0% found this document useful (0 votes)
76 views12 pagesChapter 05 A Projection Method
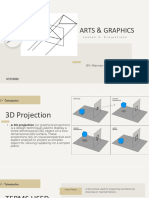
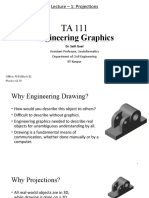
This document discusses different methods for projecting 3D objects onto 2D surfaces. It explains the concepts of line of sight and plane of projection that underlie projection methods. Parallel and perspective projections are introduced, with orthographic projection described as a type of parallel projection where the lines of sight are perpendicular to the projection plane. Multiview and axonometric drawings are presented as techniques for orthographic projection that show object dimensions and shapes.
Uploaded by
Chris UdonsiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
76 views12 pagesChapter 05 A Projection Method
This document discusses different methods for projecting 3D objects onto 2D surfaces. It explains the concepts of line of sight and plane of projection that underlie projection methods. Parallel and perspective projections are introduced, with orthographic projection described as a type of parallel projection where the lines of sight are perpendicular to the projection plane. Multiview and axonometric drawings are presented as techniques for orthographic projection that show object dimensions and shapes.
Uploaded by
Chris UdonsiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd