Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What is the thyroid gland and how does it affect your body
Uploaded by
DIVYA MAHALSEKAR-2GI18CV0260 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views10 pagesOriginal Title
Thyroid Gland Presentation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views10 pagesWhat is the thyroid gland and how does it affect your body
Uploaded by
DIVYA MAHALSEKAR-2GI18CV026Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
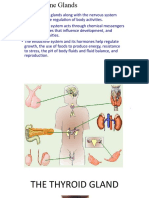
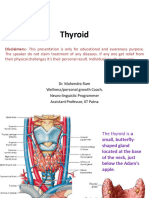
What is the thyroid?
• The thyroid gland is a small organ that’s located
in the front of the neck, wrapped around the
windpipe (trachea)→ ಶ್ವಾಸನಾಳ.
• It’s shaped like a butterfly, smaller in the middle
with two wide wings that extend around the side
of your throat.
What does the thyroid do?
• Thyroid gland plays a major roles in growth,
development and body temperature of body.
• Thyroid hormones helps to regulate functions
of many vital organs such as heart, brain,
kidneys and liver.
• It makes hormones that helps to control
metabolism.
What is metabolism?
• Metabolism is a process where the food you take into
your body is transformed into energy.
• This energy is used throughout your entire body to keep
many of your body’s systems working correctly.
• Metabolism is the reason some people can eat a lot
without gaining weight, while others seem to need less
to accumulate fat.
• The speed of your metabolism is commonly known
as metabolic rate.
How does thyroid affect the
body?
• The hormones produced by the thyroid control
your metabolism with the two main hormones
— T4 (thyroxine, contains four iodide atoms)
and T3 (triiodothyronine, contains three iodide
atoms).
• These hormones affect every organ —
influencing your heart rate, digestion, weight,
energy levels and mood.
• When your thyroid doesn’t work properly, it
can impact your entire body.
Thyroid hormones: T3 & T4
• It is located in front of the neck and is
responsible for the production of thyroid
hormones.
• These hormones play an important role in
regulation of your weight, energy levels,
internal temperature, skin, hair, nail
growth, and more.
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
• The thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) is produced by the
pituitary gland.
• TSH helps the thyroid gland to release T4 and T3.
Hyperthyroidism.
• When the thyroid makes too much thyroid hormone, your body
uses energy too quickly. This is called hyperthyroidism.
• Symptoms of an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) can include:
Experiencing anxiety, irritability and nervousness.
Having trouble sleeping.
Losing weight.
Having an enlarged thyroid gland or a goiter.
Having muscle weakness and tremors.
Experiencing irregular menstrual periods or having your
menstrual cycle stop.
Feeling sensitive to heat.
Having vision problems or eye irritation.
Hypothyroidism
• If your body makes too little thyroid hormone, it’s called
hypothyroidism.
• Symptoms of an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) can
include:
Feeling tired (fatigue).
Gaining weight.
Increase in cholesterol level.
Muscle weakness.
Feel down or depressed.
Having frequent and heavy menstrual periods.
Thinning hair.
Experiencing an intolerance to cold temperatures.
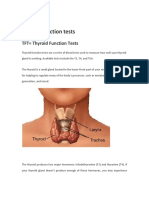
Diagnosis
• The most definitive ways to diagnose a thyroid problem is
through blood tests.
• Thyroid blood tests are used to diagnose thyroid disorders
associated with hyper- or hypothyroidism.
How to support a healthy thyroid?
• Movement is important: exercise is important especially for
hypothyroid patients, whose metabolisms have slowed down. We can
do lower-impact workouts, such as
Walking
Yoga
Strength training
• Eating well: Focus on eating nutritious food. These should include
fruits, vegetables, fatty fish, beans, whole grains, and lean proteins.
• Water importance.
• Avoid foods that are no nutritious or full of
empty calories. Skip and reduce processed foods
(anything in a bag or box), candies, sodas, and
junk foods.
You might also like
- Thyroid Diet: How to improve and cure thyroid disorders, lose weight, and improve metabolism with the help of food!From EverandThyroid Diet: How to improve and cure thyroid disorders, lose weight, and improve metabolism with the help of food!No ratings yet
- Thyroid Hormone E07Document1 pageThyroid Hormone E07Ahsen HafizNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Disease: An Introduction: Dealing with Thyroid Symptoms with Diet and TreatmentFrom EverandThyroid Disease: An Introduction: Dealing with Thyroid Symptoms with Diet and TreatmentNo ratings yet
- Щитоподібна залоза ангDocument24 pagesЩитоподібна залоза ангdenysvorobchak-12No ratings yet
- Endocrine Gland FunctionsDocument33 pagesEndocrine Gland FunctionsUngays ungaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Diet : Thyroid Solution Diet & Natural Treatment Book For Thyroid Problems & Hypothyroidism Revealed!From EverandThyroid Diet : Thyroid Solution Diet & Natural Treatment Book For Thyroid Problems & Hypothyroidism Revealed!Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Thyroid GlandDocument19 pagesThyroid GlandTanya SinghNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Health: The Thyroid Solution Diet ExposedFrom EverandThyroid Health: The Thyroid Solution Diet ExposedRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Sahil Gunjal HypothyroidismDocument30 pagesSahil Gunjal HypothyroidismSahil ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Hypothroidism NEWDocument27 pagesCase Study of Hypothroidism NEWDarling DadaNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Hypothroidism SAHIL GUNJALDocument27 pagesCase Study of Hypothroidism SAHIL GUNJALDarling DadaNo ratings yet
- Archivo en Ingles-Patologias TiroideasDocument4 pagesArchivo en Ingles-Patologias Tiroideasesther avilaNo ratings yet
- Causes of HypothyroidismDocument1 pageCauses of HypothyroidismCyrus FernzNo ratings yet
- NCM 116 Midterm PDFDocument130 pagesNCM 116 Midterm PDFPonciana PasanaNo ratings yet
- What is the thyroid gland and how does it regulate metabolismDocument6 pagesWhat is the thyroid gland and how does it regulate metabolismΚυριακη ΖαρβαληNo ratings yet
- Thyroid and Adrenal MedullaDocument32 pagesThyroid and Adrenal MedullaDipika RawatNo ratings yet
- Thyroid FinalDocument25 pagesThyroid Finalgowrie sangkarNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands RevisedDocument47 pagesEndocrine Glands RevisedXyress Archer GosinganNo ratings yet
- AssigmentDocument27 pagesAssigmentAndleeb RajNo ratings yet
- Thyroid: Endocrine DiseaseDocument20 pagesThyroid: Endocrine DiseasehoneymishraNo ratings yet
- ThyroidDocument19 pagesThyroidjetes67387No ratings yet
- Graves and Hashimoto'sDocument82 pagesGraves and Hashimoto'sAndrew FongNo ratings yet
- Hormones and Young Living Essential Oils PresentationDocument30 pagesHormones and Young Living Essential Oils Presentationapi-150039816100% (9)
- Thyroid Disorders Guide: Causes, Symptoms & TreatmentsDocument81 pagesThyroid Disorders Guide: Causes, Symptoms & Treatmentschetankumarbhumireddy50% (2)
- EndocrinologyDocument15 pagesEndocrinologyAbdullah EmadNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument51 pagesHomeostasisKarla HyltonNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland Dont Erase Ate KatDocument24 pagesThyroid Gland Dont Erase Ate KatThess Tecla Zerauc AzodnemNo ratings yet
- What Is The Function of The Thyroid Gland?: Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone (TRH)Document4 pagesWhat Is The Function of The Thyroid Gland?: Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone (TRH)Jessel Mae JavierNo ratings yet
- Hypo Thyroid Is MDocument5 pagesHypo Thyroid Is Mwiktoria WójcikNo ratings yet
- Endo Lect 7-THDocument30 pagesEndo Lect 7-THdoctorrfarrukhNo ratings yet
- Talking Thyroid FactsDocument6 pagesTalking Thyroid FactsVegan Future100% (4)
- Endocrine SystemDocument11 pagesEndocrine SystemPunong Grande NHS Banga NHS Annex (R XII - South Cotabato)No ratings yet
- Understanding Thyroid Function & DiseaseDocument2 pagesUnderstanding Thyroid Function & DiseasePintu KumarNo ratings yet
- Thyroid and Antithyroid DrugsDocument71 pagesThyroid and Antithyroid DrugsNiza GuarinNo ratings yet
- Hormones SubtopicsDocument77 pagesHormones SubtopicsSulaiman UmraniNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System2023Document30 pagesEndocrine System2023April MagnoNo ratings yet
- What Is HyperthyroidismDocument7 pagesWhat Is HyperthyroidismBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Class 1 Endocrine - SystemnewMay 17 - 22Document22 pagesClass 1 Endocrine - SystemnewMay 17 - 22ELIANA TIPACTI PAPENNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINE SYSTEM DISORDERS Unit 1Document8 pagesENDOCRINE SYSTEM DISORDERS Unit 1Rizza Mae MaglacionNo ratings yet
- Hyperthyroid Is MDocument2 pagesHyperthyroid Is MMelo RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Thyroid DisordersDocument10 pagesThyroid Disordersmir-medicinaNo ratings yet
- What Is HyperthyroidismDocument7 pagesWhat Is HyperthyroidismGelo LeañoNo ratings yet
- Hyperthyroidism 2011Document30 pagesHyperthyroidism 2011Elyza MagsaysayNo ratings yet
- Hyperthyroidism & HypothyroidismDocument109 pagesHyperthyroidism & Hypothyroidismmadelynmas75% (4)
- Hypothyroidism and Pregnancy What Should I Know FactsheetDocument1 pageHypothyroidism and Pregnancy What Should I Know FactsheetNicole KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Multi Dosing GuideDocument23 pagesThyroid Multi Dosing GuideDaniel AlbrechtNo ratings yet
- Presentation4 - MahhDocument8 pagesPresentation4 - MahhAyah MahmoudNo ratings yet
- What Is The Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Endocrine SystemAishwarya WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument58 pagesEndocrine SystemBeBs jai SelasorNo ratings yet
- Understanding Hyperthyroidism Causes and SymptomsDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Hyperthyroidism Causes and SymptomsPutri LoongNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument22 pagesEndocrine SystemkwatsNo ratings yet
- TFT Thyroid Function TestsDocument2 pagesTFT Thyroid Function TestsMohammed HabibNo ratings yet
- 05 Endo GIT RenalDocument131 pages05 Endo GIT RenalMaria Arlyn Lacuña SagosoNo ratings yet
- Thyroid DisorderDocument16 pagesThyroid DisorderfahadNo ratings yet
- Hypothyroidism: Erbil Polytechnic University Erbil Health Technical College MLT Department Third Stage Group: CDocument5 pagesHypothyroidism: Erbil Polytechnic University Erbil Health Technical College MLT Department Third Stage Group: CRayan JabbarNo ratings yet
- Hormonal ChangesDocument6 pagesHormonal Changesvin DVCNo ratings yet
- 35.3 The Endocrine System: Bio 30 NWRCDocument22 pages35.3 The Endocrine System: Bio 30 NWRCnancie8No ratings yet
- Thyroid PresentationDocument38 pagesThyroid Presentation천사자No ratings yet
- ScreenshotDocument11 pagesScreenshotDIVYA MAHALSEKAR-2GI18CV026No ratings yet
- Buckingham pi theorem for drag force analysisDocument11 pagesBuckingham pi theorem for drag force analysisDIVYA MAHALSEKAR-2GI18CV026No ratings yet
- Application of Interpolation and Finite DifferenceDocument29 pagesApplication of Interpolation and Finite DifferenceZain ul AbideenNo ratings yet
- ScreenshotDocument11 pagesScreenshotDIVYA MAHALSEKAR-2GI18CV026No ratings yet
- 3BHK House Plan Layout with Room DimensionsDocument1 page3BHK House Plan Layout with Room DimensionsDIVYA MAHALSEKAR-2GI18CV026No ratings yet
- HHM ProcedureDocument1 pageHHM ProcedureDIVYA MAHALSEKAR-2GI18CV026No ratings yet
- INTERNSHIP POLICY - Department of Civil Engineering - StudentsDocument4 pagesINTERNSHIP POLICY - Department of Civil Engineering - StudentsDIVYA MAHALSEKAR-2GI18CV026No ratings yet
- Acknowledgement Receipt IBMRCOL 21 UG 10182Document1 pageAcknowledgement Receipt IBMRCOL 21 UG 10182DIVYA MAHALSEKAR-2GI18CV026No ratings yet
- Green Rating For Integrated Habitat AssessmentDocument4 pagesGreen Rating For Integrated Habitat AssessmentDIVYA MAHALSEKAR-2GI18CV026No ratings yet
- QC Lab Tests Concrete StrengthDocument6 pagesQC Lab Tests Concrete StrengthDIVYA MAHALSEKAR-2GI18CV026No ratings yet
- 2gi19cv418 Pratik-PatilDocument1 page2gi19cv418 Pratik-PatilDIVYA MAHALSEKAR-2GI18CV026No ratings yet
- Profile of The OrganizationDocument9 pagesProfile of The OrganizationDIVYA MAHALSEKAR-2GI18CV026No ratings yet
- Salient Features of The ProjectDocument23 pagesSalient Features of The ProjectDIVYA MAHALSEKAR-2GI18CV026No ratings yet
- Internship Progress ReportDocument1 pageInternship Progress ReportDIVYA MAHALSEKAR-2GI18CV026No ratings yet
- Format For SUBMISSION of Priority For GuideDocument1 pageFormat For SUBMISSION of Priority For GuideDIVYA MAHALSEKAR-2GI18CV026No ratings yet
- Format For SUBMISSION of Priority For GuideDocument1 pageFormat For SUBMISSION of Priority For GuideDIVYA MAHALSEKAR-2GI18CV026No ratings yet
- 2gi19cv418 Pratik-PatilDocument1 page2gi19cv418 Pratik-PatilDIVYA MAHALSEKAR-2GI18CV026No ratings yet
- Vicco Turmeric Skin CreamDocument10 pagesVicco Turmeric Skin CreamDIVYA MAHALSEKAR-2GI18CV026No ratings yet
- 2gi19cv418 Pratik-PatilDocument1 page2gi19cv418 Pratik-PatilDIVYA MAHALSEKAR-2GI18CV026No ratings yet
- Acknowledgement Receipt IBMRCOL 21 UG 10182Document1 pageAcknowledgement Receipt IBMRCOL 21 UG 10182DIVYA MAHALSEKAR-2GI18CV026No ratings yet
- 2gi19cv418 Pratik-PatilDocument1 page2gi19cv418 Pratik-PatilDIVYA MAHALSEKAR-2GI18CV026No ratings yet
- Vicco Turmeric Skin CreamDocument10 pagesVicco Turmeric Skin CreamDIVYA MAHALSEKAR-2GI18CV026No ratings yet
- Acknowledgement Receipt IBMRCOL 21 UG 10182Document1 pageAcknowledgement Receipt IBMRCOL 21 UG 10182DIVYA MAHALSEKAR-2GI18CV026No ratings yet
- Fuel System Upgrades For Your QSK-60Document6 pagesFuel System Upgrades For Your QSK-60Josh JonesNo ratings yet
- 6 Review of Related LiteratureDocument2 pages6 Review of Related Literaturerusty0% (2)
- Three Vital Elements of Qigong Exercise by Master Chunyi LinDocument3 pagesThree Vital Elements of Qigong Exercise by Master Chunyi LinTengriNo ratings yet
- 1Document7 pages1mmNo ratings yet
- BergHOFF - серия посуды EssentialsDocument160 pagesBergHOFF - серия посуды EssentialsAntonNo ratings yet
- DD Cen TS 15534-3-2007Document14 pagesDD Cen TS 15534-3-2007MladenMarkovicNo ratings yet
- KalasarpaDosha RemedyDocument28 pagesKalasarpaDosha RemedyAnita Kadavergu100% (1)
- Pest Management Practices of Farmers in PambujanDocument13 pagesPest Management Practices of Farmers in PambujanLucille MoralesNo ratings yet
- Translation of The Original Operating Manual: Epg-Sprint XeDocument100 pagesTranslation of The Original Operating Manual: Epg-Sprint XePatricio Exequiel Silva ColileoNo ratings yet
- Egg Powder Manufacturing Plant Ecom Final Ppt1Document19 pagesEgg Powder Manufacturing Plant Ecom Final Ppt1brickses100% (2)
- Gualberto Vs GualbertoDocument16 pagesGualberto Vs GualbertoTalina BinondoNo ratings yet
- hc2019 Re Use Recycle To Reduce CarbonDocument68 pageshc2019 Re Use Recycle To Reduce CarbonFatemeh DavariNo ratings yet
- Soft Skills in The Pharmacy Curriculum: Lilian M. AzzopardiDocument14 pagesSoft Skills in The Pharmacy Curriculum: Lilian M. Azzopardishailendra patilNo ratings yet
- Can Capitalism Bring Inclusive Growth?: - Suneel SheoranDocument4 pagesCan Capitalism Bring Inclusive Growth?: - Suneel SheoranSandeepkumar SgNo ratings yet
- Inserto de Concreto PZI - Sellsheet - 2006Document1 pageInserto de Concreto PZI - Sellsheet - 2006CardenasNo ratings yet
- CHALLENGES - IN - DEVELOPING - MARGINAL - FIELD - COMPLEXITY, - CO MPILATION - & - IMPROVEMENT - NEEDED - Nik - Edit - 3Document22 pagesCHALLENGES - IN - DEVELOPING - MARGINAL - FIELD - COMPLEXITY, - CO MPILATION - & - IMPROVEMENT - NEEDED - Nik - Edit - 3Wan Mohd ShaharizuanNo ratings yet
- Adan2000 Crocodile FarmingsDocument4 pagesAdan2000 Crocodile FarmingsThe MarketingNo ratings yet
- Intro To Psychology Crash Course Psychology 1Document3 pagesIntro To Psychology Crash Course Psychology 1Hahaha YeahNo ratings yet
- School Form 2 Daily Attendance Report of Learners For Senior High School (SF2-SHS)Document2 pagesSchool Form 2 Daily Attendance Report of Learners For Senior High School (SF2-SHS)Charly Mint Atamosa IsraelNo ratings yet
- 15419Document29 pages15419Sadashiva SahooNo ratings yet
- Bio-Diesel Production From Waste Cooking OilDocument51 pagesBio-Diesel Production From Waste Cooking OilDemostenes DeceoNo ratings yet
- Induction Training Program For Newly Recruited NursesDocument17 pagesInduction Training Program For Newly Recruited NursesNisha sutariyaNo ratings yet
- GOVT - Departments - Contact - Details - MF-14-06-2021 UpdatedDocument32 pagesGOVT - Departments - Contact - Details - MF-14-06-2021 Updatedadf_raghuNo ratings yet
- Health Impact AssessmentDocument16 pagesHealth Impact AssessmentjrynNo ratings yet
- Human Heredity Principles and Issues 10th Edition Michael Cummings Solutions Manual 1Document10 pagesHuman Heredity Principles and Issues 10th Edition Michael Cummings Solutions Manual 1yvette100% (39)
- Doctor and Clinical AssistantsDocument2 pagesDoctor and Clinical AssistantsIvan DwiputraNo ratings yet
- Dip Zinc 7-Tank ProcessDocument3 pagesDip Zinc 7-Tank ProcessAmit Chauhan100% (1)
- Starch Industry Effluent Treatment PlantDocument30 pagesStarch Industry Effluent Treatment PlantBSridhar50% (2)
- Trophy Winners 2019Document10 pagesTrophy Winners 2019blackguard999No ratings yet
- Cancer Treatment HomeopathyDocument121 pagesCancer Treatment Homeopathykshahulhameed100% (1)