Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electromagnetic Induction E Motor Autosaved
Uploaded by
Phylicia Ramos0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views27 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views27 pagesElectromagnetic Induction E Motor Autosaved
Uploaded by
Phylicia RamosCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 27
ELECTROMAGNETISM
A branch of physical science that
deals with the physical relations
between electricity and
magnetism.
It explains how electric current
create magnetic fields and vice-
versa.
Scientists in the
field of
Electromagnetism
Hans Christian Oersted- a
physics professor at the
Copenhagen University observed
that when current flowed through
the wire, the compass needle was
deflected 90 when the direction
0
of the current was reversed, the
needle moved 900 in the opposite
direction.
William Sturgeon (1783-1850)-
invented the first electromagnet.
Joseph Henry (1797-1878)-
improved and popularized
electromagnets.
Michael Faraday- made an
experiment about
electromagnetic induction.
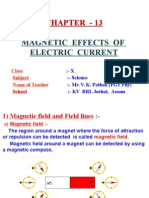
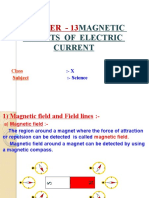
MAGNETIC FIELD
ON A CURRENT-
CARRYING WIRE
The magnetic field produced
by a straight current-carrying
wire is found to be very
small compared to the
normal magnets. One way to
increase the magnetic field B
is to increase the current
flowing in the wire.
Right hand rule no. 1
Imagine that you are holding the wire
with your right hand. Point the thumb in
the direction of the electric current I.
Your fingers curl in the direction of B.
Right hand rule no. 2
Magnetic Field: Imagine you have a permanent magnet (a magnet that
always has a magnetic field) and a coil of wire.
Electric Current: When you pass an electric current through the coil of
wire, it creates a magnetic field around the wire. This magnetic field
interacts with the permanent magnet's field.
Movement: According to the basic principle of magnetism, opposite
magnetic poles attract while like poles repel. The interaction of the
magnetic fields causes the coil of wire to experience a force.
Rotation: If the coil is free to move, this force will make it rotate. In an
electric motor, the coil is usually attached to a shaft, and as it rotates, it
can do mechanical work.
So, in simple terms, an electric motor converts electrical energy (from
the flow of electric current in the coil) into mechanical energy (the
rotation of the coil), and this rotation can be used to drive various
mechanical devices like fans, wheels, or anything else depending on the
design of the motor.
General
applications of
Electromagnetic
induction
1. Electric motor- is an
electrical machine that
converts electrical energy
into mechanical energy.
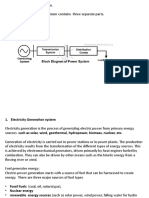
2. Generator- is a device that
converts mechanical energy
to electrical energy for use in
an external circuit.
3. Transformer- is an electrical
device that transfers electrical
energy between two or more
circuits through electromagnetic
induction.
- Commonly, transformers are
used to increase or decrease the
voltages of alternating current in
electric power applications.
4. Galvanometer- is a type of a
sensitive ammeter. An instrument
for detecting electric current
5. Ammeter- is a measuring
instrument used to measure the
electric current in a circuit. Current
are measured in amperes.
6. Ohmmeter- is an electrical
instrument that measures electrical
resistance.
7. Voltmeter- is an instrument used
for measuring electrical potential
difference between two points in
an electric circuit.
8. Multimeter or multitester- also
known as a VOM ( Volt-Ohm-
Milliammeter) is an electronic
measuring instrument that
combines several measurement
functions in one unit.
You might also like
- Electromagnetism Part 2Document24 pagesElectromagnetism Part 2Mikela DelatoreNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism SlidesDocument45 pagesElectromagnetism Slideskaushik247No ratings yet
- Basic Principle of ElectricityDocument5 pagesBasic Principle of ElectricityFavour OgbonnaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Electric CurrentDocument13 pagesMagnetic Effect of Electric Currentanjupal100% (4)
- Project Sciencegroup4Document19 pagesProject Sciencegroup4Sean Matthew Del cruzNo ratings yet
- Magnetism & ElectromagnetismDocument38 pagesMagnetism & ElectromagnetismganapathiNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism: Sonny P. de Leon MT1Document58 pagesElectricity and Magnetism: Sonny P. de Leon MT1iMer22100% (1)
- Mag ElectromagDocument38 pagesMag ElectromagJames Paul Micael GargantaNo ratings yet
- 2 Electromagnetism BESTDocument26 pages2 Electromagnetism BESTSuriani DharmaNo ratings yet
- Pajunar J Jonna P. - Assignment 2Document4 pagesPajunar J Jonna P. - Assignment 2Jonna PajunarNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Week 4 Electricity and MagnetismDocument22 pages3rd Quarter Week 4 Electricity and MagnetismStephanie AquinoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism 2Document22 pagesElectromagnetism 2abegail chuNo ratings yet
- Electic & ElectroDocument40 pagesElectic & ElectroMohamad Hafiz SariffNo ratings yet
- InductionDocument12 pagesInductionAhmad Ibsais100% (1)
- Electricity Magnetism and ElectromagnetismDocument51 pagesElectricity Magnetism and ElectromagnetismJun OrbitaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9.3 ElectromagnetismDocument32 pagesLesson 9.3 ElectromagnetismJericho JacaNo ratings yet
- What Is Electrical Induction?Document3 pagesWhat Is Electrical Induction?Wak Sidek TgKarangNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument13 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentkunalNo ratings yet
- Dow 00068Document150 pagesDow 00068Kunal Bagade.No ratings yet
- Electromagnetism: By: Joshua Alfred de La Cruz Nicole Marie Dela Cruz Stephen MiayoDocument32 pagesElectromagnetism: By: Joshua Alfred de La Cruz Nicole Marie Dela Cruz Stephen Miayo10march1965No ratings yet
- Science 10-Lesson 10Document34 pagesScience 10-Lesson 10afloresNo ratings yet
- ElectromagnetsDocument51 pagesElectromagnetsRoanne Mae MañalacNo ratings yet
- EM WaveDocument47 pagesEM WaveKia LeighNo ratings yet
- Assignment Work1Document4 pagesAssignment Work1Osarondor OsarondorNo ratings yet
- Faraday's & Lenz LawDocument14 pagesFaraday's & Lenz LawPnDeNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument22 pagesPhysics ProjectthaswikaamaraNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument9 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectKURRA DIVIT SOSHNo ratings yet
- Reviewer: Build A Motor Activity: Topic: MagnetismDocument14 pagesReviewer: Build A Motor Activity: Topic: MagnetismOP GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Part 2 ElectromagnetismDocument12 pagesUnit 7 Part 2 Electromagnetism123yousss2222No ratings yet
- 3-5 Physics Elec MagDocument34 pages3-5 Physics Elec MagPrecious BalgunaNo ratings yet
- Heating Effect of Electric CurrentDocument7 pagesHeating Effect of Electric CurrentPawan KordeNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism 2: Factors Affecting Induced EMIDocument38 pagesElectromagnetism 2: Factors Affecting Induced EMIChello Marielle San GabrielNo ratings yet
- ElectromagnetsDocument15 pagesElectromagnetsJullian G. CortinaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Field X Class Module 2Document9 pagesMagnetic Field X Class Module 2Gamers For Life . comNo ratings yet
- MotorsDocument13 pagesMotorsSandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- EMEC 1 5th Aug 2013Document25 pagesEMEC 1 5th Aug 2013Harsha DuttaNo ratings yet
- HowStuffWorks GalvanometerDocument2 pagesHowStuffWorks GalvanometerPi PoliNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument17 pagesMagnetic Effects of Electric CurrentKunalKaushik100% (2)
- CH 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current NotesDocument12 pagesCH 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current NotesAkshithNo ratings yet
- Artikel Listrik MagnetDocument7 pagesArtikel Listrik MagnetAgnes NovitaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes in Electromagnetic Spectrum and InductionDocument2 pagesLecture Notes in Electromagnetic Spectrum and InductionAlAr-JohnTienzoTimeniaNo ratings yet
- Electricity Magnetism and ElectromagnetismDocument64 pagesElectricity Magnetism and ElectromagnetismFe DNo ratings yet
- Grd10 Q2 K-12 (Electricity and Magnetism) NOTES AND QUESTIONSDocument9 pagesGrd10 Q2 K-12 (Electricity and Magnetism) NOTES AND QUESTIONSIonacer Viper75% (4)
- EEU NotesDocument5 pagesEEU NotesNero MonNo ratings yet
- Electrical Energy GenerationDocument27 pagesElectrical Energy GenerationAlfred WunumNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Electromagnetic Effects PDFDocument10 pagesTopic 4 Electromagnetic Effects PDFHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNo ratings yet
- Group 3 PresentsDocument18 pagesGroup 3 PresentsShannie Longakit RacomaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument45 pagesMagnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDipayan BiswasNo ratings yet
- Applications of Electromagnetic InductionDocument6 pagesApplications of Electromagnetic InductionLivombo AveloNo ratings yet
- Final Exam in ElectricityDocument7 pagesFinal Exam in ElectricityNiko Igie Albino PujedaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument16 pagesMagnetic Effects of Electric CurrentAnshika AggarwalNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2 ReviewerDocument22 pagesGeneral Physics 2 Reviewercharydel.oretaNo ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument11 pagesMagnetismRonit BiswalNo ratings yet
- Utilities 1 ReviewerDocument11 pagesUtilities 1 ReviewerESCARO, JOSHUA G.No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction ArmanDocument12 pagesElectromagnetic Induction ArmanMalikNo ratings yet
- Kashish Physics ProjectDocument6 pagesKashish Physics ProjectNirmit JaiswalNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 Introduction To Electricity Copy For StudentsDocument31 pagesLESSON 3 Introduction To Electricity Copy For Studentsixearth84No ratings yet
- How Do Electric Motors Work? Physics Books for Kids | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandHow Do Electric Motors Work? Physics Books for Kids | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Himanshu Seminar Report 2Document28 pagesHimanshu Seminar Report 2himanshuNo ratings yet
- Physics Project - Mapping The Magnetic FieldDocument26 pagesPhysics Project - Mapping The Magnetic Fieldmohammadumair2006No ratings yet
- Kuhnke IA Series Relay DatasheetDocument4 pagesKuhnke IA Series Relay DatasheetKishore KNo ratings yet
- Cabt 17Document15 pagesCabt 17محمد خالدNo ratings yet
- Gen - Phy 2 12 Q3 SLM8Document13 pagesGen - Phy 2 12 Q3 SLM8coffeeandu07No ratings yet
- TWM Yokes - Operating Manual - Feb22Document7 pagesTWM Yokes - Operating Manual - Feb22Michael LloydNo ratings yet
- 4.2.4 - Ohms Law WorksheetDocument1 page4.2.4 - Ohms Law Worksheettomas garciaNo ratings yet
- Imp QusDocument17 pagesImp QusBck SreedharNo ratings yet
- Practical Journal PhysicsDocument39 pagesPractical Journal Physicsarish ahmedNo ratings yet
- Phsc2112 ExamDocument15 pagesPhsc2112 ExamRussianOmeleteNo ratings yet
- f1 Meter Reading - New SheetDocument88 pagesf1 Meter Reading - New SheetPrince RanaNo ratings yet
- Ed Exp 3Document3 pagesEd Exp 3Promit MandalNo ratings yet
- RelaysDocument48 pagesRelaysSai Teja SakeNo ratings yet
- Ari 12 CH 9 Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDocument54 pagesAri 12 CH 9 Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsCommandoNo ratings yet
- 3 Point StarterDocument2 pages3 Point StarterAkash ANo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering CapsuleDocument209 pagesElectrical Engineering CapsuleAravindmadhav AravindmadhavNo ratings yet
- Free Energy FilesDocument9 pagesFree Energy FilesPeter Frk KchNo ratings yet
- Electrical Control For Machines 7th Edition Lobsiger Solutions ManualDocument3 pagesElectrical Control For Machines 7th Edition Lobsiger Solutions Manualhanhanselmuv0smNo ratings yet
- 1.optical FibersDocument23 pages1.optical FibersYashNo ratings yet
- EM-I - Lecture Notes PDFDocument75 pagesEM-I - Lecture Notes PDFChinna SriNo ratings yet
- EFT Finalterm Fall 2021Document2 pagesEFT Finalterm Fall 2021Tayyab AbbasNo ratings yet
- Electric Generator Project FileDocument27 pagesElectric Generator Project Filegudias375No ratings yet
- Principles of Electric Circuits - 9780135073094 - Ejercicio 41 - QuizletDocument5 pagesPrinciples of Electric Circuits - 9780135073094 - Ejercicio 41 - QuizletasdfNo ratings yet
- Ac Part 3Document9 pagesAc Part 3Lester James SaingNo ratings yet
- Wa0004.Document8 pagesWa0004.mountain KingNo ratings yet
- CH 4-MCM-WSDocument8 pagesCH 4-MCM-WSmmkishore067No ratings yet
- f4 Phy Part 2 - MergedDocument43 pagesf4 Phy Part 2 - Merged苏恩恩No ratings yet
- A Novel Double Stator Hybrid-Excited Flux Reversal Permanent Magnet Machine With Halbach PM ArraysDocument2 pagesA Novel Double Stator Hybrid-Excited Flux Reversal Permanent Magnet Machine With Halbach PM Arrayskyaw winNo ratings yet
- ZMC10Document2 pagesZMC10Michael MitchellNo ratings yet
- CBIP Manual 311 - 2011Document230 pagesCBIP Manual 311 - 2011Muralikrishna RNo ratings yet