Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MAGLALANG, Ivabradine
Uploaded by
Jessica Christel MaglalangCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MAGLALANG, Ivabradine
Uploaded by
Jessica Christel MaglalangCopyright:
Available Formats
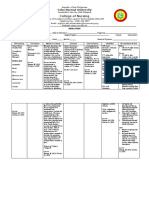
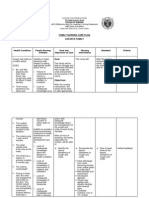
Ivabradine Classification: antianginal agent Drug Action: acting by selective and specific inhibition of the cardiac pacemaker; controls
the spontaneous diastolic depolarisation in the sinus node and regulates heart rate. The cardiac effects are specific to the sinus node with no effect on intra-atrial, atrioventricular or intraventricular conduction times, nor on myocardial contractility or ventricular repolarisation Indication/s: This medication is a cardiotonic agent, prescribed for angina pectoris. It helps to lower the heart rate Contraindication/s: Contraindicated in patients with severe heart disease, and hypersensitivity. It should not be administered along with calcium channel blockers. Adverse Reaction/s: Heart - Slow heart rate, palpitations, heart block, abnormal heart rhythm, difficulty in breathing and fainting. Central Nervous System - Headache, and dizziness. Eye - Blurred vision. Gastrointestinal - Nausea, vomiting and constipation. Blood -
Eosinophilia. Musculoskeletal - Muscle cramps and muscle weakness. Nursing Responsibilities: 1) Monitor BP and pulse before therapy, during dosage titration, and periodically throughout therapy. 2) Assess for signs of CHF (peripheral edema, crackles, dyspnea, weight gain, jugular venous distention). 3) Angina: Assess location, duration, intensity and precipitating factors of patient's anginal pain. 4) Hypertension: Check frequency of refills to monitor adherence. 5) Monitor serum potassium periodically. Hypokalemia increases the risk of arrhythmias and should be corrected.
You might also like
- Verapamil HCLDocument3 pagesVerapamil HCLMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- IrbesartanDocument3 pagesIrbesartanapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument1 pageDrug StudycliffordbuenoNo ratings yet
- Drug study cilostazol intermittent claudicationDocument2 pagesDrug study cilostazol intermittent claudicationart_mutantNo ratings yet
- AripiprazoleDocument2 pagesAripiprazoleKrisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Final Magnesium SulfateDocument3 pagesFinal Magnesium SulfateGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- CoversylDocument3 pagesCoversylianecunarNo ratings yet
- Drug Analysis: Malaise, Fatigue, Dizziness, Tremors, AtaxiaDocument2 pagesDrug Analysis: Malaise, Fatigue, Dizziness, Tremors, AtaxiaFerdinand Sherwin MorataNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Stugeron and Kalium DuruleDocument1 pageDrug Study Stugeron and Kalium DuruleawesomedawnNo ratings yet
- Felodipine CefuroximeDocument3 pagesFelodipine CefuroximecotyboyNo ratings yet
- KaliumDocument2 pagesKaliumJustine Kaye Iballa HarligaNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Administration Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageDrug Name Mechanism of Action Administration Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesIvan Liquiran AvenadoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ICUDocument5 pagesDrug Study ICUEcko MoawiaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Table 3Document5 pagesDrug Study Table 3Juliet De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ON Atropine Sulfate: Maa Tripura College of Nursing, Jhabua (M.P.)Document3 pagesDrug Study ON Atropine Sulfate: Maa Tripura College of Nursing, Jhabua (M.P.)amitNo ratings yet
- NCP KateDor NewDocument6 pagesNCP KateDor NewSteffi GolezNo ratings yet
- Isosorbide nitrates guide for angina reliefDocument2 pagesIsosorbide nitrates guide for angina reliefSNo ratings yet
- Nifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyDocument5 pagesNifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyAllyne GavinoNo ratings yet
- F. Case Study Thesis-Drug Study (Revised)Document5 pagesF. Case Study Thesis-Drug Study (Revised)Lopirts NiganiNo ratings yet
- 13 DexamethasoneDocument2 pages13 DexamethasoneKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- As Pi LetDocument7 pagesAs Pi Letianecunar100% (1)
- Enoxaparin (Lovenox)Document1 pageEnoxaparin (Lovenox)ENo ratings yet
- FluconazoleDocument3 pagesFluconazoleMary Kate ClarosNo ratings yet
- Digoxin (Lanoxin) Dosage, Mechanism of Action, Indications and Nursing ConsiderationsDocument2 pagesDigoxin (Lanoxin) Dosage, Mechanism of Action, Indications and Nursing ConsiderationsRaidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Drug - Htm#description.: Reference: Submitted By: Date Submitted: Submitted ToDocument2 pagesDrug - Htm#description.: Reference: Submitted By: Date Submitted: Submitted ToSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- DantriumDocument2 pagesDantriumAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Discharge Instructions For Lap CholeyDocument1 pageDischarge Instructions For Lap CholeyAnne Marie Angelica BilonoNo ratings yet
- SeroquelDocument2 pagesSeroqueldanaNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Carnicor Generic Name: L-Carnitine Indications: Chronic Myocardia IschemiaDocument2 pagesBrand Name: Carnicor Generic Name: L-Carnitine Indications: Chronic Myocardia Ischemiaianecunar100% (1)
- Clonidine (Catapres)Document2 pagesClonidine (Catapres)Vianca Louriele LavarroNo ratings yet
- Drug Study InsulinDocument2 pagesDrug Study InsulinGrant Kenneth Dumo AmigableNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyXio PauNo ratings yet
- AztreonamDocument2 pagesAztreonamHannahShaeHayesNo ratings yet
- Glipizide Glucotrol XL Drug CardDocument1 pageGlipizide Glucotrol XL Drug CardSheri490No ratings yet
- EsmololDocument2 pagesEsmololtherock316_995149No ratings yet
- Drug Name Mecahnism of Action Indication Side Effects Generic NameDocument2 pagesDrug Name Mecahnism of Action Indication Side Effects Generic NamehahahaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study LosartanDocument2 pagesDrug Study LosartanIris BalinoNo ratings yet
- Vitamin KDocument2 pagesVitamin KMuvs RazonNo ratings yet
- Drug Action Indication/Contraindicatio N Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument6 pagesDrug Action Indication/Contraindicatio N Nursing ResponsibilitiesBryan BosqueNo ratings yet
- Drug Study2Document8 pagesDrug Study2zbestgurlNo ratings yet
- Therabloc Antihypertensive Drug Atenolol Side Effects and Nursing ConsiderationsDocument2 pagesTherabloc Antihypertensive Drug Atenolol Side Effects and Nursing ConsiderationsMsOrangeNo ratings yet
- Drug study on Isosorbide mononitrateDocument1 pageDrug study on Isosorbide mononitratemarsh155No ratings yet
- Drug Study QIDocument8 pagesDrug Study QImaeDonitaNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityShiva TorinsNo ratings yet
- Check The Physician's Observe and Follow The 14 Warn The Mother AboutDocument2 pagesCheck The Physician's Observe and Follow The 14 Warn The Mother AboutJust nowNo ratings yet
- Amiodarone Hydro ChlorideDocument4 pagesAmiodarone Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Anti-Diabetic Drug Vildagliptin: Mechanism, Indication, Side Effects and Nursing CareDocument2 pagesAnti-Diabetic Drug Vildagliptin: Mechanism, Indication, Side Effects and Nursing CareChris Denver BancaleNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyArnel MacabalitaoNo ratings yet
- HypertensiveDocument2 pagesHypertensiveReinhard Lumbag PacitengNo ratings yet
- Imdur for Angina Relief in 60 SecondsDocument23 pagesImdur for Angina Relief in 60 SecondsJoyce Anne SupnetNo ratings yet
- Creatin. Creatin. Creatin. Creatin. Creatin. CreatinDocument2 pagesCreatin. Creatin. Creatin. Creatin. Creatin. CreatinEna PaparićNo ratings yet
- Piperacillin-Tazobactam AntibioticDocument9 pagesPiperacillin-Tazobactam Antibiotic배기숭No ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument7 pagesEmergency Drugspraiseiswhatido9440No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyMaurence John Feliciano LuluquisenNo ratings yet
- Pharmacologic: Cardiovascular: FlushingDocument2 pagesPharmacologic: Cardiovascular: Flushingitsmeaya100% (5)
- Cardiovascular Agents: Florianne E. Adlawan, R.NDocument31 pagesCardiovascular Agents: Florianne E. Adlawan, R.NadlawanflorianneNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Agent: Prof. Clement Belvis RN, RM, MPHDocument86 pagesCardiovascular Agent: Prof. Clement Belvis RN, RM, MPHEimhie Lee CasiNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY SUMMARYDocument7 pagesDRUG STUDY SUMMARYEloisa Abarintos RacalNo ratings yet
- IV Abra DineDocument1 pageIV Abra DineYel MValinNo ratings yet
- Cardio DrugsDocument68 pagesCardio DrugsIconMaicoNo ratings yet
- Managing Depression and Suicide in Non-Psychiatric SettingsDocument4 pagesManaging Depression and Suicide in Non-Psychiatric SettingsJessica Christel MaglalangNo ratings yet
- Group Psychotherapy and Existential Concerns: An Interview With Irvin YalomDocument14 pagesGroup Psychotherapy and Existential Concerns: An Interview With Irvin YalomJessica Christel MaglalangNo ratings yet
- N 207 Unit Exam II Part 1Document9 pagesN 207 Unit Exam II Part 1Jessica Christel MaglalangNo ratings yet
- MH FaciltiiesDocument1 pageMH FaciltiiesJessica Christel MaglalangNo ratings yet
- King's Goal Attainment TheoryDocument76 pagesKing's Goal Attainment TheoryJessica Christel Maglalang100% (3)
- Code of Ethics for Filipino NursesDocument2 pagesCode of Ethics for Filipino NursesJessica Christel MaglalangNo ratings yet
- MAGLALANG, FurosemideDocument2 pagesMAGLALANG, FurosemideJessica Christel MaglalangNo ratings yet
- MAGLALANG, FurosemideDocument2 pagesMAGLALANG, FurosemideJessica Christel MaglalangNo ratings yet
- Maglalang, TramadolDocument2 pagesMaglalang, TramadolJessica Christel MaglalangNo ratings yet
- FNCP1Document8 pagesFNCP1Jessica Christel MaglalangNo ratings yet
- Using computers to enhance learning skillsDocument9 pagesUsing computers to enhance learning skillsJessica Christel MaglalangNo ratings yet
- Face PaintingDocument1 pageFace PaintingJessica Christel MaglalangNo ratings yet
- Substance AbuseDocument24 pagesSubstance AbuseJessica Christel MaglalangNo ratings yet
- AsdfghjklDocument1 pageAsdfghjklJessica Christel MaglalangNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT #5 COLLOIDS: PROPERTIES AND PREPARATIONDocument6 pagesEXPERIMENT #5 COLLOIDS: PROPERTIES AND PREPARATIONJessica Christel MaglalangNo ratings yet