Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Endo Pulp Diseases
Endo Pulp Diseases
Uploaded by
Nik NikOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Endo Pulp Diseases
Endo Pulp Diseases
Uploaded by
Nik NikCopyright:
Available Formats
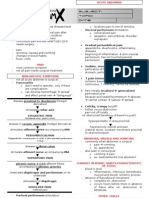
Reversable pulpitis - hyperemia
D e f
Irreversible pulpitis
Acute pulpitis ( painful ) Occurs when the amount of irritation intensifies causing great increase in the interpulpal pressure beyond the threshold limits of the sensory nerves causing variables degrees of pain. Chronic pulpitis (painless) Chronic ulcerative pulpitis Chronic hyperplastic pulpitis ( pulp polyp) Chronic inflammation of cariously Chronic inflammation of cariously exposed pulp characterized by exposed pulp characterized by ana formation of abcess at the point over growth of granulomatous of exposure leading to ulceration. tissue into the carious cavity forming a polyp. This response may arise at the end of acute phase or may develop from onset in case where the irritant is of low grade. Usually seen secondry to acute pulpitis
Pulpal necrosis
Pulp undergo necrosis ass a sequel of acute or chronic pulpitis , as the inflammation progress tissue continue to disintegrate until entire pulp is necrotic .
E t i o l o g y
Incipient caries Cervical erosion Occlusal attrition Deep periodontal curettage Filling without insulation Leaking restoration Exposed dentinal tubules Acute Irreversible , starts initial then moderate & lastly advanced Nature of pain: Type of pain : Initially :mild shooting By time: sharp shooting ( by lying down) Stimulus: initially : cold (last 4 few mins) By time: spontaneous without stimulus Course of pain : initially : intermittent By time: continues Vitality testing : normal Palpitation & percussion test : -ve Stimulus : initially : cold Followed by a stage : cold & hot Advanced stage : heat causes sever pain( relieved 4 few sec.s by cold application Hot tooth ) Pain referred neighboring teeth , opposing dentition & temporal area & ear Distribution of pain: always diffuse , cannot localize correctly offended tooth . Pain control : initially : by analgesics Advanced stage : nothing can stop pain
S i g n s & -
Its a reversible inflammation , if cause eliminated , inflammation reverse pulp will return to normal Nature of pain: Type of pain : Sharp transient pain Stimulus : cold ( immediately after removal of stimulus) Course of pain :transient Vitality testing : normal Palpitation & percussion : -ve
Nature of pain: Pain : usually abscent as no accumulation of fluids occur iside pulp & intra-pulpal pressure does not rise Stimulus: heat sometimes
Nature of pain: Pain : usually polyp not painful , it bleeds easily on probing ( open apex)
Nature of pain:
Pain:very mild & mostly abscent
s y m p t o m s
Vitality testing : respond at higher stimulation Palpitation & percussion : -ve Visual examination reveals the presence of long standing carious cavity
Vitality testing : pulp responds Palpitation & percussion : -ve This form seen in young patients where this polyp appears as pinkish red globule of tissue protruding from the pulp chamber.
Vitality testing : negative Palpitation & percussion : -ve
h i s t o
Local vasodilatation & in permeability of blood vessels can cause slight in local pulpal pressure. Infiltration for few numbers of inflammatory cells . if irritation of pulp continues or , case changesto irreversible pulpitis & eventually necrosis. Normal
pulpal pressure , tissue damage & bacterial toxins lead to formation of micro-abcesses at the site of the carious exposure. The neutrophils are the primary cells present. Surrounding the abcess , a dense infiltration of lymphocytes, plasma cells & macrophages is seen.
A zone of necrosis is seen at the surface of the pulp followed by a zone of leukocytic infiltration. Beyond this zone, a zone of proliferating fibroblasts is seen.
The polyp is a complex of new capillaries, proliferating fibroblasts & inflammatory cells.
R a d i o g r a p h i c
No radiographic changes except Advanced stage :some widening in the periodontal membrane space
No changes seen, except in some cases there can be some widening in the periodontal membrane space.
No changes seen, except in some cases there can be some widening in the periodontal membrane space.
No changes seen, except some cases there can be some widening in the periodontal membrane space.
You might also like
- Concept Map On AppendicitisDocument6 pagesConcept Map On Appendicitisitalisayan_rondario80% (5)
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (NCP)Document4 pagesDeep Vein Thrombosis (NCP)24 PAULINO ALDRIN MUJAR0% (1)
- 16 Tamburino Transverse Dimension 2010 RWISO JOURNAL (Final Bleed) (08-02) .PDF - Adobe Acrobat ProDocument10 pages16 Tamburino Transverse Dimension 2010 RWISO JOURNAL (Final Bleed) (08-02) .PDF - Adobe Acrobat ProMayleen Asbheer100% (1)
- Varicose Case ProformaDocument2 pagesVaricose Case ProformaSneha Naulakha100% (1)
- Jurnal Internasional PicotDocument6 pagesJurnal Internasional PicotTHE COMUNITAS PASAPUA ANGKATAN 2017100% (1)
- Endo AcuteDocument1 pageEndo AcutebouglaglastellaNo ratings yet
- Endodontic Diagnosis: DR - Suchetaprabhu Third Year Mds 2 8 / 0 6 / 1 8Document77 pagesEndodontic Diagnosis: DR - Suchetaprabhu Third Year Mds 2 8 / 0 6 / 1 8Tuan NguyenNo ratings yet
- MassDocument8 pagesMassYara YousefNo ratings yet
- Curs 10-Pulp Pathology II-1Document32 pagesCurs 10-Pulp Pathology II-1Bianca BurcăNo ratings yet
- Soft Tissue SwellingDocument34 pagesSoft Tissue Swellingsp25hgmc9jNo ratings yet
- 2 Examination of SwellingDocument43 pages2 Examination of SwellingSneha ThiagarajanNo ratings yet
- Opath Lab. Pulp Periapical Diseases CompleteDocument3 pagesOpath Lab. Pulp Periapical Diseases CompleteJaira LaguidaoNo ratings yet
- Abscess Dr. Nasrin Sultana JuyenaDocument4 pagesAbscess Dr. Nasrin Sultana JuyenaShakil MahmodNo ratings yet
- Pain NCP BillrothDocument2 pagesPain NCP BillrotharjayNo ratings yet
- Reso Urce Name Operative Dentistry: Treatment PlanningDocument49 pagesReso Urce Name Operative Dentistry: Treatment PlanningHamza AdeelNo ratings yet
- Dizziness HXDocument4 pagesDizziness HXbadmanNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Pain in BiliodigestiDocument19 pagesPathophysiology of Pain in Biliodigestiprabowoaji12No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Pain in BiliodigestiDocument19 pagesPathophysiology of Pain in Biliodigestiprabowoaji12No ratings yet
- Summary of Orlpt MTDocument7 pagesSummary of Orlpt MTGlea Marie EscanlarNo ratings yet
- Nerve Nerve Nerve Nerve Entrapment Entrapment Syndromes (Nes) Syndromes (Nes)Document52 pagesNerve Nerve Nerve Nerve Entrapment Entrapment Syndromes (Nes) Syndromes (Nes)teshaleNo ratings yet
- Endodontic Emergency (Dr. Imran)Document2 pagesEndodontic Emergency (Dr. Imran)aelessyaNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 5Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 5JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Hernia Case ProformaDocument2 pagesHernia Case ProformaTanmay SaxenaNo ratings yet
- ??mass & Ulcer ExaminationDocument5 pages??mass & Ulcer ExaminationAli SafaaNo ratings yet
- PALPATION of Swelling D Hussain NazeeshaDocument17 pagesPALPATION of Swelling D Hussain NazeeshaHUSSAIN NAZEESHANo ratings yet
- Pain Definitions and Taxonomy of PainDocument40 pagesPain Definitions and Taxonomy of PainmorfisstefNo ratings yet
- Oral Pathology NotesDocument2 pagesOral Pathology NotesMohamedNo ratings yet
- BLS - First Aid 2Document5 pagesBLS - First Aid 2jerry spiritNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The PulpDocument1 pageDiseases of The PulpFidz LiankoNo ratings yet
- 10 Pulp and Periapical DiseaseDocument7 pages10 Pulp and Periapical Diseasedoctorgame085No ratings yet
- Cyriax ConceptDocument26 pagesCyriax ConceptMeenakshiputraeashwarprasad MacherlaNo ratings yet
- Cap 49 Guyton 259710 Downloable 1847976Document7 pagesCap 49 Guyton 259710 Downloable 1847976Keidy P Quen AedoNo ratings yet
- Inflammation 2Document4 pagesInflammation 2honovezaann.a.campita.ctucvmNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document15 pagesPresentation 2KaviyaNo ratings yet
- Pulpal and Periapical PathologyDocument101 pagesPulpal and Periapical Pathologyammara100% (1)
- Acute Scrotal Pain in Adults and Adolescents - Approach To The Patient - DynaMedDocument66 pagesAcute Scrotal Pain in Adults and Adolescents - Approach To The Patient - DynaMedSebastian ChavesNo ratings yet
- Sorting Out Endodontic Symptoms: ©JK Mitchell, DDS, Med April 2012Document2 pagesSorting Out Endodontic Symptoms: ©JK Mitchell, DDS, Med April 2012sao_tren_troi100% (1)
- Lecture 5 - Pulp and Periapical IDocument116 pagesLecture 5 - Pulp and Periapical IAlex ChangNo ratings yet
- NCP Ectopic PregnancyDocument2 pagesNCP Ectopic PregnancykatrinajhorelletillesNo ratings yet
- Inv Asion P Hase: (Depression Phase)Document1 pageInv Asion P Hase: (Depression Phase)Kamille PinoNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 12Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 12JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Acute AbdomenDocument4 pagesAcute Abdomensarguss14No ratings yet
- Pulp DiseasesDocument10 pagesPulp DiseasesAdham AshrafNo ratings yet
- Inv A Sion Pha Se: (Depression Phase)Document1 pageInv A Sion Pha Se: (Depression Phase)rossvieNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Pain: No. Features Explanation Associated WithDocument4 pagesAbdominal Pain: No. Features Explanation Associated WithNazmun LailahNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Acute Abdomen 2013ADocument4 pagesEvaluation of Acute Abdomen 2013AEdison Tan SantamariaNo ratings yet
- 27.neck SwellingsDocument4 pages27.neck SwellingsDurga VoraNo ratings yet
- Gynecological Assessment: DateDocument4 pagesGynecological Assessment: Dateanne laureNo ratings yet
- PREOP3 1 DocxDocument1 pagePREOP3 1 DocxCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Peripheral VasculatureDocument5 pagesAssessment of Peripheral VasculatureCraigyyNo ratings yet
- Inv A Sion Pha Se: Rabies PatophysiologyDocument1 pageInv A Sion Pha Se: Rabies PatophysiologyRudelsa Agcolicol LangamanNo ratings yet
- Ulcer Case by S.P.KamthankarDocument14 pagesUlcer Case by S.P.KamthankarJaweria SyedNo ratings yet
- Dr. Praveen K. YadavDocument32 pagesDr. Praveen K. YadavRaj RajNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseasesDocument14 pagesCommunicable DiseasesKristine ManioNo ratings yet
- Inv A Sion Pha Se: Bill Julius Samuel G. Alferez BSN IiiDocument1 pageInv A Sion Pha Se: Bill Julius Samuel G. Alferez BSN IiiRudelsa Agcolicol LangamanNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Rheumatoid and OsteoarthritisDocument4 pagesComparison of Rheumatoid and OsteoarthritisWaseem Khan AfridiNo ratings yet
- Head Nursing TemplateDocument9 pagesHead Nursing TemplateBianca MaeNo ratings yet
- ORTHOPAEDICS MANUAL PaulDocument62 pagesORTHOPAEDICS MANUAL PaulRNo ratings yet
- Cme: Septic Arthritis: by Syafi'ie Syukri Bin Mohammed FaridzDocument23 pagesCme: Septic Arthritis: by Syafi'ie Syukri Bin Mohammed FaridzGraldoNo ratings yet
- PREOP3Document1 pagePREOP3Void LessNo ratings yet
- DeQuervain Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandDeQuervain Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Park 2012Document6 pagesPark 2012Yassin SalahNo ratings yet
- Prediction of Soft Tissue Deformations After CMF Surgery With Incremental Kernel Ridge Regression Pan2016Document9 pagesPrediction of Soft Tissue Deformations After CMF Surgery With Incremental Kernel Ridge Regression Pan2016Yassin SalahNo ratings yet
- Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry: Bibin BhaskaranDocument50 pagesProsthetic Options in Implant Dentistry: Bibin BhaskaranYassin SalahNo ratings yet
- IPS E-Max CAD For CEREC SpeedFire (Dentsply Sirona)Document2 pagesIPS E-Max CAD For CEREC SpeedFire (Dentsply Sirona)Yassin SalahNo ratings yet
- IPS E-Max CAD-IPS E-Max Press - Adhesive 1mm CrownDocument1 pageIPS E-Max CAD-IPS E-Max Press - Adhesive 1mm CrownYassin SalahNo ratings yet
- Applications of 3D Imaging in Orthodontics: Part 1Document10 pagesApplications of 3D Imaging in Orthodontics: Part 1Yassin SalahNo ratings yet
- Ms PresentDocument3 pagesMs PresentYassin SalahNo ratings yet
- Yassin Salah Mohammed YassinDocument3 pagesYassin Salah Mohammed YassinYassin SalahNo ratings yet
- A Review of The Properties of Some Denture Base PolymersDocument15 pagesA Review of The Properties of Some Denture Base PolymersYassin SalahNo ratings yet
- Rolul Uleiurilor Esentiale in Managementul Pneumoniilor Cu Germeni Multirezistenti La CopilDocument18 pagesRolul Uleiurilor Esentiale in Managementul Pneumoniilor Cu Germeni Multirezistenti La CopilAdrian CraciunNo ratings yet
- CV Updated 3/21Document5 pagesCV Updated 3/21Abbey FritschNo ratings yet
- Ejh 13396Document8 pagesEjh 13396elyza putri novitasariNo ratings yet
- Polyhydramnios (Revised)Document34 pagesPolyhydramnios (Revised)Edward Munyaradzi KutsanziraNo ratings yet
- Psoriatic ArthritisDocument6 pagesPsoriatic ArthritisAndu1991No ratings yet
- Fowl PoxDocument7 pagesFowl PoxLisa VaughnNo ratings yet
- Full Slide Notes of OSHDocument279 pagesFull Slide Notes of OSHFunny tinny08No ratings yet
- RTRMF-CM - Pedia Clinics GuideDocument7 pagesRTRMF-CM - Pedia Clinics GuideKo HakuNo ratings yet
- Pep Certificate 1Document1 pagePep Certificate 1api-283487476No ratings yet
- Jktlfkku Yksd Lsok VK KSX) VtesjDocument2 pagesJktlfkku Yksd Lsok VK KSX) VtesjJeshiNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Sleep Deprivation On The Academic Performance of College StudentsDocument9 pagesThe Effects of Sleep Deprivation On The Academic Performance of College StudentsGav SacdalanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Guillan-Barre SyndromeDocument2 pagesDrug Study - Guillan-Barre SyndromeKyle VargasNo ratings yet
- Unity 3Document3 pagesUnity 3Gabigames CarottiNo ratings yet
- Legs Cramp While SleepingDocument6 pagesLegs Cramp While SleepingJawad AdsNo ratings yet
- Adaptive ImmunityDocument6 pagesAdaptive ImmunityAvinash SahuNo ratings yet
- Confidential: Health Survey For AdolescentsDocument4 pagesConfidential: Health Survey For AdolescentsamritaNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect Costs of An AccidentDocument2 pagesDirect and Indirect Costs of An Accidentshru sivaNo ratings yet
- Incidence and Relative Risk of Hearing Disorders in Professional MusiciansDocument5 pagesIncidence and Relative Risk of Hearing Disorders in Professional MusiciansIntan Winta PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation On GastroenteritisDocument17 pagesCase Presentation On GastroenteritisSafoora RafeeqNo ratings yet
- Active Recreational Activities Study GuideDocument3 pagesActive Recreational Activities Study Guideanoymous 123No ratings yet
- Depresión (Dos Semanas)Document3 pagesDepresión (Dos Semanas)AcdaNo ratings yet
- 2 Kerala PSC Staff Nurse Previous Solved Papers Part 2 - Kerala PSC QuestionsDocument8 pages2 Kerala PSC Staff Nurse Previous Solved Papers Part 2 - Kerala PSC QuestionsMrudula SureshNo ratings yet
- W3health6 q1 Mod1of2 PersonalHealthIssuesSelf-MngtSkills v2-1Document22 pagesW3health6 q1 Mod1of2 PersonalHealthIssuesSelf-MngtSkills v2-1Rona DindangNo ratings yet
- Kler CVDocument2 pagesKler CVapi-455711018No ratings yet
- Inovasi Implementasi Puskesmas Poned Dalam Upaya A PDFDocument7 pagesInovasi Implementasi Puskesmas Poned Dalam Upaya A PDFSVJ officialNo ratings yet
- Buku AnestesiDocument33 pagesBuku AnestesiAan AnharNo ratings yet
- Seminar On FibroadenosisDocument23 pagesSeminar On FibroadenosisSk Saklin MustakNo ratings yet
- QUIZ Critical Thinking in Nursing PracticeDocument16 pagesQUIZ Critical Thinking in Nursing Practicegabrielle magdaraogNo ratings yet