Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ADHD
Uploaded by
Camille Joy BaliliCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ADHD
Uploaded by
Camille Joy BaliliCopyright:
Available Formats
HOLY NAME UNIVERSITY
THE PREMIER CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY IN THE PROVINCE OF BOHOL
College of Health Sciences – Nursing Department
FAIR USE NOTICE AND
DISCLAIMER
This PowerPoint presentation
contains copyrighted materials.
The use of such materials has
not been specifically authorized
by the copyright owners but the
use falls within the standards of
“FAIR USE". This teaching-
learning material is created and
intended for educational use only.
Trailblazing Excellence in Educating Servant Leaders
Copyright © 2020 dcasquejo@hnu.edu.ph
HOLY NAME UNIVERSITY
THE PREMIER CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY IN THE PROVINCE OF BOHOL
College of Health Sciences – Nursing Department
ATTENTION DEFICIT
HYPERACTIVITY
DISORDER (ADHD)
ADHD is one of the most common
neurobiologic conditions in
childhood that can also persist into
adulthood.
Sometimes also called Attention
Deficit Disorder, ADD when there is
less hyperactivity
It is a significant impairment in
functioning in at least 2 settings
(usually in the home & at school)
due to impulsivity, inattention,
and /or hyperactivity.
Trailblazing Excellence in Educating Servant Leaders
Copyright © 2020 dcasquejo@hnu.edu.ph
HOLY NAME UNIVERSITY
THE PREMIER CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY IN THE PROVINCE OF BOHOL
College of Health Sciences – Nursing Department
Boys are affected more frequently
than girls
The cause of ADHD is unknown
but several factors contribute to
ADHD such as:
Environment
Low socio-economic status
Foster care
Very Low Birth Weight
Genetic (family history)
Physiologic
The disorder is characterized by
three major behaviors --- and can
present differently depending on
the age at presentation:
1. Inattention
2. Impulsiveness
3. Hyperactivity
Trailblazing Excellence in Educating Servant Leaders
Copyright © 2020 dcasquejo@hnu.edu.ph
HOLY NAME UNIVERSITY
THE PREMIER CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY IN THE PROVINCE OF BOHOL
College of Health Sciences – Nursing Department
1. Inattention
Inattention can include symptoms
such as:
Difficulty organizing tasks
Reluctance to do tasks that
require mental effort over time
A child who easily gets bored of a
task
A child who jumps from one task
to another without completing the
first task
A child who is easily distracted or
does not follow tasks carefully
2. Impulsiveness
Impulsiveness includes:
A child acting before thinking and
therefore having difficulty with
such tasks like waiting for his/her
turn
A child blurting answers before a
question is completed
A child interrupting or intruding on
others’ conversations
Trailblazing Excellence in Educating Servant Leaders
Copyright © 2020 dcasquejo@hnu.edu.ph
HOLY NAME UNIVERSITY
THE PREMIER CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY IN THE PROVINCE OF BOHOL
College of Health Sciences – Nursing Department
3. Hyperactivity
Hyperactivity includes:
A child may shift excessively from
one activity to another
A child can be described as “on
the go” or “acts as if driven by
a motor”
A child who can’t seem to sit still
and who is constantly moving,
roaming, touching things,
squirming or fidgeting.
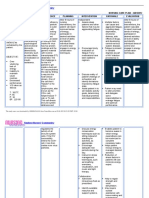
ASSESSMENT
Preschool Elementary Adolescence
Age School
Hyperactive Struggles with Academic demands
listening in class become
(Inattention) overwhelming
Impulsive Poor Struggles with
organizational attention, learning,
skills & executive
functioning
Not flexible Struggles with
social interaction
May be Difficulty
aggressive functioning
with peers independently
Trailblazing Excellence in Educating Servant Leaders
Copyright © 2020 dcasquejo@hnu.edu.ph
HOLY NAME UNIVERSITY
THE PREMIER CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY IN THE PROVINCE OF BOHOL
College of Health Sciences – Nursing Department
DIAGNOSING ADHD
A child who is inattentive, impulsive,
or hyperactive does not necessarily
have ADHD.
Many normal children have some of
these symptoms especially young
children…and the symptoms could be
caused by another disorder entirely.
The criteria for diagnosis of ADHD
includes a thorough initial history,
physical examination, and completion
of evidenced-based rating scales by an
individual who is familiar with the child
such as:
Parents & Teachers
Primary care providers
other caretakers
A complete H&P (History & Physical
exam) is designed:
To look into other causes of
behavior problems such as
neurologic & genetic problems
Trailblazing Excellence in Educating Servant Leaders
Copyright © 2020 dcasquejo@hnu.edu.ph
HOLY NAME UNIVERSITY
THE PREMIER CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY IN THE PROVINCE OF BOHOL
College of Health Sciences – Nursing Department
To rule out conditions with similar
symptoms or which may coexist
with ADHD such as:
Anxiety
Depression
Sleep disturbances (e.g. apnea)
Substance abuse
Oppositional defiant disorder
Conduct disorder
Learning disorder
For example, a child with visual
impairment who is unable to see the
board may not have ADHD but gets
“off task” because he/she cannot
see assignments or instructions
clearly.
As a rule, children with ADHD do not
have a deficit in intelligence,
although they may seem to because
of their impulsive behavior and an
unawareness that their behavior is
upsetting to family, friends, and
teachers.
Trailblazing Excellence in Educating Servant Leaders
Copyright © 2020 dcasquejo@hnu.edu.ph
HOLY NAME UNIVERSITY
THE PREMIER CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY IN THE PROVINCE OF BOHOL
College of Health Sciences – Nursing Department
THERAPEUTIC
MANAGEMENT
A variety of treatment methods are
used , often in combination, in the
management of ADHD.
Environmental Modification
Stable learning environment – is
crucial for children with ADHD so
that instruction can be free from
distractions
Educational accommodations which
may include:
Preferential seating - placing a
student's seat in a location that is
most beneficial for their learning in
the classroom)
Extended time for test taking,
Written list of assignments & due
dates, &
Note-taking support
Provide a structured and predictable
environment at home & in school –
children with ADHD respond best in
Trailblazing Excellence in Educating Servant Leaders
Copyright © 2020 dcasquejo@hnu.edu.ph
HOLY NAME UNIVERSITY
THE PREMIER CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY IN THE PROVINCE OF BOHOL
College of Health Sciences – Nursing Department
an environment with clear and
consistent rules & expectations.
The main goal of behavior
management is to increase
appropriate behavior and decrease
negative behavior.
Ways to help manage a child’s
behavior:
Encourage parents to be fair but
firm and to set limits to reduce
arguments.
Teach parents to give instructions
slowly and make certain that they
have the child’s attention before
beginning instructions
Remind parents to break down a
chore in several steps to help child
follow easily
Encourage parents to understand
that anger is normal (when they
correct a child’s behavior) and
should be directed at the child’s
disruptive behavior, and not on
the child.
Trailblazing Excellence in Educating Servant Leaders
Copyright © 2020 dcasquejo@hnu.edu.ph
HOLY NAME UNIVERSITY
THE PREMIER CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY IN THE PROVINCE OF BOHOL
College of Health Sciences – Nursing Department
Family Support
Parents of a child with ADHD may
have more frequent healthcare visits
because of unintentional injuries, such
as lacerations or simple burns. Ask
parents during these encounters if they
are having difficulty raising a child with
hyperactivity. Help them to understand
that because of a very complex and ill-
understood syndrome, the behavior is
the best their child can achieve.
Organizations of ADHD children may
be available online & can be of great
help to parents.
Although hyperactivity fades with late
adolescence, some children with
ADHD continue to experience
problems with impulsivity & inattention
into adulthood. These children may
need counselling to find a career that
fits with these behaviors and allows
them to succeed as adults.
Trailblazing Excellence in Educating Servant Leaders
Copyright © 2020 dcasquejo@hnu.edu.ph
HOLY NAME UNIVERSITY
THE PREMIER CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY IN THE PROVINCE OF BOHOL
College of Health Sciences – Nursing Department
Medications
Medication management is a proven
treatment for many individuals with
ADHD, but not all children and teens
with ADHD need to take medication.
Those with milder forms may be
successful with structured environment
and firm, but fair types of discipline &
reward.
Most frequently prescribed stimulant
medications for ADHD:
methylphenidate and amphetamines
Stimulants work by stimulating
dopamine receptors so there is regular
nerve transmission, which results in
increased attention span.
Side-effects:
1. Insomnia - to relieve the insomnia,
the drug must be taken during the
day
2. Anorexia – administer medication
before breakfast and offering nutri-
tious snacks between meals.
Trailblazing Excellence in Educating Servant Leaders
Copyright © 2020 dcasquejo@hnu.edu.ph
HOLY NAME UNIVERSITY
THE PREMIER CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY IN THE PROVINCE OF BOHOL
College of Health Sciences – Nursing Department
CAUTION:
Parents must be cautioned that this
drug offers a “high” effect to children
who do not have ADHD, so their child
must be conscientious that the
medication is not stolen by other
children to use for euphoria effect.
Other meds for ADHD:
Nonstimulant drugs such as
atomoxetine (Strattera) – first-line
medication for children with ADHD
who cannot tolerate stimulants.
Must be used cautiously with
children because of a black box
warning about increased risk of
suicidal thoughts
guanfacine (Intuniv)
guanfacine hydrochloride (Tenex)
Trailblazing Excellence in Educating Servant Leaders
Copyright © 2020 dcasquejo@hnu.edu.ph
HOLY NAME UNIVERSITY
THE PREMIER CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY IN THE PROVINCE OF BOHOL
College of Health Sciences – Nursing Department
END OF
PRESENTATION
Trailblazing Excellence in Educating Servant Leaders
Copyright © 2020 dcasquejo@hnu.edu.ph
You might also like
- ADHD Parent Skills Training ManualDocument85 pagesADHD Parent Skills Training ManualLalita Marathe100% (1)
- ADHD Parent Skills Training ManualDocument85 pagesADHD Parent Skills Training ManualLalita MaratheNo ratings yet
- Adhd Supporting Strategies Ebook-Print1Document123 pagesAdhd Supporting Strategies Ebook-Print1Tatiana ArnoldNo ratings yet
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: (ADHD)Document24 pagesAttention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: (ADHD)Tatiana ArnoldNo ratings yet
- Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Function BRDocument11 pagesBehavior Rating Inventory of Executive Function BRPatti Stroud GermanNo ratings yet
- Stephen M Stahl Laurence Mignon Stahl S Illustrated ADHD - 1Document175 pagesStephen M Stahl Laurence Mignon Stahl S Illustrated ADHD - 1May Rc100% (1)
- Resource Notebook FinalDocument18 pagesResource Notebook Finalapi-315861901No ratings yet
- Vanderbilt Rating Scale Scoring InstructionsDocument2 pagesVanderbilt Rating Scale Scoring InstructionsYeon Ae Narita100% (2)
- Disorders in Childhood and AdolescenceDocument7 pagesDisorders in Childhood and AdolescenceCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Caars Self L Int1Document9 pagesCaars Self L Int1Mona Refaei100% (1)
- ADHD Quick Fact Sheet For Parents Guardians and School PersonnelDocument2 pagesADHD Quick Fact Sheet For Parents Guardians and School Personnelinetwork2001No ratings yet
- How Prevalent Is ADHD?Document42 pagesHow Prevalent Is ADHD?881118No ratings yet
- Case 3Document21 pagesCase 3Mustabeen TairNo ratings yet
- Adhd ArticleDocument6 pagesAdhd Articleapi-115513756No ratings yet
- The Psychopath MagnetizedDocument9 pagesThe Psychopath MagnetizedAvengingBrainNo ratings yet
- Motionally IsturbedDocument12 pagesMotionally Isturbedapi-280439402No ratings yet
- ADHD PresentationDocument21 pagesADHD PresentationZainab Ali HassanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine AssessmentDocument16 pagesEndocrine AssessmentCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Children With Special Needs in The ClassroomDocument29 pagesChildren With Special Needs in The ClassroomHo Yan LeeNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Disorders PPT 3 1Document9 pagesNervous System Disorders PPT 3 1Camille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Helping A Child Who May Have ADHDDocument15 pagesHelping A Child Who May Have ADHDMaria VacarNo ratings yet
- ADHD and The QbTestDocument7 pagesADHD and The QbTestPaul AsturbiarisNo ratings yet
- Police Officer SuicideDocument14 pagesPolice Officer SuicideLjubitelj SamNo ratings yet
- Adhd and Foreign LanguageDocument33 pagesAdhd and Foreign Languageneezisnis100% (2)
- Assignment September 2013 SemesterDocument19 pagesAssignment September 2013 SemesterMangala Rupini SegaranNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument3 pagesAnxiety DisordersCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Adhd PMTDocument16 pagesAdhd PMTBhanu Dahiya100% (1)
- Other Health Impairment: CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesOther Health Impairment: CharacteristicsJanine BinbingNo ratings yet
- Course Audit CompilationDocument161 pagesCourse Audit Compilationmark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- The ADHD Parenting Guide for the Boy Child: Thriving Minds, Unleashing Potential: Nurturing Boys with ADHD - A Practical Parenting GuideFrom EverandThe ADHD Parenting Guide for the Boy Child: Thriving Minds, Unleashing Potential: Nurturing Boys with ADHD - A Practical Parenting GuideNo ratings yet
- Adhd New ContentDocument9 pagesAdhd New ContentAsha jiluNo ratings yet
- Crime and Human NatureDocument9 pagesCrime and Human NatureDavna LopezNo ratings yet
- Autism Spectrum DisorderDocument12 pagesAutism Spectrum DisorderCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- LDExplained Learning DisabilitiesDocument59 pagesLDExplained Learning Disabilitiesbhupendra kumarNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) : I. Executive SummaryDocument5 pagesCase Study: Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) : I. Executive SummaryJenipe CodiumNo ratings yet
- ApppDocument4 pagesApppDRANo ratings yet
- Strategies For Implementing Evidence-Based Psychosocial Interventions For Children With Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity DisorderDocument15 pagesStrategies For Implementing Evidence-Based Psychosocial Interventions For Children With Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity DisorderCristinaNo ratings yet
- ADHD. Arancon ReadingDocument6 pagesADHD. Arancon ReadingDRANo ratings yet
- HTTP Umm Edu Health Medical Altmed Condition Attention-Deficit-hyperactivity-disorderDocument15 pagesHTTP Umm Edu Health Medical Altmed Condition Attention-Deficit-hyperactivity-disorderClarkSmithNo ratings yet
- Ese411 - Bernardine Phyllis Anak Phill Franes - E30401210008Document19 pagesEse411 - Bernardine Phyllis Anak Phill Franes - E30401210008Bernardine Phyllis Anak Phill FranesNo ratings yet
- Acronyms GlossaryDocument5 pagesAcronyms Glossarygaurav.rohankarNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous Task For Students With ADHDDocument3 pagesAsynchronous Task For Students With ADHDTenor BaliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document13 pagesChapter 8niroannabellaNo ratings yet
- Week 11 NCM 109 LectureDocument49 pagesWeek 11 NCM 109 LecturePolicarpio AprilNo ratings yet
- Adhd f1282 A4 BW Final Dec16Document4 pagesAdhd f1282 A4 BW Final Dec16jimNo ratings yet
- PETA Research Paper TemplateDocument14 pagesPETA Research Paper TemplateIrish Leigh GotiangcoNo ratings yet
- May Jun 2Document6 pagesMay Jun 2inetwork2001No ratings yet
- Research Paper (RESEARCHERS)Document28 pagesResearch Paper (RESEARCHERS)Jhanna Lou100% (1)
- ADHD EssayDocument3 pagesADHD EssayArnel E. Sarte Jr.No ratings yet
- Attention Deficit Disorder:: FINAL TERM Examination-Spring 2021Document3 pagesAttention Deficit Disorder:: FINAL TERM Examination-Spring 2021Malik ShehramNo ratings yet
- Grp3 MacarandangDocument4 pagesGrp3 MacarandangCARLOS MARCIAL MACARANDANGNo ratings yet
- Emotional DisorderDocument6 pagesEmotional DisorderGoerge CabuntasNo ratings yet
- FEINSTEIN Research AssignmentDocument12 pagesFEINSTEIN Research AssignmentMarshie FeinsteinNo ratings yet
- Skip To Main ContentDocument33 pagesSkip To Main ContentCharmaine BeltranNo ratings yet
- ADHD in The ClassroomDocument9 pagesADHD in The ClassroomAi LeenNo ratings yet
- ADHDDocument40 pagesADHDAnit LamichhaneNo ratings yet
- Lai 574 Ohi-Adhd BrochureDocument3 pagesLai 574 Ohi-Adhd Brochureapi-259258566No ratings yet
- Addressing Emotionally Based School AvoidanceDocument9 pagesAddressing Emotionally Based School AvoidancePolina ThemistokleousNo ratings yet
- ADHD - Friday GroupDocument18 pagesADHD - Friday GroupMaria TeresaNo ratings yet
- Autism Spectrum DisorderDocument6 pagesAutism Spectrum DisorderbarutonejinoNo ratings yet
- Oppositional Defiant DisorderDocument15 pagesOppositional Defiant Disorderapi-710987491No ratings yet
- A Guide On ADHD Using Neural ConnectionsDocument13 pagesA Guide On ADHD Using Neural ConnectionsNehad BalochNo ratings yet
- Déficit de AtenciónDocument4 pagesDéficit de AtenciónCecilia CasalesNo ratings yet
- Parent NewsletterDocument4 pagesParent Newsletterapi-301094873No ratings yet
- Arch Dis Child 2005 Harpin I2 7Document7 pagesArch Dis Child 2005 Harpin I2 7phenorenNo ratings yet
- Acronym: OHI Characteristics For Other Health ImpairmentsDocument3 pagesAcronym: OHI Characteristics For Other Health ImpairmentsJenelle Catherina MagbutayNo ratings yet
- 6403 1 (Assignment)Document29 pages6403 1 (Assignment)Qasim AliNo ratings yet
- Tips For Parents Understanding Adhd and Learning DisabilitiesDocument2 pagesTips For Parents Understanding Adhd and Learning DisabilitiesCyndi WhitmoreNo ratings yet
- Highly Gifted Children With Attention Deficit DisorderDocument1 pageHighly Gifted Children With Attention Deficit Disorderpaulo.693No ratings yet
- Nursing Students With AdhdDocument5 pagesNursing Students With AdhdMikhail NikitopoulosNo ratings yet
- ADHD Patient Information Version 3Document4 pagesADHD Patient Information Version 3Erika Johanna SeguraNo ratings yet
- Adhdppt 181127060105Document18 pagesAdhdppt 181127060105Joseph MuzabulaNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document13 pagesPresentation 1Daniar AtaNo ratings yet
- St. Johns ADHD PresentationDocument31 pagesSt. Johns ADHD PresentationChitrah RNo ratings yet
- Teachers Booklet For ADHDDocument24 pagesTeachers Booklet For ADHDAnthony LaniganNo ratings yet
- Intro Research EngDocument24 pagesIntro Research EngRupert John LeeNo ratings yet
- Definition: Mental Retardation Is A Generalized, TriarchicDocument5 pagesDefinition: Mental Retardation Is A Generalized, TriarchicSelvi PrigeeNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Disorders PPT 1Document4 pagesNervous System Disorders PPT 1Camille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- February 2023 Little Bible Plan PDFDocument1 pageFebruary 2023 Little Bible Plan PDFCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- SOAP Bible Study Pages 1 PDFDocument1 pageSOAP Bible Study Pages 1 PDFCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- SOAP Bible Study Printable PDFDocument2 pagesSOAP Bible Study Printable PDFCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Maternal Mortality PDFDocument101 pagesMaternal Mortality PDFCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Jerish Verania Laboratory Activity 1 PDFDocument5 pagesJerish Verania Laboratory Activity 1 PDFCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Pecha KuchaDocument3 pagesPecha KuchaCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- A 3.1 Sudden Pregnancy Complications PDFDocument47 pagesA 3.1 Sudden Pregnancy Complications PDFCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- TOP 10 LEADING CAUSE OF MATERNAL AND INFANT MORBIDITY in The Philippines and WOH PDFDocument7 pagesTOP 10 LEADING CAUSE OF MATERNAL AND INFANT MORBIDITY in The Philippines and WOH PDFCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Untitled Document - Edited 8 PDFDocument2 pagesUntitled Document - Edited 8 PDFCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- NSH1 Preterm Labour and Pemature Rupture of Membranes 1 New PDFDocument35 pagesNSH1 Preterm Labour and Pemature Rupture of Membranes 1 New PDFCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Disorder 1 QuizletDocument12 pagesCognitive Disorder 1 QuizletCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics of Efficiencies and Outcomes of The Patients - Edited PDFDocument5 pagesNursing Informatics of Efficiencies and Outcomes of The Patients - Edited PDFCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- C304 Task 1 Word A PDFDocument33 pagesC304 Task 1 Word A PDFCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- U2A3 Hero Definition Essay Draft PDFDocument4 pagesU2A3 Hero Definition Essay Draft PDFCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Disorder 2 QuizletDocument5 pagesCognitive Disorder 2 QuizletCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument4 pagesAnxiety DisordersCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Cognitive DisordersDocument5 pagesCognitive DisordersCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics in Health Car1 PDFDocument9 pagesNursing Informatics in Health Car1 PDFCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Aids HivDocument2 pagesAids HivCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Cancer of The Stomach Stomach CancerDocument2 pagesCancer of The Stomach Stomach CancerCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Cancer of The LungsDocument4 pagesCancer of The LungsCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Cancer of The ThyroidDocument1 pageCancer of The ThyroidCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Cancer of The ProstateDocument3 pagesCancer of The ProstateCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- NUR2226 AT2 Part ADocument7 pagesNUR2226 AT2 Part ACamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Giltendez Prelim Activity International Arrivals PDFDocument2 pagesGiltendez Prelim Activity International Arrivals PDFCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- HMB200 Lecture 9: Beyond The Reward Pathway The Neuroscience of AddictionDocument72 pagesHMB200 Lecture 9: Beyond The Reward Pathway The Neuroscience of Addictionbluetooth opencvNo ratings yet
- Use of The MoxoDocument1 pageUse of The MoxoaviramsalomonNo ratings yet
- Cornelissen (5683823) ThesisDocument48 pagesCornelissen (5683823) ThesisAbbey Joy CollanoNo ratings yet
- Procrastination - Newton Chapter123Document26 pagesProcrastination - Newton Chapter123Mykho AstillaNo ratings yet
- Literature Review 1Document7 pagesLiterature Review 1anushankarcNo ratings yet
- Child Psychology Psychiatry - 2022 - Sonuga BarkeDocument27 pagesChild Psychology Psychiatry - 2022 - Sonuga BarkeAlejandra GettarNo ratings yet
- From Insight To Impact Utilizing The Power of Neuroscience Safety To Tackle The Human Factor in Health and SafetyDocument24 pagesFrom Insight To Impact Utilizing The Power of Neuroscience Safety To Tackle The Human Factor in Health and SafetyjoseNo ratings yet
- Arts-Based Therapy For Children With Disabilities: GRANT REQUESTED BY: Bhavini GandhiDocument17 pagesArts-Based Therapy For Children With Disabilities: GRANT REQUESTED BY: Bhavini Gandhiapi-25886263No ratings yet
- UDocument90 pagesUAina HaravataNo ratings yet
- Background Results: Sarah E. Lade & Laurel J. Trainor Livelab, Mcmaster University, Ontario, CanadaDocument1 pageBackground Results: Sarah E. Lade & Laurel J. Trainor Livelab, Mcmaster University, Ontario, CanadaAnonymous GqwolA5kjaNo ratings yet
- Peculiarities of Impulsive Purchasing in The Market of Consumer GoodsDocument9 pagesPeculiarities of Impulsive Purchasing in The Market of Consumer GoodsNguyen MinhNo ratings yet
- Apitherapy Congres PresentationDocument13 pagesApitherapy Congres PresentationAlina AlexandruNo ratings yet
- Effect of Mood On Problem Solving 1Document21 pagesEffect of Mood On Problem Solving 1LolaManijaDanijaNo ratings yet
- Santos Gantan Vs Gantan G.R. No. 225193Document8 pagesSantos Gantan Vs Gantan G.R. No. 225193chrizel.hdcNo ratings yet
- 07 - Chapter 1 PDFDocument35 pages07 - Chapter 1 PDFVaithisVaishuNo ratings yet
- Midterm Revalida NotesDocument16 pagesMidterm Revalida NotesJanine PenalosaNo ratings yet
- (RRL) Eating DisordersDocument2 pages(RRL) Eating DisordersMark Brandon VitorNo ratings yet