Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Theory, Cell Structure and Function Vocabulary
Uploaded by
jennymabilen0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesOriginal Title
september3.doc
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesCell Theory, Cell Structure and Function Vocabulary
Uploaded by
jennymabilenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
1
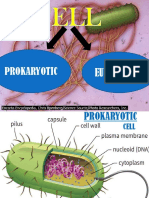
Cell Theory, Cell Structure and Function Vocabulary
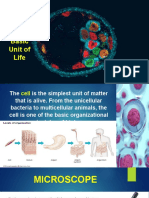
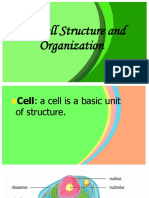
Cell a basic unit of structure and function in all organisms; the smallest unit of matter
that can carry on all the processes of life.
Unicellular composed of only one cell.
Multicellular composed of more than one cell.
Cell Membrane the structure that surrounds a cell to provide protection.
Cell Wall a rigid structure that surrounds the cell membrane of plant cells providing
support and protection to the cell.
Cytoplasm fluid, made mostly of water, that fills most of the space within a cell.
Organelle a structure inside a cell that carries out a specific process of life.
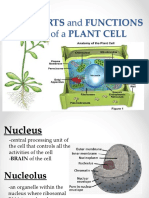
Nucleus the central part of a cell that serves as a control center by directing most cell
activities.
Nuclear Membrane the membrane that surrounds the nucleus of a cell
Nucleolus a small rounded body within a nucleus that contains RNA and proteins and
is involved in the production of ribosomes
Mitochondria the cell structure responsible for changing energy from nutrients into a
form that cells can use
ATP- a chemical compound that cells use for energy.
Ribosome an organelle where proteins are synthesized
Endoplasmic Reticulum an extensive network of membranes in a cell that acts like a
highway along which molecules can move from one part of the cell to another.
Golgi Apparatus the organelle that modifies and packages proteins for specific uses
in the cell.
Lysosome the organelle that contains enzymes to break down or digest organic
compounds and old organelles.
Chloroplasts a cell organelle that stores chlorophyll and serves as the site for
photosynthesis.
Vacuole a membrane bound sac use to store nutrients and wastes while helping in the
digestive processes of the cell.
You might also like
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument14 pagesAnimal and Plant Cellslea a delgadoNo ratings yet
- Parts of Animal CellDocument27 pagesParts of Animal CellJomhel Callueng100% (1)
- Parts and Functions: of A Plant CellDocument15 pagesParts and Functions: of A Plant CellAlleen Joy SolivioNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument9 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsMlshin LaoNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument3 pagesAnimal and Plant CellsBeth AlcontinNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Lesson 3: Lesson 3: Cell Cell Structures Structures AND AND Functions FunctionsDocument4 pagesLesson 3: Lesson 3: Cell Cell Structures Structures AND AND Functions Functionskruyll vlogsNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument7 pagesAnimal CellLezircYojDapmalNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Organelles: Prepared By: SAPANA JHADocument14 pagesEukaryotic Cell Organelles: Prepared By: SAPANA JHAAppu JhaNo ratings yet
- Unit II: Cell, Tissues, Glands, and MembranesDocument10 pagesUnit II: Cell, Tissues, Glands, and MembranesEds BernardoNo ratings yet
- Plant Cells: by Fortunate Refil Bsed Sci 2Document20 pagesPlant Cells: by Fortunate Refil Bsed Sci 2Marifer DapatNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 REVIEWDocument16 pagesUnit 4 REVIEWJuliana RiveraNo ratings yet
- A Sub-Cellular Structure That Has One or More Specific Jobs To Perform in The Cell, Much Like An Organ Does in The BodyDocument1 pageA Sub-Cellular Structure That Has One or More Specific Jobs To Perform in The Cell, Much Like An Organ Does in The BodySarthepandabearNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure VocabDocument1 pageCell Structure VocabFatima ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Ploginpartpppppp: Parts of Animal CellsDocument2 pagesPloginpartpppppp: Parts of Animal CellsNelson De LimaNo ratings yet
- Cells: Characteristics of The CellDocument4 pagesCells: Characteristics of The CellRashidah R. DisomaNo ratings yet
- STM123 OutlineDocument19 pagesSTM123 OutlineNur-Aiza AlamhaliNo ratings yet
- Biochem CellsDocument5 pagesBiochem Cellsleviona halfNo ratings yet
- Kingdom: Animal CellDocument8 pagesKingdom: Animal CellShaila IvoryNo ratings yet
- Cell The Basic Unit of Life 1Document22 pagesCell The Basic Unit of Life 1Matt Andrei AmorosoNo ratings yet
- Parts & Function of CellsDocument25 pagesParts & Function of CellsHariet ObieNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology PresentationDocument14 pagesCell Biology Presentationahmadihamed1459No ratings yet
- 1C-Tabugoc - LA2 Plant CellDocument5 pages1C-Tabugoc - LA2 Plant CellClint Jhun TabugocNo ratings yet
- CELLSDocument6 pagesCELLSFenny May SebonNo ratings yet
- The Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument10 pagesThe Cell Structure and TaxonomyKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- CellDocument5 pagesCellapi-267979304No ratings yet
- 2 CellsDocument31 pages2 CellsRashed NadaNo ratings yet
- Plant Cells Cristae Mitochondria Chloroplasts: The Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy TermsDocument15 pagesPlant Cells Cristae Mitochondria Chloroplasts: The Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy TermsanyoyoyNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles - Notes Cell Theory Cells Are The Basic Unit of Life. The Cell Theory States ThatDocument7 pagesCell Organelles - Notes Cell Theory Cells Are The Basic Unit of Life. The Cell Theory States ThatSpongie BobNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument37 pagesNotesDaideepya SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Vocab: The Material or Protoplasm Within A Living Cell, Excluding The NucleusDocument2 pagesChapter 6 Vocab: The Material or Protoplasm Within A Living Cell, Excluding The NucleusabNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell by Pitogo, ChereyDocument28 pagesAnimal Cell by Pitogo, ChereyPixie DurstNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Complex Lysosomes Microtubules Mitochondria Ribosomes Nucleolus NucleoporeDocument2 pagesCell Membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Complex Lysosomes Microtubules Mitochondria Ribosomes Nucleolus NucleoporedominicNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell StructureDocument2 pagesAnimal Cell StructureShaik HamedNo ratings yet
- Rebosura - Lec Asst 1 - Cell OrganizationDocument4 pagesRebosura - Lec Asst 1 - Cell OrganizationBSN Mary Ellaine RebosuraNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell - The Definitive Guide Biology DictiDocument8 pagesAnimal Cell - The Definitive Guide Biology DictiKolade YousuffNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument2 pagesCell OrganellesSurminie Muksin100% (1)
- BiotechDocument2 pagesBiotechKristel Faye Cortez SubiaNo ratings yet
- Cell MembraneDocument1 pageCell Membraneleih jsNo ratings yet
- NucleusDocument10 pagesNucleusjhariesargente05No ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 2 Organisation of The Organism - CAIE Biology IGCSE PDFDocument3 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 2 Organisation of The Organism - CAIE Biology IGCSE PDFZaid Bin salmanNo ratings yet
- Assign 2 BioA 3201Document6 pagesAssign 2 BioA 3201Princess CabardoNo ratings yet
- Major-Parts-Of-The-Cell - ReviewerDocument5 pagesMajor-Parts-Of-The-Cell - Reviewerjadenn busiaNo ratings yet
- BIO ReviewerDocument14 pagesBIO ReviewerRenjyl Gay DeguinionNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2.3 Basic Cell TypesDocument6 pagesLESSON 2.3 Basic Cell TypessandraNo ratings yet
- By: Tom Anthony A. Tonguia, RMT: Eukaryotic CellDocument9 pagesBy: Tom Anthony A. Tonguia, RMT: Eukaryotic CellTom Anthony TonguiaNo ratings yet
- Cells ACTIVITYDocument3 pagesCells ACTIVITYVanessa BedeoNo ratings yet
- Parts of Cells and Its FunctionDocument6 pagesParts of Cells and Its FunctionMary CartonNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Remedial AnsweranDocument2 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Remedial AnsweranJoviNo ratings yet
- Cells and Its PartDocument34 pagesCells and Its PartAra PaguioNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument6 pagesCell Structure and FunctionYeshua Dan BigasaNo ratings yet
- Membrane-Bound Organelles Which Are Found in Animal Cells. Enzymes Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesMembrane-Bound Organelles Which Are Found in Animal Cells. Enzymes Digestive SystemFarah Jaye Verde CayayanNo ratings yet
- Cell AnalogyDocument17 pagesCell AnalogyJianne CabildoNo ratings yet
- CellDocument4 pagesCellPrincess MillanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 SummaryDocument2 pagesChapter 2 SummaryAnas AymanNo ratings yet
- Louie John L. Caballero BSMT 1Y1 - 2: Happ Experiment #3Document3 pagesLouie John L. Caballero BSMT 1Y1 - 2: Happ Experiment #3Louie John CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Hannah Belle Catharine M. Malinis Bsn1B: Assignment No. 1 - Cell OrganizationDocument5 pagesHannah Belle Catharine M. Malinis Bsn1B: Assignment No. 1 - Cell OrganizationAngelo AbulenciaNo ratings yet
- Nucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticDocument5 pagesNucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticHustler ZaydeNo ratings yet
- Cytoplasm 2.: Cell OrganellesDocument6 pagesCytoplasm 2.: Cell OrganellesSai Deekshita VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Science PROKARYOTICEUKARYOTICDocument8 pagesScience PROKARYOTICEUKARYOTICsecurity securedNo ratings yet