Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eukaryotic Prokaryotic Cells
Uploaded by
changemakergrade80 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views14 pagesOriginal Title
Eukaryotic prokaryotic cells
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views14 pagesEukaryotic Prokaryotic Cells
Uploaded by
changemakergrade8Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
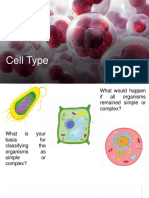
Types of Cells
• Plant v/s Animal Cells
• Prokaryotic v/s Eukaryotic cells
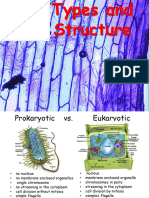
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells
• What are they? Examples.
• Compare the two types of cells
• Identify parts of a prokaryotic cell
Fill in as you watch the video…..
FEATURE PROKARYOTIC CELL EUKARYOTIC CELL
Cell wall
Cell membrane
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
Genetic material
Membrane bound
organelles
Any other differences
FEATURE PROKARYOTIC CELL EUKARYOTIC CELL
Cell wall Present – made of Present- made of
PEPTIDOGLYCAN Plants: CELLULOSE
Fungi: CHITIN
Cell membrane present present
Cytoplasm present present
Nucleus absent present
Genetic material DNA DNA
Organelles Not membrane bound Bound by membranes
Any other differences Much smaller larger
RIBOSOMES present present
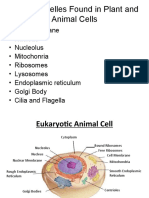
Organelles in Animal Cells
Common Membrane-bound Organelles
Features of cells common to all living
organisms
1. Cytoplasm
2. Cell membrane
3. DNA as genetic material
4. Ribosomes used for protein synthesis
Type of Cell
PROKARYOTIC CELL: EUKARYOTIC CELL:
• No true nucleus • True nucleus enclosing
• Genetic material usually chromosomes made up
consists of a single of DNA.
circular DNA which is not
enclosed in a nucleus.
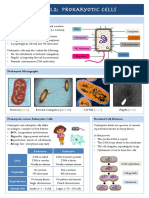
Bacteria
Inside a bacterium
Inside a bacterium
Compare: Plant cell and bacterial cell
You might also like
- Microbiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideFrom EverandMicrobiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Cell TypesDocument16 pagesCell TypesyvetteNo ratings yet
- 2.1 A. Cell Theory B. Prokaryote Eukaryote 1Document24 pages2.1 A. Cell Theory B. Prokaryote Eukaryote 1saidatulNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes & EukaryotesDocument10 pagesProkaryotes & EukaryotesJogie De GuiaNo ratings yet
- Struckture of ProkaryoticDocument5 pagesStruckture of ProkaryoticAuni NaemiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Cell BiologyDocument23 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Cell BiologyghhfhNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Prokaryotic CellsDocument1 page1.2 Prokaryotic CellsSaiam ShahNo ratings yet
- Nihar-Lecture5 - Ultrastructure of Cells Complete ClassDocument64 pagesNihar-Lecture5 - Ultrastructure of Cells Complete ClassRajnandni SharmaNo ratings yet
- L1.3 - Cell Structures Note PackageDocument4 pagesL1.3 - Cell Structures Note Package中华雅思王No ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument5 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsCrocky CookNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Prokaryotes vs. EukaryotesDocument20 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Prokaryotes vs. EukaryotesKerubin Mamaril67% (3)
- What Is A Prokaryotic Cell?: Genetic MaterialDocument7 pagesWhat Is A Prokaryotic Cell?: Genetic MaterialAnkan RoyNo ratings yet
- Lecture Differences Between Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument16 pagesLecture Differences Between Prokaryotes and EukaryotesAyesha MasoodNo ratings yet
- Arindam Mondal: School of Bio ScienceDocument39 pagesArindam Mondal: School of Bio ScienceSohini RoyNo ratings yet
- Flagellum For Locomotion Pili Help Cells Move Across SurfacesDocument18 pagesFlagellum For Locomotion Pili Help Cells Move Across SurfacesEvangeline WongNo ratings yet
- Unit 2.1 Interactive Notes 2223Document8 pagesUnit 2.1 Interactive Notes 2223thomasNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and EukaryoticDocument4 pagesProkaryotic and EukaryoticG- 6 ODL Trisha Mae Clemente100% (1)
- Cells NotesDocument7 pagesCells Notesshinde.sampada1923No ratings yet
- List All The Structures of Both Cell Types and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesList All The Structures of Both Cell Types and Their FunctionsFayeann Vedor LoriegaNo ratings yet
- Cell TopicDocument29 pagesCell TopicChynna PorneteNo ratings yet
- Cell TopicDocument29 pagesCell TopicChynna PorneteNo ratings yet
- Farmasi 1Document50 pagesFarmasi 1Suci Umniyah RamadaniNo ratings yet
- Cell The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument54 pagesCell The Fundamental Unit of LifeAxyahh 99No ratings yet
- Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells: Distinguishing Their FeaturesDocument14 pagesProkaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells: Distinguishing Their FeaturesDaniella Pasilbas SabacNo ratings yet
- Tugas KLP 1 Biologi SelDocument25 pagesTugas KLP 1 Biologi SeldeweweweweweNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument21 pagesProkaryotes and EukaryotesJeff Hambre100% (2)
- Prokaryote Vs EukaryoteDocument48 pagesProkaryote Vs Eukaryotesunifeb128075No ratings yet
- Cell AnatomyDocument17 pagesCell AnatomyparekhpragneshNo ratings yet
- Class9 - The Fundamental Unit of Life Notes by Zenith ClassesDocument7 pagesClass9 - The Fundamental Unit of Life Notes by Zenith ClassesabhishekNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles Found in Plant and Animal CellsDocument18 pagesCell Organelles Found in Plant and Animal CellsMCTCOLTDNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document100 pagesChapter 2AQEESHA NUWAIRA BINTI USMAN BN21110154No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument80 pagesUnit 2 Cell Structure and FunctionNICOLE ANGELIQUE M. DINOYNo ratings yet
- 2) ) Cell PartsDocument18 pages2) ) Cell PartsFaryad AliNo ratings yet
- Micro para 1Document6 pagesMicro para 1glen bert banuaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document32 pagesLecture 2alizeh amanNo ratings yet
- Botany LAB Plant and Animal CellsDocument7 pagesBotany LAB Plant and Animal CellsJasmine SandroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: BASIC BIOLOGY: Cell Theory Discovery of CellsDocument17 pagesChapter 1: BASIC BIOLOGY: Cell Theory Discovery of CellsMawareNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument3 pagesDifference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsWareesha BatoolNo ratings yet
- Cell-The Unit of LifeDocument26 pagesCell-The Unit of LifeHridyanshu Singh RoyNo ratings yet
- Mrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeDocument40 pagesMrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeAnamika SahuNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology) : From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument14 pagesCell (Biology) : From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediarycasiquinNo ratings yet
- Unit Mahluk Hidup - Penyusun Mahluk HidupDocument21 pagesUnit Mahluk Hidup - Penyusun Mahluk HiduprinaNo ratings yet
- Unit Mahluk Hidup Penyusun Mahluk HidupDocument21 pagesUnit Mahluk Hidup Penyusun Mahluk HidupYunita RahmaniNo ratings yet
- Tour of The CellDocument60 pagesTour of The Celladisty sncNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Prokaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic CellsDocument11 pagesDifference Between Prokaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic CellsMuhammed Sabdat100% (1)
- Cell The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument54 pagesCell The Fundamental Unit of LifeAxyahh 99No ratings yet
- MicroPara 03 - Prokaryotic CellsDocument23 pagesMicroPara 03 - Prokaryotic CellsJianne CaloNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument19 pagesCell Structure and Functionsrazen sisonNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Diagram 01Document13 pagesThe Cell: Diagram 01MELANY FERNANDA TUME CASTAÑEDANo ratings yet
- Micro Chapter 2Document34 pagesMicro Chapter 2Farrah GwynethNo ratings yet
- LESSON Cell StructureDocument22 pagesLESSON Cell StructureAhnim NimNo ratings yet
- Course Task 1 (Make A Comparison Between A Prokaryotic Cell and A Eukaryotic Cell)Document2 pagesCourse Task 1 (Make A Comparison Between A Prokaryotic Cell and A Eukaryotic Cell)JULIA ANDREA BAGTASNo ratings yet
- Agr122 Lab ReportDocument12 pagesAgr122 Lab ReportNur AthirahNo ratings yet
- 2 Organisation of The Organism NotesDocument5 pages2 Organisation of The Organism Notesarayana sharmaNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument16 pagesCellsAntiAlshabaab AntiHypocriteNo ratings yet
- BIO1 - Lessons3J4J5 - Prokaryotic Vs EukaryoticJ Plant Vs Animal CellJ Cell ModificationsDocument49 pagesBIO1 - Lessons3J4J5 - Prokaryotic Vs EukaryoticJ Plant Vs Animal CellJ Cell Modificationsraphaelleflorenog1No ratings yet
- Basic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsDocument28 pagesBasic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsMary Ann Gonzales Abeñon100% (1)
- Unit Mahluk Hidup - Penyusun Mahluk HidupDocument56 pagesUnit Mahluk Hidup - Penyusun Mahluk HidupYahya RhamadanNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotics CellsDocument18 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotics CellsClaire JosephNo ratings yet
- Bio Chapter 2Document57 pagesBio Chapter 2Xue Yi LamNo ratings yet