Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Perlis Paper3 & Answer
Uploaded by
smtspOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Perlis Paper3 & Answer
Uploaded by
smtspCopyright:
Available Formats
SULIT
4551/3 Nama: …………………………………………………………
Biologi
Kertas 3
Ogos/ PEPERIKSAAN PERCUBAAN BERSAMA
September SIJIL PELAJARAN MALAYSIA 2008
2008 ANJURAN BERSAMA
1 1/2jam
PERSIDANGAN KEBANGSAAN PENGETUA-PENGETUA
SEKOLAH MENENGAH CAWANGAN NEGERI PERLIS
DAN JABATAN PELAJARAN PERLIS
BIOLOGI
Kertas 3
Satu jam tiga puluh minit
JANGAN BUKA KERTAS SOALAN INI SEHINGGA DIBERITAHU
1. Tulis nama anda pada ruang yang Kod pemeriksa
disediakan.
Soalan Markah Markah
2. Kertas soalan ini adalah dalam dwibahasa. penuh diperoleh
1 33
3. Soalan dalam Bahasa Inggeris mendahului
soalan yang sepadan dalam Bahasa 2 17
Melayu. Jumlah 50
4. Calon dibenarkan menjawab keseluruhan
atau sebahagian soalan sama ada dalam
Bahasa Melayu atau Bahasa Inggeris.
5. Calon dikehendaki membaca maklumat di
halaman 2.
____________________________________________________________________
Kertas soalan mengandungi 11 halaman bercetak termasuk kulit.
4551/3 [Lihat sebelah
SULIT
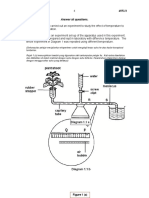
1. Diagram 1 shows the experiment that was carried out to study the effect of
temperature on the transpiration rate of Hibiscus shoot by using an air bubble
potometer. The potometer was placed under different temperatures.
Rajah 1 menunjukkan satu eksperimen yang telah dijalankan untuk mengkaji
kesan suhu ke atas kadar transpirasi ranting bunga raya dengan menggunakan
potometer gelembung. Potometer diletakkan di bawah keadaan suhu yang
berbeza.
The distances for the movement of air bubble along capillary tube within 5
minutes were measured using a ruler.
Jarak yang dilalui oleh gelembung udara di sepanjang tiub kapilari diukur dengan
menggunakan pembaris
The experiment was set up as shown in Diagram 1(a) and was repeated using
different temperatures.
Eksperimen disediakan seperti yang ditunjukkan pada rajah 1(a) dan diulang
dengan menggunakan suhu yang berbeza.
Diagram 1 (b) shows the position of the meniscus at the initial of the experiment.
X is the air bubble. The distance of the movement of air bubble is measured at
meniscus position as shown in diagram 1(a) and 1(b).
Rajah 1(b) menunjukkan kedudukan awal gelembung udara pada awal
eksperimen. X ialah gelembung udara. Ukuran jarak dibuat berdasarkan
kedudukan miniskus yang di tunjukkan dalam rajah 1(a) dan 1(b)
Table 1.1 shows the reading of temperature and location of meniscus in the
capillary tube after 5 minutes.
Jadual 1.1 menunjukkan bacaan suhu dan lokasi miniskus dalam tiub kapilari
selepas 5 minit.
4551/3 [Lihat sebelah
SULIT
Diagram 1(a)
Rajah 1(a)
Diagram 1(b)
Rajah 1(b)
4551/3 [Lihat sebelah
SULIT
Temperature
Distance of air bubble movement within 5 minutes (cm)
Suhu (oC)
Jarak pergerakan gelembung udara dalam masa 5 minit (cm)
Table 1.1
4551/3 [Lihat sebelah
SULIT
Jadual 1.1
(a) Record the temperature and the distance for the movement of air bubble along
the capillary tube in table 1.1.
Catatkan suhu dan jarak yang diambil oleh gelembung udara untuk bergerak
dalam tiub kapilari pada ruang yang disediakan pada jadual 1.1.
1(a)
[3 marks]
(b)(i) State two different observations made from Table 1.1.
Nyatakan dua pemerhatian yang berbeza yang dibuat daripada Jadual 1.1.
Observation 1 / Pemerhatian 1:
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
Observation 2 / Pemerhatian 2:
….………………………………………………………………………………………..
……………………………………………………………………………………………
1(b)(i)
……………………………………………………………………………………………
[3 marks]
(b) (ii) State the inferences which corresponds to the observations in 1(b)(i).
Nyatakan inferens yang sepadan dengan pemerhatian di 1(b)(i).
Inference from observation 1 / Inferens daripada pemerhatian 1 :
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
Inference from observation 2 / Inferens daripada pemerhatian 2 :
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………….. 1(b)(ii)
[3 marks]
4551/3 [Lihat sebelah
SULIT
1(c) Based on this experiment, complete table 1.2.
Berdasarkan eksperimen di atas, lengkapkan jadual 1.2.
Variable Method to handle the variable
Pembolehubah Cara mengendali pembolehubah
Manipulated variable:
Pembolehubah diimanipulasikan:
Responding variable:
Pembolehubah bergerak balas:
Constant variable
Pembolehubah diimalarkan:
Table 1.2
Jadual 1. 2 1(c)
[3 marks]
1(d) State the hypothesis for this experiment.
Nyatakan hipotesis bagi eksperimen ini.
………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
1(d)
[3 marks]
4551/3 [Lihat sebelah
SULIT
1(e)(i) Construct a table and record all the data collected in this experiment which
includes the following titles:
Bina satu jadual untuk merekodkan semua data yang dikumpul dalam
eksperimen ini. Jadual hendaklah mengandungi tajuk-tajuk berikut:
• Temperature (oC)
Suhu ( 0C)
• The distance of meniscus movement (cm)
Jarak pergerakan gelembung udara (cm)
• Rate of transpiration (cm/ minute )
Kadar transpirasi (cm/ minit )
1(e)(i)
[3 marks]
(e)(ii) Based on your table in (e)(i) plot a graph of temperature (°C) against the plant
transpiration rate on the graph paper provided on page 8.
Berdasarkan jadual anda di (e) (i), plotkan graf suhu melawan kadar
transpirasi tumbuhan pada kertas graf di muka surat 8.
1(e)(ii)
[3 marks]
4551/3 [Lihat sebelah
SULIT
4551/3 [Lihat sebelah
SULIT
(e)(iii) Based on the graph, explain the relationship between transpiration rates of the
plant and temperature.
Berdasarkan graf yang telah dilukiskan, terangkan perkaitan antara kadar
transpirasi tumbuhan dengan suhu.
………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………....... 1(e)(iii)
[3 marks]
(f)(i) Based on the experiment, define transpiration operationally.
Berdasarkan eksperimen, definisikan transpirasi secara operasi.
………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………....... 1(f)(i)
[3 marks]
(f)(ii) If the experiment is repeated using 40OC with higher light intensity, predict the
distance for the movement of air bubble after 5 minutes. Explain your
prediction.
Jika eksperimen di atas diulangi pada suhu 40OC dengan menggunakan
keamatan cahaya yang tinggi, ramalkan jarak pergerakan gelembung udara
selepas 5 minit. Terangkan ramalan anda.
………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
……………….……………………………………………………………………..
1(f)(ii)
[3 marks]
4551/3 [Lihat sebelah
SULIT
(g) A group of students carried out an experiment to study the effect of light
intensity on the transpiration rate. The following list is part of the apparatus and
materials used in this experiment.
Sekumpulan pelajar telah menjalankan satu eksperimen untuk mengkaji kesan
keamatan cahaya ke atas kadar transpirasi. Senarai berikut adalah
sebahagian daripada radas dan bahan yang telah digunakan untuk
exsperimen itu.
Lamp, meter rule, stop watch, capillary tube, rubber tube,
knife, basin, retort stand, vaseline and plant shoot.
Lampu, pembaris meter, jam randik, tiub kapilari, salur getah,
pisau kecil, takungan air, kaki retort, vaselin dan pucuk
berdaun.
Construct a table and classify the apparatus and materials used in the
experiment in the space below.
Bina satu jadual dan kelaskan bahan-bahan di atas mengikut kumpulan bahan
dan radas dalam ruang di bawah ini.
1(g)
[3 marks]
4551/3 [Lihat sebelah
SULIT
2.
Cells are basic units of living organism.
They consist of cellular components and organelles that
can be seen by using microscope.
Design an experiment to investigate the difference of structures in a plant cell
and an animal cell that can be seen under a light microscope.
The planning of your experiment must include the following aspects:
• Problem statement
• Aim of investigation
• Hypothesis
• Variables
• List of apparatus and materials
• Technique used
• Experimental procedure or method
• Presentation of data
• Conclusion
[17 marks]
END OF QUESTION PAPER
4551/3 [Lihat sebelah
SULIT
INFORMATION FOR CANDIDATES
1. This question paper consists of two questions. Answer all questions.
2. Write your answers for Question 1 in the spaces provided in the question paper.
3. Write your answers for Question 2 on the ‘helaian tambahan’ provided by the
invigilators. You may use equations, diagram, tables, graphs and other suitable
methods to explain your answer.
4. Show your working, it may help you to get marks.
5. If you wish to change your answer, neatly cross out the answer that you have
done . Then write down the new answer.
6. The diagrams in the questions are not drawn to scale unless stated.
7. Marks allocated for each question or part question are shown in brackets.
8. The time suggested to answer Question 1 is 45 minutes and Question 2 is 45
minutes.
9. You may use a non/programmable scientific calculator.
10. Hand in all your answer sheets at the end of the examination.
Marks awarded:
Score Description
3 Excellent : The best response
2 Satisfactory : An average response
1 Weak : An inaccurate response
0 No response or wrong response
4551/3 [Lihat sebelah
SULIT
MARKING SCHEME : PAPER THREE – TRIAL BIOLOGY 2008
Question 1 : 1(a)
Score Explanation
Able to record all readings of temperature and the distance movement of water in
the potometer correctly.
3 10 oC = 3.0 cm
20 oC = 5.0 cm
30 oC = 8.5 cm
40 oC = 9.0 cm
2 Able to record any three distances.
1 Able to record any two distance.
0 No response or wrong response
1(b)(i)
Score Explanation
Able to state two correct observations based on following criteria.
C1 – Temperature
3 C2 – The distance of air bubble movement within 5 minutes.
Sample Answer:(either 2):
1. The air bubble moves from 0 cm to 5.0 cm at the temperature 20oC after 5
minutes
2 . The air bubble moves from 0 cm to 8.5 cm at the temperature 30oC after 5
minutes
3 . The air bubble moves from 0 cm to 9.0 cm at the temperature 40oC after 5
minutes
2 Able to state one correct observation and one inaccurate response.
1 Able to state one correct observation or two inaccurate response or idea.
0 No response or wrong response (response like hypothesis)
1(b) (ii)
Score Explanation
3 Able to state two reasonable inferences for the observation.
Sample answer:
1. The water molecules evaporate from surface of the leaves slowly under low
temperature causing the air bubble to move in short distance.
2. The water molecules evaporate from surface of the leaves rapidly under high
temperature causing the air bubbles to move in long distance.
2 Able to state one correct inference and one inaccurate inference.
1 Able to state one correct inference or two inaccurate inference or idea.
0 No response or wrong response (inference like hypothesis)
4551/3 [Lihat sebelah
SULIT
1(c)
Score Explanation
Able to state all the variables and the method to handle variable correctly
(√) for each variable and method
Manipulated Variable: Temperature (√)
Method to handle: The potometer is put under different
3 temperature. (√)
Responding Variable: The distance of air bubble . (√)
Method to handle: Measure and record the distance by using
the ruler. (√)
Controlled variable : Size of plant shoot/ size of air bubble/
humidity/intensity of light (√)
Method to handle: Use the plant shoot with the same size/
maintain the size of air bubble/
humidity / intensity of light. (√)
Able to get 6 √
2 Able to get 4 – 5 √
1 Able to get 2 – 3 √
0 No response or wrong response
1(d)
Score Explanation
3 Able to state the hypothesis correctly based on the following criteria:
V1 – State the temperature.
V2 – State the meniscus movement
R - State the relationship between V1 and V2.
As the temperature increases, the rate of transpiration increases too. //
The rate of transpiration/(meniscus movement) is higher when the temperature
increase
2 Able to state the hypothesis but less accurate.
1 Able to state the idea of the hypothesis
0 No response or wrong response
1(e)(i)
Score Explanation
Able to construct a table and record the result of the experiment with the
following criteria:
3 C – State all four temperature reading. (√) – with unit
D – Transfer all data correctly. (√)
T – Calculate the rate of transpiration (1/minute) (√)
If without unit (x).
Temperature (0C) Distance of air Rate of transpiration (cm/min)
bubble (cm)
10 3.0 0.6
20 5.0 1.0
30 8.5 1.7
40 9.0 1.8
2 Able to construct a table and record any two criteria
1 Able to construct a table and record any one criteria
0 No response or wrong response
4551/3 [Lihat sebelah
SULIT
1(e)(ii)
Score Explanation
Able to draw a graph of rate of transpiration against the temperature.
3 Axes (A) – both axis are labeled with units, uniform scales, independent
variable on horizontal axis. (√)
Point (P) – All points are correctly plotted. (√)
Shape (S) – All points are connected smoothly (√).
(If the graph attaches the axis (x).
2 Graph with any two criteria.
1 Graph with any one criteria.
0 No response or wrong response.
1(e)(iii)
Score Explanation
Able to explain the relationship between the rate of transpiration and
3 temperature correctly.
When the temperature increase, the rate of transpiration increase because water
molecules evaporate faster.
2 Able to explain briefly the relationship between rate of transpiration and the
temperature
1 Able to explain the idea of the relationship between rate of transpiration and the
temperature
0 No response or wrong response
1(f)(i)
Score Explanation
3 Able to state the definition of transpiration operationally, complete and correct,
based on the following criteria.
C1 – the function of transpiration
C2 – the effect on plant
C3 – the factor that affect on transpiration.
Transpiration is the loss of water vapour from the hibiscus leaves causing the air
bubble move in the capillary tube and affected by the temperature.
2 Able to state the definition of transpiration based on any two criteria.
1 Able to state the definition of transpiration based on any one criteria.
0 No response or wrong response
4551/3 [Lihat sebelah
SULIT
1(f)(ii)
Score Explanation
3 Able to predict correctly and explain the prediction based on the following item:
C1 – the distance of air bubble.
C2 – higher light intensity cause faster rate of photosynthesis
C3 – the opening of stomata bigger, the rate of transpiration higher.
The distance of the air bubble is further/more than 9 cm because the
photosynthesis rate is higher due to a higher light intensity and cause higher rate
of transpiration.
2 Able to predict based on any two criteria.
1 Able to predict based on any one criteria.
0 No response or wrong response
1(g)
Score Explanation
Able to classify the apparatus and materials used.
Lamp, meter rule, stop watch, capillary tube,
Apparatus rubber tube, knife, basin, retort stand.
Material Vaseline, plant shoot
3 Able to classify all the apparatus and materials correctly.
2 Able to classify all the apparatus correctly but only one material //
5-7 apparatus correctly with 2 materials. //
6-7 apparatus correctly with 1 material.
1 Able to classify 3-4 apparatus correctly with 2 materials
0 No response or wrong response
4551/3 [Lihat sebelah
SULIT
Question 2 :
Aspect Sample Answer Remarks
Aim/objective To investigate different cellular structures that present in a plant cell 1 mark
and animal cell that can be seen under light microscope. √
Problem Do cellular structures in plant cell differ from that of in animal cell? 3 marks
statement
How can we see plant cell and animal cell? 2 marks
KB061201
( without question mark ) 1 mark
√
Hypothesis More cellular components can be seen in plant cell compared to
animal cell. 3 marks
Plant cell different from animal cell. 2 marks
1 mark
√
Variables Manipulative variable: types of cells
Responding variable: the presence of cellular components 3 marks
Fixed variable: same microscope, same magnification
Only two correct variables 2 marks
Only one correct variable 1 mark
√
Apparatus and Materials : Cheek cell, Onion bulb ,iodine solution , distilled water, All present –
materials methylene blue 3marks
2 materials
KB061205 Apparatus : a light microscope, glass slide, cover slips, a scalpel , and 2 app –
forceps, a glass dropper, mounting needle and filter paper. 2 marks
– 1 mark
√
Technique Observe and draw the shape and cellular structure of plant cell and 3 mark
used animal by using light microscope. for report
Observe the shape and structure of plant cell 2 marks
Observe the shape /structure of plant cell 1 mark
√
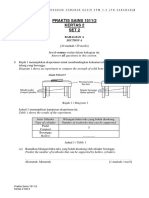
Procedure 1.Obtain scale leaf from onion bulb
2. Using a pair of forceps, peel off the transparent epidermis
KB061204 from the inner surface of onion scale leaf. 8/9P – 3 m
3. Put a drop of water onto the middle of the slide and place the
epidermis on the drop of water. 5-7P – 2 m
4. With help of mounting needle, cover the specimen with cover
slip 3/4P - 1m
5. Add a drop of iodine solution onto one side of cover slip.
6. Place a filter paper at the opposite end of the cover slip to allow
the iodine solution to spread through the epidermis. √
7. Use a piece of filter paper to absorb the excess iodine solution.
8. Examine the slide under light microscope using the low power
objective lens and then the high power objective lens.
9. Draw the epidermis and label the structure which can be
4551/3 [Lihat sebelah
SULIT
observe.
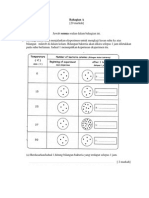
Observation Correct Diagram 1mark
Labelling – membrane cell,cell wall ,nucleus , vacuole 1 mark
Magnification 1 mark
Conclusion There are more cellular components that can be seen in plant cell
under light microscope compared to animal cell. 1 mark
Hypothesis accepted. √
Planning Able to state correctly
KB061203 7 aspects (7 ticks) - 3 marks
5/6 aspects (5/6 ticks) - 2 marks
3-4 aspects (3-4 ticks) - 1 mark
<3 - 0 mark
END OF MARKING SCHEME
4551/3 [Lihat sebelah
SULIT
You might also like
- Q&A Bio k3 Trial SPM PHG 09Document26 pagesQ&A Bio k3 Trial SPM PHG 09Mohd Khairul AnuarNo ratings yet
- Soalan Sains T5 K2Document20 pagesSoalan Sains T5 K2Shamshul DidarellyNo ratings yet
- SPM Biologi Bio k3 Set 2Document12 pagesSPM Biologi Bio k3 Set 2api-3841296No ratings yet
- Johor Paper 3 QuestionDocument7 pagesJohor Paper 3 QuestionsmtspNo ratings yet
- Fizik p3 f4 Final SBP 07Document18 pagesFizik p3 f4 Final SBP 07shazillaNo ratings yet
- Ujian Diagnostik Biologi Kertas 2 2021Document31 pagesUjian Diagnostik Biologi Kertas 2 2021Kah Lok OoiNo ratings yet
- Paper 3 Trial SMK SimanggangDocument9 pagesPaper 3 Trial SMK SimanggangelvivNo ratings yet
- Bio 07 K3 (Melaka Pra)Document8 pagesBio 07 K3 (Melaka Pra)Ferguson TehNo ratings yet
- Paper 3 Trial SPM SBP 2008Document13 pagesPaper 3 Trial SPM SBP 2008kamil muhammadNo ratings yet
- TP1743 - Kertas 1 Dan 2 Peperiksaan Percubaan SPM Sains 2023-20242Document21 pagesTP1743 - Kertas 1 Dan 2 Peperiksaan Percubaan SPM Sains 2023-20242Felix ChewNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS P2 2008 KedahDocument30 pagesPHYSICS P2 2008 KedahMohd Khairul Anuar100% (1)
- Ulangkaji KPSadj 2Document67 pagesUlangkaji KPSadj 2Saiful Anuar Bin SaidNo ratings yet
- Kertas Trial Sains Daerah Kota Marudu Sabah K2 2021Document13 pagesKertas Trial Sains Daerah Kota Marudu Sabah K2 2021litaNo ratings yet
- Kertas 3 BiologiDocument11 pagesKertas 3 Biologiina50% (2)
- SPM Mid Year 2008 SBP Physics Paper 3Document10 pagesSPM Mid Year 2008 SBP Physics Paper 3ChinWynn.com100% (2)
- Bahan Galus SPMDocument10 pagesBahan Galus SPMmohas_apisNo ratings yet
- Trial Terengganu Bio p3 PDFDocument14 pagesTrial Terengganu Bio p3 PDFYen QingNo ratings yet
- PATKIMIAK3KSSMDocument6 pagesPATKIMIAK3KSSMWAN HADHURAH BINTI WAN HALIM KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- 1PAPER 3 BIOLOGI SPM EnzimDocument7 pages1PAPER 3 BIOLOGI SPM EnzimMarzila MohamedNo ratings yet
- Kertas 1,2,3 Dan SkemaDocument89 pagesKertas 1,2,3 Dan SkemaAthirah MaestroNo ratings yet
- Kertas 3Document13 pagesKertas 3Ismaliza IshakNo ratings yet
- Trial SPM Sains Kertas 2 - SBP 2016Document25 pagesTrial SPM Sains Kertas 2 - SBP 2016Izeliwani Haji IsmailNo ratings yet
- Fizik Tingkatan 4 Kertas 3 2018Document10 pagesFizik Tingkatan 4 Kertas 3 2018MadAm JaJa100% (2)
- Kertas 2 Bahagian Ab F4 2021Document20 pagesKertas 2 Bahagian Ab F4 2021farah621460% (5)
- Latihan Ulangkaji 1Document12 pagesLatihan Ulangkaji 1Maryati KematNo ratings yet
- T4 2018Document14 pagesT4 2018serul1930No ratings yet
- SPM Bio K3 Set 2Document12 pagesSPM Bio K3 Set 2Athirah KhamizarNo ratings yet
- SPM 2005 - Kertas 3Document10 pagesSPM 2005 - Kertas 3kiongocNo ratings yet
- Soalan Percubaan SPM Fizik k3 2018 (Repaired)Document14 pagesSoalan Percubaan SPM Fizik k3 2018 (Repaired)jacylin_a_663291230No ratings yet
- Kertas 2 Biologi Tingkatan 4 KSSMDocument17 pagesKertas 2 Biologi Tingkatan 4 KSSMhairul67% (3)
- Question 1paper 3 - Modul 4 BiologiDocument24 pagesQuestion 1paper 3 - Modul 4 BiologiTian XiangNo ratings yet
- 2021 SPM - Modul - Sarawak Science K2 Set 2-5-23Document19 pages2021 SPM - Modul - Sarawak Science K2 Set 2-5-23Kogi vaaniNo ratings yet
- Sains SPM Pertengahan 2008 K2Document21 pagesSains SPM Pertengahan 2008 K2Marc AL Murobbi0% (1)
- Set 1 P2 PerakUlangkajiDocument18 pagesSet 1 P2 PerakUlangkajiZky afiqNo ratings yet
- SPM Percubaan 2008 MRSM Biology Paper 3Document12 pagesSPM Percubaan 2008 MRSM Biology Paper 3ChinWynn.com100% (1)
- Sains K2 Trial SPM Pahang 2008Document20 pagesSains K2 Trial SPM Pahang 2008Mohd Khairul Anuar100% (4)
- Skema Fizik Percubaan K1 F5 Kedah 2016Document14 pagesSkema Fizik Percubaan K1 F5 Kedah 2016Cheah Soon TikeNo ratings yet
- Latihan K3Document13 pagesLatihan K3nsa_daNo ratings yet
- Bio P3 PPT F4 2018Document10 pagesBio P3 PPT F4 2018veronica francisNo ratings yet
- Soalan Paper 3 Utk Mesyuarat Panitia DaerahDocument28 pagesSoalan Paper 3 Utk Mesyuarat Panitia DaerahNoorhayati AhmadNo ratings yet
- Kimia f5 Setengah Tahun 2015Document10 pagesKimia f5 Setengah Tahun 2015Normah MisparNo ratings yet
- Kertas 3 JulaiDocument6 pagesKertas 3 Julaizulhariszan abd mananNo ratings yet
- Percubaan 2014Document22 pagesPercubaan 2014cikguwanismktslNo ratings yet
- (Putrajaya 2023) - Sains Kertas 2 Set 1Document25 pages(Putrajaya 2023) - Sains Kertas 2 Set 1kurikulumjadualwaktuNo ratings yet
- Per - Spm. 2015Document45 pagesPer - Spm. 2015Hasnah Othman100% (1)
- Modul UlangkajiDocument7 pagesModul UlangkajishidaaghaniNo ratings yet
- Sarawak P3-Perealisasian Item Percubaan SPM 2017 Sri Aman (Fizik)Document18 pagesSarawak P3-Perealisasian Item Percubaan SPM 2017 Sri Aman (Fizik)nezuko akashiNo ratings yet
- Fizik Kertas 2 Peperiksaan Akhir Tahun SBP 2011 Ting 4Document30 pagesFizik Kertas 2 Peperiksaan Akhir Tahun SBP 2011 Ting 4nurul atiqah91% (11)
- Kertas 2 Pat Ting 4 2020 PPDDocument20 pagesKertas 2 Pat Ting 4 2020 PPDGDM SMKSPKNo ratings yet
- Kertas 2 pks1 SainsDocument15 pagesKertas 2 pks1 SainsIlman MohamadNo ratings yet
- Sains Sains SPM Set3 k2Document12 pagesSains Sains SPM Set3 k2api-3841296No ratings yet
- SBP Bio Paper 2Document20 pagesSBP Bio Paper 2smtspNo ratings yet
- Johor Paper 2 QuestionDocument23 pagesJohor Paper 2 QuestionsmtspNo ratings yet
- Kelantan Schema Answer Paper 1 & 2Document33 pagesKelantan Schema Answer Paper 1 & 2smtsp100% (2)
- Paper 2 Trial SPM 2008 TerengganuDocument21 pagesPaper 2 Trial SPM 2008 TerengganusmtspNo ratings yet
- Melaka Biology Paper 3Document12 pagesMelaka Biology Paper 3smtspNo ratings yet
- Kelantan Biology Paper 3 QuestionDocument30 pagesKelantan Biology Paper 3 QuestionsmtspNo ratings yet
- Terengganu Biology Trial Paper 3Document12 pagesTerengganu Biology Trial Paper 3smtspNo ratings yet
- Selangor Paper 1 Biology Trial SPM Question AnswerDocument33 pagesSelangor Paper 1 Biology Trial SPM Question AnswerArash HalimNo ratings yet
- Melaka Biology Paper 2Document25 pagesMelaka Biology Paper 2smtspNo ratings yet
- Selangor Paper 2 - Question & AnswerDocument36 pagesSelangor Paper 2 - Question & AnswersmtspNo ratings yet
- Perlis Paper2 & AnswerDocument36 pagesPerlis Paper2 & AnswersmtspNo ratings yet
- Perak Paper 2Document19 pagesPerak Paper 2smtspNo ratings yet
- Perak Paper 3 AnswerDocument12 pagesPerak Paper 3 AnswersmtspNo ratings yet