Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Experiment No. 1 Name: Date: .. Aim: Apparatus
Uploaded by
siddharthpande777Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment No. 1 Name: Date: .. Aim: Apparatus
Uploaded by
siddharthpande777Copyright:
Available Formats
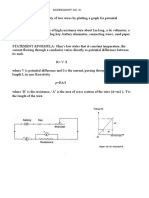
Experiment No.
1
Name:
Date:..
Aim:
To verify Ohms law
Apparatus:
.. Coiled resistor, Ammeter 0 to 3 A, Voltmeter 0-3V, 100 Rheostat,
Plug Key, 4V DC source, Connecting wires
Procedure:
1
Set up the circuit as shown in the figure.
Note the least count of the ammeter and the voltmeter.
Insert the plug key. Adjust the rheostat to obtain a low current in the
ammeter. Note the ammeter and voltmeter readings for the setting.
Move the variable terminal of the rheostat to increase the current slightly
and note the ammeter and voltmeter reading. Repeat this step for a set of
five readings.
Use the recorded reading to determine the value of resistance using Ohms
law . (R = V/I)
Plot a graph between V and I. Draw the best fit line and determine its slope.
5
6
Observations:
Least count of the ammeter:.A
Least count of the voltmeter:.V
S.No.
Ammeter reading (I)
[in ampere]
Voltmeter reading (V)
[in volt]
Resistance (R)
R=V/I [in ohm]
1
2
3
4
5
Mean value of resistance R =
Slope R = V/I = .
Conclusion :
The current flowing through the conductor is found to be directly
proportional to the potential difference between the ends of the conductor
with the resistance R being constant. This verifies the Ohms Law.
The mean value of resistance is calculated as .
The value of resistance determined from the graph is .
Precautions:
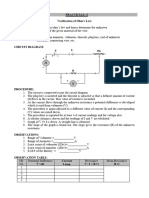
(i) The connections should be tight.
(ii) The rheostat, the key, ammeter, and the resistance are connected in series
with the dc source.
(iii) The positive side of the ammeter should be towards the positive terminal of
the dc source.
(iv) The voltmeter should be connected in parallel to the resistor.
(v) The positive side of the voltmeter should be towards the positive side of
the dc source.
(vi) The applied voltage and the supplied current should not exceed the range of
the measuring instruments and other components of the circuit.
i.
Key
( )
Rheostat
.. Resistance
V -
Circuit diagram
2
You might also like
- PROSPERITY PRAYER BY DR Joseph MurphyDocument1 pagePROSPERITY PRAYER BY DR Joseph Murphysiddharthpande777100% (2)
- Seed Money EbookDocument125 pagesSeed Money Ebookanon-689215100% (11)
- Restricted Earth Fault Application GuideDocument12 pagesRestricted Earth Fault Application GuidementongNo ratings yet
- Physics 221 Experiment 3: Simple DC Circuits and Resistors: October 1, 2008Document6 pagesPhysics 221 Experiment 3: Simple DC Circuits and Resistors: October 1, 2008lady GNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter I.C.T 10 ReviewerDocument13 pages1st Quarter I.C.T 10 ReviewerLinsay Alaine Yap100% (1)
- Agile Questions and AnswersDocument33 pagesAgile Questions and Answerssiddharthpande77770% (10)
- Physics Practical Class 12Document14 pagesPhysics Practical Class 12Sahil Midha100% (2)
- Soul Coaching: 28 Days To Discovering Your Authentic SelfDocument13 pagesSoul Coaching: 28 Days To Discovering Your Authentic Selfsiddharthpande77750% (2)
- SD Wan Comparison Guide UpdatedDocument1 pageSD Wan Comparison Guide UpdatedAlberto Ciaffardoni80% (5)
- Report On "Basic Ohm's Law & Series and Parallel Circuits"Document18 pagesReport On "Basic Ohm's Law & Series and Parallel Circuits"JEJUNG67% (3)
- Direct Current Meter: by M. Rahmad Physics Education Fkip Ur 2013Document26 pagesDirect Current Meter: by M. Rahmad Physics Education Fkip Ur 2013Melsa AtsawatiNo ratings yet
- Voltmeter Connected. SensitivityDocument30 pagesVoltmeter Connected. SensitivityzsssxNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Specifications: TIPO I.2: C-BXA-80033/8-MDocument1 pageMechanical Specifications: TIPO I.2: C-BXA-80033/8-MafalvarezanNo ratings yet
- EE6211-Electric Circuits Laboratory MANUALDocument78 pagesEE6211-Electric Circuits Laboratory MANUALsakilakumaresanNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 9 Name: Date: .. AimDocument3 pagesExperiment No. 9 Name: Date: .. AimSiddharth PandeNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument2 pagesOhm's LawkirtiNo ratings yet
- Physics Record Book 2023 24Document62 pagesPhysics Record Book 2023 24easedaeNo ratings yet
- Aim of ProjectDocument5 pagesAim of Projectaayush sinhaNo ratings yet
- 12th Physics Practical - 1Document6 pages12th Physics Practical - 1TanishkaNo ratings yet
- Experiment B6 Aim: Apparatus:: Characteristics of DiodeDocument9 pagesExperiment B6 Aim: Apparatus:: Characteristics of DiodeAnurag BajpaiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document14 pagesExperiment 3Abdullah AnsariNo ratings yet
- Report On Basic Ohm S Law Series and Parallel Circuits PDFDocument18 pagesReport On Basic Ohm S Law Series and Parallel Circuits PDFhaikal100% (1)
- BEEE Lab ManualDocument45 pagesBEEE Lab ManualYašh JaínNo ratings yet
- XII - EXPERIMENT1 PhysicsDocument6 pagesXII - EXPERIMENT1 PhysicsSamicshaaNo ratings yet
- Lab 1: DC Multimeter Measurements: ObjectiveDocument11 pagesLab 1: DC Multimeter Measurements: ObjectiveAli AdnanNo ratings yet
- Experiment ManualDocument17 pagesExperiment ManualKavita BishtNo ratings yet
- Experiment No - Measurement of ResistanceDocument5 pagesExperiment No - Measurement of ResistanceAppu ParoorNo ratings yet
- Verification of Ohm's Law: Experiment No# 02Document3 pagesVerification of Ohm's Law: Experiment No# 02Saad AliKhan50% (2)
- Ace Ahead .Physics Vol 2. Student. Practical GuideDocument15 pagesAce Ahead .Physics Vol 2. Student. Practical GuideJolyn May LingNo ratings yet
- XII Practical Lab Manual (2022 - 2023)Document29 pagesXII Practical Lab Manual (2022 - 2023)Kanishk KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Data Presentation and RecordingDocument166 pagesData Presentation and RecordingPelly Pee MugobaNo ratings yet
- BEEE Lab ManualDocument45 pagesBEEE Lab ManualVishal Gupta100% (1)
- Physics Practical FinalDocument27 pagesPhysics Practical Finalsanjuktabhoi461No ratings yet
- Practical Material 21-22Document62 pagesPractical Material 21-22Raj BarathNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuit Lab1Document44 pagesElectrical Circuit Lab1rahmahamjad90No ratings yet
- Physics Practical File 2Document5 pagesPhysics Practical File 2Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 How Things WorkDocument42 pagesUnit 4 How Things WorkDanielNo ratings yet
- ET Lab ManualDocument52 pagesET Lab Manualcholleti sriram100% (1)
- NOTES (2023-2024) Subject: PHYSICS Class: XII Experiment No.1: Ohm'S LawDocument5 pagesNOTES (2023-2024) Subject: PHYSICS Class: XII Experiment No.1: Ohm'S LawMichael IbrahimNo ratings yet
- 1.ohms's LawDocument3 pages1.ohms's LawPartikNo ratings yet
- Physics Record Writing Class XII PDFDocument138 pagesPhysics Record Writing Class XII PDFnida ghaniNo ratings yet
- Practical Notes-Mock ExamDocument8 pagesPractical Notes-Mock ExamannalisaNo ratings yet
- LCA Lab ManualDocument51 pagesLCA Lab ManualUzairYaseenNo ratings yet
- Usha Martin World School, Patna Experiment-1: Science Class-12 PhysicsDocument4 pagesUsha Martin World School, Patna Experiment-1: Science Class-12 PhysicsSNEHAL MUSKANNo ratings yet
- 16817257554035phy Expt 1 To 8Document29 pages16817257554035phy Expt 1 To 8G. SRIVANNo ratings yet
- Phy Practical Activities FormatDocument12 pagesPhy Practical Activities Formatapi-384758875% (16)
- Xii Physics Experiment 1Document5 pagesXii Physics Experiment 1Solomon Peter SunilNo ratings yet
- Xii Physics Experiment 1Document5 pagesXii Physics Experiment 1Solomon Peter SunilNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document14 pagesLab 2ihsanghani7676No ratings yet
- Lab ManualsDocument24 pagesLab ManualsPranoy MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Phy108 Lab Manual PDFDocument30 pagesPhy108 Lab Manual PDFSumaya Akter Ruhi 2022610642No ratings yet
- XII Physics Practicals and Activities 202223Document15 pagesXII Physics Practicals and Activities 202223Pearl MalikNo ratings yet
- Experiment A1: Aim: To Determine The Resistance Per CM of A Given Wire by Plotting A Graph of PotentialDocument9 pagesExperiment A1: Aim: To Determine The Resistance Per CM of A Given Wire by Plotting A Graph of PotentialMohammed Aftab AhmedNo ratings yet
- Circuit Lab: NameDocument6 pagesCircuit Lab: NameBerna DetteNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1: Verificati O N of TH Eve Nin 'S Theor emDocument37 pagesExperiment No. 1: Verificati O N of TH Eve Nin 'S Theor emakashdeep tickooNo ratings yet
- Verification of KIRCHHOFF'S VOLTAGE LAW (Mesh Analaysis) : S. No. Component Description Specification QuantityDocument10 pagesVerification of KIRCHHOFF'S VOLTAGE LAW (Mesh Analaysis) : S. No. Component Description Specification QuantityVARUNNo ratings yet
- Practicals - Class XiiDocument38 pagesPracticals - Class XiiTITAN KALOS100% (1)
- EE131.1 - Instruments and MeasurementsDocument25 pagesEE131.1 - Instruments and MeasurementsMark John Lerry CaseroNo ratings yet
- Section A PracticalsDocument38 pagesSection A PracticalsAnshul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Measurement ElectricityDocument4 pagesMeasurement ElectricityMd HamzaNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law 1Document5 pagesOhm's Law 1rajesh_patel_007No ratings yet
- Practical 2024 12Document9 pagesPractical 2024 12mahendrapatel6344No ratings yet
- Experiment No 1Document13 pagesExperiment No 1Norman ElizagaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 15: Ohm's LawDocument5 pagesExperiment 15: Ohm's Lawmanoj rsNo ratings yet
- 6.verification of Ohms LawDocument2 pages6.verification of Ohms Laweee departmentNo ratings yet
- G12 Physics Experiment 23-24Document43 pagesG12 Physics Experiment 23-24anonymous3256tNo ratings yet
- KLKLKDocument1 pageKLKLKsiddharthpande777No ratings yet
- FGFHDocument2 pagesFGFHsiddharthpande777No ratings yet
- TyruuDocument2 pagesTyruusiddharthpande777No ratings yet
- HjyjDocument2 pagesHjyjsiddharthpande777No ratings yet
- GBVGHNGHDocument2 pagesGBVGHNGHsiddharthpande777No ratings yet
- SddsDocument2 pagesSddssiddharthpande777No ratings yet
- IooDocument2 pagesIoosiddharthpande777No ratings yet
- ZDFFDocument2 pagesZDFFsiddharthpande777No ratings yet
- WertDocument3 pagesWertsiddharthpande777No ratings yet
- QaweDocument2 pagesQawesiddharthpande777No ratings yet
- WdertDocument5 pagesWdertsiddharthpande777No ratings yet
- QawserDocument3 pagesQawsersiddharthpande777No ratings yet
- SDFGDocument2 pagesSDFGsiddharthpande777No ratings yet
- SasDocument1 pageSassiddharthpande777No ratings yet
- QaweDocument2 pagesQawesiddharthpande777No ratings yet
- TneDocument1 pageTnesiddharthpande777No ratings yet
- WesdDocument2 pagesWesdsiddharthpande777No ratings yet
- TyuDocument3 pagesTyusiddharthpande777No ratings yet
- GHGHGDocument2 pagesGHGHGsiddharthpande777No ratings yet
- RdinfoDocument2 pagesRdinfosiddharthpande777No ratings yet
- DFGDocument2 pagesDFGsiddharthpande777No ratings yet
- NFTqqweDocument1 pageNFTqqwesiddharthpande777No ratings yet
- Find Pre-Recorded Guided Meditations atDocument22 pagesFind Pre-Recorded Guided Meditations atanon_511092790No ratings yet
- ErtytuDocument2 pagesErtytusiddharthpande777No ratings yet
- TesteeDocument1 pageTesteesiddharthpande777No ratings yet
- AngularJs Interview Q ADocument24 pagesAngularJs Interview Q Asiddharthpande777No ratings yet
- TP5088 PDFDocument6 pagesTP5088 PDFGerman GodiNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics Question BankDocument3 pagesDigital Electronics Question BankMinu PriyaNo ratings yet
- Pic 18F45K22Document494 pagesPic 18F45K22AlexandruTomescu100% (1)
- Catalogo NILOX SPORT - 2014 PDFDocument26 pagesCatalogo NILOX SPORT - 2014 PDFmanryNo ratings yet
- GW - SDT G2 PLUS+ - Datasheet-ENDocument2 pagesGW - SDT G2 PLUS+ - Datasheet-ENAntonioNo ratings yet
- Brocade 1Document76 pagesBrocade 1yugi17100% (1)
- Orakel Support Services: Read More About Cheating and Plagiarism HereDocument4 pagesOrakel Support Services: Read More About Cheating and Plagiarism HereSr SeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Basic Signaling ProceduresDocument68 pagesChapter 6 Basic Signaling ProceduresEfosa AigbeNo ratings yet
- Generic Memory Compiler PDFDocument2 pagesGeneric Memory Compiler PDFAnonymous Wu14iV9dqNo ratings yet
- User Manual DuraMON G-Line Rev FDocument37 pagesUser Manual DuraMON G-Line Rev Fwijang08No ratings yet
- 8085 Instruction Set: Noteshub - Co.In - Download Android AppDocument15 pages8085 Instruction Set: Noteshub - Co.In - Download Android AppHardik SethNo ratings yet
- Physical LayerDocument3 pagesPhysical LayershivaprasadmvitNo ratings yet
- IUIa GiV EnglDocument3 pagesIUIa GiV EnglJavierNo ratings yet
- Circuito Integrado Q0465RSDocument24 pagesCircuito Integrado Q0465RSmarcosNo ratings yet
- Ird 880 ManualDocument97 pagesIrd 880 ManualEnrique Javier González HenríquezNo ratings yet
- UniOP Instalation GuideDocument63 pagesUniOP Instalation Guidezvonkomihajlovic4891No ratings yet
- Lecture 10 - PV SystemDocument31 pagesLecture 10 - PV Systemruhuna013No ratings yet
- Philips 6-IE550/ V Interstage Slope EqualizersDocument4 pagesPhilips 6-IE550/ V Interstage Slope Equalizersjose angel guzman lozanoNo ratings yet
- A4988 Stepper Motor Driver Carrier, Black EditionDocument5 pagesA4988 Stepper Motor Driver Carrier, Black EditionRadersNo ratings yet
- SmartAX MA5800 BrochureDocument2 pagesSmartAX MA5800 Brochuremansilla_hernan8781No ratings yet
- TransducersDocument19 pagesTransducersTsihatesfaNo ratings yet
- Tonocare 2.0: Wireless Non-Contact TonometerDocument3 pagesTonocare 2.0: Wireless Non-Contact TonometerĐình ChungNo ratings yet
- Synopsis On Underground Cable Fault DetectionDocument4 pagesSynopsis On Underground Cable Fault DetectionROBOMAXX100% (1)
- List of Worked in First LVDC ConfrenceDocument24 pagesList of Worked in First LVDC ConfrencejunaidNo ratings yet
- HCC/HCF4042B: Quad Clocked "D" LatchDocument13 pagesHCC/HCF4042B: Quad Clocked "D" LatchjuenkkinNo ratings yet