Professional Documents
Culture Documents
9th Grade - The Endocrine System
Uploaded by
Anika Hinkova0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views6 pagesOriginal Title
9th grade - The Endocrine system
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views6 pages9th Grade - The Endocrine System
Uploaded by
Anika HinkovaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
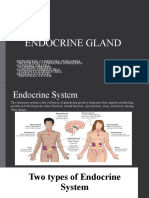
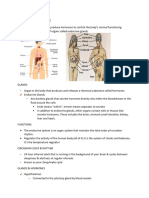
The endocrine system
1. Hypophysis (pituitary gland)
• Under the diencephalon – the hypothalamus
• Consists of two lobes – anterior and posterior
• The anterior releases the gonadotropins (FSH
and LSH) and the growth hormone –
somatotropin.
• The posterior lobe secretes oxytocin and
antidiuretic hormone (ADH). The ADH acts on
kidney nephrons decreasing water loss with the
urine. Thus, it controls the water content of the
blood.
2. Epiphysis (pineal gland)
• Produces melatonin – a
hormone that is released at
night and regulates sleep. It also
exhibits the early start of
puberty.
• In the day time the pineal gland
produces the hormone of
happiness – serotonin.
3. Thyroid gland and parathyroid glands
• At the beginning of the trachea, under
the larynx.
• Secretes thyroxine which controls the
body’s metabolic rate and increases
protein synthesis in the body.
• The thyroid hormones contain iodine.
When there is iodine deficiency, the
thyroid enlarges, causing a disease –
goitre.
• The parathyroid glands release
hormones that participate in the
regulation of calcium and phosphorus
exchange in the body.
4. Pancreas
• Mixed gland – both exocrine and endocrine
secretion.
• Exocrine – pancreatic juice in the duodenum
• Endocrine – hormones – insulin and glucagon.
• Insulin – lowers the level of glucose in blood. When
not enough insulin is produced a disease called
diabetes occurs.
• Glucagon – opposite to the insulin – when blood
glucose is low, it stimulates the breakdown of
glycogen to glucose.
5. Adrenal gland
• Made of two parts – cortex and medulla
• The medulla produces adrenaline – the
stress hormone. It is produced at
excessive excitement, anger, or fear.
• ‘Fight or flight’ hormone – the breathing
rate increases, the heart beats faster,
blood is diverted away from intestines in
the muscles, in the liver, the stored
carbohydrates are changed into glucose,
the pupils dilate, mental awareness is
increased.
You might also like
- 8 Endocrine SystemDocument22 pages8 Endocrine Systemeeza408No ratings yet
- Biology PPT 8 THDocument19 pagesBiology PPT 8 THyazgansivNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System GlandsDocument40 pagesEndocrine System Glandsqty9jgkpnzNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EndocrinologyDocument53 pagesIntroduction To EndocrinologyAli ArainNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument30 pagesEndocrine SystemBrenda Domaneo BaseNo ratings yet
- 35 3Document21 pages35 3nancie8100% (1)
- Endocrine System - Class - 10 - Icse.Document2 pagesEndocrine System - Class - 10 - Icse.zoha afshanNo ratings yet
- How Are Endocrine Glands Designed To Perform TheirDocument23 pagesHow Are Endocrine Glands Designed To Perform TheirEA CatalanNo ratings yet
- The Structure and Function of Central and Peripheral HormonDocument34 pagesThe Structure and Function of Central and Peripheral HormonrichardiaNo ratings yet
- Class 1 Endocrine - SystemnewMay 17 - 22Document22 pagesClass 1 Endocrine - SystemnewMay 17 - 22ELIANA TIPACTI PAPENNo ratings yet
- Endocrine - Feb12Document39 pagesEndocrine - Feb12cabilesrobilyn479No ratings yet
- HCT Endocrine SystemDocument23 pagesHCT Endocrine SystemMa. Angelina EradNo ratings yet
- Control of Our Bodies HomeostasisDocument20 pagesControl of Our Bodies HomeostasisJohn Philip VerastigueNo ratings yet
- Anfis EndokrinDocument25 pagesAnfis EndokrinVia ResaNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument38 pagesThe Endocrine SystemJennyNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument38 pagesFunctional Anatomy and PhysiologyNawalNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument20 pagesEndocrine SystemHediarta Widiana PutraNo ratings yet
- BSC NotesDocument9 pagesBSC NotesTayyaba ShahNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands RevisedDocument47 pagesEndocrine Glands RevisedXyress Archer GosinganNo ratings yet
- Hand Out EndoDocument3 pagesHand Out EndoAaron RoxasNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument43 pagesEndocrine SystemJeanette RiosNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: 1. DefinationDocument11 pagesEndocrine System: 1. DefinationMaleeha Ayub100% (1)
- Adrenal GlandDocument47 pagesAdrenal GlandsuthaNo ratings yet
- Seminor On Hormons Slide2 by Prof - Dr.HariharDocument49 pagesSeminor On Hormons Slide2 by Prof - Dr.Hariharhariharb999_23960100No ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument16 pagesEndocrine SystemJelyn Rose CuetoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument35 pagesEndocrine SystemLinkNo ratings yet
- Glandular SystemDocument18 pagesGlandular SystemAashishNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument22 pagesEndocrine SystemkwatsNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Reviewer LecDocument3 pagesEndocrine System Reviewer LecNOELLE LAURAINNE TANZONo ratings yet
- Endocrine System and Excretion WordDocument10 pagesEndocrine System and Excretion WordJoachim “Jayrz” MwambireNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument70 pagesEndocrinehamidNo ratings yet
- 35.3 The Endocrine System: Bio 30 NWRCDocument22 pages35.3 The Endocrine System: Bio 30 NWRCnancie8No ratings yet
- The Endocrine Glands and The Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesThe Endocrine Glands and The Nervous SystemLyanna MormontNo ratings yet
- OhohohDocument34 pagesOhohohuriNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System - Part 2Document31 pagesEndocrine System - Part 2Maryem NabawiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine GlandsDocument4 pagesEndocrine GlandsEzeh PrincessNo ratings yet
- 10 Endocrine SystemDocument35 pages10 Endocrine SystemALICIA GOMEZNo ratings yet
- Endocrine To IGCSE BiologyDocument23 pagesEndocrine To IGCSE BiologyyarinaosuNo ratings yet
- Psychology - Endocrine Glands (SEM - 2 - CC-6)Document7 pagesPsychology - Endocrine Glands (SEM - 2 - CC-6)Srinivasu ChintalaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Abbreviations and Pathologies - 2-CombinedDocument98 pagesEndocrine Abbreviations and Pathologies - 2-Combinedahin3470No ratings yet
- Endocrine System2023Document30 pagesEndocrine System2023April MagnoNo ratings yet
- Anatomi & Fisiologi Kel EndokrinDocument46 pagesAnatomi & Fisiologi Kel Endokrinclaresta100% (1)
- Endocrine System: Prepared By: Danish AhmedDocument47 pagesEndocrine System: Prepared By: Danish AhmedHira KhanNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument10 pagesThe Endocrine SystemStephen Mark Garcellano DalisayNo ratings yet
- 34-2 PowerPointDocument24 pages34-2 PowerPointLeo HellawellNo ratings yet
- PNKND Les 0 V 9 VWR60 B RCNDocument4 pagesPNKND Les 0 V 9 VWR60 B RCNaadeshthite476No ratings yet
- (Biology) The Endocrine SystemDocument10 pages(Biology) The Endocrine SystemNiharikaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System &gland ChartDocument18 pagesEndocrine System &gland ChartMerlintaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine!!!!!!!Document33 pagesEndocrine!!!!!!!Ungays ungaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System 2017Document28 pagesEndocrine System 2017cyber sec100% (1)
- Endocrine SystemDocument20 pagesEndocrine SystemJamie BagundolNo ratings yet
- The Role of Hormones in Female and Male Reproductive Systems 1Document45 pagesThe Role of Hormones in Female and Male Reproductive Systems 1j.jizuniNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System The Endocrine System: © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. 1Document12 pagesThe Endocrine System The Endocrine System: © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. 1lourd nabNo ratings yet
- EndocrinologyDocument15 pagesEndocrinologyAbdullah EmadNo ratings yet
- 3rd BSC Endocrinology NotesDocument25 pages3rd BSC Endocrinology NotesPratyashaNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 22 PDFDocument8 pages11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 22 PDFSaurav SoniNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument9 pagesEndocrine System•Svbrinv29•No ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument9 pagesThe Endocrine SystemMaisha IslamNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Diet : Thyroid Solution Diet & Natural Treatment Book For Thyroid Problems & Hypothyroidism Revealed!From EverandThyroid Diet : Thyroid Solution Diet & Natural Treatment Book For Thyroid Problems & Hypothyroidism Revealed!Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Thyroid Health: The Thyroid Solution Diet ExposedFrom EverandThyroid Health: The Thyroid Solution Diet ExposedRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- ESS Nile-Case-StudyDocument9 pagesESS Nile-Case-StudyAnika HinkovaNo ratings yet
- Soil Mismanagement Case StudyDocument1 pageSoil Mismanagement Case StudyAnika HinkovaNo ratings yet
- Positive and Negative Feedback WorksheetDocument2 pagesPositive and Negative Feedback WorksheetAnika HinkovaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 QuizDocument3 pagesTopic 1 QuizAnika HinkovaNo ratings yet
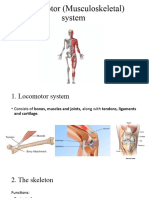
- 9th Grade - Locomotor SystemDocument9 pages9th Grade - Locomotor SystemAnika HinkovaNo ratings yet
- 9th Grade - ImmunityDocument8 pages9th Grade - ImmunityAnika HinkovaNo ratings yet
- 10th Grade - PopulationsDocument10 pages10th Grade - PopulationsAnika HinkovaNo ratings yet
- 10th Grade - Mutations TypesDocument5 pages10th Grade - Mutations TypesAnika HinkovaNo ratings yet
- 1 4-SustainabilityDocument11 pages1 4-SustainabilityAnika HinkovaNo ratings yet
- Test - IB ESS Topic 8 - Human Systems & Resource Use - QuizletDocument4 pagesTest - IB ESS Topic 8 - Human Systems & Resource Use - QuizletAnika HinkovaNo ratings yet
- Topic 2.1 Species and Populations - The Mathematics of Populations - Describing PopulationsDocument8 pagesTopic 2.1 Species and Populations - The Mathematics of Populations - Describing PopulationsAnika HinkovaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 QuizDocument3 pagesTopic 1 QuizAnika HinkovaNo ratings yet
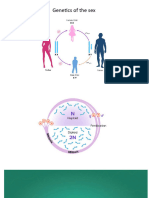
- 10th Grade Genetics of The SexDocument7 pages10th Grade Genetics of The SexAnika HinkovaNo ratings yet