Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Workshop Technology
Uploaded by
vishwanath0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
81 views51 pagesWORKSHOP TECHNOLOGY
Original Title
WORKSHOP TECHNOLOGY
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentWORKSHOP TECHNOLOGY
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
81 views51 pagesWorkshop Technology
Uploaded by
vishwanathWORKSHOP TECHNOLOGY
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 51
WORKSHOP TECHNOLOGY
Introduction to basic materials.
• Engineering materials refers to the group of materials that
are used in the construction of manmade structures and
components.
• The primary function of an engineering material is to
withstand applied loading without breaking and without
exhibiting excessive deflection.
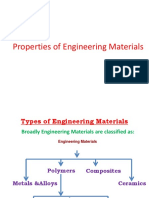
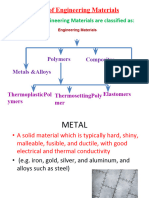
• The major classifications of engineering materials include
metals, polymers, ceramics, and composites.
• Metals are minerals or substances that form naturally
below the surface of the Earth. Most metals are lustrous or
shiny.
Classification of engineering materials
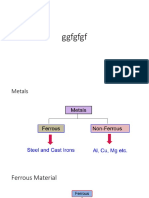
• Ferrous metal
• it is defined as a metal which contains iron as their main
constituent.
• In addition to iron ferrous metal also contains carbon ,silicon
,phosphorus ,manganese, silicon etc.
• In latin the word “ferrum” is known as iron hence these materials
are called as ferrous metals.
• Ex : cast iron ,pig iron, wrought iron , steel, carbon steel, alloy steel
• Non ferrous metals
• It is defined as a metal which contains elements other than iron as
their main constituents.
• Ex: copper, aluminum, magnesium, zinc, cobalt, lead, tin,
chromium, nickel and its alloys.
• Timber
• Timber is wood that is used for building houses and making
furniture.
• It is also known as “lumber” in US and Canada.
• Basically, timber or Lumber is a wood or firewood of growing
trees.
• Properties of timber
Color , Appearance, Hardness, Specific Gravity, Moisture
Content, Grain, Shrinkage and Swelling, Strength, Density,
Toughness ,Elasticity, Warping, Durability, Defect less, Workability,
Soundness, Free of abrasion
• Applications
Construction and Fencing, Household Uses, Art Industry, Sports
Equipment, Commercial Uses.
Abrasives:
Abrasives are substances used to smooth out or machine (to mold or
finish by machinery) other softer materials through extensive rubbing.
• Abrasives are widely classified as -
• Natural Abrasives - Calcite, Diamond, Iron oxide, Sand, Sandstone, and
powdered feldspar.
• Synthetic Abrasives - Borazon, ceramic, aluminum oxide, dry ice, glass powder,
steel abrasive, silicon carbide, and slags.
• Bonded Abrasives - These abrasives are composed of an abrasive material that is
contained within the matrix.
• Coated Abrasives - These abrasives consist of backing material like paper, cloth,
etc. Coated with abrasive material.
• properties of materials
• hardness, toughness (or rigidity), grain shape and size, character of fracture (or
cleavage), and purity (or uniformity)
• Applications:
• Buffing.Honing.Drilling.Grinding.Sanding.Polishing.Cutting.Sharpening.
• Silica
Silica is another name for the chemical compound composed of
silicon and oxygen with the chemical formula SiO2, or silicon dioxide.
The properties of silica include both chemical and physical properties
such as hardness, color, melting and boiling point, and reactivity.
Applications of silica
glass, foundries, construction, ceramics, and the chemical industry.
Silica in its finest form is also used as functional filler for paints,
plastics, rubber, and silica sand is used in water filtration and
agriculture.
Ceramics:
A ceramic is an inorganic non-metallic solid made up of
either metal or non-metal compounds that have been shaped and
then hardened by heating to high temperatures. In general, they are
hard, corrosion-resistant and brittle.
Applications:
They are used in space industry because of their low weight.
They are used as cutting tools.
They are used as refractory materials.
They are used as thermal insulator.
They are used as electrical insulator.
Glass:
Glass, is an inorganic solid material that is usually transparent as well as hard and brittle.
building construction, housewares, and telecommunications
Graphite:
a soft black shining form of carbon that conducts electricity and is used in lead pencils
and electrolytic anodes, as a lubricant, and as a moderator in nuclear reactors.
Diamond:
• Diamond is a solid form of pure carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal. Hardness.
Wear components, Cutting tools, semiconductor devices ,Optical components ,Other high
performance applications
• Properties:
1. Low coefficient of friction
2. High thermal conductivity
3. High electrical resistivity
4. Low thermal expansion coefficient
5. High strength
6. Broad optical transparency from ultra violet to infra red
7. Resistant to chemical corrosion
8. Biologically compatible
• Plastic, polymeric material that has the capability of being
molded or shaped.
• Properties
1. Strong and ductile
2. Poor conductors of heat and electricity
3. Easily molded into different shape and size
4. Resist corrosion and are resistant to many chemicals.
• Application
• Plastic is used across almost every sector, including to produce
packaging, in building and construction, in textiles, consumer
products, transportation, electrical and electronics and industrial
machinery.
• composite material:
• A composite material is a combination of two materials with
different physical and chemical properties.
• high strength high modulus; low density; excellent resistance
to fatigue, creep, creep rupture, corrosion, and wear; and
low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE).
• Composites are ideal for applications in corrosive
environments, such as chemical processing plants, pulp and
paper converting, oil and gas refineries and water treatment
facilities. Common applications include fans, grating, tanks,
ducts, hoods, pumps and cabinets.
• Heat treatment of steels.
Heat treatment may be defined as combination of heating and cooling
of metals or alloys in order to obtain desired properties.
Purposes of heat treatment:
1. To improve machinability
2. To refine grain structure
3. To improve mechanical properties and to soften the metal
4. To produce hard surfaces on ductile material
5. To relive internal stresses developed during machining.
Types of heat treatment process:
6. Annealing
7. Normalizing
8. Hardening
9. Tempering
10. Nitriding
11. Cyaniding
• Annealing:
In which steel parts are heated to the temperature at or near the
recrystallization temperature or critical temperature and hold them for
some time at the same temperature to penetrate the heat throughout
the parts and then allowed to cool slowly in furnace itself only.
• Objectives:
1. To soften the metal
2. To improve machinability
3. To improve mechanical properties
4. To refine grain size
5. To relieve internal stresses
6. To produce a definite microstructure
7. To modify electrical and magnetic properties.
Annealing is the costliest process because cooling of materials is carried
out in furnace itself only
• Types of annealing:
1. Process annealing
2. Full annealing
In process annealing metal parts are heated to the temperature
below the recrystallization temperature then allowed it to cool
slowly in furnace itself only.
In full annealing metal parts are heated at or near the
recrystallization temperature then allowed it to cool slowly in
furnace itself only.
• Normalizing:
In which steel parts are heated to the temperature at 50˚C above
the recrystallization temperature or critical temperature and hold
them for some time at the same temperature to penetrate the heat
throughout the parts and then allowed to cool slowly in air or at
room temperature.
Objectives:
1. To refine grain size or structure.
2. To improve machinability of low carbon steels
3. To increase strength of medium carbon steel.
4. To relieve internal stress.
5. To improve mechanical and electrical properties.
• Hardening:
In which the Steel parts are heated to the temperature at or
near the recrystallization temperature or critical temperature and
hold them for sometime at the same temperature to penetrate the
heat well inside the parts and then allowed to cool rapidly by
quenching in water or oil bath.
This process is carried out to increase the hardness of Steel.
• Objectives or purpose:
1. To increase the hardness
2. To refine the grain size
3. To increase wear resistance of Steels
4. To improve the magnetic properties
5. To reduce ductility to minimum
• Tempering:
It is defined as the process of reheating the hardened Steel
components to the temperature at or below the critical
temperature or recrystallization temperature and then allowed cool
rapidly by quenching in water or oil bath.
Objectives or purposes:
1. To increase the toughness
2. To decrease hardness
3. to relieve internal stresses
4. To reduce the brittleness
• Nitriding:
It is a surface hardening process in which nitrogen gas is used to
obtain hard surfaces of the Steel. The Steel parts are heated in the
atmosphere of ammonia for sometime and then cooled slowly.
Objectives or purposes:
1. To increase hardness of surfaces
2. To increase wear resistance of Steel
• Cyaniding:
It is also a surface hardening process in which the Steel parts to be
hardened are immersed in a bath of molten Sodium and potassium
sodium and left it about 15 to 20 minutes in bath ,then the parts are
taken out and quenched in lime water to neutralize the particles of
Cyanide salt sticking to the surface of Steel parts.
• Objectives or purposes
1. To Harden the surfaces.
• Indian Factory Acts on safety:
The Factories Act, 1948, has been promoted primarily to provide safety
measures and to promote the health and welfare of the workers employed in
factories.
• workshop-safety-rules:
1. Don´t run in the workshop
2. Always wear an apron
3. Wear strong shoes
4. Don´t rush your projects
5. Tie up long hair
6. Roll up sleeves
7. Never work alone in the workshop
8. When necessary wear goggles
9. Turn the machine off before cleaning it
10. Always listen to the teacher
11. Know where the emergency button is located
12. Listen carefully when a teacher is demonstrating something
13. A machine must be operated by one student at a time
14. Enter the workshop only with a teacher´s permission
15. Report any damage done to the machines
• Welding:
The Welding is a process of joining two or more, similar or
dissimilar metals by heating them to a suitable temperature , with
or without the application of pressure, filler materials and flux.
Welding is used for making permanent joints.
TYPES OF WELDING :
Plastic Welding or Pressure Welding: The piece of metal to be
joined are heated to a plastic state and forced together by external
pressure (Ex) -Resistance welding
Fusion Welding or Non-Pressure Welding: The material at the joint
is heated to a molten state and allowed to solidify (Ex)- Gas
welding, Arc welding.
Types of electrodes
Consumable electrodes:
these are made up of same material as that of the
workpiece,during welding process melts and combine with molten
metal of the work piece to form a joint and helps to strike or generate
arc.
Non Consumable electrodes:
These are made up of tungsten and graphite. These are used only
to strike out arc and is not consumed during welding process.
Types of welding joints:
Edge preparation in welding:
To ensure good welding and proper weld penetration
edges of the work pieces are prepared as shown below
• Welding techniques and equipment's:
1. Gas welding(Oxy- Acetylene)
2. Arc welding(Metal Arc)
3. Resistance welding
4. Solid state welding
5. Thermo-chemical welding
6. Low Temperature welding
• Arc welding equipment's:
Arc welding machine ,electrodes, electrode holder, welding cable or
electrode cable, earthing clamp, wire brush, chipping hammer, hand
gloves,shoes,protective shield, apron ,safety goggles.
• Gas welding equipment's:
Oxygen gas cylinder, Acetylene gas cylinder, Regulator,Hoses,Check
valves, Flash back arrestor, Cylinder caps, welding nozzle
• Arc welding:
• Arc welding process is a fusion type of welding.
• In this process the edges of the work pieces are heated up to molten state by using
a intensity of arc generated by electric current between two conducting materials.
• The work piece is connected to the one pole of the electric circuit and electrode is
connected to the other pole of the electric circuit. An electric Arc generated when
the tip of the electrode is brought in contact with work piece and momentarily
separated by 2 to 4 mm.
• The electric energy is thus converted into heat energy. The high heat of the electric
arc melts the edges of the work pieces.
• joining takes place by combining molten metal of the work pieces and then allowed
to solidify to form single component.
• Gas welding
It is a fusion type of welding process in which the work pieces are joined
by heat of a long flame generated by the combustion of fuel gas and
oxygen.
The fuel gas may be acetylene, hydrogen, butane etc.
The fuel gas and oxygen are mixed in suitable proportions in a welding
torch and ignited.
The flame resulting at the tip of the torch is sufficient enough to melt the
edges of the work pieces.
a solid continuous joint is formed upon cooling.
The two familiar fuel gases used in gas welding are
Mixture of Oxygen and acetylene gas known as oxy acetylene gas welding
Mixture of Oxygen and hydrogen gas known as oxy hydrogen gas welding
process
Oxy-acetylene welding is most widely used for gas welding process due to
its low flame temperature up to 3500 degrees Celsius weight of oxy
hydrogen process up to 2500 degree Celsius
• Soldering
• it is a method of joining two or more thin metals using a material known
as solder by the application of heat.
• Applications:
1. Soldering is using to join automobile radiator cores.
2. Used to plumbing.
3. Mainly useful in electronic industries like radio, TV and computers.
4. For joining wires and cables to lugs in electrical industries.
• Brazing
• It is a method of joining two similar or dissimilar metals by using special
fusible alloys. the fusible alloys used in brazing process are copper base
alloy, silver base alloy and Zinc etc .
• It is used for electrical components, pipe fittings. Metals having uneven
thickness can be joined by brazing.
Measuring instruments and gauges
Forging and smithying
Forging is a mechanical process where metal stock is heated in
closed door hearth furnace & then pressure is locally applied by
using press or hammer to give a desired shape & size.
Hot forging: if the process is carried out above the recrstlysation
temperature then it is called as hot forging.
Cold forging: if the process is carried out below the recrstlysation
temperature then it is called as hot forging.
Smithy is also a forging operation which is carried out for
relatively small stock size by heating in a open hearth or furnace &
then shaping the stock by hammering by hand or using small
hammer machine or press.
Smithy is mostly done to manufacture forging tools, tackles, cutting
tools used in machining / fabrication process, tools & appliances for
farming in daily use.
• Forging Tools and Equipment
1. Furnace or Hearth: It is used for heating purpose during the
forging operation .
2. Anvil: The anvil is an important smiths tool. It is used for
supporting the work while hot metal hammering.
Hammers:
1. Ball‐ Peen Hammer: A ball peen hammer has a flat face which is used for
general work and a ball end, particularly used for riveting.
2. Cross‐Peen Hammer: It is similar to ball peen hammer, except the shape of the
peen. This is used for chipping, riveting, bending and stretching metals and
hammering inside the curves and shoulders
3. Straight‐Peen Hammer: This is similar to cross peen hammer, but its peen is in‐
line with the hammer handle. It is used for swaging, riveting in restricted places
and stretching metals.
4. Sledge Hammer: It has double faces on both ends as shown in figure. Sledge
hammers are comparatively heavier than hand hammers. Therefore, they are
used for heavy type of forging work when heavy blows are needed.
5. Tongs:
The tongs are used for holding the hot metal while is being
worked. These are made of mild steel.
6. Chisels:
chisel is used for cutting and chipping out metal.
7. Punches and Drifts:
These types of forging tools are made of high carbon steel which
helps in making hot hole on hot metal pieces. This forging tool is
available in different sizes and has a common shape.
Drift is a large size of punch used in enlarging holes.
8. Flatters:
this forging tool is used to flatten the surface of the work piece.
9. Swage Block:
this forging equipment is made of cast iron or cast steel rectangular
block, having several holes in it. The holes are made of different sizes
and shapes.
10. Set Hammer:
set hammer is a forging tool used for making surface plane,
forming and making corners.
11. Bench Vice: The bench vice is a work holding device.
Forging Operations:
Upsetting or jumping:
Upsetting is the process through which the cross-section of a metal piece is
increased with a corresponding reduction in its length.
Bending:
it is an important operation in forging and is very frequently used. In this
process the item is heated and bent as desired.
Drawing down:
In this process the length of a bar stock may increased with a
corresponding decrease or reduction in its thickness, width or both of a bar
stock. In other words, it is exactly a reverse process to that of upsetting or
jumping.
Cutting:
Cutting of metals in hot or cold state is done by means of hot or cold
chisels respectively.
This operation is required in removing extra metal from the job before
finishing it, cutting required lengths of pieces from a stock, splitting a metal
piece into two at a desired location and similar other requirements.
Punching and drifting
• Punching and drifting are used for producing and finishing
holes and preparatory for producing other shapes.
Setting down
• It is a localized drawing down or swaging operation.
defects of forging:
1) Unfilled Section:
As the name implies in this type of defect some of the forging section remain unfilled. This is
due to poor design of die or poor forging technic. This is also due to less raw material or
poor heating. This defect can be removed by proper die design, proper availability of raw
material and proper heating.
2) Cold Shut:
Cold shut includes small cracks at corners. These defects occur due to improper design of forging
die. It is also due to sharp corner, and excessive chilling in forging product. The fillet radius of
the die should be increase to remove these defects.
3) Scale Pits:
Scale pits are due to improper cleaning of forged surface. This defect generally associated with
forging in open environment. It is irregular deputations on the surface of forging. It can be
removed by proper cleaning of forged surface.
4) Die Shift:
Die shift is caused by misalignment of upper die and lower die. When both these dies are not
properly aligned the forged product does not get proper dimensions. This defect can be removed
by proper alignment. It can be done by provide half notch on upper die and half on lower die so
at the time of alignment, both these notches will matched.
5) Flakes:
These are internal cracks occur due to improper cooling of forge product.
When the forge product cooled quickly, these cracks generally occur which
can reduced the strength of forge product. This defect can be removed by
proper cooling.
6) Improper Grain Growth:
This defect occurs due to improper flow of metal in casting which changes
predefine grain structure of product. It can be removed by proper die design
7) Incomplete Forging Penetration:
This defect arises due to incomplete forging. it is due to light or rapid hammer
blow. This defect can be removed by proper control on forging press.
8) Surface Cracking:
Surface cracking occurs due to exercise working on surfaces at low
temperature. In this defect, So many cracks arise on work piece. This defect
can be removed by proper control on working temperature.
9) Residual Stresses in Forging:
This defect occurs due to improper cooling of forged part. Too much rapid
cooling is main causes of this type of defects. This can be removed by slow
cooling of forged part.
Carpentry:
Carpentry may be defined as the process of making wooden
articles and components such as roots, floors, partitions, doors and
windows. Carpentry involves cutting, shaping and fastening wood
and other materials together to produce a finished product.
Carpentry Tools
Carpentry tools are used to produce components to an exact size.
The types of carpentry tools are as follows. 1. Marking tools 2.
Measuring tools 3. Holding tools 4. Cutting tools 5. Planning tools 6.
Boring tools 7. Striking tools 8. Miscellaneous tools
Marking tools :
It is used to marking lines parallel to the edges of a wooden piece.
Measuring tools:
The carpentry measuring tools are classified as follows 1. Steel tape 2.
Steel rule 3. Caliper Steel tapes and steel rules are mainly used for
measuring short and lengths in millimeters.
A try square is used for testing squareness and marking of joints.
A meter square is used for marking and measuring an angle of 45
degree.
A bevel square is used for marking and listing angles between 0
degree to 180 degree
Calipers are used for the precision measurement of cylindrical
surface.
Inside calipers are used for measuring outside diameter and outside
calipers are used to measure inner diameter of pipe.
• Holding tools :
• Carpentry vice
A carpentry vice is the common work holding device. It consists of one
fixed jaw and one movable jaw. Its one jaw is fixed to the side of the
table while the other is movable by means of a screw and a handle.
• Bar clamp
The bar clamp (or) sash cramps are generally used in pairs in gluing up
operations at the final assembly of joinery work. It is made up of a steel
bar of T-section, wine malleable iron fittings and a steel screw.
• G-clamp
G-clamp is made up of malleable iron with acme threads of high quality
steel .It can be used for clamping small work when gluing up.
Saws:
A saw is used to cut wood into pieces.
Chisels:
Chisels are used for cutting and shaping wood accurately.
Types of Wood
Softwood Pine wood
Teak wood Cedar wood
Rose wood Spruce wood
Oak wood Deodar wood
Maple wood
Ash wood
Mango wood
Neem wood
Mahogany wood
Beech wood
Walnut wood
Marandi wood
• The most common way all woods are differentiated is the
classification of
• hardwoods and softwoods.
• The wood from confiner-type trees (such as Pine) is called
softwoods, while the wood from usually broad-leaved
dicotyledons (such as oak) are called hardwoods. The
actual hardness can vary between them, leading to
hardwoods which have very soft wood structure and
softwoods which are very hard, strong and durable .
Types of Softwood
While softwoods can be used in construction, furniture manufacture and
more, one of the largest use case scenarios is in the production of
manufactured wood – chipboard, fiberboard, and plywood.
Here are the most popular types of softwood:
Pine – Pines come in wide variety of density and strength, making them
suitable for creation of an incredible variety of indoor and outdoor objects,
which includes construction, wood pulp production, ornamental uses, and
others.
Spruce - One of the most common evergreen trees in the family of Pinaceae
is known for its versatility of timber. Since it lacks durability against insect
attacks, wooden objects made from spruce wood are extensively used only
indoors.
Cedar – Cedars are the most common softwoods in the mountainous
regions of Mediterranean and Himalayas, where they are used for creating
objects (such as chests) that have excellent durability against insects and
moths. They are also used for the production of unique cedar wood shoes.
Fir – Evergreen Fir trees can grow to the impressive 80m in height, making
their softwood highly sought after for manufacture of industrial timber,
pulp, plywood. Similarly, like many other softwood trees, the Fir wood has
very poor insect resistance, making it usable only in indoor environments.
Larch – Native to colder parts of northern hemisphere and one of the most
common evergreen trees of Siberia and Canada, wood of these trees is
commonly praised for its durability, strength and waterproofing, which make
it excellent for production of outdoor furniture, support beams,
boatbuilding, and both indoor and outdoor flooring and paneling.
Western hemlock – Originating from western Alaska, the timber of this large
evergreen coniferous tree is often used in the creation of pallets, boxes,
plywood and other construction objects.
Yew – Yew is a type of softwood that features strong density and often
strong rot resistance, making it suitable for the production of wide variety of
wooden objects, including furniture, cabinets, musical instruments, turned
objects and archery bows.
• Types of Hardwood
• While the most famous (and most expensive) type of hardwood is mahogany,
other types are also very well represented on the worldwide market, including:
• Oak - The staple of the woodworking industry. The reliable hardwood that can
be used for almost any application, both indoors and outdoors.
• Maple - High-quality hardwood that can elevate the visual impact of any room.
Used extensively for both furniture and high-end objects.
• Basswood - Hardwood of great acoustic quality, most commonly found in
musical instruments, carvings and lumber products.
• Ipe Wood - Ipe is known for its durability, which is why it can today be found in
flooring, paneling and objects that must endure a lot of usages (door handles,
tool handles, and others).
• Cherry wood – Chery hardwood is excellent for both construction, flooring,
furniture, as well as the creation of smaller durable objects and specialty wood
items.
• Olive wood – Cream or yellowish-brown olive wood is today used for the
creation of high-end and stylish furniture, art objects and expensive small
specialty wood items.
Wenge wood – Black stripes that flow across the medium brown, yellowish and reddish
hues of wenge are praised for their acoustic properties in music instruments, but this
hardwood is also used in furniture, paneling, veneer and turned objects.
Walnut wood – Wood taken from many varieties of walnut trees can be used for the
creation of wide array of products, including furniture, paneling, and small turned
objects.
Teak - Golden or medium brown hardwood of Teak is praised all around the world for
its excellent durability, strength, and visual appeal. Also, to use in both indoor and
outdoor applications, it is also regularly used in boatbuilding.
Cocobolo – Incredibly diverse variety of Cocobolo hardwood (including orange, yellow,
red and brown shades) have found popularity all over the world in musical instruments,
fine furniture, and small specialty items. The worldwide supply of Cocobolo is currently
very limited.
Curly Maple - Moderately-priced maple hardwood is very durable and versatile, which
has enabled it to be regularly used for flooring, furniture, musical instruments to an
incredible variety of wooden objects.
Rosewood – Dark and visually rich hardwood of rosewood are famous for its top of the
line resilience to decay, which makes it the perfect material for building high-end
furniture, flooring, musical instruments and turned objects. Rosewood is very
expensive, and its trade is currently closely regulated by several South American
governments.
• Sapele – This famous tropical Africa hardwood with golden to dark
reddish-brown hues was regularly used in boatbuilding, flooring,
furniture, and creation of musical instruments, but in recent years
its trade was severely limited due to overexploitation.
• Teak – Teak is one of the most popular sources of highly-durable
and versatile hardwood in modern woodworking and processing
industry. Originally found in Asia, today plantations of teak can be
found across tropical regions of Africa, Asia, and Latin America.
• Mango wood – Famous moderately-durable hardwood tree of
Tropical Asia and Oceania is a traditional source of wood for
Hawaiian and Pacific ukuleles, furniture and turning objects.
• Mahogany – The undisputed king of hardwoods. Its incredible visual
appeal and strong properties have made it a highly sought-after
source for the creation of high-end furniture, fine instruments, art
objects and other specialty wood items.
Few of the characteristics of wood
• It is light weight and sturdy
• Wood retains its thermal properties, hence it is resistant to
high temperatures
• Heat conductivity of wood is relatively low compared to
aluminum, marble, steel or glass
• It can absorb sound and echo
• It is a bad conductor of electricity.
• A bandsaw (also written band saw) is a power saw with a long,
sharp blade consisting of a continuous band of toothed metal
stretched between two or more wheels to cut material. They
are used principally in woodworking, metalworking,
and lumbering,
You might also like
- A Glossary of Interior Design TerminologyDocument19 pagesA Glossary of Interior Design Terminologyoljaorlic0% (1)
- Hitachi Seiki Manual 15SII 20SIIDocument309 pagesHitachi Seiki Manual 15SII 20SIInoneno12100% (4)
- MECH-STEEL-ALLOYSDocument12 pagesMECH-STEEL-ALLOYS337-ME- KIRTHAN DEVADIGANo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Materials (Em) 1Document26 pagesElectrical Engineering Materials (Em) 1Hezron gibronNo ratings yet
- Steel in Industrial Construction: Jyoti Chaurasiya Priyanka Siddharth Agarwal Zeenat ParveenDocument14 pagesSteel in Industrial Construction: Jyoti Chaurasiya Priyanka Siddharth Agarwal Zeenat ParveenSanjay SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Engineering MaterialsDocument34 pagesEngineering Materialssourav mahajanNo ratings yet
- 11 Introduction To Engineering MaterialsDocument20 pages11 Introduction To Engineering MaterialsomkardashetwarNo ratings yet
- Cutting Tool Materials ME MechanicalDocument4 pagesCutting Tool Materials ME MechanicalManish Kumar100% (1)
- Unit 37 Session 03Document45 pagesUnit 37 Session 03amdan srlNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Materials-OKDocument104 pagesIntroduction To Materials-OKMan Nguyen TheNo ratings yet
- Material Science NotesDocument11 pagesMaterial Science NotesRyan Ryan RyanNo ratings yet
- ME007 - Mechanical Properties and Metals-1Document44 pagesME007 - Mechanical Properties and Metals-1albert narioNo ratings yet
- Alloys and Heat Treatment ProcessesDocument33 pagesAlloys and Heat Treatment ProcesseshenryNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - ECE 2215 PDFDocument24 pagesLecture 2 - ECE 2215 PDFRando ClintonNo ratings yet
- Properties of Engineering MaterialsDocument39 pagesProperties of Engineering Materialsdaisyclare vernyuyNo ratings yet
- ME007 - ProcessesDocument59 pagesME007 - Processesalbert narioNo ratings yet
- Aircraft MaterialsDocument44 pagesAircraft MaterialsIan100% (2)
- Mechanical Engy MaterialsDocument37 pagesMechanical Engy MaterialsKouame AdjepoleNo ratings yet
- Raw Materials and Classifications of Metallic and Non-Metallic MaterialsDocument91 pagesRaw Materials and Classifications of Metallic and Non-Metallic Materialshemarubini96No ratings yet
- Case Hardening Heat TreatmentsDocument15 pagesCase Hardening Heat Treatmentsmohit1990dodwalNo ratings yet
- 2-BMCG2312 Manufaturing MaterialsDocument80 pages2-BMCG2312 Manufaturing MaterialsMuhd IzzNo ratings yet
- SeminarDocument12 pagesSeminarRaunak RajpalNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Engineering CeramicsDocument20 pagesUnit 4 - Engineering Ceramicsmaximus4682No ratings yet
- Engineering MaterialsDocument53 pagesEngineering MaterialsRAGINI PASUPULETINo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Indexing Drill Jig For Inclined Profile ComponentDocument47 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Indexing Drill Jig For Inclined Profile ComponentANAND KRISHNANNo ratings yet
- MaterialsDocument27 pagesMaterialsmankaniviraj55No ratings yet
- Type MaterialDocument31 pagesType MaterialChristopherGunawanNo ratings yet
- CeramicsDocument34 pagesCeramicsArun Raj A CNo ratings yet
- Module-5: Typical Engineering MaterialsDocument39 pagesModule-5: Typical Engineering Materialssrinidhi kulkarniNo ratings yet
- M&M AssignmentDocument5 pagesM&M AssignmentNo-fuel CharmyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Processing of Automotive MaterialsDocument34 pagesLecture 5 - Processing of Automotive MaterialsKamal SurenNo ratings yet
- DV07PUB1 E Study GuideDocument5 pagesDV07PUB1 E Study Guideasjdkfjskaldjf;klasdfNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Processes 1Document208 pagesManufacturing Processes 1sayan halderNo ratings yet
- MPSC BCM Notes - 2 - 5312194Document320 pagesMPSC BCM Notes - 2 - 5312194akash rathodNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Processes, Fuels, Materials, and Instrumentation GuideDocument19 pagesManufacturing Processes, Fuels, Materials, and Instrumentation GuideChristian Angelo AndoyNo ratings yet
- Advanced Materials - Ceramics PDFDocument83 pagesAdvanced Materials - Ceramics PDFVinaykumar NaiduNo ratings yet
- Cutting Tool MaterialDocument41 pagesCutting Tool MaterialDheerajOmprasadNo ratings yet
- 11 Engineering MaterialsDocument20 pages11 Engineering MaterialsAbdul Hai MohammedNo ratings yet
- ME137L - Heat TreatmentDocument34 pagesME137L - Heat TreatmentDiego LoyzagaNo ratings yet
- Metals: Dato, Dominic M. Esquillo, Mark Ryan L. Fabia, Bernardo M. Sison, Elijah G. Tan, Nicolas TDocument30 pagesMetals: Dato, Dominic M. Esquillo, Mark Ryan L. Fabia, Bernardo M. Sison, Elijah G. Tan, Nicolas TJOSEPH REFUERZONo ratings yet
- Role of Alloying ElementsDocument9 pagesRole of Alloying Elementsbraveheart236No ratings yet
- Metal Cutting Tools and Machine ProcessesDocument131 pagesMetal Cutting Tools and Machine Processesthirumalaikumaran100% (1)
- Automotive Innovation of MaterialsDocument23 pagesAutomotive Innovation of MaterialsMina IsakNo ratings yet
- Steel MaterialsDocument10 pagesSteel Materialsmanideep219No ratings yet
- 5 Applications and Processing of Metal AlloysDocument31 pages5 Applications and Processing of Metal AlloysJeffersonTalanNo ratings yet
- CeramicsDocument39 pagesCeramicsraja keshavNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document12 pagesLecture 1siphosakhemdunge114No ratings yet
- Manufacturing of Flange CouplingsDocument15 pagesManufacturing of Flange CouplingsAbhijit Kudva100% (1)
- BASIC METALLURGY & MANUFACTURE OF LIFTING EQUIPMENTDocument57 pagesBASIC METALLURGY & MANUFACTURE OF LIFTING EQUIPMENTikponmwonsaNo ratings yet
- EMS 223 Chapter 1Document38 pagesEMS 223 Chapter 1charles makasabiNo ratings yet
- Foundry ProcessDocument54 pagesFoundry ProcessgovindarajaluvNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER - Heat Treatment 3rd Sem ManufacturingDocument11 pagesCHAPTER - Heat Treatment 3rd Sem Manufacturingkaranragav12No ratings yet
- 4.. Ceramics - 20Document14 pages4.. Ceramics - 20KumudNo ratings yet
- Alloy & Special SteelsDocument33 pagesAlloy & Special Steelstanishka narayanNo ratings yet
- Powder Metallurgy ProjectDocument54 pagesPowder Metallurgy ProjectDhruv Raj33% (3)
- General Design Considerations: Unit - 1Document35 pagesGeneral Design Considerations: Unit - 1vinay.rathore.che21No ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Weldability and How to Improve ItDocument15 pagesFactors Affecting Weldability and How to Improve ItAnant Ajithkumar100% (2)
- Imp ReviewerDocument12 pagesImp ReviewerJohn Jeric de LunaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Technology GuideDocument72 pagesManufacturing Technology GuideRamya Ranjan senapatiNo ratings yet
- MCW - 4 PDFDocument5 pagesMCW - 4 PDFAtul Goswami 21BME1315No ratings yet
- Heat Treatment PPTDocument70 pagesHeat Treatment PPTJhonrey QuejadaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Feb 23, 2023Document9 pagesAdobe Scan Feb 23, 2023vishwanathNo ratings yet
- Provisional Selection List 2022 27022023 Blore DivDocument126 pagesProvisional Selection List 2022 27022023 Blore DivvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Types of dimensioning arrangementsDocument6 pagesTypes of dimensioning arrangementsvishwanathNo ratings yet
- List of Government Industrial Training Institutes (Division/Distric/Taluk Wise List)Document6 pagesList of Government Industrial Training Institutes (Division/Distric/Taluk Wise List)vishwanathNo ratings yet
- Reciprocation PumpDocument29 pagesReciprocation PumpMary Judy GabisanNo ratings yet
- Karnataka University BED SyllabusDocument126 pagesKarnataka University BED SyllabusvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Drilling MachineDocument79 pagesDrilling MachineMunem ShahriarNo ratings yet
- Erik Erikson's 8 Stages of Psychosocial DevelopmentDocument11 pagesErik Erikson's 8 Stages of Psychosocial DevelopmentJhulie San NicolasNo ratings yet
- Karnataka University BED SyllabusDocument126 pagesKarnataka University BED SyllabusvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Instructions 2Document1 pageInstructions 2vishwanathNo ratings yet
- General Paper-I-320Document4 pagesGeneral Paper-I-320vishwanathNo ratings yet
- Mechanical MachinesDocument21 pagesMechanical MachinesvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Reciprocating Pump - Useful EquationsDocument3 pagesReciprocating Pump - Useful EquationsvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Thermo: DynamicsDocument17 pagesThermo: DynamicsCarlos RamosNo ratings yet
- 4 TH UnitDocument10 pages4 TH UnitvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Reciprocation PumpDocument29 pagesReciprocation PumpMary Judy GabisanNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet For HIT RE 500 V4 Injectable Mortar in Concrete Technical Information ASSET DOC 13527227Document44 pagesTechnical Data Sheet For HIT RE 500 V4 Injectable Mortar in Concrete Technical Information ASSET DOC 13527227José Felix Steegmann ZafortezaNo ratings yet
- Chicago School of ArchitectureDocument20 pagesChicago School of ArchitectureJASHIN BANSALNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Introduction To PlumbingDocument72 pagesModule 6 - Introduction To PlumbingKevin Nichols Abacan100% (1)
- 18520041-An Nisa' Sakinatul Ahliyah (Pkpbi D)Document8 pages18520041-An Nisa' Sakinatul Ahliyah (Pkpbi D)An Nisa Sakinatul AhliyahNo ratings yet
- 1.luzhong Machine Catalog NewDocument57 pages1.luzhong Machine Catalog Newautomationdynamics20No ratings yet
- Adjustable Vertical Edge Router GuideDocument9 pagesAdjustable Vertical Edge Router GuideOscar TNNo ratings yet
- Facom Tool DescriptionDocument2 pagesFacom Tool Descriptionnahum crNo ratings yet
- Wooden Scrub Plane From ScrapDocument9 pagesWooden Scrub Plane From ScrapRod HyattNo ratings yet
- Edea CatalogoDec 2022Document33 pagesEdea CatalogoDec 2022Rene GordonNo ratings yet
- (Artigo) Ajuste de Projeção Do Espelho Do ViolinoDocument15 pages(Artigo) Ajuste de Projeção Do Espelho Do ViolinoRodolfo MinhotoNo ratings yet
- TLE6 IA Q3 Mod1 EnhancingDecoratingBamboo, WoodAndMetalProducts v4Document15 pagesTLE6 IA Q3 Mod1 EnhancingDecoratingBamboo, WoodAndMetalProducts v4ERIC DE LUNANo ratings yet
- Equipment Parts: Trabajo Final Del Curso InglesDocument13 pagesEquipment Parts: Trabajo Final Del Curso InglesAngela reyes cortezNo ratings yet
- Connectors Installed On SCL Columns: Technical BulletinDocument1 pageConnectors Installed On SCL Columns: Technical BulletinJorge Enrique MenesesNo ratings yet
- TOPL FSRU Buyer Supply Items Final ListDocument52 pagesTOPL FSRU Buyer Supply Items Final ListPiyush KumarNo ratings yet
- Ordinary Portland CementDocument5 pagesOrdinary Portland CementMohammad AashikSS34No ratings yet
- Starlink: - AccessoriesDocument18 pagesStarlink: - AccessoriesMaram MonNo ratings yet
- Artifact DissectionDocument13 pagesArtifact DissectionPrashant TolaniNo ratings yet
- Tools & Instruments List: # I N D Q - (U)Document2 pagesTools & Instruments List: # I N D Q - (U)Aous H100% (1)
- Front Elevation Rear Elevation Side Elevation: Reception Table 01Document1 pageFront Elevation Rear Elevation Side Elevation: Reception Table 01Niyati ThakarNo ratings yet
- SharpeningturningtoolsbookdoDocument74 pagesSharpeningturningtoolsbookdoK Sz100% (2)
- Naams Asc021Document5 pagesNaams Asc021Andrea Mendez ZNo ratings yet
- Structural DwgsDocument11 pagesStructural DwgsELaAruNo ratings yet
- Crucible Tool Steel and Specialty Alloy Selector GuideDocument1 pageCrucible Tool Steel and Specialty Alloy Selector Guidegeav25653855No ratings yet
- Session PlanDocument3 pagesSession PlanRey Anthony Carpentero Zambrana100% (1)
- Assignment 04 PDFDocument2 pagesAssignment 04 PDFVidya sagarNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Multi-Spindle MachineDocument6 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Multi-Spindle MachineIJIRSTNo ratings yet
- Timber PlantsDocument24 pagesTimber PlantsDHANUSRI K 1840747No ratings yet
- Rustic wooden garbage box in 6 stepsDocument14 pagesRustic wooden garbage box in 6 stepsHogen KoglerNo ratings yet