Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Determining Area of Polygonal Field Using Tape
Uploaded by
Ralph GalvezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Determining Area of Polygonal Field Using Tape
Uploaded by
Ralph GalvezCopyright:
Available Formats
4
[DETERMINING THE AREA OF A POLYGONAL FIELD
USING ONLY THE TAPE]
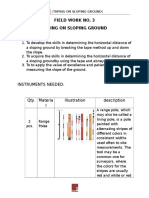
FIELD WORK NO. 4
Determining the area of a polygonal field using only the
tape
OBJECTIVES:
1. To develop the skills in determining the horizontal distance of
a uneven ground by breaking the tape method up and down
the slope.
2. To acquire the skills in determining the horizontal distance of
a sloping ground by using the tape and the automatic level.
3. To to apply the value of excellence and patience in
measuring the distance of the ground.
REASERCH
Measuring the polygonal field with different sides are called
measuring of irregular polygons.
An irregular polygon is any polygon that is not a regular polygon.
It can have sides of any length and each interior angle can be any
measure. They can be convex or concave, but all concave
polygons are irregular since the interior angles cannot all be the
same. If you drew a polygon at random, it would probably be
irregular.
Specific irregular polygons such as a parallelogram have some
interesting properties and have their own web pages.
So how to do it?
One approach is to break the shape up into pieces that
you can solve - usually triangles, since there are many ways to
calculate the area of triangles. Exactly how you do it depends on
what you are given to start. Since this is highly variable there is
[DETERMINING THE AREA OF A POLYGONAL FIELD
USING ONLY THE TAPE]
no easy rule for how to do it. The examples below give you some
basic approaches to try.
1. Break into triangles, then add
In the figure on the right, the polygon
can be broken up into triangles by drawing all the diagonals from
one of the vertices. If you know enough sides and angles to find
the area of each, then you can simply add them up to find the
total. Do not be afraid to draw extra lines anywhere if they will
help find shapes you can solve.
Here, the irregular hexagon is divided in to 4 triangles by the
addition of the red lines.
2. Find 'missing' triangles, then subtract
In the figure on the left, the overall shape
is a regular hexagon, but there is a triangular piece missing.
We know how to find the area of a regular polygon so we just
subtract the area of the 'missing' triangle created by drawing the
red line.
3. Consider other shapes
[DETERMINING THE AREA OF A POLYGONAL FIELD
USING ONLY THE TAPE]
In the figure on the right, the shape is an
irregular hexagon, but it has a symmetry that lets us break it into
two parallelograms by drawing the red dotted line. (assuming of
course that the lines that look parallel really are!)
We know how to find the area of a parallelogram so we just find
the area of each one and add them together.
As you can see, there an infinite number of ways to break down
the shape into pieces that are easier to manage. You then add or
subtract the areas of the pieces. Exactly how you do it comes
down to personal preference and what you are given to start.
4. If you know the coordinates of the vertices
If you know the x,y coordinates of the vertices (corners) of the
shape, there is a method for finding the area directly.. This works
for all polygon types (regular, irregular, convex, concave). There
is also a computer algorithm that does the same.
INSTRUMENTS NEEDED:
Qty. Materia
l
2
pcs.
Illustration
description
A range pole, which
may also be called a
lining pole, is a pole
painted with
Range
Poles
3
pcs.
[DETERMINING THE AREA OF A POLYGONAL FIELD
USING ONLY THE TAPE]
alternating stripes of
different colors in
consistent widths
used often to site
measurements. The
tool may be a
common one for
surveyors, where
the colors for the
stripes are usually
red and white or red
and yellow. The
colors are picked
based on their
visibility. One end of
the pole will
typically have either
a pointed tip or
gripping shoe to aid
in standing it on
edge. Longer range
poles may be
equipped with a
tripod or stand.
is a soft, white,
porous sedimentary
rock, a form of
limestone composed
of the mineral
calcite. This is used
in marking
measurements on
ground.
Chalk
2
Pcs.
Plumb
bobs
1 pc.
50
meter
tape
[DETERMINING THE AREA OF A POLYGONAL FIELD
USING ONLY THE TAPE]
A plumb bob is a
tool used to ensure
that a building
structure like a door
frame or a shelving
support is as vertical
as possible. It is also
used to measure if
an object is placed
directly under a
point above it, such
as placing a shower
drain relative to
some point on the
ceiling, or putting
something right
under a lighting
fixture.
A tape measure or
measuring tape is a
flexible form of ruler.
It consists of a
ribbon of cloth,
plastic, fiber glass,
or metal strip with
linear-measurement
markings. It is a
common measuring
tool. Its flexibility
allows for a measure
of great length to be
easily carried in
pocket or toolkit and
permits one to
[DETERMINING THE AREA OF A POLYGONAL FIELD
USING ONLY THE TAPE]
measure around
curves or corners.
Today it is
ubiquitous, even
appearing in
miniature form as a
keychain fob, or
novelty item.
Surveyors use tape
measures in lengths
of over 100 m
(300+ ft).
PROCEDURE:
A. Determination of the area of triangle components using
the basic formula.
A= B x H
2
1. The students designates the locations of 5 random
points that is likely to be a pentagonal shape.
2. The chief of party divides the field area into convenient
triangular components and calls them A1 ,A2 and A3.
3. For first trial use the basic formula to compute the field
and designate this as the base of the triangle.
4. Determine the length of the altitude to this base. The
determination of the altitude is done by locating a point
on this base after dropping a line perpendicular to this
from opposite vertex by swaying.
5. Record the length of the base and altitude in the
fieldwork computation sheet provided.
6. Repeat the same procedures 4-6 with the rest of the
triangular components of the polygonal field and the
sum up the areas.
[DETERMINING THE AREA OF A POLYGONAL FIELD
USING ONLY THE TAPE]
B. Determination of the triangles by using the formula.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Area = ab sin C
2
The same triangular field will be used for this second
trial but change the naming of the vertices of polygonal
filed.
The chief of party divides the field area into convenient
triangular components and calls them A1 ,A2 and A3.
For second use the basic formula in B to compute the
field and designate this as the base of the triangle.
Determine the measurement of the angles between the
lines.
Record the lengths of two sides and and included angle
in the field work. Record in the data.
Repeat procedures 4-6 with the rest of triangular
components of the polygonal area to compute the
entire area.
C. Determination of the area using the formula.
A= s(sa)(sb)(sc)
S=
A+ B+C
2
1. The same triangular field will be used for this second
trial but change the naming of the vertices of polygonal
filed.
2. The chief of party divides the field area into convenient
triangular components and calls them A1 ,A2 and A3.
3. For third use the basic formula in C the herons formula
to compute the field and designate this as the base of
the triangle.
4. Record the lengths of the three sides of each triangles.
5. Repeat procedures 3-5 with the rest of the triangular
components until the data is complete.
[DETERMINING THE AREA OF A POLYGONAL FIELD
USING ONLY THE TAPE]
COMPUTATIONS:
A=
bxh
2
A= area of the triangle
B= Base of the triangle
H= Altitude of the triangle
A=
absin
2
A= area of the triangle
b and a = random two sides of the triangle
sin = sine of the included angle of the measured sides a and b
s (sa)(sb)(sc)
S=
A= area in triangle in square meters
S = half perimeter of triangle
a,b and c= sides of the triangles
PRINCIPLE
A+ B+C
2
[DETERMINING THE AREA OF A POLYGONAL FIELD
USING ONLY THE TAPE]
There are several ways that we can measure the distance of the
ground. It can be accomplished by breaking the tape method, by
making a irregular polygon. A horizontal line of sight is
established if the bubble is centered while sigthing through the
tube. This device is simply a level adopted for measuring vertical
angles. Vertical aide is acted on where angles are read. It gives
the value and the slope in terms of arc measure.
Final Data Sheet
A)1st method: By base and altitude
Triangle
1
2
3
Base
21.9m
21.9m
21.9m
Altitude
12.1m
14.4m
8.6m
Total
Area
132.485sqm
156.68sqm
93.68sqm
382.845sqm
B)2nd method by two sides and included angle
Triangle
[DETERMINING THE AREA OF A POLYGONAL FIELD
USING ONLY THE TAPE]
Angle in
Sides
Area
82.89
90.97
100.71
a
17.55m
b
15.2m
21.9m
21.8m
17.6m
10.75m
Total
132.39sq
m
156.51sq
m
92.95sqm
381.80sq
m
C)3rd method: By herons formula
Triangl
e
1
2
3
Sides
a
17.55
m
21.9m
b
15.2m
c
21.9m
21.8m
10.75
m
17.6m
15.86
m
21.8m
Semi
perimeter
s
27.325m
29.58m
25.058m
Total
ILLUSTRATION
Area
132.55sq
m
157.97sq
m
93.77sqm
384.29sq
m
[DETERMINING THE AREA OF A POLYGONAL FIELD
USING ONLY THE TAPE]
Marking the 5points of the polygon.
[DETERMINING THE AREA OF A POLYGONAL FIELD
USING ONLY THE TAPE]
[DETERMINING THE AREA OF A POLYGONAL FIELD
USING ONLY THE TAPE]
Measuring the field by breaking the tape method.
CONCLUSION
Based on my own observation to get more accurate
results you need to measure the measurement slowly and
carefully to obtain better results. You may also measure
along the ground on a. But to obtain horizontal distances,
you will need to correct these ground measurements
afterwards by using correct mathematical formulas . As
an additional information we must also apply the value of
patience in making the task because the location is
outside so expect extreme heat or rain. Calculate all
solutions properly and make the distance measured more
[DETERMINING THE AREA OF A POLYGONAL FIELD
USING ONLY THE TAPE]
accurate. We need to be patient and follow all the
procedures carefully to make the measurement accurate.
You might also like
- Dubbel-Handbook of Mechanical EngineeringDocument918 pagesDubbel-Handbook of Mechanical EngineeringJuan Manuel Domínguez93% (27)
- Fieldwork 4 CE140Document18 pagesFieldwork 4 CE140Jonas CayananNo ratings yet
- 8$20 AreaDocument26 pages8$20 AreaBaskaran SeetharamanNo ratings yet
- Mthn14e Lec 2Document26 pagesMthn14e Lec 2Aly BueserNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of SurveyingDocument28 pagesFundamentals of SurveyingPHEBY MOOGNo ratings yet
- Linear Survey ReportDocument15 pagesLinear Survey ReportSyahmi Fadzi100% (1)
- Visualizing Solid Shapes Class VIIIDocument9 pagesVisualizing Solid Shapes Class VIIIDivyanshiNo ratings yet
- Building Material Estimates and Rates Build Up: Second EditionFrom EverandBuilding Material Estimates and Rates Build Up: Second EditionNo ratings yet
- Field Work No. 4 Determining The Area of A Polygonal Field Using Only The Tape PDFDocument8 pagesField Work No. 4 Determining The Area of A Polygonal Field Using Only The Tape PDFJawahir Gomez33% (3)
- Field Work No 3 SurveyingDocument8 pagesField Work No 3 SurveyingRalph GalvezNo ratings yet
- TSKEP1313 TangramDocument6 pagesTSKEP1313 TangramDanielle VezinaNo ratings yet
- Earned ValueDocument24 pagesEarned ValueRalph GalvezNo ratings yet
- Surveying Lab Exercise OutlineDocument19 pagesSurveying Lab Exercise OutlineBenjie Latriz40% (5)
- Chain Surveying ReportDocument3 pagesChain Surveying ReportAthiyo Martin64% (25)
- Algebra TextbookDocument483 pagesAlgebra TextbookRituraj Gautam100% (2)
- Earned Value System pdf1Document18 pagesEarned Value System pdf1Ralph GalvezNo ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument14 pagesMathematicsSkyler MontalvoNo ratings yet
- PMP 02282021Document175 pagesPMP 02282021Ralph GalvezNo ratings yet
- Chain SurveyingDocument3 pagesChain SurveyingAhmadGhanem100% (1)
- Field Work No 4 SurveyingDocument12 pagesField Work No 4 SurveyingAubrey Camille CabreraNo ratings yet
- Pinto Pm4 Inppt 13-PrDocument24 pagesPinto Pm4 Inppt 13-PrAbdullahRafiqNo ratings yet
- Pinto Pm4 Inppt 13-PrDocument24 pagesPinto Pm4 Inppt 13-PrAbdullahRafiqNo ratings yet
- Measurement Lesson PlanDocument30 pagesMeasurement Lesson Plannegus russellNo ratings yet
- Field Work No 5 SurveyingDocument14 pagesField Work No 5 SurveyingRalph GalvezNo ratings yet
- FW4Document7 pagesFW4Ian Ag-aDoctorNo ratings yet
- Mabuti, Roy Jason M.: Field Work Report No. 4Document9 pagesMabuti, Roy Jason M.: Field Work Report No. 4JasonNo ratings yet
- Square Pyramid: Your Measurements Down. Down. Down, TooDocument6 pagesSquare Pyramid: Your Measurements Down. Down. Down, TooCik WaniNo ratings yet
- Offset SurveyDocument10 pagesOffset SurveygladysNo ratings yet
- Geoinformatics LabDocument12 pagesGeoinformatics Labhamidreza shafieeNo ratings yet
- Unit - 4: Materials and Principles of ConstructionDocument7 pagesUnit - 4: Materials and Principles of ConstructionShriya MadooriNo ratings yet
- Survey-I-Practicals Final Form 21 Oct 2011Document17 pagesSurvey-I-Practicals Final Form 21 Oct 2011Muhammad Farooq Zia100% (1)
- Surveying 18 60Document52 pagesSurveying 18 60Devika shettyNo ratings yet
- CE8361 - Surveying and Levelling Lab ManualDocument48 pagesCE8361 - Surveying and Levelling Lab ManualSelvam GanesanSelvamNo ratings yet
- ECV 304 Surveying III Area and Volume ComputationDocument10 pagesECV 304 Surveying III Area and Volume ComputationPaulpablo ZaireNo ratings yet
- Field Work No.1 Determining The Polygonal Area of A Piece of Land Using Only The Meter TapeDocument9 pagesField Work No.1 Determining The Polygonal Area of A Piece of Land Using Only The Meter TapePatrickTulayNo ratings yet
- Area and Volume Calculations for Earthwork ProjectsDocument20 pagesArea and Volume Calculations for Earthwork ProjectsKenny BoatNo ratings yet
- FW4Document13 pagesFW4Cristine Joy Mag-isaNo ratings yet
- GEOMETRIC CONSTRUCTION TECHNIQUESDocument7 pagesGEOMETRIC CONSTRUCTION TECHNIQUESJohara Bayabao-AngniNo ratings yet
- Math B, G8 3rdDocument13 pagesMath B, G8 3rdBen sik ali mohamedNo ratings yet
- English Stake Out: State Polytechnic of JakartaDocument33 pagesEnglish Stake Out: State Polytechnic of JakartaRuth AnggelaNo ratings yet
- Ce Lab Imp 1Document44 pagesCe Lab Imp 1D RNo ratings yet
- Area Formula MathDocument23 pagesArea Formula MathEmmanuel de LeonNo ratings yet
- CE8361Document48 pagesCE8361Darshan NarasgoudNo ratings yet
- GEE1 Assessment 5Document5 pagesGEE1 Assessment 5Christian John Resabal BiolNo ratings yet
- How to Find the Area of a Parallelogram by SubtractionDocument10 pagesHow to Find the Area of a Parallelogram by SubtractionJenonymouslyNo ratings yet
- YunisDocument10 pagesYunisAbdla DoskiNo ratings yet
- ArMath1 - Presentation3Document31 pagesArMath1 - Presentation3Jayson RamirezNo ratings yet
- Geometry: College Admission Test ReviewDocument9 pagesGeometry: College Admission Test ReviewdonlynNo ratings yet
- Chain SurveyingDocument3 pagesChain SurveyingUlfathbary AB100% (2)
- Calculating Area Using Grids and FormulasDocument5 pagesCalculating Area Using Grids and Formulasminnett pinnockNo ratings yet
- Survey CampDocument45 pagesSurvey Campskkpblr0% (1)
- Math 2 Ch6 ReteachingDocument5 pagesMath 2 Ch6 Reteachingksimmons82No ratings yet
- Math BitsDocument7 pagesMath BitsSimon BridgeNo ratings yet
- Lab3 OdtDocument2 pagesLab3 OdtEldie Junior ApostolNo ratings yet
- Map Work Techniques and SkillsDocument18 pagesMap Work Techniques and SkillsDealNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 TANGONAN - PlanimeterDocument9 pagesActivity 3 TANGONAN - PlanimeterBryan TangonanNo ratings yet
- Airline Tickets: Unit SquareDocument1 pageAirline Tickets: Unit SquareCarol LizardoNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter - PrelimDocument2 pages3rd Quarter - PrelimShiela Marie Galo Sanico-DespoyNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document9 pagesExperiment 2Narry StrummerNo ratings yet
- Class 4Document21 pagesClass 4Rahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Field Work No 2 SurveyingDocument8 pagesField Work No 2 SurveyingRalph GalvezNo ratings yet
- Camp PrjoectDocument55 pagesCamp PrjoectyudhishtherNo ratings yet
- 01 - Performing Mensuration andDocument59 pages01 - Performing Mensuration andjude metanteNo ratings yet
- 1triangulation SurveyDocument120 pages1triangulation SurveySumit PrajapatNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument5 pagesGeometrylolileeNo ratings yet
- Drawing 1Document25 pagesDrawing 1Art Lorenz AntigaNo ratings yet
- Surveying Tools and Equipments1Document39 pagesSurveying Tools and Equipments1JEAN DE DIEU MUVARANo ratings yet
- Moving in Space Chapter 6 Math 1b Prob DoneDocument24 pagesMoving in Space Chapter 6 Math 1b Prob Doneapi-245320669No ratings yet
- Physical Geography MsceDocument96 pagesPhysical Geography MsceYamikani MicahNo ratings yet
- galvez, Ralph Marrion A. - Use of multiple influence tacticsDocument6 pagesgalvez, Ralph Marrion A. - Use of multiple influence tacticsRalph GalvezNo ratings yet
- Written Output format enpowermentDocument3 pagesWritten Output format enpowermentRalph GalvezNo ratings yet
- Module 06 Adv PM Budget MGMTDocument49 pagesModule 06 Adv PM Budget MGMTshakeelzafarNo ratings yet
- Slides 11.3 Calculate Schedule and Cost Variances With EarneDocument63 pagesSlides 11.3 Calculate Schedule and Cost Variances With EarneElisa VadalàNo ratings yet
- Capitol - Balance CHB & Painting 12052023Document21 pagesCapitol - Balance CHB & Painting 12052023Ralph GalvezNo ratings yet
- Module 06 Adv PM Budget MGMTDocument49 pagesModule 06 Adv PM Budget MGMTshakeelzafarNo ratings yet
- Earned Value System PDF 2Document91 pagesEarned Value System PDF 2Ralph GalvezNo ratings yet
- Earned Value Management Tutorial Module 1: Introduction To Earned Value ManagementDocument25 pagesEarned Value Management Tutorial Module 1: Introduction To Earned Value ManagementImtiaz KianiNo ratings yet
- 2022 Duraroof Brochure (Atlanta)Document4 pages2022 Duraroof Brochure (Atlanta)Ralph GalvezNo ratings yet
- Trench DetailDocument1 pageTrench DetailRalph GalvezNo ratings yet
- TRENCHDocument1 pageTRENCHRalph GalvezNo ratings yet
- TRENCHDocument1 pageTRENCHRalph GalvezNo ratings yet
- Trench Canal DetailsDocument1 pageTrench Canal DetailsRalph GalvezNo ratings yet
- Additional RubberDocument1 pageAdditional RubberRalph GalvezNo ratings yet
- Rubber - UpdatedDocument1 pageRubber - UpdatedRalph GalvezNo ratings yet
- Stadium Balance of WorkDocument1 pageStadium Balance of WorkRalph GalvezNo ratings yet
- ASPHAL-UPDATED OvalDocument1 pageASPHAL-UPDATED OvalRalph GalvezNo ratings yet
- Specifications for steel bars of 7 precast concrete structuresDocument12 pagesSpecifications for steel bars of 7 precast concrete structuresRalph GalvezNo ratings yet
- Marcos Stadium - Landscape Estimate - For EvaluationDocument2 pagesMarcos Stadium - Landscape Estimate - For EvaluationRalph GalvezNo ratings yet
- Billing Monitoring PB14 Aug2022Document4 pagesBilling Monitoring PB14 Aug2022Ralph GalvezNo ratings yet
- TB-1 rebar specifications for multiple gridsDocument14 pagesTB-1 rebar specifications for multiple gridsRalph GalvezNo ratings yet
- Stadium Suspension-3Document6 pagesStadium Suspension-3Ralph GalvezNo ratings yet
- Pressure Slab Rebar ComputationDocument9 pagesPressure Slab Rebar ComputationRalph GalvezNo ratings yet
- Retaining Wall ComputationDocument3 pagesRetaining Wall ComputationRalph GalvezNo ratings yet
- Computation For TanksDocument6 pagesComputation For TanksRalph GalvezNo ratings yet
- Mensuration of Plane FiguresDocument7 pagesMensuration of Plane FiguresXlyth RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Fur Gen ManualDocument10 pagesFur Gen ManualAdnan DervicNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 - Graphics PrimitivesDocument10 pagesChapter - 2 - Graphics Primitivesnaod abrehamNo ratings yet
- Topic 4: PolygonDocument14 pagesTopic 4: PolygonChee Poh TayNo ratings yet
- Digital Text BookDocument12 pagesDigital Text BookBindu Vinu100% (1)
- POLYLINES AND SPLINESDocument9 pagesPOLYLINES AND SPLINESkimNo ratings yet
- TesselationsDocument12 pagesTesselationskrittinkalraNo ratings yet
- Module 4 PolygonDocument8 pagesModule 4 PolygonI Need Lyrics DudeNo ratings yet
- ACT Geometry - PolygonsDocument8 pagesACT Geometry - PolygonsaftabNo ratings yet
- Ade 7.unit 1-Cool Downs-EnDocument12 pagesAde 7.unit 1-Cool Downs-Enjhariprasad.sarmaNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Math Notes Chapter 14 SymmetryDocument6 pagesClass 7 Math Notes Chapter 14 SymmetryManishNo ratings yet
- GiD User ManualDocument169 pagesGiD User ManualjcazNo ratings yet
- 05-GIS Tutorial 1 - Chapter 6 PDFDocument37 pages05-GIS Tutorial 1 - Chapter 6 PDFali zia khalidNo ratings yet
- Modifications Made To Modelmuse To Add Support For The Saturated-Unsaturated Transport Model (Sutra)Document12 pagesModifications Made To Modelmuse To Add Support For The Saturated-Unsaturated Transport Model (Sutra)Haili JiaNo ratings yet
- Review Exercise 27 Objective)Document7 pagesReview Exercise 27 Objective)Vimalraj MoghanNo ratings yet
- Archimedes Polygon Method for Approximating PiDocument10 pagesArchimedes Polygon Method for Approximating Pi乐轩No ratings yet
- Filesdocuments6886c86c 6f69 4da0 849b Dfd973c85eeb PDFDocument12 pagesFilesdocuments6886c86c 6f69 4da0 849b Dfd973c85eeb PDFJana HaithamNo ratings yet
- Computer Notes Clipping IIDocument11 pagesComputer Notes Clipping IIecomputernotesNo ratings yet
- Strategic Intervention for Sum of Interior AnglesDocument21 pagesStrategic Intervention for Sum of Interior AnglesDanny VelardeNo ratings yet
- 360 Chapter 9 Objects and Classes: Rogramming XercisesDocument5 pages360 Chapter 9 Objects and Classes: Rogramming XercisesBito ChungNo ratings yet
- An Efficient Fence Fill Algorithm Using Inside-Outside TestDocument5 pagesAn Efficient Fence Fill Algorithm Using Inside-Outside TestHarman SinghNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Mapping (MATH 7) First Quarter Week Content Standards Performance Standards Student Assessment Activity/ies Teaching Activities 1Document11 pagesCurriculum Mapping (MATH 7) First Quarter Week Content Standards Performance Standards Student Assessment Activity/ies Teaching Activities 1FairyLeen PitogoNo ratings yet
- Polygon Power PointDocument14 pagesPolygon Power PointDog GodNo ratings yet
- 20 Properties of Regular PolygonsDocument9 pages20 Properties of Regular Polygonsapi-299265916No ratings yet