Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Laboratory: Session 10 Lesson Review: X 1. Skeletal Muscles Do Have Shorter Size Than Cardiac Muscles
Laboratory: Session 10 Lesson Review: X 1. Skeletal Muscles Do Have Shorter Size Than Cardiac Muscles
Uploaded by
zimoneOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Laboratory: Session 10 Lesson Review: X 1. Skeletal Muscles Do Have Shorter Size Than Cardiac Muscles
Laboratory: Session 10 Lesson Review: X 1. Skeletal Muscles Do Have Shorter Size Than Cardiac Muscles
Uploaded by
zimoneCopyright:
Available Formats
Laboratory: Session 10
Lesson Review
X 1. Skeletal muscles do have shorter size than cardiac muscles.
2. Nervous system can make skeletal muscles move in an involuntary.
3. When a muscle tissue contracts the muscle fibers shortens.
X 4. There are 4 types of muscle tissues.
5. When a muscle tissue contracts the muscle fibers shortens.
Check for understanding
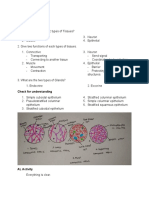
Muscle type Location Muscle Activity Striated
Skeletal 1. Attached to bone or 2. Movement of the 3. Striated
other connective tissue body, voluntary control
Cardiac 4. In the heart 5. Contracts heart to 6. Striated
pump blood,
involuntary control
Smooth 7. In hollow organs, 8. Regulates the size of 9. Not striated
such as the stomach organs, involuntary
and intestine. control
Glia - important supportive functions.
Dendrite – receives nerve impluses from other cells and carry them to the cell body.
Axon – transmits nerve impluse away from the cell body and towards other cell at axon
terminal.
Cell body of nueron – coatain the nuclues and the site of general function
Nuclues – responsible for conductong action potential
Nuclei of glia - protect and nourish neuron.
AL Activity
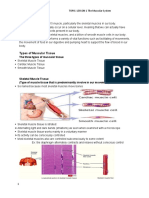
Muscular tissue consists of elongated cells called muscle fibers or myocytes that can use ATP to
generate force. As a result, muscular tissue produces body movements, maintains posture, and
generates heat. It also provides protection. Based on location and certain structural and functional
features, muscular tissue is classified into three types: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. Skeletal muscle
tissue is attached to bones for body movement and is striated and voluntary. The action of cardiac
muscle tissue, which forms most of the heart wall that contracts heart to pump blood and is striated, is
involuntary. Smooth muscle tissue is found in the walls of hollow internal structures (blood vessels and
viscera) and is nonstriated and involuntary.
You might also like
- Specialized Tissue That Enable The Body and Its Parts To MoveDocument23 pagesSpecialized Tissue That Enable The Body and Its Parts To MoveJJ Almagro100% (1)
- The Muscular System NotesDocument32 pagesThe Muscular System NotesVivien Talavera0% (1)
- Activity 9 Group 3 Muscle Physiology - OdtDocument9 pagesActivity 9 Group 3 Muscle Physiology - OdtAMEER MUHMIEN JALMAANI. LERIOSNo ratings yet
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Muscular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Muscular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Unit - 6 Muscular SystemDocument17 pagesUnit - 6 Muscular SystemChandan ShahNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Muscular SystemDocument54 pagesAnaphy Muscular SystemZosia SageNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Muscular System: Semi Detailed, With Lesson ContentsDocument19 pagesLesson Plan in Muscular System: Semi Detailed, With Lesson ContentsToffee Perez85% (26)
- Unit 5 Body System: Name: Akanksh Grade: 10KC Lesson: Skeletal System & Muscular SystemDocument4 pagesUnit 5 Body System: Name: Akanksh Grade: 10KC Lesson: Skeletal System & Muscular SystemAkanksh SubramanyaNo ratings yet
- Health Education ClassDocument8 pagesHealth Education ClassAlicia ValverdeNo ratings yet
- Basic Human Anatomy 1Document55 pagesBasic Human Anatomy 1ZzzNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal SystemDocument13 pagesMusculoskeletal Systemmelbert nacuNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document8 pagesPresentation 2Season RaiNo ratings yet
- Exercise No. 6 Muscle TissueDocument10 pagesExercise No. 6 Muscle TissueRyan Aaron Cruz ParNo ratings yet
- What Is The Muscular SystemDocument2 pagesWhat Is The Muscular SystemJoshua Capa FrondaNo ratings yet
- Module 5 MUSCULAR SYSTEMDocument20 pagesModule 5 MUSCULAR SYSTEMMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Muscle TissueDocument14 pagesLesson 3 Muscle TissueFaith SimbulanNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: John Benedict Vocales Bsed 3-2Document3 pagesSubmitted By: John Benedict Vocales Bsed 3-2John Benedict VocalesNo ratings yet
- Ns Elec 4 - Muscular SystemDocument5 pagesNs Elec 4 - Muscular SystemONGLENGCO WILSON JAKE V.No ratings yet
- Vocabulary - Muscular SystemDocument3 pagesVocabulary - Muscular SystemArxk DevNo ratings yet
- YU - General - Muscles 1Document57 pagesYU - General - Muscles 1Mohammad BarakatNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System: Parts & FunctionsDocument4 pagesThe Muscular System: Parts & FunctionsNeil AdelanNo ratings yet
- MUSCLE B.Sc-IIDocument13 pagesMUSCLE B.Sc-IIAjinkya BansodeNo ratings yet
- Bones Muscles and SkinDocument17 pagesBones Muscles and SkinThene Truthe NoweNo ratings yet
- Functions of MusclesDocument5 pagesFunctions of MusclesJoseph RefuerzoNo ratings yet
- AnaphyDocument5 pagesAnaphyRhona Angela CruzNo ratings yet
- The Muscular SystemDocument8 pagesThe Muscular SystemMika SaldañaNo ratings yet
- Written Report Group 1 HSHSHSHSJSJDNXNXBDocument23 pagesWritten Report Group 1 HSHSHSHSJSJDNXNXBNoronisa PendalidayNo ratings yet
- Pe 1 Module 3Document25 pagesPe 1 Module 3Dimple BolotaoloNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues Notes 2 MUSCULAR TISSUEDocument3 pagesAnimal Tissues Notes 2 MUSCULAR TISSUESrijita RoyNo ratings yet
- Ns Elec 4 - Muscular SystemDocument4 pagesNs Elec 4 - Muscular SystemONGLENGCO WILSON JAKE V.No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Muscular SystemDocument7 pagesLesson 2 - Muscular SystemCherubim GimaranganNo ratings yet
- Muscle TissueDocument20 pagesMuscle TissueBrian MirasolNo ratings yet
- K00429 - 20180831110050 - Muscular SystemDocument14 pagesK00429 - 20180831110050 - Muscular Systemroesil juniNo ratings yet
- Muscular System Trans Week 1Document9 pagesMuscular System Trans Week 1olaya.xyzanigaia.bsnNo ratings yet
- Mthapp100 Chapter 7Document8 pagesMthapp100 Chapter 7lizdestacamento0625No ratings yet
- Body Map: Smooth or Visceral MuscleDocument2 pagesBody Map: Smooth or Visceral MuscleFani Try Utami BoedaxRed'waterzzNo ratings yet
- The Musculoskeletal SystemDocument27 pagesThe Musculoskeletal SystemEduardoAlejoZamoraJr.No ratings yet
- Types of MusclesDocument1 pageTypes of Musclesapi-323449449No ratings yet
- Types of MusclesDocument1 pageTypes of Musclesapi-323141584No ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument9 pagesMuscular SystemFrely Jane PanilagaoNo ratings yet
- BONES and MUSCLES Handout 2nd QuarterDocument4 pagesBONES and MUSCLES Handout 2nd Quarterlei SaguitariusNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument5 pagesMuscular SystemTyrone LeeNo ratings yet
- Voluntary Muscle: Muscle We Can Control It: The Muscular SystemDocument4 pagesVoluntary Muscle: Muscle We Can Control It: The Muscular SystemAbrar HussamNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument20 pagesMuscular SystemAltaf Hussain KhanNo ratings yet
- Body SystemDocument22 pagesBody SystemNAWRAS ALAZZAMNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument2 pagesMuscular SystemRonel AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Muscles EngDocument3 pagesMuscles Engkaneki.ghoul1710No ratings yet
- Submitted By: John Benedict Vocales Bsed 3-2Document2 pagesSubmitted By: John Benedict Vocales Bsed 3-2John Benedict VocalesNo ratings yet
- NerveDocument5 pagesNervesolanasnowieNo ratings yet
- Muscle TissuesDocument2 pagesMuscle TissuesCathleen MarquezNo ratings yet
- ST - John'S School, Greater Noida West Class IX ScienceDocument4 pagesST - John'S School, Greater Noida West Class IX ScienceIndia Tech with AstitvaNo ratings yet
- INS (1)Document28 pagesINS (1)Junaisah P. PangaponNo ratings yet
- Muskuloskeletal DisordersDocument15 pagesMuskuloskeletal DisordersLienyPerasNo ratings yet
- Mited Second Stage: Msc. Samar M.ShakirDocument11 pagesMited Second Stage: Msc. Samar M.ShakiraliNo ratings yet
- Anatomy ReviewerDocument5 pagesAnatomy Reviewercath draftNo ratings yet
- MYOLOGYDocument20 pagesMYOLOGYNatty ChikumbaNo ratings yet
- Studyguide360: The Skeletal System Is The Bony Framework of Our BodyDocument3 pagesStudyguide360: The Skeletal System Is The Bony Framework of Our BodyAman DalalNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 PPT - Science - Q2 - Lesson 14Document26 pagesGrade 4 PPT - Science - Q2 - Lesson 14John Benedict CruzNo ratings yet
- Презентация На Английском Языке «Human Tissues and Muscles» (Мышцы и Ткани Человека) Для Студентов Медицинских Специальностей.Document28 pagesПрезентация На Английском Языке «Human Tissues and Muscles» (Мышцы и Ткани Человека) Для Студентов Медицинских Специальностей.Гулбахор ИсаковаNo ratings yet
- Laboratory: Session 14 Lesson PreviewDocument1 pageLaboratory: Session 14 Lesson PreviewzimoneNo ratings yet
- Laboratory: Session 12 Lesson ReviewDocument2 pagesLaboratory: Session 12 Lesson ReviewzimoneNo ratings yet
- Laboratory: Session 13 Lesson ReviewDocument2 pagesLaboratory: Session 13 Lesson ReviewzimoneNo ratings yet
- Laboratory: Session 11 Lesson ReviewDocument2 pagesLaboratory: Session 11 Lesson ReviewzimoneNo ratings yet
- Telophase - 4 Metaphase - 2 Anaphase - 3 Prophase - 1: Laboratory: Session 8 Lesson PreviewDocument1 pageTelophase - 4 Metaphase - 2 Anaphase - 3 Prophase - 1: Laboratory: Session 8 Lesson PreviewzimoneNo ratings yet
- Laboratory: Session 9 Lesson PreviewDocument1 pageLaboratory: Session 9 Lesson PreviewzimoneNo ratings yet
- O 1. Exchanges of O2 and CO2 in The Lungs D o 3. The Process of Dialysis ODocument2 pagesO 1. Exchanges of O2 and CO2 in The Lungs D o 3. The Process of Dialysis OzimoneNo ratings yet
- Sas 5Document1 pageSas 5zimoneNo ratings yet
- Laboratory: Session 6 Lesson PreviewDocument2 pagesLaboratory: Session 6 Lesson PreviewzimoneNo ratings yet
- Sas 1Document1 pageSas 1zimoneNo ratings yet
- Sas 4Document1 pageSas 4zimoneNo ratings yet
- Sas 3Document1 pageSas 3zimoneNo ratings yet
- Sas 2Document1 pageSas 2zimoneNo ratings yet