Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ntoplgy
Ntoplgy
Uploaded by
rajesh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views12 pagesOriginal Title
ntoplgy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views12 pagesNtoplgy
Ntoplgy
Uploaded by
rajeshCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
NETWORK TOPOLOGIES
There are three basic
configurations used to connect
computers they are the
•Bus
•Ring
•Star
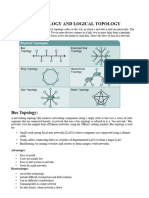
Bus topology
This type of network was widely used in the 1980’s
In this configuration every computer (node) shares
the networks total bus capacities.
In this configuration adding more computers will
reduce the access speed on the network.
Each computer communicates to other computers
on the network independently this is referred to as
PEER-TO-PEER networking
How a Bus Peer to Peer
Network Works
All computers on a network have a distinct
address just like your house does
a message would be send from one
computer with the address of another
computer attached to the message
The message is broadcasted to all the
computers on the network until the
addressed PC accepts the message
How it worked
The type of wires used for Bus Networks in the
80’s were called Thicknet and Thinnet
A Thicknet cable (very large about 1 inch in
diameter usually yellow was hung around a room)
Thinnet cables were connected to the PC’s NIC
and a Transceiver. The Transceiver was tapped
into the Thicknet cable
To stop the message from bouncing back and
forward down the wire (known as signal bounce)
both ends of the network are terminated with 50Ω
resistors
Problems
One of the main problems with this type of
network is that it is not very fault tolerant, a
break or defect in the bus would affect the
whole network
Ring Topology
In Ring topology each node is connected to the
two nearest nodes so the entire network forms a
circle
Data only travels in one direction on a Ring
network
How this Topology works
a node has information to send to another
computer on the network so it sends the
information out on the network to the PC it is
connected to, if the information is for this PC (the
recipients NIC address is attached to the
message, which is like putting an address on an
envelope) then the PC accepts the data
otherwise it passes the information on to the next
PC by repeating the data back out on the line
This method of repeating the data helps keep the
integrity of the data readable by other computers
How it Works
As it is better to have computers take turns
using the connecting Data cable, Ring
topologies incorporated a system called
Token passing
In this topology, to transmit on the wire your
computer must have control of the token or
wait for the token to be free
Larger Token Ring networks use multiple
tokens
Problems and Solutions
The drawback to this type of topology is that a single
malfunctioning workstation can disable the whole network
To make sure all the information is sent the receiving PC
sends the token back to the sending PC after it has
received all the data
If the sending PC is finished sending it passes the token to
the next PC
This type of network was also widely used in the 1980’s
This type of network used Thinnet cable joining nodes.
In the mid 1980’s Thinnet cable was replaced by
Category 3 Ethernet cable capable of handling up to
10Mbps
Star topology
HUB
In a Star topology every node is connected
through a central device such as a Hub,
Switch or Router
Compared to a Ring or Bus topology a Star
topology requires that more thought be put
into its setup
The Good and Bad of a
Star Network
The upside of a star network is that if any
one cable fails then only the node
connected on that cable would be affected
Another positive point to this type of network
is that it is very simple to join two star
networks together by connecting their
central devices to each other
The Good and Bad of a
Star Network
As each computer is connected to a central
device (Hub) the location of the Hub must
be made as central as possible, so as to
reduce cable lengths
The drawback to this type of topology is if a
central device was to fail then all computers
connected to that device would not be able
to see the network
You might also like
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1From EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Network TopologyDocument7 pagesNetwork TopologyJayvee Puntalba CalinogNo ratings yet
- Notes On Computer Networks Unit1Document14 pagesNotes On Computer Networks Unit1Rohit Chaudhary100% (4)
- GSM BoosterDocument29 pagesGSM BoosterAHMED ALANINo ratings yet
- New Network TopologiesDocument31 pagesNew Network TopologiesZain MalikNo ratings yet
- Basics of NetworksDocument66 pagesBasics of NetworksBibin Jose100% (1)
- Comparison Between Network TopologiesDocument2 pagesComparison Between Network TopologiesMahmoud Youssef72% (32)
- (Tutorials in Electronic Materials, Circuits and Devices) Milin Zhang, Zhihua Wang, Jan Van Der Spiegel, Franco Maloberti - Advanced Tutorial On Analog Circuit Design-River Publishers (2023)Document449 pages(Tutorials in Electronic Materials, Circuits and Devices) Milin Zhang, Zhihua Wang, Jan Van Der Spiegel, Franco Maloberti - Advanced Tutorial On Analog Circuit Design-River Publishers (2023)PANKAJ KUMARNo ratings yet
- Trends Q2 w4Document32 pagesTrends Q2 w4Randy Magbudhi60% (10)
- Omputer Communications and NetworksDocument70 pagesOmputer Communications and NetworksMomina ButtNo ratings yet
- Different Kinds of Network Topology in Computer NetworksDocument4 pagesDifferent Kinds of Network Topology in Computer Networksmuna cliffNo ratings yet
- ICT Lecture 12Document41 pagesICT Lecture 12Muhammad UmarNo ratings yet
- Presentacion 7 PDFDocument22 pagesPresentacion 7 PDFJose Leonardo Simancas GarciaNo ratings yet
- Mcse Note Topology by Wahidullah ShahaadatDocument30 pagesMcse Note Topology by Wahidullah ShahaadatmcseaNo ratings yet
- Data Communication Unit1 As Per Pune UniversityDocument22 pagesData Communication Unit1 As Per Pune UniversityDr. Hitesh MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks 1Document18 pagesComputer Networks 1Edwin NfehNo ratings yet
- Cne Chapter2 NotesDocument24 pagesCne Chapter2 Noteskirantamanna63No ratings yet
- Types of Network TopologiesDocument41 pagesTypes of Network TopologiesKolenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 1 and 2 21Document17 pagesChapter 2 1 and 2 2119Siddhesh DhumalNo ratings yet
- Cchapter 1 - Part IIDocument39 pagesCchapter 1 - Part IIBezabh AbebawNo ratings yet
- Cables and TopologiesDocument9 pagesCables and TopologiesRafayetNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 LAN (Part 1)Document43 pagesTopic 4 LAN (Part 1)suhailiNo ratings yet
- Types of Network TopologiesDocument41 pagesTypes of Network TopologiesKolenNo ratings yet
- Basic NetworkingDocument8 pagesBasic NetworkingDavid Atoroyo SikaNo ratings yet
- Class 1, 2-MergedDocument346 pagesClass 1, 2-MergedDevNo ratings yet
- Topology 1Document12 pagesTopology 1ingawalemadhura5722No ratings yet
- How LAN Switches Work: Interview Notes - Data Communications & NetworkDocument24 pagesHow LAN Switches Work: Interview Notes - Data Communications & Networkapi-19915961No ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument164 pagesComputer NetworkBipin PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Network TopologiesDocument27 pagesNetwork Topologieskamran haiderNo ratings yet
- TopologyDocument32 pagesTopologyJatin SatijaNo ratings yet
- Data Communication Network and Internet PDFDocument20 pagesData Communication Network and Internet PDFpooja guptaNo ratings yet
- Bus Linear Topology (Commonly Known As Bus Topology) :: It Is The Simplest Method ofDocument3 pagesBus Linear Topology (Commonly Known As Bus Topology) :: It Is The Simplest Method ofnano0206No ratings yet
- Evolution of Network:: Arpa United States Department of Defense Cold War InternetDocument8 pagesEvolution of Network:: Arpa United States Department of Defense Cold War InternetDEEPTI SHARMANo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument20 pagesComputer NetworksCharice RamosNo ratings yet
- Network Topologies: Prepared By:Ronnel P. Agulto, Cpe ObjectivesDocument28 pagesNetwork Topologies: Prepared By:Ronnel P. Agulto, Cpe ObjectivesBilal AhmadNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Computer Networks: Network TopologyDocument25 pagesBasic Concepts of Computer Networks: Network TopologyAmritansh SinghNo ratings yet
- Network TopologyDocument25 pagesNetwork TopologySSB WORLDNo ratings yet
- Network TopologyDocument25 pagesNetwork Topology421 Rushikesh Bhavsar IFNo ratings yet
- Basic NetworksDocument14 pagesBasic NetworksGilgamesh berserkerNo ratings yet
- 3.0 Internet Technology: 3.1 Network Basics 3.1.1 Network TopologyDocument34 pages3.0 Internet Technology: 3.1 Network Basics 3.1.1 Network TopologyAsrul Nizam AliNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Toplogys1Document9 pagesComputer Networks Toplogys1ammapetNo ratings yet
- 4335 NetworkingemisDocument4 pages4335 NetworkingemisFavour JamesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Computer NetworksDocument33 pagesLecture 2 Computer NetworksJay JembeNo ratings yet
- It 111: Introduction To Information TechnologyDocument33 pagesIt 111: Introduction To Information TechnologyJay JembeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-1Document43 pagesLecture 1-1joeh angeloNo ratings yet
- Computer Network Topologies - JavatpointDocument8 pagesComputer Network Topologies - JavatpointP DNo ratings yet
- Ring NetworkDocument8 pagesRing Networkzackcore98100% (1)
- A) Types of Computer NetworksDocument4 pagesA) Types of Computer NetworksPrincez MaNi RenGaNo ratings yet
- Network System Administration and SecurityDocument137 pagesNetwork System Administration and SecurityKevin NeshNo ratings yet
- CN Unit 1Document26 pagesCN Unit 1vijayNo ratings yet
- 5 Network TopologiesDocument20 pages5 Network TopologiesRashad MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document27 pagesLecture 2Mstafa MhamadNo ratings yet
- 6 Network TopologiesDocument17 pages6 Network TopologiesRashad MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking: Class XIIDocument47 pagesComputer Networking: Class XIISanjyoti SinghNo ratings yet
- Physical Topology and Logical TopologyDocument3 pagesPhysical Topology and Logical TopologyNO NameNo ratings yet
- Network Topologies: The Configuration of A Communication NetworkDocument15 pagesNetwork Topologies: The Configuration of A Communication NetworkMuskan GargNo ratings yet
- Working2022 PDFDocument9 pagesWorking2022 PDFKrrish KumarNo ratings yet
- ICT Fundamentals ReportDocument49 pagesICT Fundamentals ReportJigs OlbesNo ratings yet
- Network LayersDocument40 pagesNetwork LayersAbhishek DishankitNo ratings yet
- Study About Basic of Network (Topologies) and Types of network-LAN, Man, WanDocument11 pagesStudy About Basic of Network (Topologies) and Types of network-LAN, Man, WanAnonymous aQxekTRNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks and Data Communication: Definition of Terms I) NetworkDocument9 pagesComputer Networks and Data Communication: Definition of Terms I) NetworkJamesNo ratings yet
- Network Systems & Protocols: Task 1Document12 pagesNetwork Systems & Protocols: Task 1qwerty2711No ratings yet
- NetworkingDocument9 pagesNetworkingalmightyfavouriteNo ratings yet
- Deng Relation Distillation Networks For Video Object Detection ICCV 2019 PaperDocument10 pagesDeng Relation Distillation Networks For Video Object Detection ICCV 2019 PaperrajeshNo ratings yet
- Hu 2018Document10 pagesHu 2018rajeshNo ratings yet
- Okabayashi 2007Document4 pagesOkabayashi 2007rajeshNo ratings yet
- Applsci 10 08912 v2Document17 pagesApplsci 10 08912 v2rajeshNo ratings yet
- Communication SystemDocument17 pagesCommunication SystemrajeshNo ratings yet
- Image ProcessingDocument22 pagesImage ProcessingrajeshNo ratings yet
- Image ProcessingDocument22 pagesImage ProcessingrajeshNo ratings yet
- Sanjaybhai Rajguru College of Engineering - Rajkot: Subject: Fundamentals of Image Processing (2181102)Document23 pagesSanjaybhai Rajguru College of Engineering - Rajkot: Subject: Fundamentals of Image Processing (2181102)rajeshNo ratings yet
- Subject: Basic Electronics (2110016) : Sanjaybhai Rajguru College of EngineeringDocument18 pagesSubject: Basic Electronics (2110016) : Sanjaybhai Rajguru College of EngineeringrajeshNo ratings yet
- Sanjaybhai Rajguru College of EngineeringDocument16 pagesSanjaybhai Rajguru College of EngineeringrajeshNo ratings yet
- 1Document18 pages1rajeshNo ratings yet
- Ds Gps l1 Inline AmplifierDocument2 pagesDs Gps l1 Inline AmplifierupdaulNo ratings yet
- Pembangunan Jaringan Komputer Studi Kasus CV Dino Mandiri KaranganyarDocument7 pagesPembangunan Jaringan Komputer Studi Kasus CV Dino Mandiri KaranganyarChatrio DestandraNo ratings yet
- Gps 103 Tracker User ManualDocument10 pagesGps 103 Tracker User Manualcarlosjr007No ratings yet
- Toshiba Satellite 2430 2435 (Compal LA-1541)Document48 pagesToshiba Satellite 2430 2435 (Compal LA-1541)Barton EletronicsNo ratings yet
- FNC-0109TX Spec V5.0Document2 pagesFNC-0109TX Spec V5.0SHING EBNo ratings yet
- 750/760 Feeder Management Relay: Release NotesDocument4 pages750/760 Feeder Management Relay: Release NotesshouryapendyalaNo ratings yet
- ES-XXX Surface Unit Operating ManualDocument45 pagesES-XXX Surface Unit Operating Manualjuan TorresNo ratings yet
- Contoh CV PDFDocument1 pageContoh CV PDFFaiz Ivan DharmawanNo ratings yet
- 01-3 - Routing BasicsDocument38 pages01-3 - Routing BasicsEmildo LahudNo ratings yet
- Antenna Selection GuideDocument41 pagesAntenna Selection GuidebrsreddyNo ratings yet
- Intensity ModulationDocument3 pagesIntensity Modulationanon-323096100% (1)
- PDM 10Document10 pagesPDM 10Rober ChicoNo ratings yet
- DX DiagDocument15 pagesDX DiagganeshabaliNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse Monitoring and Control System Based On Wireless Sensor NetworkDocument4 pagesGreenhouse Monitoring and Control System Based On Wireless Sensor NetworkFolkes LaumalNo ratings yet
- State Network: The of TheDocument22 pagesState Network: The of TheDaphne100% (1)
- 3 Tally Prime Course Annex - 1 Bill EntryDocument34 pages3 Tally Prime Course Annex - 1 Bill EntryManjulaNo ratings yet
- KNS Z12MK3 Stabilised 1.2 M VSAT AntennaDocument1 pageKNS Z12MK3 Stabilised 1.2 M VSAT AntennaMauricio SallasNo ratings yet
- HUAWEI CLOUD Stack 8.1.1 Solution Description 05 - HuaweiDocument2 pagesHUAWEI CLOUD Stack 8.1.1 Solution Description 05 - HuaweiEmk KhanNo ratings yet
- IoT-Lecture-05 Embedded SystemDocument29 pagesIoT-Lecture-05 Embedded Systemutkarsh.shrivastava.ug21No ratings yet
- Fractal Image Compression Based On Discrete Wavelet TransformDocument5 pagesFractal Image Compression Based On Discrete Wavelet TransformfarhanNo ratings yet
- Best Buys Audio AV - Issue 7 2023Document84 pagesBest Buys Audio AV - Issue 7 2023Kinga KapitanyNo ratings yet
- Inv Tron 080923Document9 pagesInv Tron 080923Omar AngloNo ratings yet
- Item 5 FG-2002 Function Generator and Power Supply Mar 2021Document14 pagesItem 5 FG-2002 Function Generator and Power Supply Mar 2021Carbon Nano TubeNo ratings yet
- The PRC Broadcast and New National Building CodeDocument49 pagesThe PRC Broadcast and New National Building CodeJericho VelardeNo ratings yet
- 02 How To Master CCNADocument2 pages02 How To Master CCNAKuldeep YadavNo ratings yet
- MAPP XT - Project ReportDocument13 pagesMAPP XT - Project ReportAhonny LarpNo ratings yet
- Network Systems: BriefingDocument8 pagesNetwork Systems: BriefingLeo KrekNo ratings yet