net and a simple roller either
on the gunwale or on the stern for easy operation of nets.
Purse seiner
Purse seiner is a vessel that operates a purse seine. The basic
design is influenced by the selection of type of net, system of
hauling the net, method of taking out fish from net and whether
the boat is to carry its own fish or it is to be carried by auxiliary
vessels. The characteristic features of the popular western type
purse seiners used in USA and Canada are as follows:
• Wide transom is provided to give more working space at the aft
• Fore foot is fairly deep to keep the bow from drifting unduly.
• The vessels have low free board aft for easy handling of gear.
The width of the vessels is rather more to have more
buoyancy.
• Rudder is placed beneath the counter to keep the net out of
fouling.
• Good speed and maneuverability are essential features for
negotiating moving shoals of fish.
• Very often these vessels are fitted with side thrusters for
maneuverability and to prevent riding over the gear while hauling .
• They are equipped with large mast and boom, purse winch,
purse davit, etc.
Long liner
Long liner is a vessel operating long lines. These are small
and medium size vessels not exceeding 30 m except tuna long
liners. The characteristic Features of tuna long liners are as
follows:
• Large displacement with deeper draft for going to far off
grounds.
• More space at the aft for handling the gear.
• Bulwark is provided with removable sections on both sides
for taking large fishes over the deck.
• A refrigerated storage room to keep bait usually at -20°C.
• Large storage spaces for fuel, fresh water, provision etc. as
the vessel remains away for a long time.
• Fish hold is located below the main deck amidships.
• Top deck house is used for keeping accessories like buoys,
floats, flag pole, etc.
• These vessels are equipped with a shooting tray on the aft
for shooting and a line hauler fitted in the forward of amid
ship on the starboard side to haul the lines.
Combination vessels
A vessel operating more than one fishing gear is termed
Combination vessel. The idea of operating a combination
vessel is to obtain maximum utilization of vessel throughout
the year. Examples of most common combinations are:
• Trawling and gill netting
• Trawling and purse seining
• Trawling and Danish seining
• Trawling and pole and line fishing
• Purse seining, gill netting and long lining
• Gill netting and seining
• Long lining and pole and line fishing
• The characteristics of the combination vessel are determined
by the requirements of main fish-catching method. Vessels
of any size can be :~;c adopted for combination fishing with
suitable arrangements and appropriate ~;?:compromise. A
good compromise is possible by having clear aft and forward
with engine and wheel house amidship. There are no limits
in sizes of ~ combination vessels. ",-eo
Carrier/transport Vessels
These are used for the transport of fish. Depending on the type
of fish carried, they are classified as:
• Live fish carrier
• Fresh fish carrier
• Iced fish carrier
• Refrigerated fish carrier
• The carrier vessels are especially used in fishing methods
like purse seining.
• They are used in the fisheries of Scandinavian countries,
Canada, USA, Japan, the Netherlands, Poland, erstwhile
USSR and even in India (purse seine fishery at Mangalore).
• Specialized arrangements are provided for each type of
transport vessel depending on the type of fish and fish
products to be transported.
• They are similar to cargo ships in general characters with
large cargo fish holds.
You might also like
- Motorboating Start to Finish: From Beginner to Advanced: The Perfect Guide to Improving Your Motorboating SkillsFrom EverandMotorboating Start to Finish: From Beginner to Advanced: The Perfect Guide to Improving Your Motorboating SkillsNo ratings yet
- Fao Classification of Fishery Vessel Types - Compress PDFDocument12 pagesFao Classification of Fishery Vessel Types - Compress PDFswapan debNo ratings yet
- Surround NetsDocument37 pagesSurround NetsRiewNo ratings yet
- Mooring: Mooring Equipment MOORING: A Vessel Is Said To Be Moored When It Is Fastened To ADocument7 pagesMooring: Mooring Equipment MOORING: A Vessel Is Said To Be Moored When It Is Fastened To AGaurav AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Food Production Technology and Management Practices: Raimi Mohamed Redwan BAP 1.13 Raimi@umk - Edu.myDocument25 pagesFood Production Technology and Management Practices: Raimi Mohamed Redwan BAP 1.13 Raimi@umk - Edu.myNurul Izzah Binti Azmi F20A0566No ratings yet
- Maritime Logistics Unit-1 Ship DesignDocument54 pagesMaritime Logistics Unit-1 Ship DesignYusuf KhanNo ratings yet
- Module 4b PRINCIPLES DESIGN at CONSTRUCTION OF FISHING BOATDocument5 pagesModule 4b PRINCIPLES DESIGN at CONSTRUCTION OF FISHING BOATErine Contrano100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Naval ArchitectureDocument18 pagesFundamentals of Naval Architecturevivek singh100% (1)
- Classification of Types of ShipsDocument46 pagesClassification of Types of ShipsNadhanie SinghNo ratings yet
- Ship Types and FeaturesDocument8 pagesShip Types and Featuresarmanimams100% (1)
- Tugboat Ques SolutionDocument39 pagesTugboat Ques Solutionsarah rashaNo ratings yet
- Ship TypesDocument19 pagesShip TypesCatalin ApetreNo ratings yet
- 4.1 ShiptypesDocument59 pages4.1 ShiptypesyetNo ratings yet
- Types of Ship - Specialized CraftDocument5 pagesTypes of Ship - Specialized CraftGorillas NgobamNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Ship ConstructionDocument18 pagesFundamentals of Ship ConstructionWAREKARNo ratings yet
- btcnaoe1Document31 pagesbtcnaoe1legenderbass7No ratings yet
- Characteristics of Good Harbours: Presentation by - Fajardo, Marvin E. 30820Document40 pagesCharacteristics of Good Harbours: Presentation by - Fajardo, Marvin E. 30820marvin fajardoNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering Petroleum Engineering Department: Drilling Engineering I Third StageDocument26 pagesFaculty of Engineering Petroleum Engineering Department: Drilling Engineering I Third StageOmer IkhlasNo ratings yet
- Know Your Sailboats: Types of Hulls, Keels & MastsDocument3 pagesKnow Your Sailboats: Types of Hulls, Keels & MastsYannick PakaNo ratings yet
- Midship Section of A Double Hull Oil TankerDocument5 pagesMidship Section of A Double Hull Oil TankerRajat BahugunaNo ratings yet
- FMO Tutorial 1 TaneshDocument8 pagesFMO Tutorial 1 TaneshHirajanSandragesanNo ratings yet
- Fish Capture and Fishing GearsDocument98 pagesFish Capture and Fishing GearsJandro KareemNo ratings yet
- Seam 1 BSMT 1.1 ADocument84 pagesSeam 1 BSMT 1.1 AJanrod RodaNo ratings yet
- Fishing Vessel TypesDocument62 pagesFishing Vessel Typesyw_oulalaNo ratings yet
- LECTURE No.6: Anchor Handlers or Anchor Handling Vessels (AHV) Is Very Powerful Ships ThatDocument12 pagesLECTURE No.6: Anchor Handlers or Anchor Handling Vessels (AHV) Is Very Powerful Ships ThatMiruna ClinciuNo ratings yet
- Docks & HarbourDocument35 pagesDocks & HarbourGopi Raju100% (1)
- Indigenous or Traditional Fishing Crafts of IndiaDocument11 pagesIndigenous or Traditional Fishing Crafts of IndiaAbhi BlackNo ratings yet
- Docks Harbours Day3Document28 pagesDocks Harbours Day3Gopi RajuNo ratings yet
- Mooring PresentationDocument15 pagesMooring PresentationReynante P. ConsulNo ratings yet
- Harbour MaterialDocument62 pagesHarbour MaterialBalaji vNo ratings yet
- ConstructionDocument34 pagesConstructionwaihtetNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Berth Structures: - PurposeDocument30 pages3.3 Berth Structures: - Purposelance carterNo ratings yet
- Cruise ManagementDocument34 pagesCruise ManagementJohnson Fernandez100% (1)
- Oating Activities: Yacht Clubs Marinas Rostock GermanyDocument3 pagesOating Activities: Yacht Clubs Marinas Rostock GermanyEthan ZacharyNo ratings yet
- Types of Ships: Bulk Carriers, Oil Tankers and Container VesselsDocument36 pagesTypes of Ships: Bulk Carriers, Oil Tankers and Container VesselsAktarojjaman MiltonNo ratings yet
- Types of Fishing Vessels and MethodsDocument2 pagesTypes of Fishing Vessels and MethodsPablo BelmonteNo ratings yet
- FishingDocument63 pagesFishingjoshigautaNo ratings yet
- UNIT-IV DOCKS AND HARBOUR ENGINEERING LECTUREDocument36 pagesUNIT-IV DOCKS AND HARBOUR ENGINEERING LECTUREGopi Raju50% (2)
- International TransportationDocument47 pagesInternational Transportationankittayal_iet100% (1)
- Liner Shipping and Tramp Shipping Services-Group 9Document31 pagesLiner Shipping and Tramp Shipping Services-Group 9Parth Chauhan100% (2)
- Nautical CompendiumDocument24 pagesNautical CompendiumMatias100% (1)
- Estimating Resistance and Power Needs of Fishing Vessels and TugsDocument11 pagesEstimating Resistance and Power Needs of Fishing Vessels and TugsBhagatsinh Geda100% (4)
- Meeting 1 (Types of Ships)Document16 pagesMeeting 1 (Types of Ships)dillaNo ratings yet
- What Are The Rules and Procedures in Berthing in A Port? ProceduresDocument3 pagesWhat Are The Rules and Procedures in Berthing in A Port? ProceduresZel ZozobradoNo ratings yet
- Recap: - Port: - Harbour: - There Are Ports That Are Not Sheltered and Harbours That Have No Ports. - RoadsteadDocument25 pagesRecap: - Port: - Harbour: - There Are Ports That Are Not Sheltered and Harbours That Have No Ports. - Roadsteadlance carterNo ratings yet
- 04 - Classification of Fishery Vessel TypesDocument16 pages04 - Classification of Fishery Vessel TypesT V ATHULNo ratings yet
- Different Parts of A Ship ExplainedDocument37 pagesDifferent Parts of A Ship Explainedmario enriquezNo ratings yet
- BoatingDocument28 pagesBoatingHortan100% (1)
- Ship Classification and TypesDocument15 pagesShip Classification and TypesPandu Prayoga HoppusNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Fishing Gear DesignDocument41 pagesBasic Principles of Fishing Gear DesignFirdaus Nawi100% (1)
- Ships and Ship TermsDocument21 pagesShips and Ship TermsMohamed Salah El DinNo ratings yet
- Barge ShipmentDocument52 pagesBarge Shipmentwyne leonheart100% (1)
- Dry Cargo ShipsDocument15 pagesDry Cargo ShipsAmitrajeet kumarNo ratings yet
- Ship'S Decks, Spaces and Equipment: Unit 3Document21 pagesShip'S Decks, Spaces and Equipment: Unit 3mingo622No ratings yet
- Types of Vessels in the Global Supply ChainDocument20 pagesTypes of Vessels in the Global Supply ChainSabre FortNo ratings yet
- Marine Power PlantsDocument25 pagesMarine Power PlantsVinz VizenNo ratings yet
- Hatch CoversDocument12 pagesHatch CoversPranjyoti SaikiaNo ratings yet
- Ship ConstructionDocument5 pagesShip ConstructionJonathan McCarthyNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan X Penanganan Proses Berlabuh JangkarDocument24 pagesPertemuan X Penanganan Proses Berlabuh JangkarRani TribuanaNo ratings yet
- HSC Machinery RequirementsDocument174 pagesHSC Machinery RequirementssasikumarmarineNo ratings yet
- Techniques in Cell Biology Manual New1Document227 pagesTechniques in Cell Biology Manual New1joshigautaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Management (Ece, Me, Ce, Cse, Ee) 3rd Year (Sumit Joshi) Set-2Document3 pagesPrinciples of Management (Ece, Me, Ce, Cse, Ee) 3rd Year (Sumit Joshi) Set-2joshigautaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Management (Ece, Me, Ce, Cse, Ee) 3rd Year (Sumit Joshi) Set-3Document3 pagesPrinciples of Management (Ece, Me, Ce, Cse, Ee) 3rd Year (Sumit Joshi) Set-3joshigautaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Management (Ece, Me, Ce, Cse, Ee) 3rd Year (Sumit Joshi) Set-3Document3 pagesPrinciples of Management (Ece, Me, Ce, Cse, Ee) 3rd Year (Sumit Joshi) Set-3joshigautaNo ratings yet
- Synopis PHDDocument6 pagesSynopis PHDjoshigautaNo ratings yet
- Genoenergy Particle Theory - by AMIT JOSHIDocument21 pagesGenoenergy Particle Theory - by AMIT JOSHIjoshigautaNo ratings yet
- Vol 6 - Nervous System AgentsDocument1,080 pagesVol 6 - Nervous System Agentsjoshigauta100% (3)
- Delhi University Objectives For MSC By: - AMITDocument110 pagesDelhi University Objectives For MSC By: - AMITjoshigauta0% (1)
- Principles of Management (Ece, Me, Ce, Cse, Ee) 3rd Year (Sumit Joshi) Set-1Document3 pagesPrinciples of Management (Ece, Me, Ce, Cse, Ee) 3rd Year (Sumit Joshi) Set-1joshigautaNo ratings yet
- Techniques in Molecular Biology Manual Part1Document77 pagesTechniques in Molecular Biology Manual Part1joshigautaNo ratings yet
- Vol 4 - Autocoids Diagnostics - and Drugs From New BiologyDocument716 pagesVol 4 - Autocoids Diagnostics - and Drugs From New Biologyjoshigauta100% (1)
- Techniques in Molecular Biology Manual Part2Document62 pagesTechniques in Molecular Biology Manual Part2joshigauta100% (1)
- Vol 1 - Drug DiscoveryDocument946 pagesVol 1 - Drug Discoveryjoshigauta100% (2)
- Medicinal Chemistry and Drug Discovery Burger S 6ed Vol5Document1,127 pagesMedicinal Chemistry and Drug Discovery Burger S 6ed Vol5Ama Fremps100% (2)
- BURGER'S MEDICINAL CHEMISTRY AND DRUG DISCOVERY Volume 2 PDFDocument817 pagesBURGER'S MEDICINAL CHEMISTRY AND DRUG DISCOVERY Volume 2 PDFnoname1919193% (14)
- Encyclopedia of Biological Chemistry - Vol - 3Document848 pagesEncyclopedia of Biological Chemistry - Vol - 3joshigauta100% (1)
- PCO 2009 - 10 Physical Chemical OceanographyDocument94 pagesPCO 2009 - 10 Physical Chemical OceanographyjoshigautaNo ratings yet
- Burgers Medicinal Chemistry and Drug Discovery 3Document885 pagesBurgers Medicinal Chemistry and Drug Discovery 3giselesilvestreNo ratings yet
- Drug Targeting Organ-Specific StrategiesDocument406 pagesDrug Targeting Organ-Specific Strategiesjoshigauta100% (1)
- Drug Discovery Strategies and Methods 2004 - Makriyannis & BiegelDocument338 pagesDrug Discovery Strategies and Methods 2004 - Makriyannis & Biegeljoshigauta100% (1)
- Encyclopedia of Biological Chemistry - Vol - 4Document503 pagesEncyclopedia of Biological Chemistry - Vol - 4joshigauta100% (1)
- M& G 2 Geography MeterologyDocument46 pagesM& G 2 Geography MeterologyjoshigautaNo ratings yet
- Water Conditions: Solute Total Dissolved Solids Salinity Freshwater Brackish Water Estuaries SeawaterDocument4 pagesWater Conditions: Solute Total Dissolved Solids Salinity Freshwater Brackish Water Estuaries SeawaterjoshigautaNo ratings yet
- P.o.aq. AquacultureDocument10 pagesP.o.aq. AquaculturejoshigautaNo ratings yet
- DAN Inland EstuarineDocument28 pagesDAN Inland EstuarinejoshigautaNo ratings yet
- PCO OceanographyDocument13 pagesPCO Oceanographyjoshigauta100% (1)
- Mathews - Biochemistry (Mathews 3rd Ed) PDFDocument2,464 pagesMathews - Biochemistry (Mathews 3rd Ed) PDFMiguel González96% (24)
- Updated Scenario of Indian Fisheries DevelopmentDocument31 pagesUpdated Scenario of Indian Fisheries DevelopmentjoshigautaNo ratings yet
- L-6 Major River Systems of India Topographical Features, Fish Faunastic Diversity & FisheriesDocument38 pagesL-6 Major River Systems of India Topographical Features, Fish Faunastic Diversity & FisheriesjoshigautaNo ratings yet
- Cold Water HatcheryDocument71 pagesCold Water Hatcheryjoshigauta100% (1)
- Chief Officer On Job Training: Cargo Plan, SequenceDocument48 pagesChief Officer On Job Training: Cargo Plan, SequenceNyan Min Htet100% (1)
- Revised guidance on shipboard towing equipmentDocument16 pagesRevised guidance on shipboard towing equipmentMaksim ZaritskiiNo ratings yet
- D 7Document57 pagesD 7Ian RidzuanNo ratings yet
- VTDPT E CLDocument55 pagesVTDPT E CLTrâm TrầnNo ratings yet
- Storage at PPADocument12 pagesStorage at PPAMarlon VillarinNo ratings yet
- Prinsip dan Tanggung Jawab Pemuatan Muatan di KapalDocument27 pagesPrinsip dan Tanggung Jawab Pemuatan Muatan di Kapalardhan pratamaNo ratings yet
- Saf 004Document7 pagesSaf 004TimmyJuriNo ratings yet
- CatamaranDocument10 pagesCatamaranAakashParanNo ratings yet
- Ship Design - Main DimensionsDocument10 pagesShip Design - Main DimensionsMuhammad Hafidz100% (5)
- Shipping IndustryDocument35 pagesShipping IndustryNureni SusilowatiNo ratings yet
- 新建 XLSX 工作表Document377 pages新建 XLSX 工作表Diana SunNo ratings yet
- 5.2.5. Freeboard (Load Line) : L) S L (TDocument26 pages5.2.5. Freeboard (Load Line) : L) S L (TismaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Maritime Industry: Prospects and ChallengesDocument13 pagesPhilippine Maritime Industry: Prospects and ChallengesJean ArcinueNo ratings yet
- Himt TFC ComDocument211 pagesHimt TFC ComSOUMYADIP BHUNIANo ratings yet
- Fixturenote 2Document4 pagesFixturenote 2George Bryan PatalinghugNo ratings yet
- Product Sheet Stabilised Monohull RoPax Ferry With LNG Propulsion 10081Document1 pageProduct Sheet Stabilised Monohull RoPax Ferry With LNG Propulsion 10081Tapan KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- 00F Ship TerminologyDocument29 pages00F Ship TerminologyGuoyi NgNo ratings yet
- Charterparty Cancellation RightsDocument2 pagesCharterparty Cancellation Rightssachin vermaNo ratings yet
- Stability Booklet 1Document28 pagesStability Booklet 1Jose MartinsNo ratings yet
- 40 Great Submarine Simulator War AdventuresDocument260 pages40 Great Submarine Simulator War Adventuresremow100% (4)
- Fishing Vessel Factory Trawler 1288Document1 pageFishing Vessel Factory Trawler 1288Ramon Velasco StollNo ratings yet
- Requirements on Carriage of PublicationsDocument5 pagesRequirements on Carriage of PublicationsSanket MahajanNo ratings yet
- Preparing Cargo Plans - Structural Limitations PDFDocument7 pagesPreparing Cargo Plans - Structural Limitations PDFSakthi JavelinNo ratings yet
- Jblfmu: Subject Code Description Day Time Room InstructorDocument1 pageJblfmu: Subject Code Description Day Time Room InstructorJoshua Elli BajadaNo ratings yet
- Oralquestionandanswer GoodDocument464 pagesOralquestionandanswer GoodMariyath Muraleedharan KiranNo ratings yet
- BM 19 - Ship ParticularDocument1 pageBM 19 - Ship Particulariankun .93No ratings yet
- Japanese Period GerphisDocument4 pagesJapanese Period GerphisCharles Ronel PataludNo ratings yet
- CV ImamDocument1 pageCV ImamMuh Reza Isra RamliNo ratings yet
- Excercises 1-18 Priit SulusteDocument47 pagesExcercises 1-18 Priit SulustePriit SulusteNo ratings yet