Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Middle Ages
Uploaded by
frances leana capellan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
199 views9 pagesAfter the Greeks: the Middle Ages science and religion enjoy a long peaceful coexistence Technology is possible with little science, up to a point
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAfter the Greeks: the Middle Ages science and religion enjoy a long peaceful coexistence Technology is possible with little science, up to a point
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
199 views9 pagesThe Middle Ages
Uploaded by
frances leana capellanAfter the Greeks: the Middle Ages science and religion enjoy a long peaceful coexistence Technology is possible with little science, up to a point
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
After the Greeks:
the Middle Ages
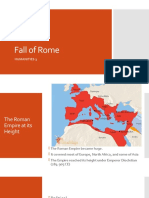
After Alexander (334-323
The Romans BC), Greek empire
flourishes for a while
Greece slowly declines as
Rome expands its empire
Empire completes conquest
of Britain, W. Europe, N.
Africa and Asia Minor
(Turkey) by about 180 AD
The Romans
Though victorious, Rome embraces Greek
learning while contributing little to natural
science
Other than compiling, popularizing, translating
Exceptions: engineering, city planning, war,
surgery and medicine
Other contributions: law, administration
Decline of Rome
Frominternal strife, barbarian attacks,
empire dead by ~500 AD
Other factors: Christians? lead poisoning?
Huns, Vandals, Goths etc. run around in
W. Europe, leaving path of destruction
Science grinds to a halt: The Dark Ages
InWest, learning confined to the Church
China, India, Middle East prospers
Science in the Middle Ages (500-1400)
Alchemy, medicine
Math (algebra)
Monasteries: Botany, agriculture
Architecture – castles, churches
New Tech in the Middle Ages
Heavy plow → farming in hard soil
Stirrup → feudalism?
Horizontal loom → computers
Soap, toilets
Paper (from China)
Ship rudder
Major Events
Crusades (11th-13thC): cultural exchange through war
Plagues: social equalizer; fatalism, labor shortage?
1066 Norman invasion of England → English
Language (Old English of barbarians + Old French)
The first universities
First
in Middle East, then Bologna (1119)
Secular, creates demand for books, lecturers
Subjects: Grammar, Latin, Greek, and Rhetoric
Celebs of the Middle Ages
AlRazi (~900), Avicenna (~1000), Averroes
(~1150): medicine, math
Al-Khwarizmi: math, optics
Charlemagne (~850) – initiated a short-lived
renaissance in W. Europe
St. Thomas Aquinas (~1200) – settled
philosophical issues between church and
society, science and religion
Any women? Hildegarde von Bingen (~1100)
Doctor, pharmacist, composer; gravitation?
Final Notes about the Middle Ages
Science and religion enjoy a long peaceful
coexistence
Technology is possible with little science,
up to a point
The West has no monopoly over science
You might also like
- 1-999 AD World History Events & PeopleDocument7 pages1-999 AD World History Events & PeopleNolaNo ratings yet
- Middle AgesDocument34 pagesMiddle AgesJose M AriasNo ratings yet
- Brief History of Europe - Print Version - Wikibooks, Open Books For An Open WorldDocument46 pagesBrief History of Europe - Print Version - Wikibooks, Open Books For An Open WorldCarlos Piña LópezNo ratings yet
- Anatolian Pontian GenocideDocument45 pagesAnatolian Pontian GenocideAnonymous Pu2x9KV100% (1)
- World Literature Periods Early Periods oDocument6 pagesWorld Literature Periods Early Periods oTristan Cooke100% (1)
- Literary PeriodsDocument6 pagesLiterary PeriodsHaleema Khalid100% (1)
- A Overview of Greek HistoryDocument19 pagesA Overview of Greek Historynetname1100% (1)
- Architectural Thesis ProposalDocument26 pagesArchitectural Thesis Proposalfrances leana capellan85% (67)
- The Fall of The Roman Empire and The Early Middle Ages in Europe and BritainDocument4 pagesThe Fall of The Roman Empire and The Early Middle Ages in Europe and Britainyacine1734No ratings yet
- Globalization Europe Ge3Document22 pagesGlobalization Europe Ge3Mhera MaturgoNo ratings yet
- HistoryDocument7 pagesHistoryAjay PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Edget Chora Secondary and Preparatory School History Handout, Chapter 4 and 5 For Grade 9 Students, 2013 E.CDocument10 pagesEdget Chora Secondary and Preparatory School History Handout, Chapter 4 and 5 For Grade 9 Students, 2013 E.Cme addisNo ratings yet
- Edition. London and New York: Routledge, 1-11Document13 pagesEdition. London and New York: Routledge, 1-11Floor RoeterdinkNo ratings yet
- The Start of The Middle AgesDocument10 pagesThe Start of The Middle AgesalbertohernandezwilsonNo ratings yet
- World History Final Exam Survival Guid1e RevisedDocument6 pagesWorld History Final Exam Survival Guid1e RevisedBrianna HufferNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Ιστορία Ευρώπης τον ΜεσαίωναDocument26 pages3.1 Ιστορία Ευρώπης τον ΜεσαίωναΔέσποινα ΝικολάουNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Ahsan Khalid 46732 Today's Activity: 7 of April'2020Document2 pagesMuhammad Ahsan Khalid 46732 Today's Activity: 7 of April'2020Ahsan KhalidNo ratings yet
- 3 Middle AgesDocument18 pages3 Middle AgesdnmnozeNo ratings yet
- Starting Around 1200 BCDocument2 pagesStarting Around 1200 BCLaleth Mendoza OjalesNo ratings yet
- Early-Periods-Of-Literature 20240207 104818 0000Document7 pagesEarly-Periods-Of-Literature 20240207 104818 0000jacqui Lei BarrettoNo ratings yet
- Early Medieval TimesDocument18 pagesEarly Medieval TimesAndres BrutasNo ratings yet
- History Lesson Note For Grade 9Document7 pagesHistory Lesson Note For Grade 9Kalkidan KebedeNo ratings yet
- Ancient History OverviewDocument2 pagesAncient History OverviewOstonal, Marco O.No ratings yet
- The Fall of Rome and The Beginning of The Middle AgesDocument53 pagesThe Fall of Rome and The Beginning of The Middle AgesJames WitcombeNo ratings yet
- The Second Rome: Byzantine Empire His 101 - Week 4Document30 pagesThe Second Rome: Byzantine Empire His 101 - Week 4aaazad22No ratings yet
- Medieval Church's Rise After Rome's FallDocument51 pagesMedieval Church's Rise After Rome's FallJustus GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Middle Age TimelineDocument4 pagesMiddle Age TimelineShanzaNo ratings yet
- European HistoryDocument8 pagesEuropean HistoryNaeem BaigNo ratings yet
- Medieval Europe HistoryDocument3 pagesMedieval Europe HistorySVPSNo ratings yet
- Europe: DemonymDocument6 pagesEurope: DemonymShaikh ShakeebNo ratings yet
- World CivilizationsDocument3 pagesWorld CivilizationsJaya ShankarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Electromagnetic Induction 2Document22 pagesChapter 11 - Electromagnetic Induction 2oystersauceeeeeNo ratings yet
- CRS Unit 0Document2 pagesCRS Unit 0zachNo ratings yet
- Module 2 (Ancient, Middle, Modern Phil Inventions) ReportpresentationDocument10 pagesModule 2 (Ancient, Middle, Modern Phil Inventions) ReportpresentationAbe BautistaNo ratings yet
- Second Year English L.M.D. Classes: Initiation To Civilization (ICL)Document14 pagesSecond Year English L.M.D. Classes: Initiation To Civilization (ICL)Yana RbNo ratings yet
- Literary Periods & MovementsDocument26 pagesLiterary Periods & MovementsChihaya AyaseNo ratings yet
- History of West-WPS OfficeDocument74 pagesHistory of West-WPS OfficenazmeenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 The Greeks (History of Western Civilization) - 2Document31 pagesChapter 3 The Greeks (History of Western Civilization) - 2bc190405823No ratings yet
- History of Western Civilization WikipediaDocument74 pagesHistory of Western Civilization WikipedianazmeenNo ratings yet
- The Historical Background of English Literature.Document1 pageThe Historical Background of English Literature.Arvin MarianoNo ratings yet
- A.P. World History Urban Revival and The Renaissance!Document27 pagesA.P. World History Urban Revival and The Renaissance!Aaron Manuel MunarNo ratings yet
- Crime and Punishment in Ancient Greece and Rome: The University of Western OntarioDocument37 pagesCrime and Punishment in Ancient Greece and Rome: The University of Western OntarioJack SummerhayesNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Medieval ScienceDocument14 pagesFoundations of Medieval ScienceMargareth RiveraNo ratings yet
- Timeline of Major Events in WestDocument2 pagesTimeline of Major Events in WestMohit JindalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.1 Historical TrajectoryDocument4 pagesLesson 2.1 Historical TrajectoryCheska VNo ratings yet
- Units 1&2 Med PerspectiveDocument5 pagesUnits 1&2 Med PerspectiveCosminMarinNo ratings yet
- Fall of RomeDocument19 pagesFall of RomeNeha PradhanNo ratings yet
- History Timeline Guide to Prehistoric, Ancient, Medieval & Renaissance ErasDocument28 pagesHistory Timeline Guide to Prehistoric, Ancient, Medieval & Renaissance ErasFlorina FloNo ratings yet
- Editedearlyeuropeanliterature 120904083525 Phpapp01 PDFDocument31 pagesEditedearlyeuropeanliterature 120904083525 Phpapp01 PDFjoemari sardaNo ratings yet
- Good Morning!Document31 pagesGood Morning!joemari sardaNo ratings yet
- Middle Ages: The Holy Roman EmpireDocument7 pagesMiddle Ages: The Holy Roman Empireratheesh1981No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - History Christian ApologeticsDocument14 pagesChapter 3 - History Christian Apologeticszerubabel AbebeNo ratings yet
- Perforance Task in Reigion - Bongais, Jeanrynne - Bsn4aDocument20 pagesPerforance Task in Reigion - Bongais, Jeanrynne - Bsn4aJean Rynne Barrameda BongaisNo ratings yet
- eskimo adventureDocument12 pageseskimo adventurenicoleagustinasalazarporcelNo ratings yet
- I Short Question and Answers:-: Medieval Europe - Christianity and The Roman Church History Chapter - 2Document6 pagesI Short Question and Answers:-: Medieval Europe - Christianity and The Roman Church History Chapter - 2Ronnith NandyNo ratings yet
- Western World: Occidens, "Sunset, West"), in Contrast To The Orient (FromDocument35 pagesWestern World: Occidens, "Sunset, West"), in Contrast To The Orient (FromFiruzaNo ratings yet
- Literary Periods & GenresDocument7 pagesLiterary Periods & GenresAtheefa NazlieNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of Western CultureDocument4 pagesA Brief History of Western CultureEmile Bou HaydarNo ratings yet
- Literary Periods & Genres - English Literature - LibGuides at Mississippi College-Leland Speed LibraryDocument6 pagesLiterary Periods & Genres - English Literature - LibGuides at Mississippi College-Leland Speed Librarybaidy diaNo ratings yet
- The MEGA Study GuideDocument13 pagesThe MEGA Study GuidehollymetzgerNo ratings yet
- Geology Reviewer On "Bagyo and Earthquakes"Document91 pagesGeology Reviewer On "Bagyo and Earthquakes"frances leana capellanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Why They Take Place (Module 7) & Rates of Chemical Reactions (Module 8)Document11 pagesChemical Reactions and Why They Take Place (Module 7) & Rates of Chemical Reactions (Module 8)frances leana capellanNo ratings yet
- Stoy Key Ah' Ma TreeDocument15 pagesStoy Key Ah' Ma Treefrances leana capellanNo ratings yet
- Properties of Matter in BulkDocument18 pagesProperties of Matter in Bulkfrances leana capellanNo ratings yet
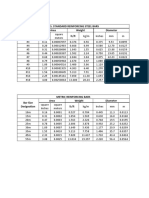
- Standard Rebar SizesDocument1 pageStandard Rebar Sizesfrances leana capellanNo ratings yet
- Geology Reviewer: PaleontologyDocument92 pagesGeology Reviewer: Paleontologyfrances leana capellanNo ratings yet
- Module 9 10Document9 pagesModule 9 10frances leana capellanNo ratings yet
- Demystifying The Emf MythDocument56 pagesDemystifying The Emf Mythfrances leana capellan100% (1)
- The RenaissanceDocument13 pagesThe Renaissancefrances leana capellan100% (1)
- Up Parish of Holy SacrificeDocument6 pagesUp Parish of Holy Sacrificefrances leana capellanNo ratings yet
- Up Parish of Holy SacrificeDocument6 pagesUp Parish of Holy Sacrificefrances leana capellanNo ratings yet
- Com 140 Report - EditedDocument32 pagesCom 140 Report - Editedfrances leana capellanNo ratings yet
- Re-Lighting The JeepneyDocument4 pagesRe-Lighting The Jeepneyfrances leana capellanNo ratings yet
- The EarthDocument28 pagesThe Earthfrances leana capellan100% (1)
- GE11 Assignment 1Document1 pageGE11 Assignment 1frances leana capellanNo ratings yet
- The Origin of LifeDocument9 pagesThe Origin of Lifefrances leana capellanNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Inequalities - ExampleDocument2 pagesQuadratic Inequalities - Examplefrances leana capellanNo ratings yet
- Science of LoveDocument36 pagesScience of Lovefrances leana capellanNo ratings yet
- Science and Non-ScienceDocument28 pagesScience and Non-Sciencefrances leana capellanNo ratings yet
- Science and Sports PresDocument26 pagesScience and Sports Presfrances leana capellan100% (1)
- Science of BeautyDocument28 pagesScience of Beautyfrances leana capellan100% (1)
- History of Science-1Document23 pagesHistory of Science-1frances leana capellanNo ratings yet
- Origin of The Universe-1Document17 pagesOrigin of The Universe-1frances leana capellanNo ratings yet
- Quadratic InequalitiesDocument2 pagesQuadratic Inequalitiesfrances leana capellanNo ratings yet
- Human Evolution - NewDocument27 pagesHuman Evolution - Newfrances leana capellanNo ratings yet
- 21 Feb - QuizDocument1 page21 Feb - Quizfrances leana capellanNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationsDocument1 pageQuadratic Equationsfrances leana capellanNo ratings yet
- What Is Science?: The First Scientist The Practice of Science Science in The PhilippinesDocument13 pagesWhat Is Science?: The First Scientist The Practice of Science Science in The Philippinesfrances leana capellanNo ratings yet