Professional Documents
Culture Documents
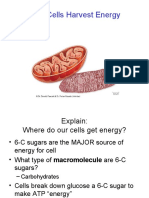
Cellular Respiration
Uploaded by
api-327711832Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cellular Respiration
Uploaded by
api-327711832Copyright:
Available Formats
Cellular Respiration
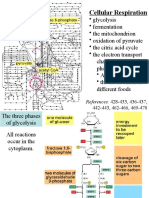
Glycolysis (sugar-breaking)
First set of reactions in cellular respiration
1 glucose (6-carbon compound)
2 ATP (to start a process)
two 3-carbon compound
2 NAD+ 4 ATP (2 net ATP)
2 NADH (carry electron)
2 pyruvic acid
Preparatory Reaction
Pyruvic acid pass through the membranes into matrix
1 carbon from each pyruvic acid become part of CO2
CO2 is released
other 2 carbon atoms rearrange and form acetic acid
joined with coenzyme A
Acetyl-CoA (2 carbon atoms + 1 oxygen atom + 3 hydrogen atom)
Krebs Cycle (Citric acid cycle)
Acetyl-CoA adds the 2-carbon acetyl group to a 4-carbon acetyl group
Citric acid
break down into 4-carbon molecule (CO2 is release)
electrons transfer > NADH
Energy released by the breaking and rearranging of carbon bonds (ATP)
FADH2
all NADH are sent to Electron Transport Chain
ETC
NADH and FADH2 passed their high energy electrons from carrier to carrier down the
electron transport chain
water is formed when oxygen accepts the electrons in combination with hydrogen ions
energy generated by the electron transport chain is is used to move hydrogen ions across
the mitochondrial membrane into the inter membrane space
32 ATP
You might also like
- Mitochondria & Cellular RespirationDocument36 pagesMitochondria & Cellular RespirationNuRien HaziQah ZaMri100% (1)
- Chapter 4 - Intermediary MetabolismDocument53 pagesChapter 4 - Intermediary MetabolismBaxxNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis, Kreb Cycle Electron TransportDocument19 pagesGlycolysis, Kreb Cycle Electron TransportShahidatul4297100% (2)
- Cellular RespirationDocument38 pagesCellular RespirationItsYaBoiRZ YTNo ratings yet
- Topic 8 Cell Respiration and PhotosynthesisDocument12 pagesTopic 8 Cell Respiration and PhotosynthesisCedric Williams100% (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mitochondria and Its Pathways: Arvin G. Concha Mst-BioDocument17 pagesMitochondria and Its Pathways: Arvin G. Concha Mst-Biocassidy conchaNo ratings yet
- How Cells Harvest EnergyDocument60 pagesHow Cells Harvest EnergyVivaMapwaNo ratings yet
- ADP, ATP and Cellular RespirationDocument30 pagesADP, ATP and Cellular RespirationJillian Lao100% (2)
- Cellular respiration and fermentation explainedDocument20 pagesCellular respiration and fermentation explainedTasfia QuaderNo ratings yet
- Rube Golderg ProjectDocument21 pagesRube Golderg Projectapi-334211165No ratings yet
- Bio Reviewer 2Document2 pagesBio Reviewer 2Prince Lawrence Garcia100% (1)
- Krebs CycleDocument2 pagesKrebs Cycleapi-327731714100% (1)
- Cellular Respiration NotesDocument1 pageCellular Respiration NotesMike MesaNo ratings yet
- ADPATPand Cellular RespirationDocument43 pagesADPATPand Cellular RespirationJessa CabusaoNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis and Krebs Cycle Produce ATPDocument7 pagesGlycolysis and Krebs Cycle Produce ATPkayannaNo ratings yet
- Cell Respiration and PhotosynthesisDocument10 pagesCell Respiration and PhotosynthesisMorgan LockeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Cellular RespirationDocument36 pagesChapter 9: Cellular RespirationMary GarciaNo ratings yet
- Respiration and PhotorespirationDocument29 pagesRespiration and PhotorespirationThảo UyênNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Harvesting Chemical Energy: 6H O + 6co + Energy C H O + 6ODocument29 pagesCellular Respiration Harvesting Chemical Energy: 6H O + 6co + Energy C H O + 6OlostgirlNo ratings yet
- Respiration - SimplifiedDocument11 pagesRespiration - SimplifiedVivaMapwaNo ratings yet
- Week 5 - GenBio1 CELLULAR RESPIRATION 1st Term SY 2021-2022Document2 pagesWeek 5 - GenBio1 CELLULAR RESPIRATION 1st Term SY 2021-2022JAN PAULINE BABINANo ratings yet
- Energy and Cell Resp ETC and GLYCOLYSIS CH 7 Part 2Document17 pagesEnergy and Cell Resp ETC and GLYCOLYSIS CH 7 Part 2mdonohueHGHSNo ratings yet
- SMSP MetabolismDocument10 pagesSMSP MetabolismPravesh NiraulaNo ratings yet
- Cell RespirationDocument10 pagesCell RespirationChristine SangilNo ratings yet
- (E BOOK) Martini Essentials of Anatomy PhysiologyDocument3 pages(E BOOK) Martini Essentials of Anatomy PhysiologyRaisa sya12No ratings yet
- Week 7 Cellular RespirationDocument32 pagesWeek 7 Cellular RespirationJiverlyn PatNo ratings yet
- How Cells Harvest EnergyDocument53 pagesHow Cells Harvest Energyjerry_brock_3No ratings yet
- How Cells Harvest EnergyDocument42 pagesHow Cells Harvest EnergyMansoor KhalidNo ratings yet
- Cell Respiration (8.2) : Oxidation Is Loss, Reduction Is Gain or OIL RIGDocument12 pagesCell Respiration (8.2) : Oxidation Is Loss, Reduction Is Gain or OIL RIGRocio Guadalupe Lopez BlandonNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: References: 428-433, 436-437Document45 pagesCellular Respiration: References: 428-433, 436-437Ciania KimNo ratings yet
- Biology: Energy & Equilibrium: RespirationDocument28 pagesBiology: Energy & Equilibrium: RespirationTimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Cellular-Respiration BioDocument7 pagesCellular-Respiration BioKiyomi LabradorNo ratings yet
- Biology 1: Major Features and Chemical Events of Cellular RespirationDocument5 pagesBiology 1: Major Features and Chemical Events of Cellular RespirationKaye Ann AbinalNo ratings yet
- Krebs - Anaerobic ReviewerDocument6 pagesKrebs - Anaerobic ReviewerdenyelNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis: How Cells Extract Energy from GlucoseDocument61 pagesGlycolysis: How Cells Extract Energy from GlucoseLê Trà GiangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 BIO 1510Document25 pagesChapter 7 BIO 1510Chachi CNo ratings yet
- Respiration: Link ReactionDocument1 pageRespiration: Link ReactionAuriceliaOliveiraNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Fermentation 2017 UPDATED Use For 2019Document36 pagesCellular Respiration Fermentation 2017 UPDATED Use For 2019aNo ratings yet
- PS and CRDocument34 pagesPS and CRErika MatiasNo ratings yet
- BiochemLecETCKrebs CycleDocument1 pageBiochemLecETCKrebs CycleReginald GironNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Study GuideDocument30 pagesCellular Respiration Study Guideroselyn acpacNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument28 pagesCellular RespirationPrecy Ann ReyesNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Hingher PlantsDocument6 pagesRespiration in Hingher PlantsTrillionare HackNo ratings yet
- Week 8 - GenBio1 CELL RESPIRATION 1st Term SY 2021-2022Document3 pagesWeek 8 - GenBio1 CELL RESPIRATION 1st Term SY 2021-2022JAN PAULINE BABINANo ratings yet
- Aerobic Respiration Process (ATPDocument13 pagesAerobic Respiration Process (ATPIshwarya LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Final ReviewerDocument7 pagesGen Bio Final Reviewermailforprinting101No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis & Respiration: By: James Grant & Aimee IrvinDocument21 pagesPhotosynthesis & Respiration: By: James Grant & Aimee IrvindunklinjNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration PowerPointDocument20 pagesCellular Respiration PowerPointTasfia QuaderNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Breaks Down Glucose to Produce ATPDocument2 pagesCellular Respiration Breaks Down Glucose to Produce ATPAirene JabagatNo ratings yet
- Link Reaction (Occurs in The Fluid Matrix of Mitochondria)Document1 pageLink Reaction (Occurs in The Fluid Matrix of Mitochondria)MaryNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration1Document40 pagesCellular Respiration1Danken Mathew P. TorresNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration ExplainedDocument43 pagesCellular Respiration ExplainedMichael Jay MesaNo ratings yet
- Krebs Cycle and Oxidative Phosphorylation ExplainedDocument6 pagesKrebs Cycle and Oxidative Phosphorylation ExplainedFelipe Henao AriasNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of the Cell Energy ProductionDocument31 pagesMetabolism of the Cell Energy ProductionLilia PopanuNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis The Krebs Cycle and The Electron Transport ChainDocument12 pagesGlycolysis The Krebs Cycle and The Electron Transport Chainrameenkamran2003No ratings yet
- Aerobic Respiration PicmonicDocument2 pagesAerobic Respiration PicmonicVinayNo ratings yet
- Pyruvate, Krebs, ElectransDocument7 pagesPyruvate, Krebs, Electransfionadaguman2002No ratings yet
- BIO20 Cell Resp Teacher Notes 2020Document39 pagesBIO20 Cell Resp Teacher Notes 2020Shariq KhanNo ratings yet
- Cellular+Respiration+ +reactionsDocument28 pagesCellular+Respiration+ +reactionsAnonno DipNo ratings yet
- PARAS, Mark Heinrich B. - Homework 6 - Lecture Biochemistry CHEM 40 BSN 1EDocument2 pagesPARAS, Mark Heinrich B. - Homework 6 - Lecture Biochemistry CHEM 40 BSN 1EMark Heinrich B. ParasNo ratings yet
- MemoirDocument5 pagesMemoirapi-327711832No ratings yet
- Miu q2 FinalDocument5 pagesMiu q2 Finalapi-327711832No ratings yet
- Health Sci EssayDocument3 pagesHealth Sci Essayapi-327711832No ratings yet
- A Streetcar Named DesireDocument7 pagesA Streetcar Named Desireapi-327711832No ratings yet
- Debate ThaiDocument15 pagesDebate Thaiapi-358561736No ratings yet
- World His NewspaperDocument2 pagesWorld His Newspaperapi-327711832No ratings yet
- DateDocument11 pagesDateapi-327711832No ratings yet
- Eng Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesEng Lesson Planapi-327712007No ratings yet
- Your Surroundings Shape YouDocument1 pageYour Surroundings Shape Youapi-327711832No ratings yet
- World His - Process JournalDocument5 pagesWorld His - Process Journalapi-327711832No ratings yet
- There Is A Difference BetweenDocument21 pagesThere Is A Difference Betweenapi-327711832No ratings yet
- Electric FieldDocument1 pageElectric Fieldapi-327711832No ratings yet
- World History - Process JournalDocument12 pagesWorld History - Process Journalapi-327711832No ratings yet
- Torque Lab ReportDocument14 pagesTorque Lab Reportapi-359061673No ratings yet
- TritationDocument23 pagesTritationapi-359061673No ratings yet
- Chemistry Lab ReportDocument17 pagesChemistry Lab Reportapi-334211165No ratings yet
- Recycle Costume EssayDocument3 pagesRecycle Costume Essayapi-327766139No ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument11 pagesIntroductionapi-327711832No ratings yet
- WH ProjectDocument7 pagesWH Projectapi-335117665No ratings yet
- World History II q1 Project GuidelineDocument5 pagesWorld History II q1 Project Guidelineapi-327711832No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledapi-327711832No ratings yet
- Gif Vs JpegDocument1 pageGif Vs Jpegapi-328383794No ratings yet
- Madjid PosterDocument1 pageMadjid Posterapi-327711832No ratings yet
- OozelessDocument1 pageOozelessapi-327711832No ratings yet
- Physics LabDocument18 pagesPhysics Labapi-327711832No ratings yet
- Lab Report DoneDocument9 pagesLab Report Doneapi-327713720No ratings yet
- Norman Conquest of EnglandDocument18 pagesNorman Conquest of Englandapi-327711832No ratings yet
- Research Report BodyDocument12 pagesResearch Report Bodyapi-327711832No ratings yet