Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Smooth and Cardiac Muscles F
Uploaded by
Karina0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views13 pagesCardiac muscle tissue forms the heart and contracts involuntarily to pump blood through the body. It is located in the heart wall and has a striated structure. Smooth muscle lines internal organs and contracts more slowly, functioning in digestion, birth, and blood flow. Both muscle types contract involuntarily but cardiac muscle has a faster rhythm. Disorders can result from genetic mutations affecting contraction.
Original Description:
Anatomy and Physiology 1: Muscular System
Original Title
Smooth and cardiac muscles F
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCardiac muscle tissue forms the heart and contracts involuntarily to pump blood through the body. It is located in the heart wall and has a striated structure. Smooth muscle lines internal organs and contracts more slowly, functioning in digestion, birth, and blood flow. Both muscle types contract involuntarily but cardiac muscle has a faster rhythm. Disorders can result from genetic mutations affecting contraction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views13 pagesSmooth and Cardiac Muscles F
Uploaded by
KarinaCardiac muscle tissue forms the heart and contracts involuntarily to pump blood through the body. It is located in the heart wall and has a striated structure. Smooth muscle lines internal organs and contracts more slowly, functioning in digestion, birth, and blood flow. Both muscle types contract involuntarily but cardiac muscle has a faster rhythm. Disorders can result from genetic mutations affecting contraction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 13
1 Anatomy & Physiology
CARDIAC MUSCLES
HE131 Lecture 4 Muscles ttamb 05/25/2023
2 Introduction
Cardiac muscle tissue, or myocardium, is a specialized type of muscle tissue that
forms the heart.
This muscle tissue, which contracts and releases involuntarily, is responsible for
keeping the heart pumping blood around the body. (https://
simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cardiac_muscle)
Muscle tissue in which the contractile fibrils are not highly ordered, occurring in
the gut and other internal organs and not under voluntary control. (https://
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Smooth_muscle)
HE131 Lecture 4 Muscles ttamb 05/25/2023
3 Cardiac Muscle
Definition of cardiac muscle:
It is an involuntary, striated muscle that constitutes the main tissue of the heart
It is also called the heart muscle or myocardium
Contraction of cardiac muscle is involuntary, vigorous and rhythmic
It is fatigue resistant. (meaning it cannot get tired of working)
HE131 Lecture 4 Muscles ttamb 05/25/2023
4Cardiac Muscle
Location:
The cardiac muscle is the
only muscle of the heart.
Therefore it is located in the
muscular wall of the heart
called the myocardium.
The myocardium is the
middle layer of the heart that
makes up most of its mass.
HE131 Lecture 4 Muscles ttamb 05/25/2023
5Cardiac Muscle
Functions:
The cardiac muscle is only
found in the heart and
therefor has only one main
function. The main function
is to pump blood through the
blood vessels of the body. It
does this through specialized
cells called pacemaker cells.
HE131 Lecture 4 Muscles ttamb 05/25/2023
Cardiac6 Muscle
Symptoms Causes
Disorder (Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy):
Thickening of muscle (may thicken in normal individuals
as a result of high blood pressure or prolong athletic Shortness of breath Dominant
mutation
training-in this case, thickening occurs without an obvious Important
cause) proteins for
Chest pain heart contraction
Normal alignment of muscle cells is absent and this
abnormality; called myocardial disarray Palpitation
Light-headed-ness
and blackouts
HE131 Lecture 4 Muscles ttamb 05/25/2023
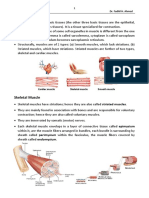
7 Smooth Muscle
Definition of smooth muscle:
Smooth muscle generally forms the supporting tissue of blood vessels and
hollow internal organs, such as stomach, intestine, bladder and uterus
Involuntary muscle
Not striated
Line walls of most internal organs
HE131 Lecture 4 Muscles ttamb 05/25/2023
8
Smooth Muscle
Location:
It is located in the walls of
hollow internal organs
Eg: Stomach, Intestines, Bladder,
Uterus, Blood Vessels
HE131 Lecture 4 Muscles ttamb 05/25/2023
9
Smooth Muscle
Function:
Smooth muscle in the uterus
helps a woman to push out
her baby
Smooth muscle determines
the flow of blood in the
arteries
And also smooth muscle
move the food through the
digestive tract
HE131 Lecture 4 Muscles ttamb 05/25/2023
10 Smooth Muscle
Symptoms Cause
Disorder(Multisystemic smooth
muscle dysfunction syndrome)
It is a disease in which the activity
Weak bladder The main cause of
of smooth muscle throughout the this syndrome is a
body is impaired. This leads to certain mutation in
the ACTA2 gene.
widespread problems including
Lung disease
blood vessel abnormalities, a
decreased response of the pupils
to light, a weak bladder, a weaken
contraction of the muscles used for Gastrintestinal
problems
the digestion of
food(hypoperistalsis).
Congenital
mydriasis (fixed
dilated pupils)
HE131 Lecture 4 Muscles ttamb 05/25/2023
11 Cardiac and Smooth Muscle
Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle
Involuntary Involuntary
Found only in the heart Line walls of most internal organs
Striated: many myofibrils in orderly Not Striated: Fewer myofibrils of
arrangement varying lengths.
Self stimulating: impulse spread Self Stimulating: Not individually
from cells to cells innervated, impulse spread from
Intermediate energy requirement cells to cells
Intermediate speed of contraction Lower energy requirement
yet contraction spreads quickly Slower contraction and rhythmic in
through tissue due to intercalated some organs producing peristaltic
discs
HE131 Lecture 4 Muscles ttamb waves along organs 05/25/2023
12 Cardiac and Smooth Muscle
Summary:
Cardiac muscle tissue, or myocardium, is a specialized type of muscle tissue that forms the
heart. This muscle tissue, which contracts and releases involuntarily, is responsible for keeping
the heart pumping blood around the body.
It is located in the muscular wall of the heart called the myocardium.
The main function of the cardiac muscle is to pump blood through the blood vessels and to the
body.
Smooth muscle generally forms the supporting tissue of blood vessels and hollow internal
organs, such as stomach, intestine, bladder and uterus
It is located in the walls of hollow internal organs
The function of smooth muscle varies as it is found in the different organs of the body.
The disorders of both the cardiac and smooth muscles are mainly cause by mutations.
HE131 Lecture 4 Muscles ttamb 05/25/2023
13 Cardiac and Smooth Muscle
Reference:
https://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cardiac_muscle
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Smooth_muscle
http://www.apsu.edu/schillerj/Biology%202010/Unit%20Reviews/Unit%203%2
0Review/CH%2009%20Smooth%20and%20Cardiac%20Muscle.htm
http://www.udel.edu/Biology/Wags/histopage/colorpage/cmu/cmu.htm
www.cvphysiology.com/Blood%20Pressure/BP026.htm
www.udel.edu
HE131 Lecture 4 Muscles ttamb 05/25/2023
You might also like
- Lesson 3 Muscle TissueDocument14 pagesLesson 3 Muscle TissueFaith SimbulanNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document6 pagesUnit 4CLAUDIU---ALIN BOARTANo ratings yet
- Activity 9 Group 3 Muscle Physiology - OdtDocument9 pagesActivity 9 Group 3 Muscle Physiology - OdtAMEER MUHMIEN JALMAANI. LERIOSNo ratings yet
- Muscular Tissues: Skeletal MusclesDocument3 pagesMuscular Tissues: Skeletal Musclesalimsaadun alimsaadunNo ratings yet
- Musc Nerv PDFDocument9 pagesMusc Nerv PDFJoshua RaninNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 (Muscular System)Document7 pagesUNIT 3 (Muscular System)Workinesh Kaynabo KambaloNo ratings yet
- Mthapp100 Chapter 7Document8 pagesMthapp100 Chapter 7lizdestacamento0625No ratings yet
- Muscular System Trans Week 1Document9 pagesMuscular System Trans Week 1olaya.xyzanigaia.bsnNo ratings yet
- Musclular SystemDocument69 pagesMusclular SystemYahya JuneydiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Midterms RevDocument26 pagesAnatomy Midterms RevErnest VincentNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System NotesDocument32 pagesThe Muscular System NotesVivien Talavera0% (1)
- Muscular-System-Handouts - BiologyDocument7 pagesMuscular-System-Handouts - BiologyApril Joy T. GrijaldoNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument20 pagesMuscular SystemAltaf Hussain KhanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Muscular SystemDocument8 pagesLesson 5 Muscular SystemRodrigo SeriozaNo ratings yet
- Ns Elec 4 - Muscular SystemDocument5 pagesNs Elec 4 - Muscular SystemONGLENGCO WILSON JAKE V.No ratings yet
- MUSCLE B.Sc-IIDocument13 pagesMUSCLE B.Sc-IIAjinkya BansodeNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity 15 - Muscular SystemDocument3 pagesLearning Activity 15 - Muscular SystemCraigyyNo ratings yet
- Histology 6Document20 pagesHistology 6mkomyu088No ratings yet
- 10 Q2 NervousMuscular-Skeletal-IntegumentaryDocument62 pages10 Q2 NervousMuscular-Skeletal-IntegumentaryHasmine Lara RiveroNo ratings yet
- Session #17 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab)Document4 pagesSession #17 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab)Nicole Ken AgdanaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledVianney LaplanaNo ratings yet
- Muscular System: Skeletal Muscle Tissue Voluntary, Striated, MultinucleatedDocument4 pagesMuscular System: Skeletal Muscle Tissue Voluntary, Striated, MultinucleatedElyka Alivan Valdez PolonioNo ratings yet
- Clinical Case: Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument73 pagesClinical Case: Anatomy and PhysiologyGeorge KoNo ratings yet
- Exercise No. 6 Muscle TissueDocument10 pagesExercise No. 6 Muscle TissueRyan Aaron Cruz ParNo ratings yet
- Basic Human Anatomy 1Document55 pagesBasic Human Anatomy 1ZzzNo ratings yet
- Human Muscular System: Biology For Engineers ISE-1Document16 pagesHuman Muscular System: Biology For Engineers ISE-1Sanket PathadeNo ratings yet
- Ns Elec 4 - Muscular SystemDocument4 pagesNs Elec 4 - Muscular SystemONGLENGCO WILSON JAKE V.No ratings yet
- Submitted By: John Benedict Vocales Bsed 3-2Document3 pagesSubmitted By: John Benedict Vocales Bsed 3-2John Benedict VocalesNo ratings yet
- Muscular System 101Document21 pagesMuscular System 101Rida IshaqNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument5 pagesMuscular SystemTyrone LeeNo ratings yet
- 3c. Muscle 22893Document15 pages3c. Muscle 22893Musharaf RehmanNo ratings yet
- Report in Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesReport in Anatomy and Physiologydowngrade840No ratings yet
- 1.2 TheMuscularSystemDocument60 pages1.2 TheMuscularSystemchaaarrNo ratings yet
- Laboratory: Session 10 Lesson Review: X 1. Skeletal Muscles Do Have Shorter Size Than Cardiac MusclesDocument2 pagesLaboratory: Session 10 Lesson Review: X 1. Skeletal Muscles Do Have Shorter Size Than Cardiac MuscleszimoneNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 7: Muscular System EXPLORE:: Cardiac - The Autonomic Nervous System Also Regulates The Cardiac Muscle ThatDocument4 pagesAssignment # 7: Muscular System EXPLORE:: Cardiac - The Autonomic Nervous System Also Regulates The Cardiac Muscle ThatKassandra Shayne CaballeroNo ratings yet
- The Tissue Level of Organization General ObjectivesDocument5 pagesThe Tissue Level of Organization General ObjectivesRjosheNo ratings yet
- Cytoskeleton and MuscleDocument43 pagesCytoskeleton and MuscleAhsan AliNo ratings yet
- Muskuloskeletal DisordersDocument15 pagesMuskuloskeletal DisordersLienyPerasNo ratings yet
- Compact Bone and Spongy Bone: OsteocytesDocument27 pagesCompact Bone and Spongy Bone: OsteocytesMark SullivanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Muscular SystemDocument20 pagesAnatomy Muscular SystemMd. Shahriar Arif 2122064630No ratings yet
- Module 5 MUSCULAR SYSTEMDocument20 pagesModule 5 MUSCULAR SYSTEMMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Smooth and Cardiac MusclesDocument16 pagesSmooth and Cardiac MusclesNzau MuangeNo ratings yet
- Unit - 6 Muscular SystemDocument17 pagesUnit - 6 Muscular SystemChandan ShahNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Muscular SystemDocument7 pagesLesson 2 - Muscular SystemCherubim GimaranganNo ratings yet
- Types of Muscle TissuesDocument2 pagesTypes of Muscle TissueswatermelonNo ratings yet
- Voluntary Muscle: Muscle We Can Control It: The Muscular SystemDocument4 pagesVoluntary Muscle: Muscle We Can Control It: The Muscular SystemAbrar HussamNo ratings yet
- Muscle PhysiologyDocument64 pagesMuscle Physiologylynn.dargham2No ratings yet
- Anaphy Muscular SystemDocument54 pagesAnaphy Muscular SystemZosia SageNo ratings yet
- Functions of MusclesDocument5 pagesFunctions of MusclesJoseph RefuerzoNo ratings yet
- CHP 6 Muscular SystemDocument9 pagesCHP 6 Muscular SystemPatricia Sofia De LeonNo ratings yet
- Science Classwork Seventh Grade-Fourth Quarter: Instructions: Answer The Following QuestionsDocument1 pageScience Classwork Seventh Grade-Fourth Quarter: Instructions: Answer The Following QuestionsValery CaceresNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document8 pagesPresentation 2Season RaiNo ratings yet
- 2-Skeletal Muscles Team441Document17 pages2-Skeletal Muscles Team441Bujeng BardaNo ratings yet
- Mascular TissueDocument4 pagesMascular TissueFadhil Hussam AhmedNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument8 pagesMuscular SystemChristine Joanne CelendroNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Notes Part B - Smooth and Cardiac Muscles 2Document95 pagesUnit 8 Notes Part B - Smooth and Cardiac Muscles 2shrilpatel2001No ratings yet
- MuscoDocument1 pageMuscoMarean NicholeNo ratings yet
- Muscular System NotesDocument6 pagesMuscular System NotesZussette Corbita VingcoNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System-251606Document8 pagesThe Muscular System-251606sselt gayNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Transgenic AnimalsDocument25 pagesLecture On Transgenic AnimalsMuhammad Ikram Anwar100% (3)
- Infant HIV TestsDocument5 pagesInfant HIV TestsProf Rakesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemsDocument8 pagesMale Reproductive SystemsHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Calcium Tetany in Broiler Breeder Hens: UPDATEDocument5 pagesCalcium Tetany in Broiler Breeder Hens: UPDATEUday PatelNo ratings yet
- HematopoiesisDocument8 pagesHematopoiesisCassandra Grace Labial PaynterNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Seeley'sDocument3 pagesEndocrine Seeley'scourseNo ratings yet
- EponymsDocument30 pagesEponymsNovaatackNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Notes PDFDocument6 pagesRespiratory System Notes PDFEna ArtyukhNo ratings yet
- Mutaciones BGM PDFDocument6 pagesMutaciones BGM PDFwaldo tapiaNo ratings yet
- Cognitive DisordersDocument9 pagesCognitive Disordersgeorgeloto12No ratings yet
- Reading Part A Hair LossDocument6 pagesReading Part A Hair Lossfernanda1rondelliNo ratings yet
- Immuno-Engineering The Next Frontier in Therapeutics DeliveryDocument2 pagesImmuno-Engineering The Next Frontier in Therapeutics DeliveryBrunaNo ratings yet
- Download textbook Handbook Of New Genetic Diagnostic Technologies In Reproductive Medicine Improving Patient Success Rates And Infant Health 1St Edition Carlos Simon ebook all chapter pdfDocument54 pagesDownload textbook Handbook Of New Genetic Diagnostic Technologies In Reproductive Medicine Improving Patient Success Rates And Infant Health 1St Edition Carlos Simon ebook all chapter pdftammy.bourassa711100% (1)
- Cardiomyopathy 1223958636063843 9Document87 pagesCardiomyopathy 1223958636063843 9Dainy ThomasNo ratings yet
- 49CDocument154 pages49Crudolfpetersson100% (2)
- Zirconia ImplantsDocument15 pagesZirconia ImplantsmusatiiNo ratings yet
- Biological Transformations Controlled by The MindDocument99 pagesBiological Transformations Controlled by The MindRomeo100% (1)
- Bostan-2020-Targets and Assay Types For COVIDDocument15 pagesBostan-2020-Targets and Assay Types For COVIDNick FloresNo ratings yet
- Current Topics in Pathology: C.L. Berry E. GrundmannDocument252 pagesCurrent Topics in Pathology: C.L. Berry E. GrundmannGustavo LatorreNo ratings yet
- 5 - DOWNLOAD Lactobacillus Acidophilus Rosell 52Document6 pages5 - DOWNLOAD Lactobacillus Acidophilus Rosell 52everstrongNo ratings yet
- Manejo de Terceros Molares - Rafetto 2015Document9 pagesManejo de Terceros Molares - Rafetto 2015Hugo HerreraNo ratings yet
- Planthormones 141025004114 Conversion Gate02 PDFDocument75 pagesPlanthormones 141025004114 Conversion Gate02 PDFSaiTimmarao100% (1)
- Understanding Autoimmune Diseases-A Review: IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences January 2013Document9 pagesUnderstanding Autoimmune Diseases-A Review: IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences January 2013Vidya UtamiNo ratings yet
- Chronic Pancreatitis: Ermias D (MD)Document30 pagesChronic Pancreatitis: Ermias D (MD)Santomi PratamaNo ratings yet
- Pathphys 2Document3 pagesPathphys 2zaydeeeeNo ratings yet
- Dr. Salma Samir: Lecturer of Dermatology & Aesthetic Medicine Alex. Faculty of MedicineDocument38 pagesDr. Salma Samir: Lecturer of Dermatology & Aesthetic Medicine Alex. Faculty of MedicineSamir Omar0% (1)
- CRISPR HandbookDocument18 pagesCRISPR Handbookgoucloud100% (1)
- Chang 2014 Social Isolation Induced Increase in NMDA Receptors in The Hippocampus Exacerbates Emotional Dysregulation in MiceDocument12 pagesChang 2014 Social Isolation Induced Increase in NMDA Receptors in The Hippocampus Exacerbates Emotional Dysregulation in MiceMarilyn GarciaNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 13 Imprinting F08Document5 pagesLECTURE 13 Imprinting F08Toman Chi To Lam100% (1)
- Z+blood TransfusionDocument16 pagesZ+blood TransfusionilhamaminsyaputraNo ratings yet