Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemistry Review Sheet
Uploaded by
Russell KatzCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemistry Review Sheet
Uploaded by
Russell KatzCopyright:
Available Formats
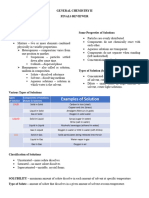
THHS Chemistry 5 Pure substance one type of matter; uniform and definite in composition can be chemically combined Mixture
ure two or more types of matter physically combined heterogeneous (e.g.: chicken noodle soup) homogenous (e.g.: salt water) Solution homogenous mixture, but all compounds are in the same physical state e.g.: an alloy (all in solid state) solute substance being dissolved solvent substance doing the dissolving (usually water) Solutions (aqueous) Homogenous Transmits light (*can be colorful) Cannot be filtered Does not settle on standing Suspension Heterogeneous Does not transmit light Can be filtered Settles on standing Colloid Heterogeneous
Russell Katz 3/14/13
Does not transmit light Cannot be filtered Does not settle on standing
Solubility how much solute will dissolve in a given solvent high solubility soluble low solubility insoluble (*Insoluble means very low solubility) Increase in temperature = Increase in solubility of salt Increase in temperature = Decrease in solubility of gas Nature of the solute Like dissolves like polar solutes dissolves in polar solvent nonpolar solute dissolves in nonpolar solvent unsaturated can hold more saturated holds how much it should supersaturated holds more than it should supersaturated solutions are very rare (*only under extreme conditions) Molarity = moles of solute / liters of solution 1M NaCl more concentrated 0.5M NaCl CONCENTRATION/DILUTE Molality = moles of solute / kilograms of solvent PARTICLE RELATIONSHIP
% mass = (mass of part / mass of whole) * 100 1mL of water = 1g of water % volume = (vol. of part / vol. of whole) * 100 1L of water = 1kg of water parts per million (ppm) = (mass of solute / mass of solution) * 1,000,000 Pure Water Freezing Point = molality (m) * #of moles of dissolved particles * 1.86oC Boiling Point = molality (m) * #of moles of dissolved particles * 0.52oC If a substance is ionic, you must count every mole. e.g.: CaCl2 3 (1+2) If a substance is covalent, you must use the given amount of moles. If no amount is given, it's usually one. Kinetics branch of chemistry concerned with the rate of chemical reaction Collision Theory reactions occur when particles collide with the right amount of energy and with the right orientation Surface Area Temperature Concentration increased surface area increased temperature increased concentration = = = increased rate of reaction increased rate of reaction increased rate of reaction
Catalyst increases rate of reaction, but does not participate in the reaction
You might also like
- Chapter 12Document10 pagesChapter 12Ayesha MohamudNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of SolutionDocument39 pagesPhysical Properties of SolutionAlice RiveraNo ratings yet
- Solutions and SolubilityDocument28 pagesSolutions and SolubilityMhimi ViduyaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2. Concentration of SolutionsDocument57 pagesLesson 2. Concentration of SolutionsFreddie NanasNo ratings yet
- Lectuer 3-FOEDocument27 pagesLectuer 3-FOEamr.120230006No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Solutions and Solution PreparationDocument35 pagesChapter 3 - Solutions and Solution Preparationbahru demekeNo ratings yet
- 1 Semester Paper No. 101 Unit 5 Solutions: SolutionDocument13 pages1 Semester Paper No. 101 Unit 5 Solutions: SolutionsjshahNo ratings yet
- Dr. Saidane Lecture Notes Properties of Solutions: Chem 200Document10 pagesDr. Saidane Lecture Notes Properties of Solutions: Chem 200Marko QuebralNo ratings yet
- Solutions and MolarityDocument24 pagesSolutions and MolarityMuhammad AhmedNo ratings yet
- The Big Chemistry Book on Solutions - Chemistry for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandThe Big Chemistry Book on Solutions - Chemistry for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument19 pagesSolutionsmuthiasaritilawahNo ratings yet
- Week 5, LarutanDocument68 pagesWeek 5, LarutanFakhryIkhsanFirdausNo ratings yet
- General ChemistryDocument12 pagesGeneral ChemistryJoshua Romea100% (1)
- Characteristics of SolutionsDocument22 pagesCharacteristics of SolutionsJunior LifeNo ratings yet
- 12stem B - Week7Document3 pages12stem B - Week7Franz SorianoNo ratings yet
- Weeks5 7solutionsDocument27 pagesWeeks5 7solutionsEmma LoreinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 SolutionDocument78 pagesChapter 1 SolutionIke Jayson Rollon0% (1)
- Chapter 16 SolutionsDocument28 pagesChapter 16 SolutionsDeepak SainiNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem II Finals ReviewerDocument5 pagesGen Chem II Finals ReviewerjkierstencvergaraNo ratings yet
- SolubilityDocument59 pagesSolubilityNadem DreemNo ratings yet
- 8 - SolutionsDocument6 pages8 - SolutionsDeng FajardoNo ratings yet
- CH 11Document26 pagesCH 11Akef AfanehNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Introduction To SolubilityDocument47 pagesLecture 1 Introduction To SolubilityshiraNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 SolutionsDocument81 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 SolutionsLol lolNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13: SolutionsDocument18 pagesChapter 13: SolutionsBSNo ratings yet
- Oc 4 Jdu 73 PST GL0 ZWDocument12 pagesOc 4 Jdu 73 PST GL0 ZWJoshua RomeaNo ratings yet
- DT Group PresentationDocument43 pagesDT Group PresentationTheresah FrimpongNo ratings yet
- GRAVIMETRICS (Aka Calculations Involving Stuff You Weigh/ Mass)Document8 pagesGRAVIMETRICS (Aka Calculations Involving Stuff You Weigh/ Mass)Robert SpaldingNo ratings yet
- Water and Solutions Unit - Notes Packet - SP 2012Document41 pagesWater and Solutions Unit - Notes Packet - SP 2012api-87739323No ratings yet
- Solutions Stoichiometry EquilibriumDocument79 pagesSolutions Stoichiometry EquilibriumKat JornadalNo ratings yet
- X-Ray Diffraction Document (1) (4) - 1Document9 pagesX-Ray Diffraction Document (1) (4) - 1MEEZAN TVNo ratings yet
- Kimia Larutan: Moondra Zubir, PH.DDocument23 pagesKimia Larutan: Moondra Zubir, PH.DmaudysakinahNo ratings yet
- Solubility of DrugsDocument147 pagesSolubility of Drugsharshagadia234No ratings yet
- Chapter 16 SolutionsDocument23 pagesChapter 16 SolutionsRacquel SupsupNo ratings yet
- GenChem2 ReviewerDocument11 pagesGenChem2 ReviewerJules Kirsten RueloNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry: Dr. Rabih O. Al-Kaysi Ext: 47247 Email: Kaysir@ksau-Hs - Edu.saDocument34 pagesGeneral Chemistry: Dr. Rabih O. Al-Kaysi Ext: 47247 Email: Kaysir@ksau-Hs - Edu.saapi-19824406100% (1)
- The Composition of SolutionsDocument17 pagesThe Composition of SolutionstinoneyNo ratings yet
- Solution, Suspension, ColloidsDocument149 pagesSolution, Suspension, ColloidsApril Eballena100% (1)
- 6.P.2.3 - SolubilityDocument9 pages6.P.2.3 - SolubilityCinta KimiaNo ratings yet
- GENERAL CHEMISTRY 2 Week4 Quarter 3Document6 pagesGENERAL CHEMISTRY 2 Week4 Quarter 3Christine MorotaNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1601430625143 6716886876762277304Document16 pagesOrca Share Media1601430625143 6716886876762277304Neil MaglalangNo ratings yet
- Is Matter Around Us PureDocument31 pagesIs Matter Around Us Purethinkiit100% (1)
- Larutan 1 PDFDocument21 pagesLarutan 1 PDFAnonymous 2xr3Y5VNo ratings yet
- Solutions G7Document44 pagesSolutions G7Rlene May MateoNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Physical Properties of Solution PDFDocument40 pagesWeek 4 Physical Properties of Solution PDFmai sasaNo ratings yet
- NonelectrolytesDocument51 pagesNonelectrolytesEmad MustafaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Properties of Solutions (Sulaiman Al-Isaee's Conflicted Copy)Document64 pagesChapter 11 Properties of Solutions (Sulaiman Al-Isaee's Conflicted Copy)iB13eNo ratings yet
- Chem PPTDocument115 pagesChem PPTBeefWith PorkNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument15 pagesCHEMISTRYPaulane Navalta100% (1)
- Simple Mixture DrShikin 2 ConDocument59 pagesSimple Mixture DrShikin 2 ConPutriNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Solutions 2023Document39 pagesCH 2 Solutions 2023Kaleb Ashiko100% (1)
- Physicalproperties of SolutionsDocument25 pagesPhysicalproperties of SolutionsJan AmoresNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Properties of Solutions: Important TermsDocument17 pagesAP Chemistry Properties of Solutions: Important TermsLuc LeNo ratings yet
- Solubility ExpressionsDocument7 pagesSolubility ExpressionsYuppie Raj100% (1)
- Water Properties and Chemistry Notes AccDocument52 pagesWater Properties and Chemistry Notes AccAngela CuiNo ratings yet
- Solutions and ConcentrationDocument18 pagesSolutions and Concentrationapi-483662721No ratings yet
- Concentration of SolutionsDocument28 pagesConcentration of SolutionsClarice Barros CatedrillaNo ratings yet
- Oil and Water Won't Mix and Other Mixture Separation Techniques - Chemistry Book for Kids 8-10 | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandOil and Water Won't Mix and Other Mixture Separation Techniques - Chemistry Book for Kids 8-10 | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Combining Chemicals - Fun Chemistry Book for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandCombining Chemicals - Fun Chemistry Book for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- THHS Election SimulationDocument1 pageTHHS Election SimulationRussell KatzNo ratings yet
- English Collateral 3 EssayDocument3 pagesEnglish Collateral 3 EssayRussell KatzNo ratings yet
- English Quiz For 2-15-13Document1 pageEnglish Quiz For 2-15-13Russell KatzNo ratings yet
- Latin Verbs (Chapters 1-8)Document2 pagesLatin Verbs (Chapters 1-8)Russell KatzNo ratings yet
- English Test 9.28.12Document2 pagesEnglish Test 9.28.12Russell KatzNo ratings yet
- Linguistics Test 5-23Document4 pagesLinguistics Test 5-23Russell KatzNo ratings yet
- Linguistics IPA and PronunciationDocument2 pagesLinguistics IPA and PronunciationRussell KatzNo ratings yet
- BioTest12 13Document2 pagesBioTest12 13Russell KatzNo ratings yet
- Biology Study Sheet: Characteristics of LifeDocument9 pagesBiology Study Sheet: Characteristics of LifeRussell KatzNo ratings yet
- Gaining Confidence With GD T - Part 2Document22 pagesGaining Confidence With GD T - Part 2Abraham ThomasNo ratings yet
- Serge Florens and Antoine Georges - Quantum Impurity Solvers Using A Slave Rotor RepresentationDocument18 pagesSerge Florens and Antoine Georges - Quantum Impurity Solvers Using A Slave Rotor RepresentationYidel4313No ratings yet
- Microsoft Word MecvinaDocument37 pagesMicrosoft Word MecvinaRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- Padlet - Physics and Roller CoastersDocument9 pagesPadlet - Physics and Roller CoasterserickaNo ratings yet
- 175 023400Document2 pages175 023400Abu Anas M.SalaheldinNo ratings yet
- MappingDocument13 pagesMappingAzzah NazNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Communication 10ec72 SolutionDocument73 pagesOptical Fiber Communication 10ec72 Solutionshashank gupta100% (1)
- Grile AerDocument14 pagesGrile AerAndreea DiaconuNo ratings yet
- Mixer GrinderDocument29 pagesMixer GrinderChockalingam AthilingamNo ratings yet
- Thermo QualsDocument26 pagesThermo QualsLuc LeNo ratings yet
- Rheflat Plus PDB EngDocument2 pagesRheflat Plus PDB EngJose AlejandroBlanco100% (1)
- Physics IA Investigzting The Mpeda EffectDocument14 pagesPhysics IA Investigzting The Mpeda EffectR - INo ratings yet
- Ultimate Capacity FractionatorsDocument26 pagesUltimate Capacity Fractionatorsrvkumar61No ratings yet
- Glass Handbook 2010 English For Eastern Europe PDFDocument300 pagesGlass Handbook 2010 English For Eastern Europe PDFAnthony Thaddeus AntonioNo ratings yet
- Week 001 Electric Forces and Fields, Electric Charge and Coulomb's LawDocument19 pagesWeek 001 Electric Forces and Fields, Electric Charge and Coulomb's LawYukiko HachiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2: Free and Force Vortex Table of ContentDocument33 pagesExperiment 2: Free and Force Vortex Table of Contentmarz95No ratings yet
- Essentials of Materials Science and Engineering Si Edition 3rd Edition Askeland Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesEssentials of Materials Science and Engineering Si Edition 3rd Edition Askeland Solutions Manualhanhgloria0hge5100% (32)
- Sae J20-2022Document15 pagesSae J20-2022Vedpal Singh ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Semester Test 1 Without Memo-2Document1 pageSemester Test 1 Without Memo-2Lencelot MalopeNo ratings yet
- Aquatic Adaptations - Poonam SinghDocument46 pagesAquatic Adaptations - Poonam Singhaksahu01234No ratings yet
- Piping PresentationDocument144 pagesPiping PresentationSUNIL TVNo ratings yet
- Form 2208 - Page 1: Surface Pump Installation DataDocument3 pagesForm 2208 - Page 1: Surface Pump Installation DataErich ThomasNo ratings yet
- Atomic Absorption SpectrometryDocument64 pagesAtomic Absorption Spectrometryanilrockzzz786No ratings yet
- Coursework Structural Integrity 2023-24Document7 pagesCoursework Structural Integrity 2023-24Yacine HalwaneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Energy Bands andDocument134 pagesChapter 1 - Energy Bands andYew Keong NgNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions Civil EngineeringDocument17 pagesMultiple Choice Questions Civil Engineeringgurumurthy38100% (2)
- The Particle Nature of MatterDocument25 pagesThe Particle Nature of MatterJessa alajid80% (5)
- WWW - Dgcaquestionpapers.In: Dgca Module 15 Gas Turbine EngineDocument4 pagesWWW - Dgcaquestionpapers.In: Dgca Module 15 Gas Turbine Enginejontis jasoliyaNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis of Narrow Dental Implants: SciencedirectDocument9 pagesFinite Element Analysis of Narrow Dental Implants: SciencedirectaDITYA GUJARENo ratings yet
- tHREAD 2 MATERI OL 2 (PG Gerak)Document4 pagestHREAD 2 MATERI OL 2 (PG Gerak)festus wikannandaNo ratings yet