Professional Documents
Culture Documents
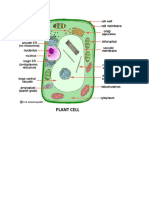
Organelle Table
Uploaded by
jamkulit29Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Organelle Table
Uploaded by
jamkulit29Copyright:
Available Formats
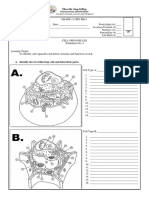
ORGANELLE
LOCATION
DESCRIPTION
FUNCTION
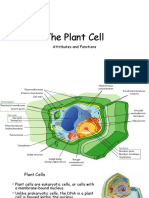
cell wall
plant, fungi and bacteria but
not animal
*outer layer
*rigid, strong, stiff
*made of cellulose
*support (grow tall)
*protection
*allows H2O, O2, CO2 to pass into and out of cell
cell membrane
both plant/animal
All cells
*plant - inside cell wall
*animal - outer layer; cholesterol
*selectively permeable
*support
*protection
*controls movement of materials in/out of cell
*barrier between cell and its environment
*maintains homeostasis
Nucleus
nucleus is absent in
prokaryotic cells
both plant/animal
*large, oval generally
.
*controls cell activities
*key organelle which has the genetic material and is
involved in multiplication of cell, growth and maintenance
of cell.
nucleolus
All cells except prokaryotes
*Found inside cells nucleus
* may have more than one
*disappears during cell division
* Make ribosomes, contains building blocks or mRNA,
tRNA, rRNA
nuclear membrane
both plant/animal
*surrounds nucleus
*selectively permeable
Centrioles
Animal cells
*paired structures near the nucleus
*stparate chromosome pairs during mitosis
*made of cylinder of microtubule pairs
cytoplasm
both plant/animal
All cells
*clear, thick, jellylike material
(sytosol)
* organelles found inside cell
membrane
*contains cytoskelon fibers
*supports /protects cell organelles
endoplasmic
reticulum (E.R.)
Smooth
Rough
both plant/animal
*network of tubes or membranes
*carries materials through cell
ribosome
both plant/animal
No ribosomes
Attached ribosome
*small bodies free or attached to E.R.
*made of rRNA and protein
*Controls movement of materials in/out of nucleus
Synthesis of fats/lipids
Ribosomes synthesis proteins for export
*synthesizes proteins
*breaks down sugar molecules into energy
*site of aerobic cellular respiration
Mitochondria
both plant/animal
*bean-shaped
*inner membranes
Double membrane outer smooth inner
folded into cristae
Golgi/golgi bodies /
golgi apparatus
both plant/animal except
Prokaryotes
* to modify and package proteins for export
These are the vacuoles or sac like
structures. They occupy a considerable *have cis and trans face
amount of cytoplasm.
*stacks of flattened sacs
vacuole
plant - few/large
animal - small
*fluid-filled sacs
* Vacuoles are pouches in the cell that store materials such
as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates, waste products
and toxic waste..
*store food, water, waste (plants need to store large amounts
of food)
Vesicles
A lot of small bubble sacs in
animals, large sac in the
middle of plant cells
These are small-sized sac like
structures. They are of different types
lysosomes, peroxisomes.
*These help in storage and release of substances as required
by the cell. For example lysosomes help in cell digestion
when cell dies. Vacuoles function is to store water.
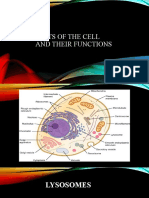
lysosome
plant - uncommon
animal - common
*small, round, with a membrane
*breaks down larger food molecules into smaller molecules
*digests old cell parts
chloroplast
plant, not animal
*green, oval usually containing
chlorophyll (green pigment)
*uses energy from sun to make food for the plant
(photosynthesis)
Cilia
Animal cells and protozoa
Have a 9-2 arrangement of
microtubules
*short but numerous
Movement of cell
flagellum
Bacteria cells and protozoan
Sex cells
*Have a 9-2 arrangement of
microtubules
*long but few in number
movement
Micro-tubules =
cytoskeleton
All cells
*micro-tubules provide structural
strength.
* These are filamentous extensions
in cytoplasm.
* the cell has a fixed structure and does not collapse
* form the cyto-skeleton
*moves organelles within the cell
http://www.biologyjunction.com/cell_functions.htm
You might also like
- Cells and OrgannellesDocument5 pagesCells and OrgannellesLionela EkNo ratings yet
- Plant CellDocument5 pagesPlant CellWilma BundangNo ratings yet
- Organelle location and function chartDocument2 pagesOrganelle location and function chartAnisa Dyah100% (1)
- Organelle Location Description Function: Cell WallDocument2 pagesOrganelle Location Description Function: Cell WallPoonam RanieNo ratings yet
- ORGANELLE Table PDFDocument2 pagesORGANELLE Table PDFDebjit BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cell Wall: Organelle Location Description FunctionDocument2 pagesCell Wall: Organelle Location Description FunctionXime OchoaNo ratings yet
- Bio, Plant & Animal CellsDocument6 pagesBio, Plant & Animal CellssparklyhinataNo ratings yet
- BIO1 The CellDocument52 pagesBIO1 The CellSeth MotaNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and FunctionsDocument2 pagesCell Parts and FunctionsMian Nakahara0% (1)
- CELLS - Are the-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesCELLS - Are the-WPS OfficeAbu DardaNo ratings yet
- 2.6 Plant and Animal CellDocument28 pages2.6 Plant and Animal Cellthethtarhoney12No ratings yet
- Cell FunctionsDocument4 pagesCell FunctionsAhmed SherifNo ratings yet
- Cell MembranesDocument4 pagesCell MembranesAnju SoniNo ratings yet
- Cells 4THDocument70 pagesCells 4THKyng GamariNo ratings yet
- Week 4 - Plant Structure and FunctionsDocument50 pagesWeek 4 - Plant Structure and FunctionsPrincess De LeonNo ratings yet
- What is a Cell? The Building Block of LifeDocument6 pagesWhat is a Cell? The Building Block of LifeWaleed Bin KhalidNo ratings yet
- BIO ReviewerDocument14 pagesBIO ReviewerRenjyl Gay DeguinionNo ratings yet
- Lesson Summaries: Human and Social Biology UNIT 1 - Living Organisms and The Environment SituationsDocument7 pagesLesson Summaries: Human and Social Biology UNIT 1 - Living Organisms and The Environment SituationsAbigaleNo ratings yet
- 8384 ST PDFDocument20 pages8384 ST PDFJohn Dave Francisco100% (1)
- GenBio Notes Lesson 1 and 2Document7 pagesGenBio Notes Lesson 1 and 2The GreatNo ratings yet
- 2-2 - Components and Functions (IB Biology SL)Document7 pages2-2 - Components and Functions (IB Biology SL)rastete195No ratings yet
- How Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersFrom EverandHow Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersNo ratings yet
- Plant CellsDocument28 pagesPlant CellsKent Lary TediosNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell OrganellesDocument13 pagesPlant Cell OrganellesKritika MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument3 pagesUntitled Documentsumedhasaha09No ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function OverviewDocument2 pagesCell Structure and Function OverviewElo KarlNo ratings yet
- What Is Plants?Document46 pagesWhat Is Plants?Genelie Abuzo CadayonaNo ratings yet
- Crop Plant Parts and FunctionsDocument11 pagesCrop Plant Parts and FunctionsJetro Neil GapasinNo ratings yet
- Cell NotesDocument7 pagesCell NotessandhyaghoshNo ratings yet
- Cell and MicrobesDocument12 pagesCell and MicrobesSUBHANo ratings yet
- Biochem CellsDocument5 pagesBiochem Cellsleviona halfNo ratings yet
- Cells - Basic Unit of LifeDocument45 pagesCells - Basic Unit of Lifeapi-202349222No ratings yet
- Robert Hooke's Discovery of Cells Using a MicroscopeDocument7 pagesRobert Hooke's Discovery of Cells Using a MicroscopelorinaNo ratings yet
- E18f338b CellsDocument42 pagesE18f338b CellsMohammad Abdullah KNo ratings yet
- The Parts of The Cell and Their FunctionsDocument2 pagesThe Parts of The Cell and Their Functionsraphael100% (1)
- Plant Organology Notes PDFDocument18 pagesPlant Organology Notes PDFCaitlin SnymanNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 NotesDocument8 pagesFundamental Unit of Life Class 9 NotesMd AurangjebNo ratings yet
- Organelle Location Description Function: Cell WallDocument3 pagesOrganelle Location Description Function: Cell WallDannyNo ratings yet
- SMA 11-1 CellsDocument111 pagesSMA 11-1 Cellsnur aulia100% (1)
- Cell Structure and Function ExplainedDocument3 pagesCell Structure and Function ExplainedalyssaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Cells GuideDocument54 pagesEarth and Life Science Cells GuideJoie MonrealNo ratings yet
- Basic BotanyDocument47 pagesBasic Botanyartadiel28No ratings yet
- 1 Cell Structure FunctionDocument124 pages1 Cell Structure FunctionIntoy, Stephanie Mae100% (1)
- Levels of Biological OrganizationsDocument23 pagesLevels of Biological OrganizationsYuu KieNo ratings yet
- A Plant CellDocument3 pagesA Plant CellDurgadharshini 21X-214No ratings yet
- Animal and Plant Cell PartsDocument5 pagesAnimal and Plant Cell PartsJess MCDNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document7 pagesChapter 2Kaness MathzNo ratings yet
- The Plant CellDocument30 pagesThe Plant CellMichael GentilesNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal CellsDocument39 pagesPlant and Animal CellsDelfin Jr UrbanoNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal CellsDocument39 pagesPlant and Animal CellsDelfin Jr UrbanoNo ratings yet
- Earth and ScieDocument3 pagesEarth and SciesideyysNo ratings yet
- Cell organelles functions guideDocument12 pagesCell organelles functions guideKatrina Marie Chan SalanioNo ratings yet
- BIO 001 Real Slide First SemesterDocument44 pagesBIO 001 Real Slide First Semestermarkwelly367No ratings yet
- Bio g7Document66 pagesBio g744mnx692cbNo ratings yet
- Cell and Its FunctionDocument26 pagesCell and Its FunctionMarielle MatunogNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelle Structure and FunctionDocument2 pagesCell Organelle Structure and FunctionMichu LeclercqNo ratings yet
- Cells OrganellesDocument54 pagesCells Organellesapi-502940689No ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom: Cell Walls Central VacuoleDocument10 pagesPlant Kingdom: Cell Walls Central VacuoleRishel Reign GasparNo ratings yet
- The Nature and Composition of PlantsDocument70 pagesThe Nature and Composition of PlantsJhunell Juan100% (3)
- Pedigree AnalysisDocument3 pagesPedigree Analysisjamkulit29No ratings yet
- Philippine Guideline For RegistrationDocument11 pagesPhilippine Guideline For RegistrationNoples RozaliaNo ratings yet
- Turbidimetry and Nephelometry1Document3 pagesTurbidimetry and Nephelometry1maxim_crank6101100% (1)
- MedsDocument1 pageMedsjamkulit29No ratings yet
- Declaration of Alma AtaDocument3 pagesDeclaration of Alma AtaJustin James AndersenNo ratings yet
- Cebuana Form SampleDocument1 pageCebuana Form Samplejamkulit29No ratings yet
- LORMA COLLEGES BACHELOR IN MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCE PROGRAMDocument2 pagesLORMA COLLEGES BACHELOR IN MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCE PROGRAMAnonymous tKTzn3wuU4No ratings yet
- Lorma College Hymn - Peaceful Seaside Village School SongDocument1 pageLorma College Hymn - Peaceful Seaside Village School Songjamkulit29No ratings yet
- Lectures No 4 Introduction & Method of Tissue Preparation & Specimen Reception & FixationDocument27 pagesLectures No 4 Introduction & Method of Tissue Preparation & Specimen Reception & FixationAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- What Is Dynamic Neuromuscular Stabilization (DNS) ?: How Is The Core Stabilized?Document5 pagesWhat Is Dynamic Neuromuscular Stabilization (DNS) ?: How Is The Core Stabilized?HONGJYNo ratings yet
- Molecular Immunology: Claire L. Harris, Richard B. Pouw, David Kavanagh, Ruyue Sun, Daniel RicklinDocument31 pagesMolecular Immunology: Claire L. Harris, Richard B. Pouw, David Kavanagh, Ruyue Sun, Daniel Ricklinguugle gogleNo ratings yet
- Growth Assessment ParametersDocument97 pagesGrowth Assessment ParametersAurthi ElamparithiNo ratings yet
- Medical Terminology CH 9Document104 pagesMedical Terminology CH 9ياسين المسطو100% (1)
- Ob Notes EditedDocument28 pagesOb Notes EditedJake IliganNo ratings yet
- ColostomyDocument45 pagesColostomydrqiekiNo ratings yet
- Antigen-Presenting CellsDocument9 pagesAntigen-Presenting Cellsnur fitrianaNo ratings yet
- The Digestive Organs Pathway To The Centre Rosina Sonnenschmidt.08154Document15 pagesThe Digestive Organs Pathway To The Centre Rosina Sonnenschmidt.08154Sohail LatifNo ratings yet
- Hematopoiesis in HumansDocument4 pagesHematopoiesis in HumanseveryoneMD100% (2)
- Evaluation of Fetal HeartDocument59 pagesEvaluation of Fetal Heartاد ريما البدر100% (3)
- A Case Study On A Pediatric Patient Diagnosed With Urinary Tract InfectionDocument55 pagesA Case Study On A Pediatric Patient Diagnosed With Urinary Tract InfectionADOLF FRUELAN HIDALGO100% (1)
- Crossmatching, Types, Principle, Procedure and InterpretationDocument5 pagesCrossmatching, Types, Principle, Procedure and InterpretationMerhan FoudaNo ratings yet
- Automation in Blood Banking - DR ShreyaDocument80 pagesAutomation in Blood Banking - DR ShreyaDr sakshiNo ratings yet
- I: Multiple Choice Questions - Select The One Best AnswerDocument7 pagesI: Multiple Choice Questions - Select The One Best AnswerDebattri DasNo ratings yet
- 20 - Pediatric Urinary DisordersDocument62 pages20 - Pediatric Urinary DisordersKhaalid AbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- 4bi1 2b Que 20230117Document20 pages4bi1 2b Que 20230117ah6643242No ratings yet
- Pe 1 Module 3Document25 pagesPe 1 Module 3Dimple BolotaoloNo ratings yet
- Cesarean Surgical Instrument GuideDocument4 pagesCesarean Surgical Instrument GuideAhmedNo ratings yet
- Blood Defenses and FunctionsDocument18 pagesBlood Defenses and FunctionsTrúc Linh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Disturbances in Perception and CoordinationDocument240 pagesDisturbances in Perception and CoordinationJeaneline Pagasian Enon50% (2)
- G11 Bio WS4. Cell OrganellesDocument2 pagesG11 Bio WS4. Cell OrganellesArlance Sandra Marie MedinaNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue StainsDocument42 pagesConnective Tissue StainsSMNo ratings yet
- Childrens FBC Reference Ranges PDFDocument1 pageChildrens FBC Reference Ranges PDFCerianne BodionganNo ratings yet
- HydrocephalusDocument40 pagesHydrocephalusAstrid Sabirin100% (1)
- Cell (XI Grade)Document27 pagesCell (XI Grade)Ahmad LuthfyNo ratings yet
- Erwin-Sheppard Autopsy Report - Redacted by Medical ExaminerDocument17 pagesErwin-Sheppard Autopsy Report - Redacted by Medical ExaminerCheryl Sullenger100% (1)
- FibrinolysisDocument26 pagesFibrinolysisCristinaGheorgheNo ratings yet
- Bone Ash Estimation of Content of Bone Ash Project Submitted by PrashanthDocument3 pagesBone Ash Estimation of Content of Bone Ash Project Submitted by PrashanthHarsh Kumar0% (3)
- K32E Alle N WWDocument180 pagesK32E Alle N WWKirilKocevskiNo ratings yet