0% found this document useful (0 votes)
310 views12 pagesParallel Lines
Parallel lines cut by a transversal
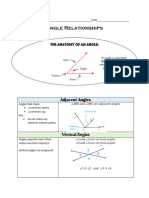
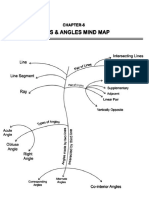
The document defines and illustrates key angle relationships that occur when parallel lines are cut by a transversal line, including corresponding angles, alternate interior angles, alternate exterior angles, same-side interior angles, and same-side exterior angles. It provides an example problem calculating the measures of various angles given one initial angle measurement.
Uploaded by
Sero ArtsCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
310 views12 pagesParallel Lines
Parallel lines cut by a transversal
The document defines and illustrates key angle relationships that occur when parallel lines are cut by a transversal line, including corresponding angles, alternate interior angles, alternate exterior angles, same-side interior angles, and same-side exterior angles. It provides an example problem calculating the measures of various angles given one initial angle measurement.
Uploaded by
Sero ArtsCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd