Professional Documents
Culture Documents
System Characteristics
System Characteristics
Uploaded by
ahmad riaz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views12 pagesThis document discusses different types of systems including:
- Lumped-parameter systems which depend only on time and distributed-parameter systems which depend on both time and space.
- Memoryless systems which depend only on the current input and memory systems which depend on past inputs.
- Causal systems where the output depends only on past and present inputs.
- Linear systems where the output is a linear combination of scaled inputs.
- Time-invariant systems where a time-shifted input results in a time-shifted output.
- Stable systems where bounded inputs produce bounded outputs.
Examples are provided to determine system properties like memory, linearity, and time-invariance.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses different types of systems including:
- Lumped-parameter systems which depend only on time and distributed-parameter systems which depend on both time and space.
- Memoryless systems which depend only on the current input and memory systems which depend on past inputs.
- Causal systems where the output depends only on past and present inputs.
- Linear systems where the output is a linear combination of scaled inputs.
- Time-invariant systems where a time-shifted input results in a time-shifted output.
- Stable systems where bounded inputs produce bounded outputs.
Examples are provided to determine system properties like memory, linearity, and time-invariance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views12 pagesSystem Characteristics
System Characteristics
Uploaded by
ahmad riazThis document discusses different types of systems including:
- Lumped-parameter systems which depend only on time and distributed-parameter systems which depend on both time and space.
- Memoryless systems which depend only on the current input and memory systems which depend on past inputs.
- Causal systems where the output depends only on past and present inputs.
- Linear systems where the output is a linear combination of scaled inputs.
- Time-invariant systems where a time-shifted input results in a time-shifted output.
- Stable systems where bounded inputs produce bounded outputs.
Examples are provided to determine system properties like memory, linearity, and time-invariance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
System Characteristics
SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS
Dr. Zaid Ahmad
COMSATS University Islamabad, Lahore Campus
Lumped-Parameter and Distributed-
Parameter Systems
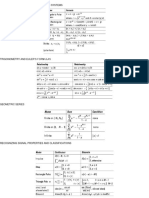
Lumped-parameter systems involve signals that are function of time only:
For example, electric wiring at home or factory
Such systems can be represented by difference or differential equation
Distributed-parameter systems involve signals that are function of both time and
space:
For example, electromagnetic signal, electrical transmission line, antenna
Such systems can be represented by partial difference or differential equation
Memoryless and Memory Systems
Memoryless Systems: Output signal value at time depends on the input signal value
corresponding to only time
No memory elements such as capacitors, inductors or registers
No derivative, integral or delay terms
Memory Systems: Output signal at time depends on input signal values
corresponding to times in addition to .
One or more energy storing elements
CT systems – differential equations, DT systems – difference equation, CT systems
with delays
Causal Systems
Causal Systems: output at time depends on the values of the input signal that occur
only at times .
Memoryless system is always causal.
System Order
The order of single-input single-output system is the order of the difference or
differential equation of the system.
CT system: order of the highest derivative
DT system: the largest delay of the output signal
Reducing order means reducing the number of storage elements
Linear Systems
Consider a CT system when
and .
The system is linear if
where and are constants.
DT linear system?
Superposition holds!
Time-Invariant System
The system (or ) is time-invariant if the output changes only by time shift if the
input shifts by ; i.e.
or
System Stability
A system possess bounded-input bounded-output (BIBO) stability if every bounded
input signal produces a bounded output signal.
Example 1
Determine whether the following systems have memory? If yes, what is the order?
Example 2
Determine whether the system is linear? Is it time-invariant?
Example 3
Determine whether the system is linear? Time invariant?
References
G. E. Carlson, (2007). Signal and Linear System Analysis. 2nd
Edition, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
You might also like
- Signals & Systems For Dummies Cheat Sheet - For DummiesDocument8 pagesSignals & Systems For Dummies Cheat Sheet - For DummiesAbdallah E. AbdallahNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1: Introduction To Discrete-Time Control Systems Digital Control SystemsDocument6 pagesCHAPTER 1: Introduction To Discrete-Time Control Systems Digital Control SystemsIzzat AzmanNo ratings yet
- W EE 418 - Lecture 1 Overview and IntroductionDocument56 pagesW EE 418 - Lecture 1 Overview and IntroductionGGAP LASTNo ratings yet
- Classification of Cont and DT System 04 April 23Document84 pagesClassification of Cont and DT System 04 April 23Md Nazmus Sadat ShadNo ratings yet
- Lecturer 4 Signals & SystemsDocument28 pagesLecturer 4 Signals & SystemsSaffi SheikhNo ratings yet
- Complex Arithmetic For Signals and SystemsDocument4 pagesComplex Arithmetic For Signals and SystemsBách Gia DươngNo ratings yet
- EE-232 Signals and Systems: System Properties & ClassificationDocument16 pagesEE-232 Signals and Systems: System Properties & ClassificationFahdNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems Is An Aspect of Electrical Engineering That Applies Mathematical Concepts To The Creation of Product DesignDocument9 pagesSignals and Systems Is An Aspect of Electrical Engineering That Applies Mathematical Concepts To The Creation of Product Designnida batoolNo ratings yet
- Unit I NotesDocument43 pagesUnit I Notesaravinth69601No ratings yet
- 4th Class, Production Engineering Department of Production Engineering and Metallurgy, University of Technology, BaghdadDocument94 pages4th Class, Production Engineering Department of Production Engineering and Metallurgy, University of Technology, BaghdadMegaroboMegaroboNo ratings yet
- Signal Processing and SensorsDocument51 pagesSignal Processing and SensorsKassimNo ratings yet
- TN 320 FinalDocument179 pagesTN 320 FinalAlango Jr TzNo ratings yet
- DSP Lecture TwoDocument18 pagesDSP Lecture TwoABITURABYAMU ANSLEMNo ratings yet
- Digital Telecommunications Instructor: MR Nasolwa Edson Room: AB14 (Ground Floor)Document157 pagesDigital Telecommunications Instructor: MR Nasolwa Edson Room: AB14 (Ground Floor)Alango Jr TzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document31 pagesChapter 2Endalk SimegnNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation & ControlDocument19 pagesInstrumentation & ControlFarrukh JavedNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems - 1Document9 pagesSignals and Systems - 1Ajay Varma100% (1)
- Handout 1: SignalsDocument12 pagesHandout 1: SignalsBryan YaranonNo ratings yet
- Electronic SystemsDocument4 pagesElectronic SystemsKram YnarNo ratings yet
- Linear Control System: Presented by Imran Basha SyedDocument35 pagesLinear Control System: Presented by Imran Basha SyedSyed Imran BashaNo ratings yet
- Control Systems: Module: Modelling of SystemsDocument19 pagesControl Systems: Module: Modelling of Systemsee210002004No ratings yet
- Introduction 23Document16 pagesIntroduction 23Ggfgsgege GegsgsNo ratings yet
- Continuous Time and Discrete Time SystemsDocument7 pagesContinuous Time and Discrete Time SystemsKartikeya KhannaNo ratings yet
- System Analysis in Control System1Document5 pagesSystem Analysis in Control System1PhanindraNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Submission Date: 10.3.2020: Question 1: Write The Differences Between Vacuum Tube & TransistorDocument2 pagesAssignment 1 Submission Date: 10.3.2020: Question 1: Write The Differences Between Vacuum Tube & TransistorMd Rayhan TanvirNo ratings yet
- Tutorials in SystemsDocument28 pagesTutorials in SystemsAbdullah Al AsikNo ratings yet
- Midterm ReviewDocument24 pagesMidterm ReviewwsovwNo ratings yet
- Introdn To SystemsDocument7 pagesIntrodn To SystemsHarshal SpNo ratings yet
- Classifications of SystemsDocument14 pagesClassifications of Systemsياسين خالدNo ratings yet
- EE2253 - Control SystemsDocument124 pagesEE2253 - Control SystemsrameshsmeNo ratings yet
- Ducment 1 ReaserchDocument41 pagesDucment 1 ReaserchAbubaker MuzayinNo ratings yet
- Lecture3 Mech SUDocument15 pagesLecture3 Mech SUNazeeh Abdulrhman AlbokaryNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document52 pagesLecture 2faruktokuslu16No ratings yet
- Control Engineering: Types of Control SystemsDocument26 pagesControl Engineering: Types of Control SystemsGilbert SigalaNo ratings yet
- ELEC-E8101 Digital and Optimal Control (5 CR), Autumn 2015: LecturesDocument70 pagesELEC-E8101 Digital and Optimal Control (5 CR), Autumn 2015: LecturesbalkyderNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1: Introduction To Discrete-Time Control Systems Digital Control SystemsDocument6 pagesCHAPTER 1: Introduction To Discrete-Time Control Systems Digital Control SystemsIzzat AzmanNo ratings yet
- Control Engineering PDFDocument164 pagesControl Engineering PDFsanthoshramrNo ratings yet
- Class Notes - Computer Relay ArchitectureDocument10 pagesClass Notes - Computer Relay ArchitecturebiswajitsahooNo ratings yet
- Synchronization System With Zero-Crossing Peak Detection Algorithm For Power System ApplicationsDocument8 pagesSynchronization System With Zero-Crossing Peak Detection Algorithm For Power System ApplicationsChairul AkbarNo ratings yet
- Signals and System Lecture 1Document16 pagesSignals and System Lecture 1Talha hayatNo ratings yet
- Automated Manufacturing SystemsDocument25 pagesAutomated Manufacturing SystemsSoto KunNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document47 pagesLecture 3KOFI BROWNNo ratings yet
- CS Two MarksDocument7 pagesCS Two MarkssivaeinfoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 ControlDocument44 pagesChapter 4 ControlFootball HDNo ratings yet
- Lec2 ME772aDocument12 pagesLec2 ME772aVivek SinghNo ratings yet
- Mnmjec - Ec6303 Signals & SystemsDocument25 pagesMnmjec - Ec6303 Signals & SystemsSonuNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems - Chapter 2Document27 pagesSignals and Systems - Chapter 2altwirqiNo ratings yet
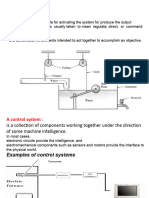
- Block Diagram Representation of A Simple Electronic System: Main DefinitionsDocument9 pagesBlock Diagram Representation of A Simple Electronic System: Main DefinitionsCansu ElizadeNo ratings yet
- DKS - EMC - 2.1,2.2,2.3 SIGNAL CONDITIONING - Part-1 - Dipak Kumar SahaDocument12 pagesDKS - EMC - 2.1,2.2,2.3 SIGNAL CONDITIONING - Part-1 - Dipak Kumar SahaPrabir PaulNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Signals and Systems: By: Mrs. MridulaDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Signals and Systems: By: Mrs. MridulaMridula SinghNo ratings yet
- Classification of SystemsDocument20 pagesClassification of SystemsGuhanNo ratings yet
- William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture: System BusesDocument47 pagesWilliam Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture: System BusesreinaldoopusNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Digital Control SystemDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Digital Control SystemApril SurNo ratings yet
- 18ECE205J - FPGA-based Embedded System Design - Unit - 1Document151 pages18ECE205J - FPGA-based Embedded System Design - Unit - 1Vikram Adithya AnandNo ratings yet
- M Hanzala, 19-Te-89Document3 pagesM Hanzala, 19-Te-89hanzala daarNo ratings yet
- ECE 331 Complete NotesDocument129 pagesECE 331 Complete NotespolygatoneoderaNo ratings yet
- DSP and FiltersDocument66 pagesDSP and FiltersShalin Doshi100% (1)
- ECM650 Communication Software and Design Lecture 2: Review On Communication SystemsDocument9 pagesECM650 Communication Software and Design Lecture 2: Review On Communication SystemsMuhammad Husaini ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Frequency Response For Control System Analysis - GATE Study Material in PDFDocument7 pagesFrequency Response For Control System Analysis - GATE Study Material in PDFNarendra AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports: Volume 5: Measurement Circuits, Safeguards and Energy StorageFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports: Volume 5: Measurement Circuits, Safeguards and Energy StorageNo ratings yet