Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EMMI Manual
EMMI Manual
Uploaded by
Srivatsa MadhaliCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EMMI Manual
EMMI Manual
Uploaded by
Srivatsa MadhaliCopyright:
Available Formats
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING III
RD
SEMESTER ELECTRICAL
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 1
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR
Department Of Electrical Engineering
III
RD
Sem Electrical Engg.
Electrical Measurement & Measuring Instruments Lab
________________________________________________________________________
INDEX
Sr.
No.
Name of Experiment Page No.
1 Measurement of medium resistance by using
Voltmeter Ammeter method.
02
2 Measurement of medium resistance by using
Wheatstones bridge.
04
3 Measurement of high resistance by using loss of
charge method.
07
4 Measurement of low resistance by using Kelvins
double bridge.
09
5 Measurement of unknown inductance by using
Hays bridge.
12
6 Measurement of unknown inductance by using
Owens bridge.
15
7 Measurement of unknown inductance by using
Maxwell bridge.
17
8 Measurement of unknown capacitance by Desauty
bridge.
20
9 Measurement of unknown capacitance by Schering
bridge.
22
10 Measurement of 3-phase power by the one-
watt meter method.
24
11 Measurement of 3-phase power by the two-watt
meter method.
26
12 Measurement of Reactive power in 3- phase circuit
by Wattmeter method.
28
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING III
RD
SEMESTER ELECTRICAL
1
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 2
Experiment No-01
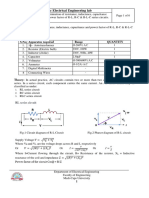
Aim:- Measurement of medium resistance by the Voltmeter , Ammeter method.
Apparatus:- DC ammeter(0-50mA)
DC Voltmeter (0-50V)
Dc power supply (0-30V)
Variable Resistance -100 ohm.
Connecting wires.
Circuit Diagram:-
V
A
V
A
(0-30v)
(0-50mA)
R
+
_
(0-30v)
(0-50mA)
(0-50v)
R
+ - -
+
-
(0-50V)
100 Ohm
100
Ohm
Fig.(1) Fig. (2)
Theory: -
Two types of the connections are done in this method. Ammeter voltmeter
method is shown in the figure (2) voltmeter and ammeter are connected in series, where
ammeter measures the total current flowing through the circuit and voltmeter measures
the voltage across the unknown resistance .The voltmeter should have ideally infinite
resistance and ammeter should have ideally zero resistance so that it will measure total
current flowing through the unknown resistance. But practically it is not possible and
measured value Rm of the resistance is the sum of resistance of ammeter and actual
resistance.
Rm =R
1
+Ra
Where
R
1
=Actual resistance.
Ra=Resistance of the ammeter.
It is clear from the expression that the value of measured resistance is equal to actual
resistance when ammeter has zero resistance.
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING III
RD
SEMESTER ELECTRICAL
1
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 3
Observation Table:-
For CASE 1 voltmeter Ammeter Method
Voltage (volt) Current (Amp) Resistance
(calculated)
Resistance
(measured)
For CASE 2 Ammeter voltmeter Method
Voltage (volt) Current (Amp) Resistance
(calculated)
Resistance
(measured)
Procedure:-
1) Make the connections as per circuit diagram.
2) Switch on the supply and note down the readings of ammeter and voltmeter.
3) Calculate the value of the unknown resistance by ohms low.
4) Perform the procedure for the other case similarly.
Result: - Hence the measured value of the unknown resistance is
found to be _________.
Viva Questions:-
1) What are the other methods of measurement of medium resistance?
2) What are the disadvantages of this method?
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING III
RD
SEMESTER ELECTRICAL
1
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 4
Experiment No.-02
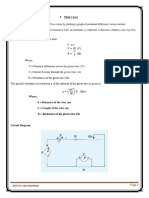
Aim: - Measurement of the medium resistance by using wheatstone bridge.
Apparatus: -
Power supply (0-32V D.C)
Resistor: - R
1
=1K, R
X
=1K, R
3
=1K, R
4
=10K.
Unknown resistor=100,
Wheatstone bridge kit.
Digital multimeter-1no,
Patch chords.
Circuit Diagram:-
G
R3
R1
R4
Rx
0-32v
a
b
c
d
I1
I2
I3
I4
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING III
RD
SEMESTER ELECTRICAL
1
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 5
Theory-
Wheat stones bridge is very important device used in the measurement of medium
resistances. It is an accurate and reliable instrument .The wheat stone bridge is an
instrument based on the principle of null indication and comparison measurements .
The basic circuit of a wheat stone bridge is shown in fig . it has four resistive
arms, consisting of resistances R
1
,R
X
,R
3
and R
4
together with a source of emf and a null
detector , usually a galvanometer G or other sensitive current meter is used. The bridge is
said to be balanced when there is no current through the galvanometer or when the
potential difference across the galvanometer is zero. This occurs when the voltage from
point a to point d equals the voltage from point d to point b or by referring to other
battery terminal, when the voltage from point a to point c equals the voltage from
point c to point b.
For bridge balance;
I
1
=I
3=
E/(R
1
+R
3
) (1)
I
2
=I
4
=E/(R
X
+R
4
) (2)
E=emf of battery.
Combining equ (1) and (2) we get
R
X
*R
3
=R
1
*R
4
OR
R
X
=(R
1
*R
4
)/R
3
Where R
X
is the unknown resistance, R
1
, R
3
and R
4
are called the ratio arms.
Observation Table: -
Ratio Arm
Resistor
Std. Arm
Resistor
Measured Rx Calculated
Rx
R
1
R
3
R
4
Procedure: -
1) Connect the patch chords as per the circuit diagram.
2) Note the resistance of R
1
,R
4
and R
3
using multimeter.
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING III
RD
SEMESTER ELECTRICAL
1
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 6
3) Switch on the power supply and adjust the resistance R4 such that galvanometer
shows the zero deflection.
4) Disconnect the supply & measure the value of R
X
.
5) Now calculate the value of unknown Resistor R, Using formula
Rx=(R
1
*R
4
)/R
3
.
Result:- Unknown Resistance found to be __________.
Viva Questions: -
1) What are the other methods used for measurement of medium resistance?
2) Why we use this method for measurement of medium resistance?
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING III
RD
SEMESTER ELECTRICAL
1
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 7
Experiment No-03
Aim:- Measurement of the high resistance by using loss of charge method.
Apparatus:-
Multimeter 1no
Voltmeter (0-30v)-1no
Capacitor-10uf-1no
Resister-100K-1no
Power supply-(0-30v)-1no
.
Circuit Diagram:-
V
(0-30V)
S1
S2
C=10uf
R
(0-30V)
Theory:-
In this method the resistance which is measured is connected in parallel with
the capacitor C and the electronic voltmeter V. The capacitor is the charged up to some
suitable voltage by means of the battery having the voltage V and is then allowed to
discharge through the resistance.
The terminal voltage is observed over the considerable period of the time
during discharge.
Let,
V=initial voltage on the charged capacitor.
v=instantaneous discharging voltage.
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING III
RD
SEMESTER ELECTRICAL
1
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 8
t=the charging time of the capacitor.
V=v exp (-t/C*R)
or
V/v=exp (-t/C*R)
or
Insulation resistance
R=t/(Clog V/v)
=0.4343*t/(C log
10
V/v)
R=0.4343*t/(C log
10
V/v)
Where R is a resistance of R
1
& R in parallel
R
1
represents the leakage Resistance &
R is the unknown resistor.
The test is then repeated with the unknown resistance R disconnected & the
capacitor discharging through R
1
R=(R*R1)/(R+R1)
Observation Table:-
S.
NO.
Time (sec) V
(withoutR)
V(with R) Log
10
(V/v)
without R
Log
10
(V/v)
with R
Procedure:-
1) Connections is make as per the circuit diagram.
2) Close the switch S
1
and keep S
2
open till the capacitor charge upto V volts.
3) Now open the switch S
1
& allow the capacitor to discharge by its Owen
leakage resistance
4) Note down the reading of the voltmeter verses equal interval of the time.
5) Calculate the unknown resistance using the formula.
6) Now close the switch S
1
& S
2
till the capacitor charge upto V volts.
7)Now open the switch S
1
& allow the capacitor to discharge through the unknown
Resistance.
Result:- Unknown value of high resistance is calculated by using loss of charge
method.
Viva Questions:-
1) Why this method is called as loss of charge method?
2)What kind of errors occurs while performing this practical?
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING III
RD
SEMESTER ELECTRICAL
1
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 9
Experiment No:-04
Aim: - Measurement of the low resistance by using Kelvins Double bridge .
Apparatus: -
Regulated dc supply-1no
Standard resistance coil-1no
Kelvins double bridge kit.
Digital multimeter-1no,
Patch chords.
Components Used: -
Q=q=10K, R
X1
=5, R
X2
=10, P=p=100,
R
B
=11K,, S=Pot of 1k.
Circuit Diagram: -
G
P Q
p
q
r
E
a
m n
S
R
R
b
c
d
Rb
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING III
RD
SEMESTER ELECTRICAL
1
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 10
Theory: -
Kelvins bridge is a modification of wheatstone bridge and always used in
measurement of low resistance. It uses two sets of ratio arms and the four terminal
resistances for the low resistance. As shown in above fig. The first set of ratio P and Q &
second set of ratio arms are p and q are used to connect to the galvanometer to a pt d at
an Approx. potential between points m and n to eliminate the effects of connecting
lead of resistance r between the known std. resistance s and unknown resistance R.
The ratio P/Q is made equal to p/q. under balanced condition there is no current flowing
through galvanometer which means voltage drop between a and b, Eab equal to the
voltage drop between a and d, Eamd.
Now
Eab = Eamd
Eab=(P*Eac/P+Q); Eac=I[R+S+[(p+q)r/p+q+r]] ---------(1)
Eamd= I[R+ p/p+q[ (p+q)r/p+q+r]]
=I[R+p*r/(p+q+r)] ----------------------- (2)
For zero deflection->
Eab=Eamd
[ P/P+Q]I[R+S+{(p+q)r/p+q+r}]=I[R+pr/p+q+r] --3)
Now, if
P/Q=p/q
Then equa (3) becomes
R=P/Q=S -(4)
Equation (4) is the usual working equation. For the Kelvins Double Bridge .It indicates
the resistance of connecting lead r. It has no effect on measurement provided that the two
sets of ratio arms have equal ratios. Equation (3) is useful however as it shows the error
that is introduced in case the ratios are not exactly equal. It indicates that it is desirable to
keep r as small as possible in order to minimize the error in case there is a diff. between
the ratio P/Q and p/q.
R=(P*S)/Q
Observation Table: -
P (ratio arm
resistor)
Q (ratio arm
resistor)
Standard resistor
S
R measured
value
Calculated
R
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING III
RD
SEMESTER ELECTRICAL
1
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 11
Procedure: -
1) The circuit configuration on the panel is studied.
2) The unknown resistance is connected as shown.
3) The value of P,Q was selected such that
P/Q=p/q
4) S was adjusted for proper balance i.e., galvanometer to shows zero deflection.
5) The value of Unknown Resistance R=(P*S/Q) was calculated.
Precautions-
1) Check all the connections before turning ON the power supply.
2) Note the readings accurately.
Result- The observed value of unknown resistance is __________.
Viva Questions:
1) Why this method is called as double bridge method?
2) Can this method be beneficial for measurement of low value of
Resistance or not?
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING III
RD
SEMESTER ELECTRICAL
1
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 12
Experiment No :-5
Aim: - Measurement of the unknown Inductance by using Hays bridge.
Apparatus:- Multimeter
LCR meter
Hays bridge kit,
Patch cords.
Components Used: -
R
2
=100, R
3
= 4.7K, R
4
= 100, C
4
= 1uf
Circuit Diagram:-
G
R3
A
D
B
C
L1
R1
R4
R2
C4
I1
I2
I1
I2
E
E1
E3
E2
E4
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING III
RD
SEMESTER ELECTRICAL
1
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 13
Observation:-
R
2
= __________.
C
4
= __________.
For Unknown Inductance Lx1:-
Calculated - Lx1 = (R
2
R
3
C
4
)
/(1+
2
R
4
2
C
4
2
).
Lx1 =________mH.
Measured - Lx1 = ________mH.
Quality factor (Q)=1/R
4
C
4
.
For Unknown Inductance Lx2:
Calculated - Lx2 = (R
2
R
3
C
4
)
/(1+
2
R
4
2
C
4
2
).
Lx2 =________mH.
Measured - Lx2 = ________mH.
Quality factor (Q)=R
4
C
4
.
Theory:-
The hays bridge is the modification of the Maxwell Bridge. This bridge uses a
resistance in series with the standard capacitor. The bridge has four resistive arms in
which the arms one is consists of the resister R
1
, Lx .The arm 2 is consists of the variable
resistance R
3
.The low value of the resistance is obtain by the low resistive arms of the
bridge. The value of R
4
and C
4
is the standard value of the capacitor and resistance.
By using the unknown inductance having a resistanceR
1
. R
2
, R
3
,R
4
-is the known
non-inductive resistance and C
4
is standard value of the capacitor. The unknown value of
inductance and Quality factor of the Bridge is obtained by formula.
Lx = (R
2
R
3
C
4
)
/(1+
2
R
4
2
C
4
2
)
Quality factor (Q)=(1/R
4
C
4
)
For value of Q greater 10, the term (1/Q)
2
will be smaller & hence neglected
.
Therefore Lx= R2*R3*C4
Basic AC bridges consist of four arms, source excitation and a balanced detector.
Commonly used detectors for AC bridges are:
(1) Head phones
(2) Vibration galvanometers
(3) Tunable amplifier detectors
Vibration galvanometer is extremely useful at power and low audio
frequency ranges. Vibration galvanometers are manufactured to work at various
frequency ranging from 5 KHZ to 1 KHZ. But one most commonly used between
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING III
RD
SEMESTER ELECTRICAL
1
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 14
200HZ.
Advantage-1) This Bridge gives very simple expression for unknown for High Q coil.
2) This bridge also gives a simple expression for Q factor.
Disadvantage- 1) The hays bridge is suited for the measurement of the High Q inductor.
2) It is used to find the inductor having the q value of the smaller then 10.
Procedure:-
1) Study the circuit provided on the front panel of the kit.
2) Connect unknown inductance L
X1
in the circuit. Make all connections to
complete the bridge.
3) Put the supply ON
4) Set the null point of galvanometer by adjusting variable resistance R
3
.
5) Note value of R
2
, R
3
, and C
4
by removing connection by patch cords.
6) Calculate theoretical value of L
X1
using L=R
2
R
3
C
4
7) Measure value of LX
2
by LCR meter and compare it.
8) Repeat process for LX
2
.
Result:- The unknown inductance is measured using Hays bridge and is found to
be___
Viva Questions:-
1) What is the Q factor of the coil?
2) Which bridges are used for measurement of inductances?
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING III
RD
SEMESTER ELECTRICAL
1
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 15
Experiment No :-6
Aim:- Measurement of the unknown inductance by using OWENS bridge method
Apparatus:-
Digital multimeter, Patch chords.
Components used:
R
3
=1K(pot), C
4
=1uF, R
2
=1K(pot),
L
1
= L
2
= ------
Galvanometer, 12VAC source.
Circuit Diagram:-
G
A
D
B
C
R1L1
R3
C4
R2
C2
Theory:-
Bridge are used for the accurate measurement of electrical quantities viz;
esistance, Capacitance, Inductance, Storage Factor, Loss factor etc. Depending upon the
excitations used , the bridge are classified as AC bridges & DC bridges.
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING III
RD
SEMESTER ELECTRICAL
1
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 16
Owens Inductance Capacitance Bridge comes under category of AC bridges and it is
used for measurement of an Inductance in terms of capacitance. General form of AC
bridges consists of four arms of impedances & AC excitation.
Let
L
1
= unknown self inductance of resistance
R
2
=variable non- inductive resistance
R
3
= fixed non- inductive resistance
C
2
=variable standard capacitor
C
4
=fixed standard capacitor
And
At balance condition,
(R
1
+jwL
1
) (1/jwC
4
)=(R
2
+1/jwC
2
)*R
3
Separating the real & imaginary terms, we obtain:
L
1
=R
2
R
3
C
4
&
R
1
=R
3
*C
4
/C
2
Procedure:-
1. Study the circuit provided on the front panel of the kit.
2. Connect unknown inductance L
X1
OR L
X2
by patch chords
3. Switch ON power supply
4. By varying the pot R
2
& R
9
make bridge balance
5. Switch off the power supply, disconnect the patch chords & measure the value of
R
3
& R
2
6. Find the value of unknown inductance by using formula
7. L
1
=R
2
R
3
C
4
Observations:
Measured value of L Calculated value of L
Result:-
Using Owens Bridge we can calculate the value of unknown inductance &
we found there is short difference between theoretical and practical value of L.
VIVA QUESTIONS:-
1) Draw the Phaser diagram of OWEN Bridge?
2) What are the balancing conditions of any a.c. bridge?
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING III
RD
SEMESTER ELECTRICAL
1
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 17
Experiment no 7
Aim:- Measurement of the unknown inductance by using Maxwells bridge.
Apparatus:-
Digital multimeter,
Patch chords.
R
2
=100, R
4
=1K, R
3
=4.7K,
C
4
=1f, L
X2=
318mH, L
X1
=73 mH
Circuit Diagram:-
G
R3
A
D
B
C
L1
R1
R2
C4
R4
E
I1
I3
I2
I4
Theory:-
The Maxwell
s bridge is used to measured inductance by comparison
with a standard variable capacitance. One of the ratio arms has a rsistance and
the capacitance in the parallel.
In this bridge at the balance condition there is no current flow in the
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING III
RD
SEMESTER ELECTRICAL
1
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 18
galvanometer.
At balanced condition,
(R
1
+jwL
1
) (R
4
/1+jwC
4
R
4
) = R
2
*R
3
By separating the real and imaginary term, the unknown value of the
resistor (R1) and the unknown value of the capacitor (C
1
) has given below.
R
1
= R
2
*R
3
/R
4
L
1
= (R
2
*R
3
*C
4
)
Observation:-
R
2
= __________.
C
4
= __________.
For Unknown Inductance Lx1:-
Calculated - Lx1 = (R
2
R
3
C
4
)
Lx1 =________mH.
Measured - Lx1 = ________mH.
Quality factor (Q)=R
4
C
4
For Unknown Inductance Lx2:
Calculated - Lx2 = (R
2
R
3
C
4
)
Lx2 =________mH.
Measured - Lx2 = ________mH.
Advantage-
1) This bridge is very useful for measurement of a wide range of a
inductance at the power and audio frequencies.
2) The frequency does not appear in any of the two equations.
Disadvantage-
1) This bridge requires a variable standard capacitor, which may be
Vary expensive if the calibration to a high degree of the accuracy.
2) The bridge is limited the measure the low Q value.
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING III
RD
SEMESTER ELECTRICAL
1
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 19
Procedure:-
1) Study circuit on kit from panel.
2) Connect unknown inductance L
X1
in circuit. Make all possible connections to
complete the network. Switch the supply on.
3) Set null point of galvanometer by adjusting variable resistance R
3
4) Note values of R
2
, R
3
, C
4
by removing their connections. Calculate theoretical
values of L
X
using L
1
=R
2
R
3
C
4
.
5) Measure actual value of L
X1
using LCR meter. Compare this value with
calculated. also calculate Q factor by using above equation.
Result:- Unknown inductance measured using Maxwells bridge is found to be
L
X1
=____ , & L
X2 =__---------.
___________
Viva Questions:-
1) What are the limitations of this bridge?
2) What is the difference between this method and Hays bridge method?
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING III
RD
SEMESTER ELECTRICAL
1
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 20
Experiment no-08
Aim:- Measurement of the unknown capacitance by using De Sautys bridge.
Apparatus:-
De Sautys bridge kit
Digital multimeter,
Patch chords,
R
2
=100, R
4
=10K, R
3
=10K,
C
2
=1f, CX
1=
1f, CX
2
=4.7f
Circuit Diagram:-
G
R3
A
D
B
C
R4
C1
C2
E
I1
I3
I2
I4
Theory:-
Bridge are used for the accurate measurement of electrical quantities viz;
Resistance, Capacitance, Inductance, Storage Factor, Loss factor etc. Depending upon the
excitations used , the bridge are classified as AC bridges & DC bridges.
De-sauty Bridge comes under category of AC bridges and it is used for measurement of
capacitance. General form of AC bridges consists of four arms of impedances & AC
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING III
RD
SEMESTER ELECTRICAL
1
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 21
excitation.
At balanced condition,
(1/jwC
1
) * R
4
= (1/jwC
2
)*R
3
Separating real & imaginary part,
C
1
= C
2
*(R
4
/R
3
)
Resistance
R
3
Calculated
C
1
=C
2
*R
4
/R
3
Measured
C
1
Procedure: -
1) Study the circuit provided on the front panel on the kit.
2) Connect the unknown capacitance of the position given.
3) Set the null point of galvanometer by adjusting the variable resistor R
3
.
4) Calculate the value of unknown capacitance by formula given
Result: -The values of unknown capacitance is measured using De Sautys bridge is
found to be C
1
= ______uF.
VIVA questions:
i) What are the limitation of this bridge?
ii) Can Dissipation factor be measured by this
bridge?
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING III
RD
SEMESTER ELECTRICAL
1
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 22
Experiment No-09
Aim:- Measurement of the unknown capacitance using schering bridge.
Apparatus:- Schearing bridge kit
digital multimeter,
patch chords,
Circuit Diagram:-
G
R3
A
D
B
C
R1
C1
C2
E
I1
I2
I3
IC4
IR4
C4
R4
Theory:-
The schering bridge is one of the most important ac bridge used extensively for the
measurement of capacitance.
In schering bridge the arm 1 contains a series combination of the resistor and the
capacitor and standard arm contain only one capacitor. The standard capacitor is usually a
standard high quality mica capacitor.
In the balance condition of the bridge the sum of the phase angles of the arms 1
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING III
RD
SEMESTER ELECTRICAL
1
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 23
and 4 is equal the sum of the phase angle of arms 2 and 3.At the balance condition there
is no current flow in the galvanometer.
At balance condition,
[R
1
+(1/jC
1
)] * [R
4
/(1+jC
4
R
4
)] =R
3
/( jC
2
)
After solving & equating real & imaginary parts, we get
R
1
= C
4
*R
3
/C
2
.
C
1
= R
4
*C
2
/R
3
Observation:-
R
4
= __________.
C
2
= __________.
For Unknown Capacitor C
1
:-
Calculated - C
1
= (R
4*
C
2
/R
3
)
C
1
=________.
Measured - C
1
= ________.
Dissipation factor (D.f)=R
4
C
4
Procedure: -
5) Study the circuit provided on the front panel on the kit.
6) Connect the unknown capacitance of the position given.
7) Set the null point of galvanometer by adjusting the variable resistor R4
8) Calculate the value of unknown capacitance by formula given
Result: -The values of unknown capacitance is found to be C1= ______uF.
Viva Questions-
1) What is the Q factor of the coil?
2) Which bridges are used for measurement of inductance
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING III
RD
SEMESTER ELECTRICAL
1
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 24
Experiment no-10
Aim-. Measurement of the 3phase power by the one watt meter method.
Apparatus:-
Three phase variable load.
Wattmeter (0-5A)-, 300v-1no
Ammeter (0-10A)-1no
Voltmeter (0-600v) , (0-300v)-2no
Three phase variac.
Circuit Diagram:-
M
L
C
V
R
Y
B
N
V
A
R
R
R
(0-5A)
(0-300v)
(0-5A,300V)
(100 Ohm,5A)
(100 Ohm,5A)
(100 Ohm,5A)
3-
Phase
,440V,
Supply
Theory:-
In this method the total power consumed is calculated by using one wattmeter .
This method is used only if the load is balanced. Current coil is connected in series with
one phase R & pressure coil of the wattmeter is connected between R phase & Neutral
of the 3- phase load.
Here-V
1
=V
2
=V
3
=V (line voltage)
& I
1
=I
2
=I
3
=Line
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING III
RD
SEMESTER ELECTRICAL
1
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 25
&V
13
-V
12
=V
23
3- phase power = 3* V
1
*I
1
*cos (The load is resistive so cos =1)
= 3* Wattmeter Reading
Observation Table:-
Sr no Voltage Current Power 3 phase watt
Procedure:-
1) Make the arrangement as per the circuit diagram.
2) Increase the dimmerstat reading
3) Note the corresponding values of voltmeter ,ammeter and wattmeter.
4) Take consequent 3 readings.
Result:- The 3phase Power by one watt meter method is ________Watts.
Viva Questions:-
1) Explain in short how the wattmeter is connected in the circuit to .
Measure the power delivered to the Load and the Line.
2) Explain How the Resistive Power is measured by the Wattmeter
Method.
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING III
RD
SEMESTER ELECTRICAL
1
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 26
Experiment no- 11
Aim:- Measurement of the 3phase power by the two watt meter method.
Apparatus:-
Ammeter (0-5A)- 1no.
Voltmeter (0-600v) 1no
Rheostat (100 ohm-5A)-3no
Wattmeter (300V-5A) -2no.
3-PHASE dimmerstat
connecting wires.
Circuit Diagram-
M
L
C
V
R
Y
B
N
V
A
R
R
(0-5A)
(0-300v)
100ohm
5A
100ohm
5A
100ohm
5A
R
300v,5A
300V,5A
3-phase,
440V,
Supply
C
V
M
L
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING III
RD
SEMESTER ELECTRICAL
1
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 27
Theory:-
Here two wattmeter are connected to measure power in 3 phase circuit.
Let V
1
,V
2
,V
3
be rms values of phase voltage and
i1,i2,i3 be rms values of line current
Phase voltage=V
1
=V
2
=V
3
=V
Line voltage=V
13
=V
23
=V
12
=3V
Power factor=cos
Reading of P1 wattmeter =V
13
*I
1
cos(30-)
= 3VIcos(30-)
Reading of P2 wattmeter= V
23
*I
2
cos(30+)
= 3VI(30+)
Sum of two wattmeter readings=P=P
1
+P
2
= 3VI[cos( 30-)- cos(30+)]
=3VIcos
Total Power consumed by the load P= W
1
+W
2
.
Observation Table:-
Sr no Voltage Current Power 3 phase watt
W
1
W
2
W
1
+W
2
Procedure:-
1) Make the arrangement as per the circuit diagram.
2) Adjust supply voltage to 100v. Take the reading when the wattmeter is connected
between the R and Y phase.
3) Repeat previous for the different reading of the voltage.
4) Also note the corresponding current.
5) Now connect wattmeter between R and B phase .
6) Repeat the previous procedure which will give by the total power consumed by
the load.
Result:- Hence it is found that the calculated power and the measured power by the two
wattmeter method is nearly same.
Viva Questions:-
1) Explain the working of 3phase wattmeter?
2) Explain in short how the wattmeter is connected in the circuit to measure
the power delivered to the Load?
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING III
RD
SEMESTER ELECTRICAL
1
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 28
Experiment no- 12
Aim:- Measurement of the 3phase Reactive power by the one watt meter method.
Apparatus:-
Ammeter (0-5A)- 1no.
Voltmeter (0-600v) 1no
Rheostat (100-5A)-3no
3- phase variable reactive load.
3-PHASE dimmerstat
connecting wires.
Circuit Diagram-
M
L
C
V
R
Y
B
N
V
A
(0-5A)
(0-300v)
(0-5A,300V)
3-
phase,
440V,
Supply
3-Phase,5A
Inductive
Load
THEORY:-
The reactive power in the ckt. Is Q = Visin. It is often convenient &
essential that reactive power be measured in the given ckt. for load connections & it also
serves the check on power factor measerement.
Tan = REACTIVE POWER / ACTIVE POWER
Reactive power in a 3-phase balance ckt. is measured by connecting current coil of
wattmeter in one line. & pressure coil across other two lines as shown in above fig.
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING III
RD
SEMESTER ELECTRICAL
1
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 29
Reading of wattmeter = V
23
* I
1
Cos( +90)
= -3V I sin
Therefore = V
23
*I
1
*Sin .
Total reactive power of 3- phase ckt.
Q= 3VISin = 3 * wattmeter Reading
Observation Table:-
Sr. no V
L
I
L
Power
(W)
3-phase Q
=3*Wattmeter
Reading
Procedure:-
2. Make the arrangement as per the circuit diagram
3. Adjust the variac to obtain line voltage.
4. Vary the load in such a way that current through phase is equal.
5. Note down the readings.
Result:- The reactive power found to be =______.
VIVA QUESTION:-
1) What are the other methods for measurement of Reactive Power?
2) What is the Difference between Active & Reactive Power?
You might also like
- Physics Practical Class 12Document14 pagesPhysics Practical Class 12Sahil Midha67% (3)
- Piezoelectric Tiles (Feasibility)Document19 pagesPiezoelectric Tiles (Feasibility)Salmaan PatelNo ratings yet
- Measurement of ResistanceDocument96 pagesMeasurement of ResistancePraveena BNo ratings yet
- Fow Seng Joe (B1757) - Lab 2 IEEDocument12 pagesFow Seng Joe (B1757) - Lab 2 IEERobert Fow JOENo ratings yet
- First Set PDF 2018-19 PDFDocument22 pagesFirst Set PDF 2018-19 PDFLavankumar MudirajNo ratings yet
- Electrical Measurement Lab (EEE-352)Document23 pagesElectrical Measurement Lab (EEE-352)DhinakarrajNo ratings yet
- Physics Practical Manual 23-24Document17 pagesPhysics Practical Manual 23-24saranya ganesanNo ratings yet
- Measurement of ResistanceDocument20 pagesMeasurement of ResistanceWanjala WilliamNo ratings yet
- Bridges, 3-Ammeter, 3-VoltmeterDocument10 pagesBridges, 3-Ammeter, 3-Voltmeterమారుతీ రామ్. ధరణీప్రగడ.వెం.సుNo ratings yet
- Ex 2 - RESISTORS IN SERIESDocument3 pagesEx 2 - RESISTORS IN SERIESMugu 123No ratings yet
- BEEE (PART A BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LAB) ManualDocument18 pagesBEEE (PART A BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LAB) Manualsiriksireesha7No ratings yet
- Electrical & Electronics Measurement Lab ManualDocument64 pagesElectrical & Electronics Measurement Lab ManualHari Krish100% (1)
- Experiment No - Measurement of ResistanceDocument5 pagesExperiment No - Measurement of ResistanceAppu ParoorNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document9 pagesExperiment 3Abel CarlosNo ratings yet
- Wheatstone BridgeDocument8 pagesWheatstone BridgeThiaga RajanNo ratings yet
- EE 2208 Lab ManualDocument50 pagesEE 2208 Lab ManualHemanth Kumar RajendakumarNo ratings yet
- Experiment ManualDocument17 pagesExperiment ManualKavita BishtNo ratings yet
- Report On Basic Ohm S Law Series and Parallel Circuits PDFDocument18 pagesReport On Basic Ohm S Law Series and Parallel Circuits PDFhaikal100% (1)
- ET Lab ManualDocument52 pagesET Lab Manualcholleti sriram100% (1)
- Verification of Ohms LawDocument3 pagesVerification of Ohms LawAdvyth Vaman AkalankamNo ratings yet
- IC 211 Lab Manual 2018-2019Document102 pagesIC 211 Lab Manual 2018-2019AdityaSoniNo ratings yet
- II PUC ManualDocument31 pagesII PUC Manuals2263001No ratings yet
- Physics Practical March 2022-1Document20 pagesPhysics Practical March 2022-1deepakrambhakt07No ratings yet
- Electrical Circuit Lab1Document44 pagesElectrical Circuit Lab1rahmahamjad90No ratings yet
- Resistance Measurement and Digital MultimeterDocument10 pagesResistance Measurement and Digital Multimetervipranshu0308No ratings yet
- Pabna University of Science and Technology Dept. of EEEDocument10 pagesPabna University of Science and Technology Dept. of EEEZannat E Noor AobonyNo ratings yet
- Potentiometer PDFDocument59 pagesPotentiometer PDFRajaa HusseinNo ratings yet
- Physics Practical FinalDocument27 pagesPhysics Practical Finalsanjuktabhoi461No ratings yet
- Electrical Machines Lab ManualDocument13 pagesElectrical Machines Lab ManualSai Sri RamNo ratings yet
- PHY108L ManualDocument58 pagesPHY108L ManualSalman Hossain SahilNo ratings yet
- Experiment-2A: Aim-To Verify Ohms Law in SeriesDocument7 pagesExperiment-2A: Aim-To Verify Ohms Law in SeriesAnsh VermaNo ratings yet
- Experimental Guidance 1.2. Voltage-Current Characteristic 2nd WeekDocument14 pagesExperimental Guidance 1.2. Voltage-Current Characteristic 2nd WeeksadmanNo ratings yet
- Lab 1: DC Multimeter Measurements: ObjectiveDocument11 pagesLab 1: DC Multimeter Measurements: ObjectiveAli AdnanNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Electrical BridgesDocument9 pagesUnit 4 Electrical Bridgesazhar3303No ratings yet
- Exp18 Ohms Law ManualDocument3 pagesExp18 Ohms Law Manualraikwaranupam323No ratings yet
- M&I LAB ManualDocument10 pagesM&I LAB ManualhoneyattriNo ratings yet
- Data Presentation and RecordingDocument166 pagesData Presentation and RecordingPelly Pee MugobaNo ratings yet
- Practicals - Class XiiDocument38 pagesPracticals - Class XiiTITAN KALOS100% (1)
- Electric Circuits ODL Manual 1-1Document6 pagesElectric Circuits ODL Manual 1-1Idk Maybe AwaisNo ratings yet
- 1.verification of Ohms LawDocument3 pages1.verification of Ohms LawTEEGALAMEHERRITHWIK 122010320035No ratings yet
- Analog Electrical Devices and MeasurementsDocument21 pagesAnalog Electrical Devices and MeasurementsGabriel MarzinottoNo ratings yet
- Pre-Lab.: Experiment 2Document4 pagesPre-Lab.: Experiment 2Waseem HaiderNo ratings yet
- 062 EC Lab-02 PDFDocument4 pages062 EC Lab-02 PDFP. Manjunath MadavalliNo ratings yet
- 2021-22 Phy Lab Manual Class 12Document31 pages2021-22 Phy Lab Manual Class 12AartibNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual: Power ElectronicsDocument23 pagesLab Manual: Power Electronicsprakhar yadavNo ratings yet
- Network Analysis I Lab GuideDocument28 pagesNetwork Analysis I Lab Guidepatrickodame05No ratings yet
- 2022-23 Phy Lab Manual Class 12Document32 pages2022-23 Phy Lab Manual Class 12Rasu 789No ratings yet
- Ee-118 Basic Electricity & Electronics - 2013Document97 pagesEe-118 Basic Electricity & Electronics - 2013abdul wakeelNo ratings yet
- Verification of Ohm's LawDocument4 pagesVerification of Ohm's LawApu SarkarNo ratings yet
- Electrical Measurements LabDocument40 pagesElectrical Measurements Labmdayyub100% (4)
- Experiment 23: Wheatstone Bridge and Resistivity of Metals: PurposeDocument5 pagesExperiment 23: Wheatstone Bridge and Resistivity of Metals: PurposeValeria MendozaNo ratings yet
- BEEI Lab Manual CompressedDocument85 pagesBEEI Lab Manual CompressedkavithaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No-4Document6 pagesExperiment No-4devanshurajpoot1No ratings yet
- Lab ManualsDocument24 pagesLab ManualsPranoy MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument86 pagesBasic Electrical EngineeringorryesNo ratings yet
- Physics Practical ManualDocument26 pagesPhysics Practical ManualABHISEKNo ratings yet
- Passive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2From EverandPassive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2No ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1No ratings yet
- Ea06 Manual enDocument6 pagesEa06 Manual enabuzer1981No ratings yet
- Service Manual: DVP-NS15/NS51P/NS43P/NS53P/K56PDocument113 pagesService Manual: DVP-NS15/NS51P/NS43P/NS53P/K56Pbiderjuanca100% (1)
- Government Polytechnic, Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Electrical Workshop LabDocument15 pagesGovernment Polytechnic, Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Electrical Workshop LabTapobroto Chatterjee100% (1)
- Practical Physics XDocument9 pagesPractical Physics Xanoj kumarNo ratings yet
- Dekra Brochure Safetyinstrument A4 Uk - v2Document44 pagesDekra Brochure Safetyinstrument A4 Uk - v2Gli OxalNo ratings yet
- Deif Product Table ListDocument57 pagesDeif Product Table Listnhocti007No ratings yet
- 10 LED Tachometer CircuitDocument5 pages10 LED Tachometer Circuittim schroderNo ratings yet
- 42pt330-Ub 42pt350-Ud 42pt350c-Ud Chassis Pu14kDocument56 pages42pt330-Ub 42pt350-Ud 42pt350c-Ud Chassis Pu14kAngel GarciaNo ratings yet
- KDL 40ex705 BR VerDocument31 pagesKDL 40ex705 BR Vernivaldo de oliveira OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Capacitor ESR MeterDocument7 pagesCapacitor ESR MeterrubemllNo ratings yet
- Measurements 41Document84 pagesMeasurements 41Rajib Ghosh100% (1)
- Electromagnetic Effects: 300 Turns 30 TurnsDocument23 pagesElectromagnetic Effects: 300 Turns 30 TurnsEdgardo Leysa100% (5)
- Electric Cells and ResistanceDocument21 pagesElectric Cells and Resistance18118No ratings yet
- Bunn Coffee Maker ManualDocument19 pagesBunn Coffee Maker ManualAlan MarkNo ratings yet
- 30 Watts, 1240 To 1300 MHZ Linear Amplifier PCB Kit or Complete KitDocument6 pages30 Watts, 1240 To 1300 MHZ Linear Amplifier PCB Kit or Complete Kitwa3yueNo ratings yet
- Bill of Material For Panels - Apl - NewDocument54 pagesBill of Material For Panels - Apl - Newp mahesh goudNo ratings yet
- 110 TOP MOST Measurement and Instrumentation - Electrical Engineering Objective Type Questions and AnswersDocument22 pages110 TOP MOST Measurement and Instrumentation - Electrical Engineering Objective Type Questions and AnswersMujahid Ahmed FadelNo ratings yet
- Circuits Virtual LabDocument2 pagesCircuits Virtual LabPaula GómezNo ratings yet
- EE6701-High Voltage EngineeringDocument16 pagesEE6701-High Voltage EngineeringKumar RajNo ratings yet
- Experiment No - Measurement of ResistanceDocument5 pagesExperiment No - Measurement of ResistanceAppu ParoorNo ratings yet
- Turbine Engine Details PDFDocument25 pagesTurbine Engine Details PDFReynaldo FloresNo ratings yet
- Mains Monitoring Panel NW400 Mains Monitoring Panels With AC-Distribution NWV-CDocument15 pagesMains Monitoring Panel NW400 Mains Monitoring Panels With AC-Distribution NWV-COleg KuryanNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Heating Currents Paper 1Document20 pagesTopic 5 Heating Currents Paper 1felNo ratings yet
- ASTM G42 Cathodic Disbonment TestDocument8 pagesASTM G42 Cathodic Disbonment TestDuy Linh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Section A PracticalsDocument38 pagesSection A PracticalsAnshul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ground Testing TechniquesDocument11 pagesGround Testing TechniquesAlliver SapitulaNo ratings yet
- 1 AcdbDocument9 pages1 AcdbmaheshknmNo ratings yet
- Resistance MFH 2011aprilDocument23 pagesResistance MFH 2011aprilHasiburNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 3Document8 pagesLab Report 3sagarchawlaNo ratings yet