Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ministry of Education and Science of Ukraine: National Aviation University Air Transportation Management Department
Uploaded by
rogy2607Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ministry of Education and Science of Ukraine: National Aviation University Air Transportation Management Department
Uploaded by
rogy2607Copyright:
Available Formats
MINISTRY OF EDUCATION AND SCIENCE OF UKRAINE
NATIONAL AVIATION UNIVERSITY
Air Transportation Management Department
REPORT
in the course of
FUNDAMENTALS OF TRANSPORT PROCESS AND SYSTEM ANALYSIS
entitled
THE SYSTEM OF HUMAN BODY
Completed by
Student Igor Perekrestenko
(Name and Surname)
Group FML ATM-206
Revised by
Matiychyk A.M.
KYIV 2014
1. The skeletal system consists of 206 bones. Its functions include:
Strengthen and support the body.
Protect important internal organs.
Provide attachments and levers for muscular contractions.
Produce blood cells.
Site to storage and liberate minerals (e.g., calcium, phosphate, etc.).
2. The muscular system contains three different kinds of muscle, which vary in shapes
and functions.
Skeletal muscles are attached to the skeleton, and can be moved according to the
mind (i.e., voluntary).
Smooth muscles is found on the wall of hollow organs inside the body, and cannot
be controlled by the mind (i.e.,involuntary).
Cardiac muscles can only be found in the heart. Its strong and powerful
contractions are also involuntary.
Functions of the muscular system include:
o
Constitute different kinds of body movements through muscular contractions (e.g.
heart beat and breathing).
o
Maintain posture, stabilize joints, and produce energy.
3. The nervous system is composed of the brain, spinal cord, and millions of nerve cells
(i.e., neurons), which constitute a huge and complicated network. The major function of
the nervous system is to pass information and nerve impulses from one part of the body to
another.
4. The respiratory system consists of the lungs and the many air tracts of different sizes.
Cells and tissues inside the human body must be continuously supplied with oxygen to
produce energy for survival. The main function of the respiratory system is to provide
passages and room for gaseous exchange.
5. The circulatory system is composed of the heart and a complicated network of blood
vessels. Its main function is to transport nutrients and oxygen to the body tissues, and
remove metabolic wastes from the cells at the same time.
6. The lymphatic system is made up of a network of lymph vessels that runs along the
veins and arteries. It is a system to drain excess fluid from the spaces between cells.
Functions of the lymphatic system include:
Drain excess fluid from the spaces between cells (i.e., lymph) back to the
bloodstream.
The lymph node along the lymph vessels contains cells that can destroy bacteria,
and helps the immune response.
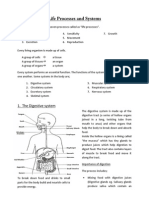
7. The digestive system contains the esophagus and certain organs responsible for
digestion (e.g., stomach, intestines, liver, and gall bladder). It main function is to break
down food into smaller substances for better absorption.
8. The urinary system is made up of two horsebean-shaped kidneys, two ureters, urinary
bladder, and the urethra. Major functions of the urinary system include:
Discharge metabolic wastes outside the body through urination.
Maintain internal balance of water and salt.
Adjust pH of blood.
9. The endocrine system is made up of special glands called the endocrine glands. Its
major functions is to secrete hormones to regulate metabolism of the body, growth,
development and reproduction.
10. The reproductive system differs very much in male and female. The major function
of the reproductive system is for the production of offspring.
Each of the above systems is responsible for the processes that are essential for life. In
physical education and sports, we are particularly interested in the skeletal system,
muscular system, nervous system, respiratory system and circulatory system.
You might also like
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument7 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyAdam Troy TaglucopNo ratings yet
- Parts of Body Nursing EnglishDocument5 pagesParts of Body Nursing EnglishZulyana PutriNo ratings yet
- Human Body Systems - Overview, Anatomy, Functions - KenhubDocument13 pagesHuman Body Systems - Overview, Anatomy, Functions - Kenhubregina.rmsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Anatomy)Document63 pagesChapter 1 (Anatomy)Phan Sokkheang100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - The Human Body: Notes: From Atoms To OrganismsDocument16 pagesChapter 1 - The Human Body: Notes: From Atoms To OrganismsIssa AvenaNo ratings yet
- FUNCTIONALOrganization of The Human BodyDocument20 pagesFUNCTIONALOrganization of The Human BodyAmela HajdinovicNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument29 pagesFunctional Anatomy and PhysiologyNawalNo ratings yet
- Physiology U-1 Introduction TeacherDocument195 pagesPhysiology U-1 Introduction Teachersinte beyuNo ratings yet
- Holy Child Colleges of ButuanDocument8 pagesHoly Child Colleges of ButuanJoseph Mark Ocampo ArtiagaNo ratings yet
- FUNCTIONALOrganization of The Human BodyDocument16 pagesFUNCTIONALOrganization of The Human BodyAuliya AlfaNo ratings yet
- The Ten Systems of The Human BodyDocument3 pagesThe Ten Systems of The Human BodyMoses AbiodunNo ratings yet
- Human OrgansDocument4 pagesHuman OrgansTishonna DouglasNo ratings yet
- SistemasDocument8 pagesSistemasSebastián HRNo ratings yet
- Introduction of AnatomyDocument71 pagesIntroduction of AnatomyPrasannaa BaleNo ratings yet
- Rt105 FinalsDocument15 pagesRt105 FinalsPeperonnie RonnieNo ratings yet
- Physiology-1 Department of Physiotherapy: BY DR - Laraib Jameel RPHDocument113 pagesPhysiology-1 Department of Physiotherapy: BY DR - Laraib Jameel RPHHashir SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- System of The Human BodyDocument31 pagesSystem of The Human BodyMari Thomas100% (1)
- Mapeh 3 - ModuleDocument19 pagesMapeh 3 - ModulePatricia Jean San SebastianNo ratings yet
- Comparison ChartDocument4 pagesComparison ChartMilangi Abe MichelangeliNo ratings yet
- Tugas Ii Task 1Document12 pagesTugas Ii Task 1Husnul KhotimahNo ratings yet
- Human Body - Wikipedia PDFDocument18 pagesHuman Body - Wikipedia PDFMavura ZwideNo ratings yet
- Nursing Second Task ORGANS AND BODY SYSTEMS 2024Document19 pagesNursing Second Task ORGANS AND BODY SYSTEMS 2024Alejandra JaraNo ratings yet
- Health TuteDocument6 pagesHealth TuteN GunaratneNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Physiology and Biochemistry-Notes For BBA (HA)Document12 pagesIntroduction of Physiology and Biochemistry-Notes For BBA (HA)devNo ratings yet
- P.E Anatomical TermsDocument26 pagesP.E Anatomical TermsGerald Mapalo FactorNo ratings yet
- Physical Education - Chapter 2Document4 pagesPhysical Education - Chapter 2Darlene CarmonaNo ratings yet
- Main Anatomical FeaturesDocument12 pagesMain Anatomical FeaturesAdelinaPredescuNo ratings yet
- W1 - 1 ModuleDocument7 pagesW1 - 1 ModuleGloryvi LatapNo ratings yet
- W1 - 1 ModuleDocument7 pagesW1 - 1 ModuleGloryvi LatapNo ratings yet
- The Human Body Terms: Dr. SuwonoDocument5 pagesThe Human Body Terms: Dr. SuwonoRed DemonNo ratings yet
- 11 Organ SystemsDocument2 pages11 Organ Systemsjonar parinasNo ratings yet
- Human Body SystemsDocument35 pagesHuman Body SystemsSir Rannie EspantoNo ratings yet
- Anat Physio Basics 2008Document108 pagesAnat Physio Basics 2008Chandan AhireNo ratings yet
- First Aid and Water Survival (Week 6-9)Document20 pagesFirst Aid and Water Survival (Week 6-9)NESIL PADASNo ratings yet
- TSC Study Material EditedDocument128 pagesTSC Study Material EditedNaina ShendeNo ratings yet
- Human Body PDFDocument9 pagesHuman Body PDFAnonymous W4MMefmCNo ratings yet
- MAKALAH. Memahami Dasar Anatomi Tubuh ManusiaDocument19 pagesMAKALAH. Memahami Dasar Anatomi Tubuh ManusiadediNo ratings yet
- Organ System 7Document2 pagesOrgan System 7verenicaNo ratings yet
- Anatomical, Physiological and Mechanical Bases of Movements: Body Really Made Of? "Document10 pagesAnatomical, Physiological and Mechanical Bases of Movements: Body Really Made Of? "Jay Carlo BagayasNo ratings yet
- Subiecte Engleza: 2. Human AnatomyDocument6 pagesSubiecte Engleza: 2. Human AnatomyMarius FeroiuNo ratings yet
- Introduction of AnatomyDocument115 pagesIntroduction of AnatomyVina Kristi DiscarNo ratings yet
- Textos I, Kinesio, Instr. Q. Level I '20Document9 pagesTextos I, Kinesio, Instr. Q. Level I '20Valeria DonzelliNo ratings yet
- Human Body Systems 3Document21 pagesHuman Body Systems 3JuLie Ann DeGuzman GeslaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - AnaphyDocument8 pagesChapter 1 - AnaphyCinderilla De AngelNo ratings yet
- PPT, Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument34 pagesPPT, Anatomy and PhysiologyAzikah RohimahhNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument5 pagesBIOLOGYKimberling SandovalNo ratings yet
- Body SystemsDocument1 pageBody SystemsJnz OlanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Human Anatomy and PhysiologySam Raven AndresNo ratings yet
- Sri Arliza Febriani TGS 2 No.1Document22 pagesSri Arliza Febriani TGS 2 No.1Sriarliza FebrianiNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER V: Tissues: Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Muscular Tissue Nervous TissueDocument10 pagesCHAPTER V: Tissues: Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Muscular Tissue Nervous TissueAem TalNo ratings yet
- Refresher Course: Names. (Biomechanics, 1990)Document21 pagesRefresher Course: Names. (Biomechanics, 1990)Kirby AnaretaNo ratings yet
- Human Body: Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Is ADocument35 pagesHuman Body: Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Is AkiruthikaNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy - ReadingDocument3 pagesHuman Anatomy - ReadingzuzanamNo ratings yet
- Vince Ford N. Marquez Grade 6 - RutherfordDocument15 pagesVince Ford N. Marquez Grade 6 - RutherfordfordmayNo ratings yet
- Human BodyDocument27 pagesHuman BodyRanbir Singh100% (1)
- The Human Body, IIDocument33 pagesThe Human Body, IICesia VilcheNo ratings yet
- The Human Musculoskeletal SystemDocument1 pageThe Human Musculoskeletal SystemFrederickVillaflorNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument10 pagesCirculatory SystemKent Clark VillaNo ratings yet
- Edit Source Editbeta: Constituents of The Human Body Constituent Weight Percent of AtomsDocument13 pagesEdit Source Editbeta: Constituents of The Human Body Constituent Weight Percent of AtomsRanbir SinghNo ratings yet
- The Exchange Student (Dedicated To Rotary International)Document163 pagesThe Exchange Student (Dedicated To Rotary International)Nikita100% (1)
- SOLIDWORKS 2022 Whitepaper UsingDesignAutomationtoReduceCostsIncreaseProfitability FinalDocument10 pagesSOLIDWORKS 2022 Whitepaper UsingDesignAutomationtoReduceCostsIncreaseProfitability FinalAlba R.No ratings yet
- GSM Rtu Controller Rtu5011 v2 PDFDocument27 pagesGSM Rtu Controller Rtu5011 v2 PDFAbdul GhaniNo ratings yet
- Battle Group Builder + Commonwealth Infantry Roster - Wargames DesignDocument12 pagesBattle Group Builder + Commonwealth Infantry Roster - Wargames DesignPete PoliNo ratings yet
- Hamilton-Resume 4Document1 pageHamilton-Resume 4api-654686470No ratings yet
- Drive Engineering - Practical Implementation SEW Disc Brakes 09202218 - G1Document90 pagesDrive Engineering - Practical Implementation SEW Disc Brakes 09202218 - G1Anonymous ntE0hG2TPNo ratings yet
- Sears Canada: Electric DryerDocument10 pagesSears Canada: Electric Dryerquarz11100% (1)
- Chain Rule 3LNDocument2 pagesChain Rule 3LNsaad khNo ratings yet
- Fruit Brearing CropsDocument177 pagesFruit Brearing CropsJoshua G. Sapin100% (1)
- PCI20107, Overview of Boiler Commissioning and Startup PDFDocument17 pagesPCI20107, Overview of Boiler Commissioning and Startup PDFMarc AnmellaNo ratings yet
- Colony Earth - Part X: The Myriad WorldsDocument7 pagesColony Earth - Part X: The Myriad WorldsV. Susan FergusonNo ratings yet
- Coca-Cola BeverageDocument17 pagesCoca-Cola BeverageMahmood SadiqNo ratings yet
- Freedom SW 2000 Owners Guide (975-0528!01!01 - Rev-D)Document48 pagesFreedom SW 2000 Owners Guide (975-0528!01!01 - Rev-D)MatthewNo ratings yet
- Eimco Elecon Initiating Coverage 04072016Document19 pagesEimco Elecon Initiating Coverage 04072016greyistariNo ratings yet
- HDMI To MIPI and LVDS To MIPI Converter Rotator Board Solutions From Q VioDocument2 pagesHDMI To MIPI and LVDS To MIPI Converter Rotator Board Solutions From Q VioSubham KumarNo ratings yet
- (FORD) Manual de Propietario Ford Ranger 1998Document160 pages(FORD) Manual de Propietario Ford Ranger 1998Marly Salas GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Student EssaysDocument41 pagesStudent EssaysAsif RahmanNo ratings yet
- Ben ChanDocument2 pagesBen ChanAlibabaNo ratings yet
- A Simple and Reliable Submental Intubation.68Document4 pagesA Simple and Reliable Submental Intubation.68Tîrban Pantelimon FlorinNo ratings yet
- Leading Airline Emirates Boosts Leisure Travel Sales - : Peakwork Case Study: EmiratesDocument3 pagesLeading Airline Emirates Boosts Leisure Travel Sales - : Peakwork Case Study: EmiratesAhmed AbboudNo ratings yet
- Adherence Tradeoff To Multiple Preventive Therapies and All-Cause Mortality After Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument12 pagesAdherence Tradeoff To Multiple Preventive Therapies and All-Cause Mortality After Acute Myocardial InfarctionRoberto López MataNo ratings yet
- Anilkumar Surendran 3-AdDocument4 pagesAnilkumar Surendran 3-AdAnil AmbalapuzhaNo ratings yet
- BIO CH04 FoundationsDocument12 pagesBIO CH04 FoundationsDyuana Stevenson0% (1)
- 3500 Ha027988 7Document384 pages3500 Ha027988 7Gigi ZitoNo ratings yet
- Software Requirements CompressDocument9 pagesSoftware Requirements CompressApni Duniya100% (1)
- Osssc JR Clerk Odia Paper 2015 - 20171207 - 0001Document7 pagesOsssc JR Clerk Odia Paper 2015 - 20171207 - 0001songspk100No ratings yet
- Barista TestDocument7 pagesBarista Testwinnie chanNo ratings yet
- 08 BQ - PADSB - Elect - P2 - R2 (Subcon Empty BQ)Document89 pages08 BQ - PADSB - Elect - P2 - R2 (Subcon Empty BQ)Middle EastNo ratings yet
- Welcome Speech For Seminar in College 2Document4 pagesWelcome Speech For Seminar in College 2Niño Jay C. GastonesNo ratings yet
- Robotech Hannibal Digital 114dpi V1.0Document119 pagesRobotech Hannibal Digital 114dpi V1.0nonfarb14thNo ratings yet
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)From EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (404)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (31)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (82)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (46)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesFrom EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1412)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (170)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- Troubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassFrom EverandTroubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (27)
- Dark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingFrom EverandDark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1138)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)