Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MODULE 2 Lesson 1
Uploaded by
Anne Rose Coderias0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views17 pagesThe document discusses volcanic eruptions and provides details about the composition of magma, including how the silica content affects viscosity, how temperature impacts viscosity and melting points, and how the volatile content of gases like water vapor and carbon dioxide influences the explosiveness of eruptions. Specific examples mentioned include the large volcano Olympus Mons on Mars, details on the 2020 eruption of Taal Volcano in the Philippines, and how magma viscosity impacts the movement and buildup of volatile gases.
Original Description:
Original Title
MODULE 2 lesson 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses volcanic eruptions and provides details about the composition of magma, including how the silica content affects viscosity, how temperature impacts viscosity and melting points, and how the volatile content of gases like water vapor and carbon dioxide influences the explosiveness of eruptions. Specific examples mentioned include the large volcano Olympus Mons on Mars, details on the 2020 eruption of Taal Volcano in the Philippines, and how magma viscosity impacts the movement and buildup of volatile gases.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views17 pagesMODULE 2 Lesson 1
Uploaded by
Anne Rose CoderiasThe document discusses volcanic eruptions and provides details about the composition of magma, including how the silica content affects viscosity, how temperature impacts viscosity and melting points, and how the volatile content of gases like water vapor and carbon dioxide influences the explosiveness of eruptions. Specific examples mentioned include the large volcano Olympus Mons on Mars, details on the 2020 eruption of Taal Volcano in the Philippines, and how magma viscosity impacts the movement and buildup of volatile gases.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 17
SCIENCE 9
QUARTER 3:EARTH and SPACE
PRE-TEST
MODULE 2
Volcanic Eruption
AMAZING FACTS
There is a volcano on
Mars called Olympus
Mons which rises nearly
25 kilometers above the
Martian surface. It is
almost 3 times as tall as
Mount Everest.
Facts About Taal Volcano in 2020
Location: Batangas (Taal)
Status: Second most active volcano
Features: Caldera (Has water/lake within a lake)
Eruption Started on: January 12, 2020
Ended on: January 22, 2020
Last eruption: 1977 (43years ago)
Type of eruption: Phreatomagmatic (main crater) has
water in it.
LESSON 1
Magma and Its Composition
Magma
• is the molten rock which lies underneath volcanoes. It
is formed at destructive plate boundaries and is rich in
silicate
• are products of crustal rocks (which are richer in silica
than the rock of the mantle).
Crystal Content
• Some magmas begin to crystallize as they reach the
surface
• high temperature minerals are formed as magma slowly
cools down followed by low temperature minerals
• always contains crystals of high temperature.
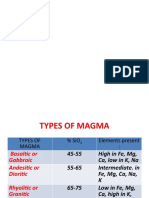
Viscosity
• the magma’s silica content affects its viscosity, the
resistance of the fluid to flow
• low viscosity magma has low silica content and is
composed mostly of basalt
• Temperature also affects the viscosity of the magma.
Magma with high temperatures have low viscosity while
magma with low temperatures have high viscosity.
Temperature
• Temperature of magma reflects the melting points of
their mineral components.
• Magmas formed by partial melting of mantle rocks are
much hotter over 1200⁰C for some basalts. Rhyolites that
reached the surface have temperature of less than
900⁰C, and have a much higher viscosity.
Volatile Content
• Magma contains small amounts of dissolved gas (water vapor,
Carbon dioxide etc.) which is released as pressure is
removed.
• Magmas formed by melting of mantle rocks have generally
low volatile contents, but those formed by partial melting of
crustal rocks are often volatile-rich.
• Water vapor is the most abundant volcanic gas, followed by
carbon dioxide and sulfur dioxide.
• There are other volcanic gases such as hydrogen sulfide,
hydrogen chloride, and hydrogen fluoride.
• Trace gases are also found in volcanic emissions and these
are: hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and volatile metal chloride.
Volatile Content
• The movement of this volatile content is
affected by the viscosity of the magma.
• As the gas continues to precipitate from the
high viscosity magma, the bubbles will be
prevented from rapidly breaking out resulting
to the increase in pressure on the magma
column.
• This causes the volcano to erupt explosively.
Get ¼ sheet of
paper.
You might also like
- Metamorphic, Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks : Sorting Them Out - Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksFrom EverandMetamorphic, Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks : Sorting Them Out - Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNo ratings yet
- Genetic Model Ore DepositsDocument109 pagesGenetic Model Ore DepositsDinanNo ratings yet
- 10.volcanoes and Other Igneous ActivityDocument39 pages10.volcanoes and Other Igneous ActivityChristine ValerioNo ratings yet
- VOLCANISMDocument25 pagesVOLCANISMdave mahilumNo ratings yet
- Endogenic ProcessesDocument7 pagesEndogenic ProcessesThe Digital Library100% (3)
- Magma FormationDocument2 pagesMagma FormationVaughn GeronimoNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes: 8 Grade Earth & Space Science - Class NotesDocument39 pagesVolcanoes: 8 Grade Earth & Space Science - Class NotesSiddharth TiwariNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan VolcanoDocument5 pagesLesson Plan VolcanoJhudi Sotto - MagtotoNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes and Mountains: Engr. Symon Allan A. CasugaDocument44 pagesVolcanoes and Mountains: Engr. Symon Allan A. Casugashey isidroNo ratings yet
- Phreatic BrecciaDocument12 pagesPhreatic BrecciaRaul MeloniNo ratings yet
- Endogenic ProcessesDocument43 pagesEndogenic ProcessesMeryNo ratings yet
- PT 5 Breccias WorkshopDocument67 pagesPT 5 Breccias WorkshopMarco Augusto Robles Ancajima89% (9)
- Magma, Lava and Pyroclastic MaterialsDocument9 pagesMagma, Lava and Pyroclastic MaterialsAdrienne BarrogaNo ratings yet
- G9 - Q3 Volcanic EruptionDocument19 pagesG9 - Q3 Volcanic Eruptionyanabrei08No ratings yet
- Volcanic EruptionDocument2 pagesVolcanic EruptionLeo Cambaya Lascuña Jr.No ratings yet
- Earths Internal Heat and MagmatismDocument23 pagesEarths Internal Heat and MagmatismJoHan Xyth RizaldoNo ratings yet
- Module 3 ReviewerDocument5 pagesModule 3 ReviewerMikyla DulinNo ratings yet
- Nature and Generation of MagmaDocument42 pagesNature and Generation of MagmaMuzmmil MianNo ratings yet
- Volcanic Eruption - Module 2Document18 pagesVolcanic Eruption - Module 2Ivy Grace Suarez CalipesNo ratings yet
- Sci9 Q3 Module2Document7 pagesSci9 Q3 Module2Gleziel Ann Sulima PacillosNo ratings yet
- MagmatismDocument18 pagesMagmatismgardenshadow139No ratings yet
- Geochemical CycleDocument13 pagesGeochemical CycleSOCKYNo ratings yet
- Types of Volcanic EruptionDocument43 pagesTypes of Volcanic EruptionahagonzalgoNo ratings yet
- Volcano - 6th FormDocument40 pagesVolcano - 6th Formshan mackNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 10 - Volcanoes and Other Igneous ActDocument38 pagesChapter - 10 - Volcanoes and Other Igneous ActRinen ParacadNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 PPT OneDocument40 pagesLesson 2 PPT OneJason AlbertoNo ratings yet
- MAGMATISMDocument27 pagesMAGMATISMMini Ivan JayNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 1-Module 7: Magmatism Endogenic ProcessDocument13 pagesEarth and Life Science: Quarter 1-Module 7: Magmatism Endogenic ProcessJulius GamayanNo ratings yet
- Batch 2 Topic 6Document24 pagesBatch 2 Topic 6Mikhael HerreraNo ratings yet
- ERUPTIONDocument3 pagesERUPTIONFerland James DelMar GumahinNo ratings yet
- Q3 Science - Volcanic EruptionDocument4 pagesQ3 Science - Volcanic EruptionAltheakim MacasadiaNo ratings yet
- Magmatism Group 3Document29 pagesMagmatism Group 3MARY JOSEPH OCONo ratings yet
- Igneous Processes and Landforms MimiDocument54 pagesIgneous Processes and Landforms MimiNoelle Mickaela SavillaNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument6 pagesDocumentMuchael NipalNo ratings yet
- Stem11a Group2Document32 pagesStem11a Group2fabbuddylizNo ratings yet
- ES Lesson-3 Endogenic-ProcessDocument2 pagesES Lesson-3 Endogenic-ProcessSakamoto MiraiNo ratings yet
- 2 - Volcanic Eruptions Hazards 2017Document7 pages2 - Volcanic Eruptions Hazards 2017NitishNo ratings yet
- VolcanoesDocument64 pagesVolcanoesKevin GeradaNo ratings yet
- Magma FormationDocument12 pagesMagma FormationAliyana Trisha HarunNo ratings yet
- Magma and Volcanism Reviewer GROUP 4Document7 pagesMagma and Volcanism Reviewer GROUP 4muhamsumandresNo ratings yet
- Earth Materials and ProcessesDocument52 pagesEarth Materials and ProcessesMay Lyn BerondoNo ratings yet
- Applied Geology Lecture 7Document15 pagesApplied Geology Lecture 7Wanambwa SilagiNo ratings yet
- Q1 M7 Magma FormationDocument40 pagesQ1 M7 Magma FormationTheo AugustusNo ratings yet
- Q2 M2 Presentation MWFDocument34 pagesQ2 M2 Presentation MWFEspinosa , Lance G.No ratings yet
- Science 9 - VolcanoesDocument6 pagesScience 9 - VolcanoesJOSHUA CABIGAYANNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Volcanoes1Document62 pagesChapter 7 Volcanoes1Jeanette FormenteraNo ratings yet
- 10 Volcanoes and Other Igneous ActivityDocument39 pages10 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activityapi-281064041No ratings yet
- Endogenic ProcessDocument60 pagesEndogenic Processsweenanne llenaNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Q3 Module 5Document4 pagesScience 9 Q3 Module 5Arthur CapawingNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes, Magma, and Volcanic Eruptions: Characteristics of Magma Types of MagmaDocument12 pagesVolcanoes, Magma, and Volcanic Eruptions: Characteristics of Magma Types of MagmaJoseph ZotooNo ratings yet
- 5b. VolcanismDocument44 pages5b. VolcanismGaurav KapseNo ratings yet
- RocksDocument19 pagesRocksTayyba sayedNo ratings yet
- How Magma Is FormedDocument21 pagesHow Magma Is FormedJAY ANDRESNo ratings yet
- MagmaDocument4 pagesMagmaapi-3808551No ratings yet
- VolcanoDocument26 pagesVolcanoDaniella SirjooNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Also Apply To Igneous Rocks.: Diorite Is An Intermediate Rock ContainingDocument7 pagesIntermediate Also Apply To Igneous Rocks.: Diorite Is An Intermediate Rock Containingedgar_chieNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science SHS 8.2 Magmatism - How Magma Is FormedDocument15 pagesEarth and Life Science SHS 8.2 Magmatism - How Magma Is FormedTrishanne PilapilNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of MagmaDocument18 pagesCharacteristics of MagmaCanggahNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes g9Document33 pagesVolcanoes g9rvnsj28No ratings yet
- Module 5 - Week 5Document26 pagesModule 5 - Week 5Alice ChanNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life MagmatismDocument21 pagesEarth and Life MagmatismMarvin MelisNo ratings yet
- Unit III PETROLOGYDocument30 pagesUnit III PETROLOGYRubel RanaNo ratings yet
- Name: Cesar John Catuburan Grade/ Section: Stem CDocument8 pagesName: Cesar John Catuburan Grade/ Section: Stem CMakapikon NagudNo ratings yet
- Module 1 LESSON 2Document24 pagesModule 1 LESSON 2Anne Rose CoderiasNo ratings yet
- Module 1 LESSON 1Document36 pagesModule 1 LESSON 1Anne Rose CoderiasNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 Lesson 4 Kinteic TheoryDocument19 pagesMODULE 1 Lesson 4 Kinteic TheoryAnne Rose CoderiasNo ratings yet
- Module 2 LESSON 1Document13 pagesModule 2 LESSON 1Anne Rose CoderiasNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 Lesson 3Document8 pagesMODULE 1 Lesson 3Anne Rose CoderiasNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 Lesson 2Document17 pagesMODULE 1 Lesson 2Anne Rose CoderiasNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document17 pagesModule 1Anne Rose CoderiasNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 Lesson 3Document14 pagesMODULE 2 Lesson 3Anne Rose CoderiasNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document18 pagesModule 2Anne Rose CoderiasNo ratings yet
- Perfomance TaskDocument6 pagesPerfomance TaskAnne Rose CoderiasNo ratings yet
- Materials and MethodsDocument31 pagesMaterials and MethodsAnne Rose CoderiasNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document20 pagesModule 4Anne Rose CoderiasNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 Lesson 2Document16 pagesMODULE 2 Lesson 2Anne Rose CoderiasNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 Lesson 2Document19 pagesMODULE 1 Lesson 2Anne Rose CoderiasNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 Lesson 3Document11 pagesMODULE 1 Lesson 3Anne Rose CoderiasNo ratings yet
- Presenting DataDocument24 pagesPresenting DataAnne Rose CoderiasNo ratings yet
- Research Title and IntroductionDocument29 pagesResearch Title and IntroductionAnne Rose CoderiasNo ratings yet
- Research ProposalDocument21 pagesResearch ProposalAnne Rose CoderiasNo ratings yet
- 1st WeekDocument12 pages1st WeekAnne Rose CoderiasNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH MODULE 2 Lesson 1Document10 pagesENGLISH MODULE 2 Lesson 1Anne Rose CoderiasNo ratings yet
- Geology, Porphyry Cu-Au, and Epithermal Cu-Au-Ag Mineralization of The Tombulilato District, North Sulawesi, IndonesiaDocument36 pagesGeology, Porphyry Cu-Au, and Epithermal Cu-Au-Ag Mineralization of The Tombulilato District, North Sulawesi, Indonesiarafles ardianNo ratings yet
- 4c Rock Cycle WebquestDocument4 pages4c Rock Cycle Webquestapi-660734816No ratings yet
- Comunicacions 14Document216 pagesComunicacions 14jmvictoria6870No ratings yet
- King's ConceptDocument5 pagesKing's ConceptGeo CUKNo ratings yet
- ELECT1-week 9 CHAPTER 5 ENDOGENIC PROCESSESDocument12 pagesELECT1-week 9 CHAPTER 5 ENDOGENIC PROCESSESRenNo ratings yet
- Caldera: EtymologyDocument11 pagesCaldera: EtymologyKarl Michael RubinNo ratings yet
- PLATE TECTONICS WORKSHEET #2.ocxDocument6 pagesPLATE TECTONICS WORKSHEET #2.ocxRaymeishNo ratings yet
- Answer Sheet in Science 9: Quarter 3 - Las No. 1Document3 pagesAnswer Sheet in Science 9: Quarter 3 - Las No. 1AmiDacunoNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Mrs. Amany Adel Gaber HussienDocument39 pagesPrepared By: Mrs. Amany Adel Gaber Hussienromaehab201912No ratings yet
- Geography 1290 - Assignment 3Document7 pagesGeography 1290 - Assignment 3jaimal dhillonNo ratings yet
- Ash Flow Tuffs Origin IdentificationDocument90 pagesAsh Flow Tuffs Origin IdentificationBaculitesNo ratings yet
- 24 MetamorphismDocument18 pages24 MetamorphismTyler PesterNo ratings yet
- VolcanoesDocument32 pagesVolcanoesapi-302968888No ratings yet
- Mount ST Helens NewDocument11 pagesMount ST Helens NewCopsewood604No ratings yet
- Earth Processes: Earth and Life ScienceDocument21 pagesEarth Processes: Earth and Life ScienceKJ MendelNo ratings yet
- Erupted Material: Volcanic GasesDocument3 pagesErupted Material: Volcanic GasesNaditaNo ratings yet
- Classification of RocksDocument5 pagesClassification of RocksStephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- Padilla, R. Et Al. (2004)Document25 pagesPadilla, R. Et Al. (2004)WilliamsRafaelMataRimacNo ratings yet
- Stratigraphic Grouping (SG) 18Document7 pagesStratigraphic Grouping (SG) 18Manicc ANo ratings yet
- ELS Final Module 7 08082020 - 022915Document26 pagesELS Final Module 7 08082020 - 022915CelerinaRusianaLonodNo ratings yet
- Document For FreeDocument3 pagesDocument For FreePrecious Nicole J. DariaNo ratings yet
- Geology For CE Module Ch2 - 2Document12 pagesGeology For CE Module Ch2 - 2Anthony LoñezNo ratings yet
- Triptico InglesDocument2 pagesTriptico InglesCésar MartínezNo ratings yet
- Geo p1Document4 pagesGeo p1VernonNo ratings yet
- Lecture-1 Study MaterialDocument28 pagesLecture-1 Study MaterialDr. Daljeet Singh SidhuNo ratings yet