Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Big Bang Theory
Uploaded by
Celerina L.Aviso0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views15 pages Here is how I would explain the Big Bang Theory by relating it to mass, volume, and density:
1. At the beginning of the Big Bang, all the mass of the observable universe was concentrated into an extremely dense singularity that had incredibly small volume. This gave the early universe an extremely high density.
2. As the universe rapidly expanded after the Big Bang, the same mass was spread out over a much larger and increasing volume. This caused the average density of the universe to decrease over time as the volume expanded faster than new mass was created.
3. As the universe continues expanding today, the density continues decreasing although very slowly. Galaxies and matter clump together via gravity, leaving large volumes between galaxies and
Original Description:
H
Original Title
Big
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document Here is how I would explain the Big Bang Theory by relating it to mass, volume, and density:
1. At the beginning of the Big Bang, all the mass of the observable universe was concentrated into an extremely dense singularity that had incredibly small volume. This gave the early universe an extremely high density.
2. As the universe rapidly expanded after the Big Bang, the same mass was spread out over a much larger and increasing volume. This caused the average density of the universe to decrease over time as the volume expanded faster than new mass was created.
3. As the universe continues expanding today, the density continues decreasing although very slowly. Galaxies and matter clump together via gravity, leaving large volumes between galaxies and
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views15 pagesBig Bang Theory
Uploaded by
Celerina L.Aviso Here is how I would explain the Big Bang Theory by relating it to mass, volume, and density:
1. At the beginning of the Big Bang, all the mass of the observable universe was concentrated into an extremely dense singularity that had incredibly small volume. This gave the early universe an extremely high density.
2. As the universe rapidly expanded after the Big Bang, the same mass was spread out over a much larger and increasing volume. This caused the average density of the universe to decrease over time as the volume expanded faster than new mass was created.
3. As the universe continues expanding today, the density continues decreasing although very slowly. Galaxies and matter clump together via gravity, leaving large volumes between galaxies and
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 15
Big Bang Theory
Big Bang Theory
• The big bang theory is cosmological model that
explains how the universe began.
• It suggests that the universe started its expansion about
13.8 billion years ago.
• The concept of big bang as not a literal explosion of
something leading to the creation of the universe.
BIG BANG THEORY AND THE BREAD-RAISIN
MODEL
• The bread represents
the universe; while
raisins are galaxies.
• The galaxies,
represented by dots,
are not expanding.
The raisin-bread model of expanding universe
• Distances in relation to other galaxies just increases
because of the expanding universe.
In the big bang theory, matter dilutes as the universe expands.
“SINGULARITY”
• The universe started as a “
singularity” - an area predicted
to be in the core of a black hole
with very high temperature and
density.
• The intense heat resulted to
formation of matter and
antimatter particles that were
destroyed every time they
An expanding universe and the
collided with each other. concept of singularity.
“NUCLEOSYNTHESIS”
• Nucleosynthesisis the
formation of elements, such
as H and He. Presence of
these elements led to the
formation of stars and
galaxies. The presence of
stars led to the formation of Nucelosynthesis of Helium (He)
other cosmic bodies such as
planets, comets, and
asteroids.
EVIDENCES THAT SUPPORT THE BIG BANG THEORY
• The expansion of the universe is supported by the
observation that galaxies are receding from us.
• The high amount of light elements like H, He and Li.
These elements were formed through the fusion of
protons and neutrons immediately after the Big Bang.
• The detection of the cosmic microwave
background (CMB) radiation which is the residue or
heat leftover from the Big Bang.
PROPONENTS OF THE BIG BANG THEORY
• Georges Henri Joseph Edouard
Lemaître was the first proponent
of the theory. He suggested the
idea of the expanding universe
• Edwin Powell Hubble who
established the Hubble’s law
which provided an evidence that
Georges H.J. the universe was not static but
Edwin Powell
Lemaitre expanding.
Hubble
PROPONENTS OF THE BIG BANG THEORY
• Arno Penzias and Robert
Wilson discovered that
microwaves with wavelengths
of about 7 centimeters were
present in space.
• These waves were referred to
Arno Penzias as the cosmic microwave Robert Wilson
background (CMB) radiation.
The Hubble’s Law:
Based on the graph, what
is the relationship
between the recession
velocity (based on
emitted spectral light of
nebulae) and the distance
of a galaxy from Earth?
Hubble’s Law
DRAWBACKS OF THE BIG BANG THEORY
• It failed to explain how the universe was created.
• It just explains how it evolve and not where it
originated.
• It also failed to explain how the galaxies formed.
Big bang theory suggests that the universe started as
a “singularity” - an area predicted to be in the core
1
of a black hole with very high temperature and
density.
Proponents of the idea of an expanding universe
22 are Georges Henri Joseph Edouard Lemaître,
Edwin Powell Hubble, Arno Penzias and
Robert Wilson.
13 Hubble’s law states that the relationship of the
velocities of distant objects in the universe is
directly proportional to their distance from Earth.
2
The big bang theory failed to explain how the
4
universe was created.
2
Identify the proponent of the theory that explains the
following statements.
1. The the universe originated in an explosive act of primeval atom or
the ‘cosmic egg’.
2. Microwaves with wavelengths of about 7 centimeters that were
present in space
3. The cosmic rays were “ashes and smoke of bright but very rapid
fireworks,” and they originated when the primeval atom
disintegrated.
4. The relationship of the velocities of distant objects in the universe is
in proportion to their distance from Earth.
5. The amount of redshift is proportional to the distance of the galaxy.
HOW WILL YOU EXPLAIN THE BIG BANG THEORY BY
RELATING IT TO MASS, VOLUME, AND DENSITY?
You might also like
- Earth and Life Science SHS 1.1 Big Bang TheoryDocument14 pagesEarth and Life Science SHS 1.1 Big Bang TheoryFranz O'neil AparejoNo ratings yet
- Earth Science SHS 1.1 Big Bang Theory.Document21 pagesEarth Science SHS 1.1 Big Bang Theory.D GarciaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science SHS 1.1 Big Bang TheoryDocument21 pagesEarth Science SHS 1.1 Big Bang TheoryGreenace AvendanoNo ratings yet
- Earth Science SHS 1.1 Big Bang TheoryDocument22 pagesEarth Science SHS 1.1 Big Bang TheoryDela peña KimberlyNo ratings yet
- Bing Bang TheoryDocument8 pagesBing Bang Theoryaadn787No ratings yet
- Big Bang Theory PresentationDocument19 pagesBig Bang Theory PresentationJuliane Rebecca PitlongayNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Big Bang TheoryDocument36 pagesLesson 1 Big Bang TheoryEthan LopezNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Grade 11Document52 pagesEarth and Life Science: Grade 11Arlynn Arcaño IslaNo ratings yet
- Earth Sci. ReviewerDocument8 pagesEarth Sci. ReviewerPrecious HannahNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument62 pagesReportSarah Shine TorresNo ratings yet
- Composition, Origin, and Evolution of The: Physical WorldDocument55 pagesComposition, Origin, and Evolution of The: Physical WorldMichael Vincent DosadoNo ratings yet
- The Big Bang: Threshold 1 of Big HistoryDocument16 pagesThe Big Bang: Threshold 1 of Big HistorySuzanne BuckleyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Formation of ElementsDocument13 pagesChapter 1 Formation of ElementsCharity CotejoNo ratings yet
- Big Bang Theory PresentationDocument7 pagesBig Bang Theory Presentationaadn787No ratings yet
- The Big BangDocument17 pagesThe Big Bangkiddie angelsNo ratings yet
- Earth Sci NotesDocument170 pagesEarth Sci NotesErekha Jicah Sheibe SayonNo ratings yet
- Origins of The TheoryDocument32 pagesOrigins of The TheoryMaria Flor PabeloniaNo ratings yet
- Origin of The UniverseDocument30 pagesOrigin of The UniverseArjie GabrielNo ratings yet
- The Origin of The Universe and The Solar SystemDocument7 pagesThe Origin of The Universe and The Solar SystemThea Aaliyah Cruz ShalimNo ratings yet
- Theories On The Origin of The UniverseDocument9 pagesTheories On The Origin of The UniverseMichael James A. DaligdigNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Big Bang and Formation of ElementsDocument27 pagesLesson 1 Big Bang and Formation of ElementsEunice AcunaNo ratings yet
- 1.lec Universe PDFDocument38 pages1.lec Universe PDFLea IoaNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument2 pagesSeminar ReportAylin111No ratings yet
- Origin and Structure of The Earth 1Document30 pagesOrigin and Structure of The Earth 1kiethlytabioNo ratings yet
- Origin of The Universe: "What Makes The Universe Hard To Comprehend Is That There's Nothing To Compare It With."Document17 pagesOrigin of The Universe: "What Makes The Universe Hard To Comprehend Is That There's Nothing To Compare It With."jessa diegoNo ratings yet
- Theories On The Origins of The UniverseDocument10 pagesTheories On The Origins of The UniverseVanilla ChroniclesNo ratings yet
- What Is The Big Bang TheoryDocument2 pagesWhat Is The Big Bang Theorystealth solutionsNo ratings yet
- Origin of The UniverseDocument21 pagesOrigin of The UniverseArnold Arada PaombongNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis On The Origin of The Universe and The Solar SystemDocument45 pagesHypothesis On The Origin of The Universe and The Solar SystemMichael Angelo VillaruelNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Assignment 1 - Give 2 Different TheoriesDocument4 pagesModule 1 - Assignment 1 - Give 2 Different TheoriesDiana JaumNo ratings yet
- Earth Science ReviewerDocument29 pagesEarth Science ReviewerAileen Joy PauloNo ratings yet
- Physical Science - ActivityDocument20 pagesPhysical Science - ActivityKate GarciaNo ratings yet
- The Universe: The Laws of Physics Breakdown at The Center of The BlackholeDocument4 pagesThe Universe: The Laws of Physics Breakdown at The Center of The BlackholeSerafin BarodiNo ratings yet
- The Universe and The Solar System: Edrick R. Pascual, LPT Edrick R. Pascual, LPTDocument64 pagesThe Universe and The Solar System: Edrick R. Pascual, LPT Edrick R. Pascual, LPTVJ MendozaNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument6 pagesEarth ScienceJean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Cosmic Calendar Origin of Universe and Solar SystemDocument76 pagesCosmic Calendar Origin of Universe and Solar SystemXia Fermo100% (1)
- Big Bang TheoryDocument29 pagesBig Bang TheoryNo NameNo ratings yet
- The Big BangDocument1 pageThe Big BangZafkiel GuilloNo ratings yet
- Q3 Week 1 A. Final The Big Bang Theory and The Formation of Light ElementsDocument17 pagesQ3 Week 1 A. Final The Big Bang Theory and The Formation of Light ElementsgtyrielNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Origin of The Universe Origin of The Solar SystemDocument21 pagesChapter 1 Origin of The Universe Origin of The Solar SystemArwind MontasNo ratings yet
- Big Bang Theory - The PremiseDocument2 pagesBig Bang Theory - The PremiseRacel AbulaNo ratings yet
- The UniverseDocument2 pagesThe UniverseArham Asnani SabturaniNo ratings yet
- #2. The Universe 2Document14 pages#2. The Universe 2MYLENE TRINIDADNo ratings yet
- Earthsci Lesson 1Document40 pagesEarthsci Lesson 1Danilo Sare IIINo ratings yet
- 1 - The Origin of The UniverseDocument19 pages1 - The Origin of The UniverseCAMILLE LOPEZNo ratings yet
- Big Bang PowerpointDocument153 pagesBig Bang Powerpointmohanty_anantakumar6332No ratings yet
- Discipleship TheologyDocument5 pagesDiscipleship TheologyCarolina AndradeNo ratings yet
- The Universe and The Solar SystemDocument69 pagesThe Universe and The Solar SystemJustin Mhel VaquilarNo ratings yet
- Es-1 3Document33 pagesEs-1 3mortezonoriNo ratings yet
- Origin of The UniverseDocument28 pagesOrigin of The UniverseJoshua Meralles100% (2)
- Big Bang TheoryDocument3 pagesBig Bang TheoryIca Joy MacayanNo ratings yet
- The Formation of The Universe and The Solar System Module Regine MontesDocument11 pagesThe Formation of The Universe and The Solar System Module Regine Montesmariatheresamenchavez232No ratings yet
- In The Beginning, After Cobe & The Big Bang - John GribbinvDocument188 pagesIn The Beginning, After Cobe & The Big Bang - John Gribbinvatila-4-everNo ratings yet
- SST Vs BBTDocument7 pagesSST Vs BBTFlaxkikare100% (1)
- RegenerateDocument1 pageRegenerateAkiesha ScottNo ratings yet
- Big Bang Theory EngDocument21 pagesBig Bang Theory Engdhruv goraiNo ratings yet
- SHS Math and Science Instructor STI College San Pablo: (Current Accepted Model On The Formation of The Universe)Document9 pagesSHS Math and Science Instructor STI College San Pablo: (Current Accepted Model On The Formation of The Universe)Emman RevillaNo ratings yet
- The Askdjk Universe and The Solar SystemDocument24 pagesThe Askdjk Universe and The Solar SystemMin-Woo ParkNo ratings yet
- (Notes) The UniverseDocument3 pages(Notes) The UniverseDenver Cho-oyNo ratings yet
- Mesoamerican Science and TechnologyDocument8 pagesMesoamerican Science and TechnologyEchuserang FrogletNo ratings yet
- Motion 4Document11 pagesMotion 4gobinda prasad barmanNo ratings yet
- (Preview) Vietaccepted Compilation (P1)Document20 pages(Preview) Vietaccepted Compilation (P1)Anh Thư Nguyễn BảoNo ratings yet
- Star Wars - Palpatine Fan FictionDocument5 pagesStar Wars - Palpatine Fan FictionJ PNo ratings yet
- Riddle of ChariotDocument6 pagesRiddle of ChariotHappy HomeNo ratings yet
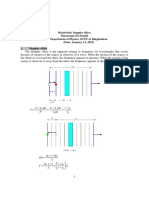
- 3 Doppler EffectDocument20 pages3 Doppler EffectengshimaaNo ratings yet
- PHYS4652 Assignment1Document2 pagesPHYS4652 Assignment1Yang Woo SeongNo ratings yet
- STS Fa1Document2 pagesSTS Fa1Margaret S. ReidNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - GNSS InstrumentationDocument32 pagesLecture 6 - GNSS InstrumentationVlaire Janrex LondoñoNo ratings yet
- Human Eye VerifiedDocument7 pagesHuman Eye VerifiedHIMNISH SHARMANo ratings yet
- Lecture # 1 GSADocument26 pagesLecture # 1 GSAMalaham Pari KhanNo ratings yet
- SETR 09: SpaceDocument13 pagesSETR 09: SpaceHoover Institution100% (1)
- Telescope Anatomy: Adapted From Presentation by Chuck Patterson, Cheyenne, WY, HS TeacherDocument12 pagesTelescope Anatomy: Adapted From Presentation by Chuck Patterson, Cheyenne, WY, HS TeacherFrenella SandovalNo ratings yet
- Buzz Aldrin PHD ThesisDocument331 pagesBuzz Aldrin PHD Thesiscrocomodx100% (1)
- PT #4.1 - Life Stages of StarDocument1 pagePT #4.1 - Life Stages of StarMarie Jo Sangalang100% (1)
- Nav Samp. QuestionDocument7 pagesNav Samp. QuestionSuleiman MusaNo ratings yet
- Nico Sneeuw, F. Kruum, Adjustment Theory - Lecture Notes 2010Document103 pagesNico Sneeuw, F. Kruum, Adjustment Theory - Lecture Notes 2010Cristian IonceaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry A Unit Circle Approach 10th Edition Sullivan Test Bank 1Document107 pagesTrigonometry A Unit Circle Approach 10th Edition Sullivan Test Bank 1Doris Golden100% (39)
- One Million YearsDocument45 pagesOne Million YearsBlue SockNo ratings yet
- 2001 Mars Odyssey - WikiwandDocument8 pages2001 Mars Odyssey - WikiwandLuis VerenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Tarot Style Slides For Middle School by SlidesgoDocument56 pagesTarot Style Slides For Middle School by SlidesgoNguyễn Kim NgânNo ratings yet
- Soal Mentah XII MIPA 1Document10 pagesSoal Mentah XII MIPA 1Felia AdityaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 35 - Tides and Tidal CurrentsDocument21 pagesChapter 35 - Tides and Tidal CurrentsEzra DaveNo ratings yet
- Nasa Technical Report Nasa TR R-277 Chronological Catalog of Reported Lunar Events From 1540 To 1966Document42 pagesNasa Technical Report Nasa TR R-277 Chronological Catalog of Reported Lunar Events From 1540 To 1966androline100% (8)
- Research Paper On SatelliteDocument8 pagesResearch Paper On Satellitehubegynowig3100% (1)
- Cosmic Influences On Human Behavior - The Planetary Factors in Personality (Michel Gauquelin) (Z-Library)Document324 pagesCosmic Influences On Human Behavior - The Planetary Factors in Personality (Michel Gauquelin) (Z-Library)Gustavo Santos100% (1)
- Celestial Origin of Climate OscillationsDocument18 pagesCelestial Origin of Climate Oscillationsclive ferebeeNo ratings yet
- Ship's Position by Long by Chron and Merpass: Here Is How To Get ItDocument21 pagesShip's Position by Long by Chron and Merpass: Here Is How To Get ItPanagiotis MouzenidisNo ratings yet
- Test Bank Lesikars Business Communication Connecting in A Digital World 13th EditionDocument6 pagesTest Bank Lesikars Business Communication Connecting in A Digital World 13th EditionRichard1LauritsenNo ratings yet
- © Ncert Not To Be Republished: The Earth in The Solar SystemDocument64 pages© Ncert Not To Be Republished: The Earth in The Solar SystemNivedya AnugrahaNo ratings yet