Professional Documents
Culture Documents
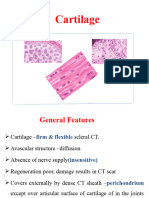
Cartilage
Uploaded by
nyashamukamba150 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views15 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views15 pagesCartilage
Uploaded by
nyashamukamba15Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 15
Cartilage
• It is a tough, slightly flexible, semi-rigid
supporting CN.
• It is capable of withstand mechanical stress.
• These features are due to the type of
extracellular matrix in cartilage.
Functions of cartilage
• Covers surfaces of bones: it has smooth, lubricated
surfaces that facilitates friction free movements at the joints.
• Acts as shock absorbers: the extracellular matrix has
abundant bound water which allows cartilage to act as a
shock absorbers.
• Framework support for softer tissues in the respiratory tract,
ears and nose
2024-04-02 3
Components of cartilage
• Composed of :
a. Cells called chondrocytes which are located
in small cavities called lacunae.
b. Extracellular matrix: secreted by
chondrocytes and consists of:
Connective tissue fibres: are of collagen and elastic
variety.
Ground substance: composed of glycosaminoglycans
(GAG’s) and proteoglycans
Nourishment of cartilage
• Cartilage is avascular (no blood or lymphatic
vessels).
• Chondrocytes receive nutrients by diffusion
from capillaries in surrounding connective
tissue (the perichondrium).
Perichondrium
• It is sheath of dense irregular connective tissue
that covers the cartilage (except fibrocartilage).
• Contains blood vessels that nourish the
chondrocytes.
• Composed of two layers:
The outer fibrous layer: consists of collagen fibres,
fibroblasts, blood & lymphatic vessels.
The inner cellular layer: consists of fibroblasts like cells
chondrogenic cells that can transform to form
chondroblasts (cartilage forming cells).
Perichondrium
Classification of cartilage
• Classified according to types of connective
tissue fibres in the extracellular matrix into:
a. Hyaline cartilage
b. Fibrocartilage
c.Elastic cartilage
a. Hyaline cartilage
• It is the most common cartilage in the body.
• Composed of:
Chondrocytes
Extracellular matrix consisting of :
Collage type II fibres
Ground substances: proteoglycans & glycoproteins
Hyaline cartilage
b. Fibrocartilage
• Found in those areas of the body where great strength
and flexibility are requires e.g. ligament of hip joint.
• Fibrocartilage is not surrounded by perichondrium.
• Nourishment provided by fliuds in joints e.g synovial
fluid.
• Composed of:
Chondrocytes
Extracellular matrix consisting of :
Collage type I fibres
Ground substances: proteoglycans with attached GAG’s that are rich
in chrondroitin sulfate & dermatan sulfate.
Fibrocartilage
c. Elastic cartilage
• It is flexible and is capable of returning to
original size after distension.
• Found in two main locations: auricle of the ear
and the epiglottis of the larynx.
• Composed of:
Chondrocytes
Extracellular matrix consisting of :
A combination of elastic fibres & collage type II fibres
Ground substances: proteoglycans & glycoproteins
You might also like
- 1cartilage DR Amam PDFDocument49 pages1cartilage DR Amam PDFSarfraz Ahmad FaniNo ratings yet
- CartilageDocument26 pagesCartilageAbdi Asiis Omar MohamedNo ratings yet
- Cartilage LectureDocument31 pagesCartilage LecturemalyaaNo ratings yet
- مستند PDF 3Document24 pagesمستند PDF 3alshb7 gamesNo ratings yet
- CartilageDocument1 pageCartilageTarlan SharifiNo ratings yet
- Cartilagedr 190528154146Document30 pagesCartilagedr 190528154146Dr.Aman SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Cartilage (Structure & Types)Document26 pagesCartilage (Structure & Types)muhammadumarnawazsattiNo ratings yet
- Cartilage: Dr. Naglaa BayomyDocument15 pagesCartilage: Dr. Naglaa BayomyAhadNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives Histology of CartilageDocument6 pagesLearning Objectives Histology of CartilageRas WhoknowsmeNo ratings yet
- L10 Cartilage and BoneDocument43 pagesL10 Cartilage and BoneCarinaTingEeNo ratings yet
- Cartilage: Ethel Marie M. Mangada, RMTDocument34 pagesCartilage: Ethel Marie M. Mangada, RMTAesthetics MinNo ratings yet
- CartilageDocument20 pagesCartilageNamra NoorNo ratings yet
- Cartilage and BoneDocument51 pagesCartilage and Bonet_225561332No ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument91 pagesConnective TissueSamuel ArikodNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument51 pagesConnective TissueYIKI ISAACNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Cartilage and JointsDocument52 pagesSeminar On Cartilage and Jointskoyachew abateNo ratings yet
- CartilageDocument5 pagesCartilageFadhil Hussam AhmedNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument41 pagesConnective TissueAstrud LabradorNo ratings yet
- CartilageDocument20 pagesCartilageDoctora NourhanNo ratings yet
- CartilageDocument17 pagesCartilageasadullah2315No ratings yet
- 2 Cartilage and BoneDocument51 pages2 Cartilage and BoneJulia Anne RosalemNo ratings yet
- CartilageDocument37 pagesCartilageFiraol DiribaNo ratings yet
- Histology of Cartilage & Bone: DR Punita Manik Department of Anatomy K G Medical Univesity U P LucknowDocument61 pagesHistology of Cartilage & Bone: DR Punita Manik Department of Anatomy K G Medical Univesity U P LucknowbeylaNo ratings yet
- Cartilage Bone (2566)Document54 pagesCartilage Bone (2566)pachara.p65No ratings yet
- CartilageDocument26 pagesCartilageMaxamed Faarax XaashiNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument65 pagesConnective Tissuesmcm11No ratings yet
- Zoo Lab UwUDocument38 pagesZoo Lab UwUHannah Danniella NapolesNo ratings yet
- Cartilage: Nto, Nto Johnson Department of Anatomy College of Medicine University of Nigeria, Enugu CampusDocument19 pagesCartilage: Nto, Nto Johnson Department of Anatomy College of Medicine University of Nigeria, Enugu CampusEzeah Uzoamaka PerpetualNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue: Dr. Jan Tambayong, PHK Histologi FK-UPHDocument51 pagesConnective Tissue: Dr. Jan Tambayong, PHK Histologi FK-UPHJoshua ObrienNo ratings yet
- Histology of Musculoskeletal ModuleDocument9 pagesHistology of Musculoskeletal Moduledrahmed1028No ratings yet
- Cartilage 2024Document23 pagesCartilage 2024rand200507No ratings yet
- Cartilage Tissue-1Document2 pagesCartilage Tissue-1Muhammet Fatih CantepeNo ratings yet
- Cartilage and Bone: in Vivo, It Fills The Lacunae (Cavities) Where It ResidesDocument5 pagesCartilage and Bone: in Vivo, It Fills The Lacunae (Cavities) Where It ResidesSharon GabrielNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Ayham FaisalDocument7 pagesLab Report Ayham Faisalayham omariNo ratings yet
- Awdal College Department of Health: General HistologyDocument24 pagesAwdal College Department of Health: General HistologyAyro Business CenterNo ratings yet
- Cartilage& BoneDocument61 pagesCartilage& BoneNihal BilalNo ratings yet
- CartilageDocument12 pagesCartilageReycy Ruth Trivino100% (1)
- 4.1 Connective Tissue - SMDocument52 pages4.1 Connective Tissue - SMManjunathNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument49 pagesConnective TissuePaapa MorrisNo ratings yet
- 2024 - Anatomy Histology - Bone and CartilageDocument49 pages2024 - Anatomy Histology - Bone and CartilageSyakir FahmieNo ratings yet
- CartilageDocument11 pagesCartilageAsmita BhattNo ratings yet
- Animal-Human TissuesDocument35 pagesAnimal-Human TissuesAlexander LimNo ratings yet
- Tissues Part 3 of 4Document26 pagesTissues Part 3 of 4Vince Martin ManaigNo ratings yet
- Tissues: Dr. Tanveer Ahmed Khan Lecturer RLCPDocument65 pagesTissues: Dr. Tanveer Ahmed Khan Lecturer RLCPShafaqat Ghani Shafaqat GhaniNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissues Presented By: D F Wangila ConnectiveDocument27 pagesConnective Tissues Presented By: D F Wangila ConnectiveGeorge MunyendoNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue, VnaDocument78 pagesConnective Tissue, Vnavaryvira6677No ratings yet
- EDR Kartilago 2018Document20 pagesEDR Kartilago 2018Artha CimutNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue Yr1Document32 pagesConnective Tissue Yr1aimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue: Cells and Extra-Cellular MatrixDocument82 pagesConnective Tissue: Cells and Extra-Cellular Matrixeyob getachewNo ratings yet
- Seminar ON Connective Tissue: DR - Gowri Arun P.G. Student V.S.D.C.HDocument77 pagesSeminar ON Connective Tissue: DR - Gowri Arun P.G. Student V.S.D.C.HgowriarunNo ratings yet
- Cartilage and Bone 2024-01Document39 pagesCartilage and Bone 2024-01jcrosa137No ratings yet
- Cartilage, Bone and Muscle 2021Document69 pagesCartilage, Bone and Muscle 2021PeachybalmnNo ratings yet
- Tissue Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument35 pagesTissue Anatomy and Physiologysnp88100% (1)
- DMS2 K3 (Kelas A) LECTURE CARTILAGE&BONE2020 PDFDocument67 pagesDMS2 K3 (Kelas A) LECTURE CARTILAGE&BONE2020 PDFdiqa aridaniNo ratings yet
- CartilageDocument7 pagesCartilageDeepashree SahNo ratings yet
- CARTILAGEDocument24 pagesCARTILAGEEdzeal Bruan JrNo ratings yet
- 7 CartilageDocument8 pages7 Cartilagegsyvj97qtdNo ratings yet
- 3b Connective TissueDocument52 pages3b Connective Tissueapi-159564163No ratings yet
- Bones and CartilageDocument69 pagesBones and Cartilagesjs6r8wwv9No ratings yet
- Blood Gas Control - Level 3 (BG Control 3)Document2 pagesBlood Gas Control - Level 3 (BG Control 3)Xuarami Estrada QuintanaNo ratings yet
- Dragon Genetics 2 ProtocolDocument2 pagesDragon Genetics 2 ProtocolSherlini LucmanNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For A Topical Approach To The Developing Person Through The Life Span, 1e Kathleen Stassen BergerDocument18 pagesTest Bank For A Topical Approach To The Developing Person Through The Life Span, 1e Kathleen Stassen BergerNail BaskoNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and EvolutionDocument99 pagesBiodiversity and EvolutionMaria Jamilla R. Pua100% (1)
- Entrance Questions 2079Document9 pagesEntrance Questions 2079Deepak Gharti (Gorkhali)No ratings yet
- Day 4. Assignment. STAAR® Blitz. Science. BiologyDocument2 pagesDay 4. Assignment. STAAR® Blitz. Science. BiologyRaul Ramirez RangelNo ratings yet
- 8 Cold Atmospheric Plasma Restores Tamoxifen Sensitivity in Resistant MCF-7Document11 pages8 Cold Atmospheric Plasma Restores Tamoxifen Sensitivity in Resistant MCF-7Ivan Alves de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Radial Forearm Flap: DR G Avinash Rao Fellow Hand and Microsurgery Skims, SrinagarDocument71 pagesRadial Forearm Flap: DR G Avinash Rao Fellow Hand and Microsurgery Skims, Srinagaravinashrao39No ratings yet
- Bahasa InggrisDocument2 pagesBahasa Inggriskartika candra dewiNo ratings yet
- 2013-MiRNA Regulatory Variation in Human EvolutionDocument9 pages2013-MiRNA Regulatory Variation in Human EvolutionJorge Hantar Touma LazoNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 OrientationDocument13 pagesGeneral Biology 1 OrientationJeM LobiLabNo ratings yet
- Human Organ Systems and Bio Designs - 1: at Myintuition4865Document8 pagesHuman Organ Systems and Bio Designs - 1: at Myintuition48651NC21IS038 POLATHALA MOUNIKANo ratings yet
- Attachment Styles 101 ADocument20 pagesAttachment Styles 101 AGia AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- LP Prof Ed 1 Unit 1Document24 pagesLP Prof Ed 1 Unit 1Jessica CabangunayNo ratings yet
- Bukan Fenomena Semulajadi?: Section ADocument6 pagesBukan Fenomena Semulajadi?: Section ANor HudaNo ratings yet
- SCHEME OF STUDIES B.SC Hons PBGDocument3 pagesSCHEME OF STUDIES B.SC Hons PBGAtif NaeemNo ratings yet
- Bruce Miller-Early Life History of Marine Fishes-University of California Press (2009)Document377 pagesBruce Miller-Early Life History of Marine Fishes-University of California Press (2009)Daniel Fernández100% (3)
- Procedure 3M Petrifilm (Aerobic Count Plate)Document6 pagesProcedure 3M Petrifilm (Aerobic Count Plate)HarryNo ratings yet
- PSSA 2023 Science Grade 8 Item SamplerDocument42 pagesPSSA 2023 Science Grade 8 Item SamplerGayathri SenthilNo ratings yet
- Tachinidae (Diptera) Rearedfromclearwingmothsinslovenia (2007)Document4 pagesTachinidae (Diptera) Rearedfromclearwingmothsinslovenia (2007)Željko PredovnikNo ratings yet
- ZOOPLANKTON SESI II-revDocument106 pagesZOOPLANKTON SESI II-revAnang S100% (2)
- Notes On The Occurrence of Porpita Porpita (Blue Button) From Pulicat LagoonDocument4 pagesNotes On The Occurrence of Porpita Porpita (Blue Button) From Pulicat LagoonresearchinbiologyNo ratings yet
- Na Mlbio Ch11Document36 pagesNa Mlbio Ch11Life with CourteneyNo ratings yet
- The Living World Class 11 Biology Chapter 1Document41 pagesThe Living World Class 11 Biology Chapter 1rajeshwariNo ratings yet
- 06 ANSWERS Remote Learning Worksheets Week 4Document2 pages06 ANSWERS Remote Learning Worksheets Week 4lumujenovicstj4No ratings yet
- Use of English Vocabulary TestDocument5 pagesUse of English Vocabulary Testmary rodchenkoNo ratings yet
- Roland Berger Trend Compendium 2030Document49 pagesRoland Berger Trend Compendium 2030gabrinaNo ratings yet
- International Standard Knowledge Olympiad - Exam Syllabus Eligibility: Class 1-10 Class - 1Document10 pagesInternational Standard Knowledge Olympiad - Exam Syllabus Eligibility: Class 1-10 Class - 1V A Prem KumarNo ratings yet
- Science 9 PeriodicalDocument5 pagesScience 9 PeriodicalJester M. SorianoNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological Universityvifaket581No ratings yet