Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dyno Report
Uploaded by
LAWRENCE KIM N. SACRISTAN0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesDyno Report
Uploaded by
LAWRENCE KIM N. SACRISTANCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Wind Energy
Irinco, Dyno M. (BSEE-4)
Harnessing the Power of the Wind
Wind Energy Overview: A sustainable and renewable source of power
Definition: Wind energy involves capturing the kinetic energy from the wind and
converting it into electricity.
Importance: Reducing carbon footprint, contributing to clean energy goals.
The Mechanics Behind Wind Power
Wind Turbine Components: Advantages:
Blades: Capture the kinetic energy from the wind. Low environmental impact.
Rotor: Transfers the spinning motion to the No greenhouse gas emissions during energy
generator. generation.
Generator: Converts rotational energy into Wind turbines require:
electricity.
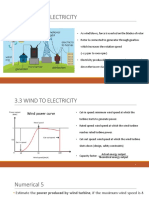
Minimum Turning Speed: 12-14 km/h for turbine
Process: activation.
Wind turns the blades, causing them to spin. Full Capacity Generation: 50-60 km/h ensures
Spinning blades transfer energy to the rotor. maximum electricity production.
Safety Shutdown: Turbines stop beyond 90 km/h to
The rotor’s motion generates electricity in the
prevent damage and ensure safety.
generator.
Pros and Cons of Wind Energy
Benefits: Challenges: Conclusion:
Renewable Resource: Intermittency: Wind is not Wind energy remains a
Wind is an abundant and constant, leading to vital component of
inexhaustible source. variations in energy sustainable energy
Carbon production. solutions.
Footprint
Reduction: Helps combat Initial Costs: High upfront
climate change by investment for installing
producing clean energy. wind turbines.
Low Operating Costs:
Once installed, wind
turbines have minimal
operational expenses.
You might also like
- Wind EnergyDocument63 pagesWind EnergyMUHAMMAD SIDDIQUENo ratings yet
- Windmill Project PDFDocument15 pagesWindmill Project PDFMoazzam AliNo ratings yet
- Alternate Energy Activities: A Look at Wind PowerDocument64 pagesAlternate Energy Activities: A Look at Wind PowerK Venkat EshNo ratings yet
- Wind Power Generation On HighwayDocument34 pagesWind Power Generation On HighwayAvaneesh mishraNo ratings yet
- Wind Energy (DAPINDER)Document24 pagesWind Energy (DAPINDER)Piyush Kumar RaiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electrical Power SystemDocument68 pagesIntroduction To Electrical Power SystemMonirul Islam100% (1)
- EE8611 Mini Project PPT Batch 8Document27 pagesEE8611 Mini Project PPT Batch 839-22-SIVAPRAKASH M-EEENo ratings yet
- Science Fair ProjectDocument10 pagesScience Fair ProjectAhmed SamirNo ratings yet
- Energy PPT (Physics)Document11 pagesEnergy PPT (Physics)phoebe100% (1)
- Project: Wind EnergyDocument3 pagesProject: Wind EnergyDelmy ParNo ratings yet
- Practical 6: Gujarat Technological University Sarvajanik College of Engineering and TechnologyDocument25 pagesPractical 6: Gujarat Technological University Sarvajanik College of Engineering and TechnologyPrashant KalgudeNo ratings yet
- Wind Power GenerationDocument14 pagesWind Power GenerationARSAL HASHMINo ratings yet
- Wind Power Plant Project PDFDocument11 pagesWind Power Plant Project PDFandreeaNo ratings yet
- Wind Energy: Department of Electrical Engineering Laxmi Devi Institute of Engineering & Technology, AlwarDocument29 pagesWind Energy: Department of Electrical Engineering Laxmi Devi Institute of Engineering & Technology, AlwarDileep SinghNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy Notes Form 1 PDFDocument3 pagesNuclear Energy Notes Form 1 PDFryanNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science and Engineering: Page 1 of 2Document2 pagesEnvironmental Science and Engineering: Page 1 of 2Alyssa OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Study of Using Induction Generator in Wind Energy ApplicationsDocument47 pagesStudy of Using Induction Generator in Wind Energy Applicationsمحمد علوانNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electrical Power Systems: by Alebachew TDocument44 pagesIntroduction To Electrical Power Systems: by Alebachew TZerihun PaulosNo ratings yet
- Wind Energy: Process of Wind CreationDocument4 pagesWind Energy: Process of Wind CreationmariyaNo ratings yet
- Rams DraftDocument7 pagesRams DraftSuan, Mike E.No ratings yet
- Lectures 3 To 6 - Module 3Document25 pagesLectures 3 To 6 - Module 3Temp LordNo ratings yet
- Wind PowerDocument40 pagesWind PowerPrajwal ShivareddyNo ratings yet
- Suspended Frictionless Windmill: Presentation OnDocument17 pagesSuspended Frictionless Windmill: Presentation OnShri PatilNo ratings yet
- Wind Energy PresentationDocument12 pagesWind Energy PresentationAtul PandeyNo ratings yet
- CASE 4dinlast.....Document7 pagesCASE 4dinlast.....najpudgeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Wind EnergyDocument13 pagesChapter 4 - Wind EnergyBac NanhNo ratings yet
- Modified Wind TurbineDocument2 pagesModified Wind TurbineUNITED CADDNo ratings yet
- Wind Energy Part IDocument22 pagesWind Energy Part IAli KamranNo ratings yet
- Irjet-Power Generation From Small Wind MillDocument7 pagesIrjet-Power Generation From Small Wind MillAna Beatriz MesquitaNo ratings yet
- Development of Vertical Axis Wind Turbine With Multi-Directional Nozzle-Ijaerdv04i1286697Document7 pagesDevelopment of Vertical Axis Wind Turbine With Multi-Directional Nozzle-Ijaerdv04i1286697MEER MUSTAFA ALINo ratings yet
- Lecture 14 - Wind - Basic and OverviewDocument13 pagesLecture 14 - Wind - Basic and OverviewDanang SuprayogoNo ratings yet
- Hydro Power Plants and Thermal Power PlantsDocument26 pagesHydro Power Plants and Thermal Power PlantsAbhishek KaleNo ratings yet
- Roof TileDocument8 pagesRoof TilejkNo ratings yet
- CH 6Document26 pagesCH 6AbrhaNo ratings yet
- Bladeless Windmill: PC Polytechnic, Mechanical DepartmentDocument21 pagesBladeless Windmill: PC Polytechnic, Mechanical Departmentvaibhav babarNo ratings yet
- Wind Energy PracticalDocument15 pagesWind Energy PracticalMahi MudgalNo ratings yet
- Energy Harvesting PresentationDocument15 pagesEnergy Harvesting PresentationHarsh GautamNo ratings yet
- Introduction - Week 1Document32 pagesIntroduction - Week 1Muhammad SohaibNo ratings yet
- KT3WINDDocument44 pagesKT3WINDAla AwoudaNo ratings yet
- 18ME651 NCES Module-4Document49 pages18ME651 NCES Module-4ShebinNo ratings yet
- 03 Wind PowerDocument71 pages03 Wind PowerMahmoud I. MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Wind EnergyDocument4 pagesWind EnergyAhmed BoumalekNo ratings yet
- Energia EolianaDocument6 pagesEnergia EolianaRazvan ApetriNo ratings yet
- Hydro Power Plants and Thermal Power PlantsDocument32 pagesHydro Power Plants and Thermal Power PlantsAbhishek KaleNo ratings yet
- Tidal Energy: By:-Aahana Solanki 7BDocument8 pagesTidal Energy: By:-Aahana Solanki 7BAahanaNo ratings yet
- Group 8 PresentationDocument53 pagesGroup 8 PresentationMahmoud SaadNo ratings yet
- Offshore Wind and Tidal Hybrid EnergyDocument13 pagesOffshore Wind and Tidal Hybrid EnergyLaurence PoeNo ratings yet
- Final Year Project Mid Presentation: Electricity Generation Through Multi Rotor Wind TurbineDocument13 pagesFinal Year Project Mid Presentation: Electricity Generation Through Multi Rotor Wind TurbineChanna AdnanNo ratings yet
- (Ajay Singh) Review On Control Techniques For VSWT NewDocument6 pages(Ajay Singh) Review On Control Techniques For VSWT NewAjay SinghNo ratings yet
- Swami Keshwanand Institute of Technology, Management and Gramothan, JaipurDocument30 pagesSwami Keshwanand Institute of Technology, Management and Gramothan, JaipurSaloni SharmaNo ratings yet
- Micro WInd TurbineDocument7 pagesMicro WInd Turbinesakale007No ratings yet
- Wind EnergyDocument10 pagesWind Energyاديان بهجتNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Project 1Document20 pagesGroup 4 Project 1Hosna HammoudNo ratings yet
- Power Generation by Stair CaseDocument26 pagesPower Generation by Stair CaseMayur Madhukar MankarNo ratings yet
- Charger WIND POWER PDFDocument17 pagesCharger WIND POWER PDFHassan TalhaNo ratings yet
- Assignment:: International Islamic University IslamabadDocument9 pagesAssignment:: International Islamic University IslamabadAaphiya NasirNo ratings yet
- Alternative Energy LessonDocument15 pagesAlternative Energy LessonTochi Krishna AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Wind Energy FinalDocument11 pagesWind Energy Finalapi-525565425No ratings yet
- Wind TreeDocument18 pagesWind TreeA48Rayan PereiraNo ratings yet
- Small Scale Electricity Generation: Business Advice & Training, #5From EverandSmall Scale Electricity Generation: Business Advice & Training, #5No ratings yet