Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Enlighten Your Polynomial Confusion: Different Strategies in Factoring Polynomials
Uploaded by
Glaiza QuingOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Enlighten Your Polynomial Confusion: Different Strategies in Factoring Polynomials
Uploaded by
Glaiza QuingCopyright:
Available Formats
Enlighten your polynomial confusion
Alyeza Cristeta Q. Quing, Teresa National High School
alyeza23quing@gmail.com
Introduction Different Strategies in Factoring C. Factoring Polynomials with Sum and Difference
of the Two Cubes WHAT IF IT IS A PERFECT SQUARE TRINOMIAL?
Polynomials
If you have a perfect Square Trinomial it is easy to factor:
In algebra, polynomial is made up of two terms, A polynomial in the form a3+ b3 is called the sum of two •Take the square root of the first term.
namely Poly (meaning “many”) and Nominal (meaning A. Factoring Polynomials with Greatest cubes. A polynomial in the form a3 – b3 is called the difference of •Take the square root of the last term.
“terms.”). A polynomial is an expression consisting of Common Monomial Factor (GCMF) two cubes. •Use the sign of the middle term, put in parenthesis and
variables and coefficients that are combined using the square the result.
mathematical operations such as addition, subtraction, Greatest Common Monomial Factor is the largest Formula for sum of two cubes: a3+ b3 = (a+b) (a2 – ab + b2)
multiplication and division (No division operation by a term that goes into a list of given terms. Formula for difference of two cubes a3- b3 = (a-b) (a2 + ab Example:
variable). + b2)
Steps in factoring polynomials with GCMF:
Steps in factoring polynomials with difference of two squares
Find the GCMF
Divide each term in the polynomial by its GCMF. 1. Get the cube root of each cube term.
Combine the answer in steps 1 and 2 as a product. 2. Taking the operation between the cubes, use the cube roots in
step 1 to obtain binomial factors.
Formula : ax + bx + cx = x ( a + b + c ) 3. Form the trinomial factors as follow:
a) Square the first cube root. Another example:
b) Multiply the two cube roots. The sign of the product is
opposite the sign between the cubes. X2 + 10x +25 = ( x + 5 ) 2
Examples: c) Square the second cube root.
a) Factor 25y5+20y4+15y3 Examples:
E. Factoring General Trinomial
GCMF: 5y3
x3+8
A trinomial is a polynomial that has three terms. The first
Thus:
Rename each term as a sum of two cubes. Then, apply the time is an x2 term, the second term is an x term, and the third
25y5+20y4+15y3 = (5y3) (5y2)+ (5y3)(4y)+(5y3)(3)
formula for sum of cubes. term is a constant (just a number).
=5y3 (5y2+4y+3)
There are special names for polynomials with 1, 2 or 3
terms: x3+8 = (x)3 + (2)3 Formula: ax2 + bx + c = 1
b) Factor 7x2+35x3
= (x+2) [(x) 2 – (x)(2) + (2)2] ax2 + bx + c ≠ 1
GCMF: 7x2
Monomial (5x2 , xy) = (x+2) (x2 – 2x + 4)
x12 – 64y6 Steps in factoring general trinomial:
Thus:
Binomial (x+5, 5x +y )
2 3 Example:
7x2+35x3= 7x2(1+5x)
Note that the binomial is a difference of squares. x2 + 6x + 8
Trinomial (x+5+y, 5x2+y3+z) 1. Identify the values for b and c.
x12 – 64y6 = (x4)3 – ( 4y2)3 = (x4- 4y2) [(x4)2 + (x4) (4y2) + (4y2)2] b=6
= (x4- 4y2) (x3 + 4x4y2 + 16y4) c=8
B. Factoring Polynomials with Difference of two = (x2- 2y) (x2+ 2y)(x3 + 4x4y2 + 16y4) 2. Find two numbers that ADD to b and MULTIPLY to c
Squares
a. List all the possible factors of 8 b. find the factor of 8 whose sum is 6
FACTORS
Factoring polynomials with difference of two squares Factor of 8 Factor of 8 Sum
When a polynomial is written as a product of is a special type of factoring a problem that is often use in D. Factoring Perfect Square Trinomial 1 5 1 5 6
polynomials, each polynomials in the product is a factor of the mathematics. -1 -5 -1 -5 -6
original polynomials. A perfect square trinomial, the ability to recognize special cases 2 4 2 4 6
Steps in factoring polynomials with difference of two of polynomials that we can easily factor in is a fundamental skill for -2 -4 -2 -4 -6
FACTORING is the process writing polynomials as a product of squares. solving any algebraic expressions that involve polynomials.
polynomials. 4 + 2 =6 (the value of b)
Get the principal square root of each of the two squares. Formulas: a2 + 2ab + b2 = (a + b) (a + b) 4 x 2 = 8 (the value of c)
Using these square roots form two factors: a sum and a a2 - 2ab + b2 = (a - b) (a + b)
difference. 3. Use the numbers you picked to write out the factors and
check.
This patter can be generalized as follows: Express the binomial factors of the trinomial: (x+2) and
(x+4)
a2 - b2 = ( a + b )( a – b )
Example:
4a2-9b2 Acknowledgement
4a2-9b2= (2a) 2-(3a)2 therefore, a=2a and b=3b
a2-b2 = (a+b)(a-b) use difference of two squares pattern I would like to thanks the teachers that participate and help
(2a) 2-(3a) 2= (2a+3a) (2a-3a) by substitution the students in this project also to the parents of those students
4a2-9b2= (2a+3a) (2a-3a) that letting us to teach them. I also want to Mrs. Geraldine Paz
for your undying support in this project. Finally thank you for the
Department of Education and Teresa National High School for
your support for the student.
You might also like
- CLMD4A MathG10Document36 pagesCLMD4A MathG10Errish R. Cuadra100% (3)
- Summative Test 1Document2 pagesSummative Test 1Charina Ortiz100% (5)
- Grade 8 Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesGrade 8 Lesson PlanBeluso DionieNo ratings yet
- 1st Summative Test Grade 9Document3 pages1st Summative Test Grade 9Hanna Grace Honrade94% (32)
- Gr8math Q1W1&W2 - LasDocument23 pagesGr8math Q1W1&W2 - LasIvanhoe BalaroteNo ratings yet
- MATH 8-Q1-WK 1 - FOR TEACHER Deped Negros OrientalDocument25 pagesMATH 8-Q1-WK 1 - FOR TEACHER Deped Negros OrientalJohnby Balasabas100% (1)
- Mathematics 8 Quarter 1 Weeks 1-2Document44 pagesMathematics 8 Quarter 1 Weeks 1-2John Aaron C. PastiasNo ratings yet
- AbcdDocument14 pagesAbcdGerald Lorenzo DomingoNo ratings yet
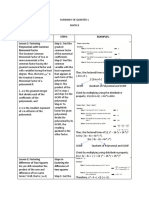
- Summary of Quarter 1Document31 pagesSummary of Quarter 1Lilacx ButterflyNo ratings yet
- ??????????? 8 - ???? 1Document2 pages??????????? 8 - ???? 1Dheigne MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lesson 1Document19 pagesModule 1 Lesson 1Teds TVNo ratings yet
- DLP and Semi-DetailedDocument12 pagesDLP and Semi-DetailedDanielNo ratings yet
- G8 Q1 Factoring Polynomials 1.2Document1 pageG8 Q1 Factoring Polynomials 1.2Aileen Joyce EscasinasNo ratings yet
- Polynomials: O Multiplication of PolynomialsDocument1 pagePolynomials: O Multiplication of PolynomialsLin PamintuanNo ratings yet
- M1 Adv. AlgebraDocument7 pagesM1 Adv. AlgebraAngel Von Heart PandesNo ratings yet
- Math 8 Q1 Week 1Document10 pagesMath 8 Q1 Week 1lau dash100% (2)
- OhhhDocument10 pagesOhhhcatsarecoolurafoolNo ratings yet
- CE11 CE BSCI 112 Lecture 3 PolynomialsDocument4 pagesCE11 CE BSCI 112 Lecture 3 PolynomialsLance vincent LuluNo ratings yet
- Different Strategies in Factoring PolynomialsDocument4 pagesDifferent Strategies in Factoring PolynomialsGlaiza QuingNo ratings yet
- 7.0 Factoring Summary WorksheetDocument4 pages7.0 Factoring Summary WorksheetRusherNo ratings yet
- 7.0 Factoring Summary WorksheetDocument4 pages7.0 Factoring Summary WorksheetKathleen A. PascualNo ratings yet
- Factoring General TrinomialDocument9 pagesFactoring General TrinomialShawn MikeNo ratings yet
- DLP Lesson 5 - Week 1Document5 pagesDLP Lesson 5 - Week 1Stephanie CastroNo ratings yet
- Quadratics, Trigonometric Equation & SeriesDocument214 pagesQuadratics, Trigonometric Equation & SeriesSam VagniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document10 pagesChapter 3api-352709549No ratings yet
- Teacher Made Learner Home Task - TemplateDocument3 pagesTeacher Made Learner Home Task - Templatedaneca teogancoNo ratings yet
- AlgebraDocument8 pagesAlgebraJovelyn Deloria EspañolNo ratings yet
- Factoring Multiple: 2a + 2b - Ax - BXDocument11 pagesFactoring Multiple: 2a + 2b - Ax - BXJulette MansuetoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Factorisation and Alegrabraic Fractions PDFDocument31 pagesChapter 5 - Factorisation and Alegrabraic Fractions PDFaurora100% (2)
- Math WorksheetDocument20 pagesMath WorksheetSheena MangampoNo ratings yet
- g8-q1-1 - Amabao-Paco, Nona Jane L.Document8 pagesg8-q1-1 - Amabao-Paco, Nona Jane L.Leo Santo EscarpeNo ratings yet
- FactoringDocument6 pagesFactoringJRMSU-TC Ginn Lloyd GamilNo ratings yet
- Factoring Polynomial 4Document3 pagesFactoring Polynomial 4Allan LegoNo ratings yet
- Factoring Out Oct. 11Document20 pagesFactoring Out Oct. 11kayleighdanielle17No ratings yet
- 004-Sets Operation On PolynomialsDocument43 pages004-Sets Operation On Polynomialscherry agaNo ratings yet
- Factoring PolynomialsDocument28 pagesFactoring PolynomialsLyre LevierNo ratings yet
- Math 8 Unit 1 Lesson 3 ModuleDocument7 pagesMath 8 Unit 1 Lesson 3 Modulemary joy buliagNo ratings yet
- Product, Factor BookletDocument16 pagesProduct, Factor BookletDiaz KaneNo ratings yet
- Summative Test 1Document2 pagesSummative Test 1Charina OrtizNo ratings yet
- DepEd Lesson Exemplar Mathematics 8 1stDocument7 pagesDepEd Lesson Exemplar Mathematics 8 1stMary Rose VillablancaNo ratings yet
- g7 q2 Week6Document3 pagesg7 q2 Week6Michelle NavaNo ratings yet
- 5 Let Basic Algebra - pdf12Document22 pages5 Let Basic Algebra - pdf12novey_casioNo ratings yet
- Binomial - A Polynomial With Two TermsDocument8 pagesBinomial - A Polynomial With Two TermsEllaAdayaMendiolaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 NotesDocument13 pagesChapter 3 NotesalariekiraNo ratings yet
- The X-Factors of Polynomials: MathematicsDocument10 pagesThe X-Factors of Polynomials: MathematicsJhiemalyn RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Q1 Week 1 2 SLK 1Document31 pagesQ1 Week 1 2 SLK 1Aileen Joyce EscasinasNo ratings yet
- L1 PPTDocument13 pagesL1 PPTkimberlyNo ratings yet
- QT1 Math8Document4 pagesQT1 Math8Jufil HombriaNo ratings yet
- How To Factor TrinomialsDocument4 pagesHow To Factor Trinomialsapi-140032165No ratings yet
- Mathematics: Arise WithDocument390 pagesMathematics: Arise Withkephas bandaNo ratings yet
- DLP Genmath W5D2Document4 pagesDLP Genmath W5D2esperidacedrickpaulNo ratings yet
- Igcse Math OlDocument172 pagesIgcse Math Oldemiyang030No ratings yet
- DLL M8 C1Document10 pagesDLL M8 C1saintEmNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Part 1Document18 pagesLesson 4 Part 1Satvin SinghNo ratings yet
- Math 8 Q1 TestDocument2 pagesMath 8 Q1 TestMark Kiven MartinezNo ratings yet
- Q1W2 DLL Math8Document6 pagesQ1W2 DLL Math8Genevee ResultayNo ratings yet
- Math Constrained Optimization IIDocument41 pagesMath Constrained Optimization IIarm.unfurledNo ratings yet
- Factoring Polynomials With Greatest Common Mononial FactorDocument2 pagesFactoring Polynomials With Greatest Common Mononial FactorFrancis LagramaNo ratings yet
- Factoring Polynomials Graphic OrgnizerDocument1 pageFactoring Polynomials Graphic Orgnizermylene castilloNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheets - Q1Document6 pagesLearning Activity Sheets - Q1Janusdenise SolisNo ratings yet
- Teacher Made Learner Home Task - TemplateDocument3 pagesTeacher Made Learner Home Task - Templatedaneca teogancoNo ratings yet
- Research 2 Module 1st GradingDocument19 pagesResearch 2 Module 1st GradingGlaiza Quing100% (1)
- Tle 8 Dressmaking PT 1 4 q1Document5 pagesTle 8 Dressmaking PT 1 4 q1Glaiza QuingNo ratings yet
- Slowdown in Rise of COVIDDocument4 pagesSlowdown in Rise of COVIDGlaiza QuingNo ratings yet
- Author Name, Affiliation, Email: Title of Your PosterDocument1 pageAuthor Name, Affiliation, Email: Title of Your PosterGlaiza QuingNo ratings yet
- Different Strategies in Factoring PolynomialsDocument4 pagesDifferent Strategies in Factoring PolynomialsGlaiza QuingNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesGlaiza QuingNo ratings yet
- Steps in Amt LP MakingDocument28 pagesSteps in Amt LP MakingGlaiza QuingNo ratings yet
- Philsin College Rizal Inc.: Poem WritingDocument4 pagesPhilsin College Rizal Inc.: Poem WritingGlaiza QuingNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document14 pagesPresentation 1Glaiza QuingNo ratings yet
- Rubrics GroupingsDocument1 pageRubrics GroupingsGlaiza QuingNo ratings yet
- Unit Assessment Template Grade 9 EnglishDocument20 pagesUnit Assessment Template Grade 9 EnglishGlaiza QuingNo ratings yet
- Demo Lesson Plan PDFDocument4 pagesDemo Lesson Plan PDFGlaiza QuingNo ratings yet
- Demo Lesson Plan Walang AssessmentDocument2 pagesDemo Lesson Plan Walang AssessmentGlaiza QuingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document13 pagesChapter 1Glaiza QuingNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 8300/1H: Higher Tier Paper 1 Non-CalculatorDocument26 pagesMathematics 8300/1H: Higher Tier Paper 1 Non-Calculatorgreg heffleyNo ratings yet
- Bscmathsv&ViDocument11 pagesBscmathsv&ViDhiraj RajputNo ratings yet
- Algebra I Post-AssessmentDocument5 pagesAlgebra I Post-Assessmentapi-290652463No ratings yet
- Solution of Quadratic Equation by Extracting The Square RootDocument6 pagesSolution of Quadratic Equation by Extracting The Square RootAlexander BautistaNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Mat183Document2 pagesTest 1 Mat183nurr aleyaaNo ratings yet
- Math 7 3rd Quarter ExamDocument6 pagesMath 7 3rd Quarter Examjan lawrence panganibanNo ratings yet
- Operators & Operands Arithmetic Operators Relational Operators Logical Operators Assignment OperatorsDocument36 pagesOperators & Operands Arithmetic Operators Relational Operators Logical Operators Assignment OperatorsNur HazwaniNo ratings yet
- 2021 AMC10B Solutions FallDocument18 pages2021 AMC10B Solutions FallHan ZhengNo ratings yet
- Notes On Discrete Maths 3Document35 pagesNotes On Discrete Maths 337 TANNUNo ratings yet
- 2012 IMAS Second Round - Junior - EngDocument9 pages2012 IMAS Second Round - Junior - EngDarma YasaNo ratings yet
- A Level Math Paper 1 TrigonometryDocument40 pagesA Level Math Paper 1 TrigonometryREMO MosesNo ratings yet
- What Is Number System in Maths?Document19 pagesWhat Is Number System in Maths?Kaushik ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Math Competition Package 2023Document13 pagesMath Competition Package 2023Arianna KetwarooNo ratings yet
- Calculus 1 Analytic Geometry Cheat SheetDocument1 pageCalculus 1 Analytic Geometry Cheat SheetStephanie DulaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 7editted PDF FreeDocument28 pagesAssignment 7editted PDF FreetauseefNo ratings yet
- K K K K K: X X X X X XDocument16 pagesK K K K K: X X X X X XCHUANG Cheng YuNo ratings yet
- Exeter Math Club Contest 2013Document41 pagesExeter Math Club Contest 2013steven_g_lee100% (1)
- M Ock Test - 1: M CQ Type Questi OnsDocument12 pagesM Ock Test - 1: M CQ Type Questi OnsJanviMahendrakarNo ratings yet
- Algebra Tutorial Guide PDFDocument2 pagesAlgebra Tutorial Guide PDFRyan bien DigmanNo ratings yet
- Jsu Add MathDocument6 pagesJsu Add MathSham RichNo ratings yet
- Perimeter and Area - Topic Test 1 H v1.1Document6 pagesPerimeter and Area - Topic Test 1 H v1.1Oana AlbertNo ratings yet
- Radiation View Factors PDFDocument23 pagesRadiation View Factors PDFhsebillalNo ratings yet
- Add Maths F4 Revision ProgramDocument60 pagesAdd Maths F4 Revision ProgramAfida HamsaniNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 - 2.pdf - Study PackDocument4 pagesGrade 10 - 2.pdf - Study PackAzmyNo ratings yet
- Hyperbolic GeometryDocument32 pagesHyperbolic GeometryspsarathyNo ratings yet
- 10th Mathematics Matriculation LevelDocument451 pages10th Mathematics Matriculation Levelbresks71% (7)
- PT g10 MathematicsDocument5 pagesPT g10 MathematicsMary MillareNo ratings yet