Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 4
Uploaded by
sattubrar30Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 4
Uploaded by
sattubrar30Copyright:
Available Formats
CONTENT OUTLINE
Networking: Definition
Need of Networking
Types of networking
Types of Networks
University School of Business 1
DEFINITION
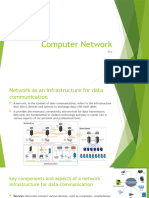
Networking refers to the practice of connecting computers and other
devices together to share resources, information, and services. It enables
communication and data exchange between devices, allowing them to
work together efficiently and effectively. Networking can occur within a
local environment (such as a home or office) or across larger geographic
areas (such as cities, countries, or the entire globe) using various
technologies and protocols.
University School of Business
NEED FOR NETWORKING
• Resource Sharing: Networking allows sharing of hardware resources (printers, scanners) and software
applications across multiple devices, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
• Data Exchange: It enables the sharing of data and information, facilitating collaboration and decision-
making.
• Communication: Networking enables real-time communication through email, messaging, video
conferencing, and voice calls.
• Centralized Management: Networks enable centralized management and control of devices, applications,
and security settings.
• Remote Access: Networking allows remote access to resources and data, enabling users to work from
different locations.
• Efficient Data Storage: Centralized storage systems, like network-attached storage (NAS) and cloud
storage, improve data accessibility and backup.
University School of Business
TYPES OF NETWORKING
1. Local Area Network (LAN):
•A LAN connects devices within a limited geographical area, such as a home,
office, or campus.
•Typically uses Ethernet cables or Wi-Fi for connectivity.
•Designed for high-speed data transfer and resource sharing.
2. Wide Area Network (WAN):
•A WAN spans larger distances, connecting LANs across different locations, cities,
or even countries.
•Utilizes technologies like leased lines, satellites, and routers to establish
connections.
•The Internet is the largest example of a WAN
University School of Business
TYPES OF NETWORKING
3. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN):
•A MAN covers a larger area than a LAN but smaller than a WAN, usually within a city or
metropolitan area.
•Connects multiple LANs or data centers to provide high-speed connectivity.
4. Campus Area Network (CAN):
•A CAN interconnects LANs within a university campus, corporate campus, or similar
environments.
•Provides efficient communication and resource sharing across different buildings or
areas.
5. Personal Area Network (PAN):
•A PAN is the smallest type of network, connecting devices within a person's personal
space, like a smartphone connecting to a smartwatch or headphones.
University School of Business
TYPES OF NETWORKING
• 6. Virtual Private Network (VPN):
• A VPN creates a secure encrypted connection over a public network (e.g., the internet).
• Enables users to access resources and services remotely while maintaining privacy and security.
• 7. Intranet:
• An intranet is a private network within an organization that uses internet technologies for internal communication,
collaboration, and resource sharing.
• 8. Extranet:
• An extranet allows limited external access to certain parts of an organization's intranet, often for partners,
suppliers, or customers.
• 9. Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Network:
• In a P2P network, devices communicate directly with each other without a central server.
• Each device can act as both a client and a server, sharing resources.
• 10. Client-Server Network: - In a client-server network, devices (clients) connect to a central server that
provides resources, services, and data. - Servers manage user authentication, file storage, and application hosting.
University School of Business
TYPES OF NETWORKING
• 11. Cloud Network: - Cloud networking involves connecting devices and services
through the cloud, allowing users to access resources hosted on remote servers.
• 12. Industrial Network: - Industrial networks are used in manufacturing and industrial
environments to connect machines, sensors, and control systems for automation and data
collection.
• 13. Sensor Networks: - Sensor networks consist of interconnected sensors that collect
and transmit data, often used in environmental monitoring and Internet of Things (IoT)
applications.
University School of Business
TYPES OF NETWORKING
• 11. Cloud Network: - Cloud networking involves connecting devices and services
through the cloud, allowing users to access resources hosted on remote servers.
• 12. Industrial Network: - Industrial networks are used in manufacturing and industrial
environments to connect machines, sensors, and control systems for automation and data
collection.
• 13. Sensor Networks: - Sensor networks consist of interconnected sensors that collect
and transmit data, often used in environmental monitoring and Internet of Things (IoT)
applications.
University School of Business
THANKS
University School of Business
You might also like
- Computer NetworksDocument8 pagesComputer NetworksScutelnic VictorNo ratings yet
- NETWORKING FUNDAMENTALS LECTURE 1updatedDocument67 pagesNETWORKING FUNDAMENTALS LECTURE 1updatedDeco SankohNo ratings yet
- Session Four Manging Computer Network TechnologiesDocument53 pagesSession Four Manging Computer Network Technologieshalilmohamed830No ratings yet
- It Era 4Document27 pagesIt Era 4jules200303No ratings yet
- Networking FundamentalsDocument19 pagesNetworking FundamentalsJerald Pacheco JoseNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NetworksDocument3 pagesIntroduction To NetworksMlondi DlaminiNo ratings yet
- MBT 105:online Social Media Marketing: Course Lecturer:Frank Agyemang Duah TTU School of Business ©OCTOBER, 2016Document61 pagesMBT 105:online Social Media Marketing: Course Lecturer:Frank Agyemang Duah TTU School of Business ©OCTOBER, 2016Manuel DivineNo ratings yet
- BBITDocument58 pagesBBITAlvo KamauNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document35 pagesUnit 1trapti191967No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Communication TechnologiesDocument21 pagesChapter 6 Communication TechnologiesTsepiso MohaleNo ratings yet
- Submodule Introduction To Communication NetworksDocument18 pagesSubmodule Introduction To Communication Networksmohamedmwakuzimu9966No ratings yet
- Quarter 1 Week 4 Module 4: Computer Systems Servicing Ncii (TVL-ICT)Document14 pagesQuarter 1 Week 4 Module 4: Computer Systems Servicing Ncii (TVL-ICT)PRESIDENT ELPIDIO QUIRINO NHSNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Computer Networks: File or Data SharingDocument44 pagesAdvantages of Computer Networks: File or Data Sharingdavid100% (1)
- Report Computer NetworkingDocument45 pagesReport Computer NetworkingTayab AbdelrhimNo ratings yet
- Computer-Networks-PPTnchup Bs Na Be BhosdyaDocument20 pagesComputer-Networks-PPTnchup Bs Na Be Bhosdyarohitsalave29No ratings yet
- CiscoDocument10 pagesCiscoEnkh-Amar JanjinbayarNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document65 pagesUnit 3Prabin ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Computer Network & Internet FileDocument32 pagesComputer Network & Internet FileHardeep SInghNo ratings yet
- Types of Network: Dr. Neha Gulati Assistant Professor University Business School Panjab University, ChandigarhDocument15 pagesTypes of Network: Dr. Neha Gulati Assistant Professor University Business School Panjab University, ChandigarhNavneet NandaNo ratings yet
- CSC 325 Exam Question Marking SchemeDocument11 pagesCSC 325 Exam Question Marking SchemeFaisal AliNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkingDocument52 pagesComputer NetworkingTech ProffesorNo ratings yet
- Enterprise NetworkingDocument13 pagesEnterprise NetworkingHoney Sheryl MoralNo ratings yet
- CN 3rd Year Unit 1notes by MasterDocument44 pagesCN 3rd Year Unit 1notes by MasterNikhil kumarNo ratings yet
- UoK - Computer NetWorksDocument18 pagesUoK - Computer NetWorksaqsaanazir12No ratings yet
- Unit 6 NetworkingDocument14 pagesUnit 6 Networkinghasat25701No ratings yet
- Computer Network Unit-1Document55 pagesComputer Network Unit-1Shivam GargNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument10 pagesComputer NetworkRUMAN CHAPAGAINo ratings yet
- NetworkcomputingDocument22 pagesNetworkcomputingKh Aqeel FarooqiNo ratings yet
- NetworksDocument15 pagesNetworksImranNo ratings yet
- Project Report On ComputerNetworkDocument18 pagesProject Report On ComputerNetworkHimangshu Borah100% (1)
- Module 5Document6 pagesModule 5Diestro Lyka Mae L.No ratings yet
- Cape Notes Unit1 Module 2 Content 7Document11 pagesCape Notes Unit1 Module 2 Content 7CrazyCrafterYTNo ratings yet
- hcs135 Introduction To Information Technology Unit 4 Lecture NotesDocument17 pageshcs135 Introduction To Information Technology Unit 4 Lecture NotesDonNo ratings yet
- Unit1 (Chapter 2) INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORKINGDocument17 pagesUnit1 (Chapter 2) INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORKINGVinutha SanthoshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document4 pagesChapter 6sainirajkumar5050No ratings yet
- Management Information System: - Networks and DataDocument40 pagesManagement Information System: - Networks and Datarishisaxena92No ratings yet
- Class-1 (Seema Kujur)Document38 pagesClass-1 (Seema Kujur)Seema KujurNo ratings yet
- Computer Network - Class1 1Document27 pagesComputer Network - Class1 1Bikash KhanalNo ratings yet
- Computer Network Prelim To MidtermDocument33 pagesComputer Network Prelim To MidtermMary JOy BOrjaNo ratings yet
- Purpose: Facilitating Communications. Using A Network, People CanDocument14 pagesPurpose: Facilitating Communications. Using A Network, People CanRevanth RaoNo ratings yet
- DCN Unit 1saqDocument9 pagesDCN Unit 1saqsravan kumarNo ratings yet
- Group of Nodes (Computers and Devices) Interconnected by Transmission MediaDocument14 pagesGroup of Nodes (Computers and Devices) Interconnected by Transmission MediaEdwin BaltizarNo ratings yet
- Computer Network: PropertiesDocument4 pagesComputer Network: Propertiesanup_verma71No ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument99 pagesComputer Networksanju chauhanNo ratings yet
- A Computer Network Is A System of Interconnected CDocument2 pagesA Computer Network Is A System of Interconnected CHaya AiraNo ratings yet
- AI - Lecture 4Document20 pagesAI - Lecture 4darkwaflorence2No ratings yet
- Montfort Computer NetworksDocument21 pagesMontfort Computer Networksrahul guptaNo ratings yet
- LMT - 1 - Introduction To Networks and Networking ConceptsDocument53 pagesLMT - 1 - Introduction To Networks and Networking Conceptslakshay187No ratings yet
- Unit IV Computer Networking Semester IDocument110 pagesUnit IV Computer Networking Semester I2023-SF028 KALAMKAR BHARAT PRAVINID:122BSC-CS0772No ratings yet
- Unit 2Document8 pagesUnit 2Bryan ChenNo ratings yet
- Lesson 25 Network FundamentalsDocument5 pagesLesson 25 Network FundamentalsAssumpta Minette BurgosNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of Computer Network: BITS Edu CampusDocument21 pagesBasic Concept of Computer Network: BITS Edu CampusVipin NagarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Computer NetworkDocument54 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Computer NetworkTom HollandNo ratings yet
- Computer Unit 5Document52 pagesComputer Unit 5Jayesh BoroleNo ratings yet
- Communications and NetworksDocument5 pagesCommunications and NetworksEarl Daniel RemorozaNo ratings yet
- Networking TodayDocument36 pagesNetworking TodayHai Kim SrengNo ratings yet
- Local Area Networking TutorialDocument31 pagesLocal Area Networking Tutorialkumarjit deyNo ratings yet
- Uses For Computer Networks: What Is A Network?Document3 pagesUses For Computer Networks: What Is A Network?RicHArdNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NetworksDocument9 pagesIntroduction To NetworksArchanaa PadmavathiNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingFrom EverandCloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingNo ratings yet
- Stucor Qp-Ec8095Document16 pagesStucor Qp-Ec8095JohnsondassNo ratings yet
- Nfpa 1126 PDFDocument24 pagesNfpa 1126 PDFL LNo ratings yet
- Final Self Hypnosis Paperback For PrintDocument150 pagesFinal Self Hypnosis Paperback For PrintRic Painter100% (12)
- Past Simple Vs Past ContinuousDocument3 pagesPast Simple Vs Past ContinuousNatalia SalinasNo ratings yet
- DS Important QuestionsDocument15 pagesDS Important QuestionsLavanya JNo ratings yet
- Verniers Micrometers and Measurement Uncertainty and Digital2Document30 pagesVerniers Micrometers and Measurement Uncertainty and Digital2Raymond ScottNo ratings yet
- Boarding House Preferences by Middle Up Class Students in SurabayaDocument8 pagesBoarding House Preferences by Middle Up Class Students in Surabayaeditor ijeratNo ratings yet
- June 2017 (IAL) MS - Unit 1 Edexcel Physics A-LevelDocument16 pagesJune 2017 (IAL) MS - Unit 1 Edexcel Physics A-LevelNyraStardollNo ratings yet
- E-Mobility and SafetyDocument77 pagesE-Mobility and SafetySantosh KumarNo ratings yet
- DNA Vs RNA - Introduction and Differences Between DNA and RNADocument10 pagesDNA Vs RNA - Introduction and Differences Between DNA and RNAKienlevyNo ratings yet
- Academic Socialization and Its Effects On Academic SuccessDocument2 pagesAcademic Socialization and Its Effects On Academic SuccessJustin LargoNo ratings yet
- De Thi Chon Hoc Sinh Gioi Cap Tinh Mon Tieng Anh Lop 12 So GD DT Thanh Hoa Nam Hoc 2015 2016Document11 pagesDe Thi Chon Hoc Sinh Gioi Cap Tinh Mon Tieng Anh Lop 12 So GD DT Thanh Hoa Nam Hoc 2015 2016Thuy LinggNo ratings yet
- Amritsar Police StationDocument5 pagesAmritsar Police StationRashmi KbNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For The Psychology of Health and Health Care A Canadian Perspective 5th EditionDocument36 pagesTest Bank For The Psychology of Health and Health Care A Canadian Perspective 5th Editionload.notablewp0oz100% (37)
- Procter and Gamble - MarketingDocument10 pagesProcter and Gamble - MarketingIvana Panovska100% (5)
- Community Architecture Concept PDFDocument11 pagesCommunity Architecture Concept PDFdeanNo ratings yet
- Plain English Part 2Document18 pagesPlain English Part 2ابو ريمNo ratings yet
- Guided-Discovery Learning Strategy and Senior School Students Performance in Mathematics in Ejigbo, NigeriaDocument9 pagesGuided-Discovery Learning Strategy and Senior School Students Performance in Mathematics in Ejigbo, NigeriaAlexander DeckerNo ratings yet
- Project ProposalDocument4 pagesProject Proposaljiaclaire2998100% (1)
- Lesser Known Homoeopathic Medicines of Alopecia Areata.20200718115446Document9 pagesLesser Known Homoeopathic Medicines of Alopecia Areata.20200718115446BruntNo ratings yet
- Benedict Anderson, Imagined CommunitiesDocument2 pagesBenedict Anderson, Imagined CommunitiesMonir Amine0% (1)
- At The Origins of Music AnalysisDocument228 pagesAt The Origins of Music Analysismmmahod100% (1)
- Pelayo PathopyhsiologyDocument13 pagesPelayo PathopyhsiologyE.J. PelayoNo ratings yet
- Women Are Better Managers Than MenDocument5 pagesWomen Are Better Managers Than MenCorazon ValdezNo ratings yet
- EZ Water Calculator 3.0.2Document4 pagesEZ Water Calculator 3.0.2adriano70No ratings yet
- Tyler Nugent ResumeDocument3 pagesTyler Nugent Resumeapi-315563616No ratings yet
- Directorate of Technical Education, Admission Committee For Professional Courses (ACPC), GujaratDocument2 pagesDirectorate of Technical Education, Admission Committee For Professional Courses (ACPC), GujaratgamailkabaaaapNo ratings yet
- Survivor's Guilt by Nancy ShermanDocument4 pagesSurvivor's Guilt by Nancy ShermanGinnie Faustino-GalganaNo ratings yet
- Case 3 SectionC Group 1 (Repaired)Document3 pagesCase 3 SectionC Group 1 (Repaired)SANDEEP AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- Galman V PamaranDocument7 pagesGalman V PamaranChow Momville EstimoNo ratings yet