Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Microsoft ® Encarta ® 2009. © 1993-2008 Microsoft Corporation. All Rights Reserved
Uploaded by
jacob_murilloOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Microsoft ® Encarta ® 2009. © 1993-2008 Microsoft Corporation. All Rights Reserved
Uploaded by
jacob_murilloCopyright:
Available Formats
Casting, process of producing solid objects by pouring molten material into a shaped mold and allowing it to cool.
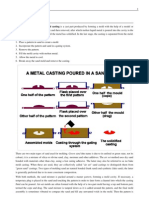
Casting is used to shape such materials as glass and plastics, as well as metals and alloys. The casting of metals has been practiced for more than 6,000 years, using first copper and bronze, then iron, and now alloys of zinc and other metals. The traditional method of casting metal is sand casting. Using a model of the object to be produced, a hollow mold is made in a damp sand and clay mix. Molten metal is then poured into the mold, taking its shape when it cools and solidifies. The sand mold is broken to release the casting. Permanent metal molds called dies are also used for casting, in particular, small items in mass-production processes where molten metal is injected under pressure into cooled dies (see Die-Casting). Continuous casting is a method of shaping slabs or sheets that involves pouring molten metal into the top of a hollow, water-cooled mold of the desired cross section and continuously withdrawing solid metal from the bottom. See Founding. Microsoft Encarta 2009. 1993-2008 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- Casting and Solidification of Molten MetalDocument7 pagesCasting and Solidification of Molten MetalVergara KoyNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metalwork on the Farm - Containing Information on Materials, Soldering, Tools and Methods of Sheet MetalworkFrom EverandSheet Metalwork on the Farm - Containing Information on Materials, Soldering, Tools and Methods of Sheet MetalworkNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing ProcessesDocument29 pagesManufacturing Processesemieel reegisNo ratings yet
- Technical Manual - The Blacksmith and the Welder - June 16, 1941From EverandTechnical Manual - The Blacksmith and the Welder - June 16, 1941No ratings yet
- Process of Jewelry Manufacturing - CastingDocument3 pagesProcess of Jewelry Manufacturing - CastingS Sonia100% (1)
- Hand-Forging and Wrought-Iron Ornamental WorkFrom EverandHand-Forging and Wrought-Iron Ornamental WorkRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- CastingDocument8 pagesCastingTody IsfitazliNo ratings yet
- Forging Operations - Machine Forging, Forging Dies and Special Forging OperationsFrom EverandForging Operations - Machine Forging, Forging Dies and Special Forging OperationsNo ratings yet
- MME 512 Note 1Document36 pagesMME 512 Note 1faithNo ratings yet
- Casting NotesDocument36 pagesCasting NotesAndrews ArunothayanNo ratings yet
- Forging of Iron and Steel - A Text Book for the Use of Students in Colleges, Secondary Schools and the ShopFrom EverandForging of Iron and Steel - A Text Book for the Use of Students in Colleges, Secondary Schools and the ShopNo ratings yet
- Cast Iron (Bollard) Iron: OxygenDocument5 pagesCast Iron (Bollard) Iron: OxygenGeleni Shalaine BelloNo ratings yet
- The Working of Steel: Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelFrom EverandThe Working of Steel: Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelNo ratings yet
- Different Processes of MetalsDocument12 pagesDifferent Processes of MetalsPj AndayaNo ratings yet
- The Home Blacksmith: Tools, Techniques, and 40 Practical Projects for the Blacksmith HobbyistFrom EverandThe Home Blacksmith: Tools, Techniques, and 40 Practical Projects for the Blacksmith HobbyistRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Casting NotesDocument32 pagesCasting NotesGanesh MandpeNo ratings yet
- Mensuration for Sheet Metal Workers - As Applied in Working Ordinary Problems in Shop PracticeFrom EverandMensuration for Sheet Metal Workers - As Applied in Working Ordinary Problems in Shop PracticeNo ratings yet
- Casting and Welding TrainingDocument120 pagesCasting and Welding TrainingMohd SamNo ratings yet
- GTU B. E. Mech Sem V MP II Topic 2 Foundry Technology NeDocument401 pagesGTU B. E. Mech Sem V MP II Topic 2 Foundry Technology NebmdbmdbmdNo ratings yet
- Ingot: Metal CastDocument4 pagesIngot: Metal CastnansaikriNo ratings yet
- Metal CastingDocument44 pagesMetal Castingtitu1993No ratings yet
- Metal CoastingDocument20 pagesMetal CoastingPranay Gaddam0% (1)
- Production TechnologyDocument60 pagesProduction Technology2mohan7100% (2)
- Applications & Processing of Metal AlloysDocument17 pagesApplications & Processing of Metal AlloysSohaibNo ratings yet
- Foundry HandoutDocument3 pagesFoundry Handoutdemmioffixial942No ratings yet
- Found AryDocument401 pagesFound AryVraj PatelNo ratings yet
- Final Metal CastingDocument38 pagesFinal Metal CastingishanNo ratings yet
- Casting Lecture MDDocument46 pagesCasting Lecture MDPAWAN NAITHANINo ratings yet
- Metal Casting Full Lecture NotesDocument51 pagesMetal Casting Full Lecture Notesumarnasar_1987105074% (19)
- Introduction 1.. FoundryDocument112 pagesIntroduction 1.. FoundryDhananjay Shimpi100% (1)
- Pouring of MetalDocument6 pagesPouring of Metalرسول ناصر كريم خريبطNo ratings yet
- Industrial Materials and ProcessesDocument14 pagesIndustrial Materials and ProcessesMNM100% (1)
- FoundryDocument2 pagesFoundryHafiz UdinNo ratings yet
- Metal CastingDocument28 pagesMetal CastingAngel ChanteyNo ratings yet
- Riser Casting ReportDocument47 pagesRiser Casting Reportganesh0% (1)
- Mechanical Process and Allied DefectsDocument17 pagesMechanical Process and Allied DefectsManish SinghNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 6: Casting Is ADocument6 pagesExperiment No. 6: Casting Is AArun kumar rouniyarNo ratings yet
- ME6352 Manufacturing Technolgy: Unit I Casting 8Document54 pagesME6352 Manufacturing Technolgy: Unit I Casting 8Aravind PhoenixNo ratings yet
- Overview of Metal CastingDocument43 pagesOverview of Metal CastingAhmad FaidhiNo ratings yet
- Casting MaterialDocument105 pagesCasting MaterialRoyalmechNo ratings yet
- Course: Metal Casting Module No. 1: INTRODUCTION: Lecture No-2 Terms and Steps in Sand CastingDocument4 pagesCourse: Metal Casting Module No. 1: INTRODUCTION: Lecture No-2 Terms and Steps in Sand CastingRishabh TrivediNo ratings yet
- Cast Iron ProcessDocument10 pagesCast Iron ProcessElvie Rose Imee EscabarteNo ratings yet
- Permanent Mold CastingDocument4 pagesPermanent Mold CastingcpprodNo ratings yet
- Foundery Shop (Ch-6)Document121 pagesFoundery Shop (Ch-6)Shubham VermaNo ratings yet
- Metal Casting Sand Mold Factories Foundries: Sand Casting, Also Known As Sand Molded Casting, Is ADocument16 pagesMetal Casting Sand Mold Factories Foundries: Sand Casting, Also Known As Sand Molded Casting, Is AMuneeb Irfan100% (1)
- Emm 315 Materials Forming Processes - CastingDocument40 pagesEmm 315 Materials Forming Processes - CastingNehemiah LemombianNo ratings yet
- METALWORKINGDocument3 pagesMETALWORKINGIrene FranchinNo ratings yet
- Metal Casting Technology: DR Srinivasan NarayananDocument95 pagesMetal Casting Technology: DR Srinivasan NarayananAkshita MuskanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing TechnologyDocument37 pagesManufacturing TechnologyHoàng MinhNo ratings yet
- Course: Metal Casting: Lecture No-2 Terms and Steps in Sand CastingDocument4 pagesCourse: Metal Casting: Lecture No-2 Terms and Steps in Sand CastingzombieNo ratings yet
- Casting Processes1Document9 pagesCasting Processes1Ahsan RiazNo ratings yet
- Casting Manufacturing Lab ReportDocument16 pagesCasting Manufacturing Lab ReportNiko KoNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Metal Forming Process and Casting ProcessDocument21 pagesDifferences Between Metal Forming Process and Casting ProcessFarhana Eyla75% (4)
- Manufacturing Summaries: Expendable Mold and Permanent MoldDocument4 pagesManufacturing Summaries: Expendable Mold and Permanent MoldSanguinius28No ratings yet
- Sand CastingDocument11 pagesSand CastingdesurkarbNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Casting ProcessDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Casting ProcessMuraliMohan0% (1)
- Types of Castings in Mechanical Engineering: Dharma Maheswara 2 1 0 5 1 4 6 1 9 2 1 3Document12 pagesTypes of Castings in Mechanical Engineering: Dharma Maheswara 2 1 0 5 1 4 6 1 9 2 1 3TM Dharma maheswaraNo ratings yet
- Metal Casting ProcessDocument51 pagesMetal Casting ProcessKamalakanta Sahoo100% (1)
- MetalsDocument3 pagesMetalsjacob_murilloNo ratings yet
- ExtrusionDocument1 pageExtrusionjacob_murilloNo ratings yet
- CorrosionDocument1 pageCorrosionjacob_murilloNo ratings yet
- Odyssey, Ancient Greek Epic Poem in 24 Books Attributed To The Poet Homer. It Was ProbablyDocument1 pageOdyssey, Ancient Greek Epic Poem in 24 Books Attributed To The Poet Homer. It Was Probablyjacob_murilloNo ratings yet
- CorrosionDocument1 pageCorrosionjacob_murilloNo ratings yet
- Static FrictionDocument2 pagesStatic Frictionjacob_murilloNo ratings yet
- A Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersFrom EverandA Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemFrom EverandThe ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemNo ratings yet
- Workbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesFrom EverandWorkbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Guidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsFrom EverandGuidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsNo ratings yet
- Practical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsFrom EverandPractical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsFrom EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Chemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesFrom EverandChemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (14)
- Rules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersFrom EverandRules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- Guidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisFrom EverandGuidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Introduction to Petroleum Process SafetyFrom EverandIntroduction to Petroleum Process SafetyRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- The Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeFrom EverandThe Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Handbook of Fire and Explosion Protection Engineering Principles: for Oil, Gas, Chemical and Related FacilitiesFrom EverandHandbook of Fire and Explosion Protection Engineering Principles: for Oil, Gas, Chemical and Related FacilitiesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Tensor Technology Guide: Tensor Ring Benefits and UsesFrom EverandTensor Technology Guide: Tensor Ring Benefits and UsesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- General Orders for Security Personnel: A Guide to Maintaining Discipline and ProfessionalismFrom EverandGeneral Orders for Security Personnel: A Guide to Maintaining Discipline and ProfessionalismNo ratings yet
- Redefining Work Health and Safety: Systems, Strategies, and Progressive ApproachesFrom EverandRedefining Work Health and Safety: Systems, Strategies, and Progressive ApproachesNo ratings yet
- Plutopia: Nuclear Families, Atomic Cities, and the Great Soviet and American Plutonium DisastersFrom EverandPlutopia: Nuclear Families, Atomic Cities, and the Great Soviet and American Plutonium DisastersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (32)
- Epidemiology and Demography in Public HealthFrom EverandEpidemiology and Demography in Public HealthJaphet KillewoRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)