Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eukaryotic Cell
Uploaded by
Vassudev Kamat0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views24 pagesOriginal Title
Eukaryotic cell
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views24 pagesEukaryotic Cell
Uploaded by
Vassudev KamatCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 24
THE TOUR OF THE CELL
• Dutch Microscopist Anton van Leeunwenhoek
– Observed the world in tiny drop of water
and explained with attractive drawings.
• Robert Hooke – studies dead cells of bark of
an Oak tree for the first time under
microscope.
• Cells show tiny organs - Organelles
• The small photograph through microscope -
Micrograph
SIZE OF THE CELL
• With the minimum size,a cell must be able to
house enough DNA , protein molecules and
internal structures to survive and reproduce.
• At maximum, the size of the cell is influenced by
its requirement for enough surface area to
obtain adequate nutrition and oxygen and
dispose off the waste.
• A large cell has more surface area than a small
cell, but less surface area Relative to their
volume.
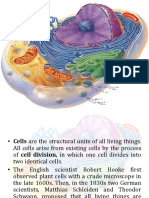
The well developed – Eukaryotic cells
• A eukaryotic cell comprise of many varied however,
interconnected structures.
• Such as Nucleus and the surrounding fluid - Cytoplasm.
• The outermost protective coverings are Cell Wall or
Plasma Membrane.
• The small organs suspended in the cytoplasm are called
as Organelles – Membranous organelles, making
compartments performing different activities.
• The chemical activities occurring in the cells – Cellular
Metabolism.
• The organelles forms their own membranes
giving additional benefit of surface area.
• This enhances formation of necessary proteins
such as enzymes or hormones.
• Cell Wall – Complex carbohydrate – Cellulose
Freely permeable.
• Plasma membrane – Fats / Lipids + proteins =
Lipoproteins.
Selectively permrable.
Eukaryotic cell
Size
Comparison
Nucleus – The controlling centre
• A separate compartment – Nuclear envelope –
Double membrane, perforated.
• Contains a highly coiled up- Chromatin- genetic
material – DNA ( De-oxyribose nucleic acid).
• At the time of cell division , it greatly coils uo
and dehydrates forming the countable
Chromosomes.
• Its own cytoplasm – Nucleoplasm
• Nucleolus – A dark body inside is the
production site for the protein factories of the
cell ie Ribosomes.
Endo-membrane system
a) Endoplasmic reticulum
The Endomembranous system has many
cell organelles which are interconnected
• ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM : A network inside
the cytoplasm of the cell.
• In continuation with the nuclear envelope ,
rise of the reticulum is seen.
• RER – Transportation of proteins prepared by
the ribosomes.
• SER – Transportation and storage of fats/lipids.
Detoxification of body at regular basis
and under heavy medication.
Endo-membrane system
b)Golgi bodies- The packaging & dispatching
units
Camillo Golgi –Golgi apparatus
Endo-membrane system
c )Lysosomes –Cleaners and helpers
• Golgi apparatus produce many vesicles are
released containing different proteins.
• Some of them contains digestive enzymes and are
called as “ Lysosomes”. – Lytic/ breaking down ;
soma – body.
• Lysosomes digests the cell debris, excess materials
and organelles of the cell.
• Hence are known as “ Demolition squad”.
• When the cell is damaged or is about to die,
lysosomes burst open to digest the whole cell.
• Hence are alos known as “ Suicidal bags” of the
cell.
• The cytoskeleton is a network of filaments and tubules that
extends throughout a cell, through the cytoplasm, which is
all of the material within a cell except for the nucleus.
• It is found in all cells, though the proteins that it is made of
vary between organisms.
a) Microfilaments : forms a three dimensional network
supporting the cell’s shape.
Ex. Muscle cells, Amoeba and amoeboid movement shown by
some of the blood cells such as WBC.
b) Intermediate filaments : Fibrous proteins ,ropelike,
provides anchorage to certain organelles such as nucleus.
c) Microtubules : Tubulin proteins, providing rigidity and
shape to the cell . Also provides tracks for organelles to
move within the cytoplasm.
• Locomotary organs :
• Flagella : - A long tail like organ found in the
prokaryotic cells. In eukaryotes, human male
reproductive cells, show flagella.
• They also show small hair like organ such Pili
( singular Pilus).
• Cilia :- small hairy organs covering the animals
body surface or any organ inside an animal’s
body on the organs for better absorption.
CELL JUNCTIONS
You might also like
- Reviewing General Biology IDocument9 pagesReviewing General Biology IRuby May Regala100% (9)
- Lec 3,4,5-Cell and Cell OrganellesDocument57 pagesLec 3,4,5-Cell and Cell OrganellesSatyam Arya100% (1)
- Human Cell AnatomyDocument56 pagesHuman Cell Anatomysanthiyasandy100% (3)
- Genetically Engineered ChildrenDocument2 pagesGenetically Engineered ChildrenPranav Varma100% (2)
- LESSON 3 Parts of The Cell and Their FunctionsDocument27 pagesLESSON 3 Parts of The Cell and Their FunctionsSophia CamachoNo ratings yet
- Bly 111 Cell and Cell Structure-1Document32 pagesBly 111 Cell and Cell Structure-1stephenalfa7No ratings yet
- World of CellDocument49 pagesWorld of CellGil Vincent Tapit YaquitNo ratings yet
- BIO101 Eukaryotic CellDocument24 pagesBIO101 Eukaryotic CellAvani PatilNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY OF CELLS AND BIOMOLECULESDocument60 pagesBIOCHEMISTRY OF CELLS AND BIOMOLECULESShaira Elyze Gabriel100% (1)
- General Education NotesDocument34 pagesGeneral Education NotesRyan M. TigbaoNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument82 pagesCellsK.R. LiberosisNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Cell - Structure - FunctionDocument94 pagesLecture 3 Cell - Structure - FunctionMuhammad Abbas WaliNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument28 pagesAnimal CellSahir koleNo ratings yet
- Pre Found BioDocument334 pagesPre Found BioAARYAN SURESH V. X DNo ratings yet
- C2-Organisation and Maintenance of The OrganismDocument39 pagesC2-Organisation and Maintenance of The OrganismyourmoNo ratings yet
- Cells and Tissues: J.C.CatolicoDocument85 pagesCells and Tissues: J.C.CatolicoGynew0% (1)
- Cell and TransportDocument77 pagesCell and TransportEugenie Francisco100% (1)
- Cell organelles and their functionsDocument4 pagesCell organelles and their functionsapplegummyNo ratings yet
- Combined Powerpoints On Cells 2017Document66 pagesCombined Powerpoints On Cells 2017api-242405009No ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function ExplainedDocument32 pagesCell Structure and Function ExplainedHC GamerNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument43 pagesCell StructureKexinNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument12 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of LifellamaNo ratings yet
- The Cell: A Generalized Cell and Its Main OrganellesDocument22 pagesThe Cell: A Generalized Cell and Its Main OrganellesSeira SusaNo ratings yet
- Cells: Structure and Functions in 40 CharactersDocument60 pagesCells: Structure and Functions in 40 CharactersFeah DaydayNo ratings yet
- The Basic Structural and Functional Unit of Life - The CellDocument87 pagesThe Basic Structural and Functional Unit of Life - The CellLovely Ann LoyogoyNo ratings yet
- 03 The Nature of CellDocument45 pages03 The Nature of CellClarisse Apresurado SapidaNo ratings yet
- 2.cells OverviewDocument28 pages2.cells Overviewcristine liggayoNo ratings yet
- Cells: By: Ms. ReisDocument24 pagesCells: By: Ms. ReisZohaib Nasir KhanNo ratings yet
- More Cells. The Cell Theory Can Be Summarized As:: Biology 12 - Cell Structure & Function: Chapter NotesDocument7 pagesMore Cells. The Cell Theory Can Be Summarized As:: Biology 12 - Cell Structure & Function: Chapter NotesJaveed KassamNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Unit of Life: Cbse, Class Ix, BiologyDocument41 pagesFundamental Unit of Life: Cbse, Class Ix, BiologySmitha JayaprakashNo ratings yet
- The Cell and Its OrganellesDocument21 pagesThe Cell and Its OrganellesKP DizonNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument33 pagesThe CellZay SalazarNo ratings yet
- The Cell Notes PDFDocument8 pagesThe Cell Notes PDFhi.blessNo ratings yet
- Bio CH 3 @keleme - 2013Document97 pagesBio CH 3 @keleme - 2013Israel HaileNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & FunctionDocument37 pagesCell Structure & FunctionAtika Ayu KusumaningtyasNo ratings yet
- 1..cell Structure and FunctionDocument53 pages1..cell Structure and FunctionAminath MeesanNo ratings yet
- IX Chapter 5 Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument69 pagesIX Chapter 5 Fundamental Unit of LifeRamChandraChauhanNo ratings yet
- Module 2 CellsDocument20 pagesModule 2 CellsLinalyn AmbrosioNo ratings yet
- Cells: Theory Movements FunctionsDocument27 pagesCells: Theory Movements FunctionsLady Sherlyn DelenNo ratings yet
- Cell PhysiologyDocument31 pagesCell PhysiologyJulie Calo PugiesNo ratings yet
- CellDocument34 pagesCellSadaf JavedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 CellDocument25 pagesLecture 2 Cellabdelrazeq zarourNo ratings yet
- Cell-The Fundamental Unit of Life. NotesDocument15 pagesCell-The Fundamental Unit of Life. Notesparth jainNo ratings yet
- Cell Basics by MuneebDocument45 pagesCell Basics by MuneebMuneeb Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument2 pagesThe Cellrosana f.rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Taxonomy ExplainedDocument46 pagesCell Structure and Taxonomy ExplainedIconMaicoNo ratings yet
- Lesson3-TheCellDocument27 pagesLesson3-TheCelly041087No ratings yet
- Chapter 3-Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument60 pagesChapter 3-Cell Structure and TaxonomyMarcos AlbaridaNo ratings yet
- 2 Cca IVD3 LX 0 F Zxy 7 NR 06914 J6 LG7 M 1 KM Oad ZNC IlDocument38 pages2 Cca IVD3 LX 0 F Zxy 7 NR 06914 J6 LG7 M 1 KM Oad ZNC IlLara AminNo ratings yet
- Cells: CG Enriquez, RMTDocument86 pagesCells: CG Enriquez, RMTJerneth Nyka FloresNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & Function: Basic Theor Y of LifeDocument34 pagesCell Structure & Function: Basic Theor Y of LifeJhea DoriaNo ratings yet
- Cell XIDocument15 pagesCell XIsaiprasadsahu504No ratings yet
- Lect 2. An Introduction To CellDocument10 pagesLect 2. An Introduction To CellMuhtasham KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 REVIEWDocument16 pagesUnit 4 REVIEWJuliana RiveraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document24 pagesChapter 4Georges SarkisNo ratings yet
- Cell and Cell Structures: Prepared By: Kristina Sevilla, RNDocument74 pagesCell and Cell Structures: Prepared By: Kristina Sevilla, RNmaria erikaNo ratings yet
- Biology Basic ConceptsDocument6 pagesBiology Basic ConceptsAhsni128No ratings yet
- CellsDocument17 pagesCellsnguyenbohaeNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & Function 2022Document43 pagesCell Structure & Function 2022Kavita MahaseNo ratings yet
- Policies: Attendance - ID & Uniform - Quizzes - Grading System - 40% Quizzes - 30% Manual - 10% Exam - 60%Document67 pagesPolicies: Attendance - ID & Uniform - Quizzes - Grading System - 40% Quizzes - 30% Manual - 10% Exam - 60%kamiya008100% (1)
- Dissertation Martin Hölzer, 2017 PDFDocument253 pagesDissertation Martin Hölzer, 2017 PDFatpowrNo ratings yet
- Dr. Djohan Ardiansyah, SP.S (K)Document60 pagesDr. Djohan Ardiansyah, SP.S (K)satyagraha84No ratings yet
- BreastDocument104 pagesBreastRamesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: BIOLOGY 9700/21Document20 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: BIOLOGY 9700/21Milinda De SilvaNo ratings yet
- The Human Genetic Code and I Ching’s 64 Hexagrams ConnectionDocument27 pagesThe Human Genetic Code and I Ching’s 64 Hexagrams ConnectionGreg HouckNo ratings yet
- Cycloheximide: For Research Use Only. Not For Use in Diagnostic ProceduresDocument1 pageCycloheximide: For Research Use Only. Not For Use in Diagnostic ProceduresRochnald PigaiNo ratings yet
- Quotes Based On Themes in GattacaDocument5 pagesQuotes Based On Themes in GattacaFelix LeNo ratings yet
- PhanerogamsDocument3 pagesPhanerogamsKrishna JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Coconut Genetic ResourcesDocument797 pagesCoconut Genetic ResourcesJohnDavidNo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering: Advantages, Disadvantages & BreakthroughsDocument7 pagesGenetic Engineering: Advantages, Disadvantages & BreakthroughsYash NagpureyNo ratings yet
- STS Final Quiz 2Document6 pagesSTS Final Quiz 2Choe Yoek SoekNo ratings yet
- Instant Cloning Kit Manual (For Amplified Products) : Genei GeneiDocument7 pagesInstant Cloning Kit Manual (For Amplified Products) : Genei GeneiHemant KawalkarNo ratings yet
- PresntationDocument10 pagesPresntationShahd MNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain Reaction 1Document8 pagesPolymerase Chain Reaction 1Ye Htut AungNo ratings yet
- Acute appendicitis, pneumonia, tuberculosis and other medical quiz diagnosesDocument23 pagesAcute appendicitis, pneumonia, tuberculosis and other medical quiz diagnoses182 ROHIL HNo ratings yet
- Graad 12: National Senior CertificateDocument15 pagesGraad 12: National Senior CertificateAthenkosi MnotozaNo ratings yet
- Sugarcane BreedingandgenomicsDocument45 pagesSugarcane BreedingandgenomicsMuhammad TauseefNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Biosystematics LectureDocument20 pagesIntroduction to Biosystematics LectureSenevirathne K.M.M.C.No ratings yet
- Baluska, Gagliano, Witzany, Memory-and-Learning-in-PlantsDocument223 pagesBaluska, Gagliano, Witzany, Memory-and-Learning-in-PlantsKamel100% (2)
- All-Natural 5-Meo-Dmt Sigma Receptor 1 Agonist and Its Therapeutic Impact in Mental and Neurodegenerative Diseases Through Mitochondrial ActivationDocument22 pagesAll-Natural 5-Meo-Dmt Sigma Receptor 1 Agonist and Its Therapeutic Impact in Mental and Neurodegenerative Diseases Through Mitochondrial ActivationLex UNo ratings yet
- Understanding Sars-Cov-2-Induced Systemic Amyloidosis: BiorxivDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Sars-Cov-2-Induced Systemic Amyloidosis: BiorxivAntonisNo ratings yet
- 02 Gene Aid Isolation KitDocument16 pages02 Gene Aid Isolation KitLusi OktavianaNo ratings yet
- Endosymbiotic HypothesisDocument1 pageEndosymbiotic HypothesisMarion NavarroNo ratings yet
- Challenges of Fungi ResearchDocument17 pagesChallenges of Fungi ResearchVagdevi GonduNo ratings yet
- Mitosis For CotDocument11 pagesMitosis For CotMel Arthur CapawingNo ratings yet
- Cytoglow ™: Catalog #: Cb5905Document21 pagesCytoglow ™: Catalog #: Cb5905Mohammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Hec Phase 2 Past PapersDocument21 pagesHec Phase 2 Past Papersgentlee80% (5)
- Class 11 Biology Notes Chapter 3 Studyguide360Document11 pagesClass 11 Biology Notes Chapter 3 Studyguide360ANo ratings yet
- Hemapathology Case: Adrian Joe G. CaballesDocument15 pagesHemapathology Case: Adrian Joe G. CaballesAdrian CaballesNo ratings yet