Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Replication, Transcription, Translation, Mutation Questions
Uploaded by
kate0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views2 pagesDNA polymerase adds new nucleotides to the growing DNA strand during replication. Differences between DNA and RNA include that DNA is usually double stranded while RNA is usually single stranded, and they contain different sugars. The backbone of DNA is formed from sugar and phosphate groups. RNA polymerases require a DNA template for transcription. A nonsense mutation changes a codon into a stop codon, while a frameshift mutation is caused by insertion or deletion of nucleotides. The diagram shows a deletion mutation of the gene.
Original Description:
central dogma
Original Title
Central Dogma
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDNA polymerase adds new nucleotides to the growing DNA strand during replication. Differences between DNA and RNA include that DNA is usually double stranded while RNA is usually single stranded, and they contain different sugars. The backbone of DNA is formed from sugar and phosphate groups. RNA polymerases require a DNA template for transcription. A nonsense mutation changes a codon into a stop codon, while a frameshift mutation is caused by insertion or deletion of nucleotides. The diagram shows a deletion mutation of the gene.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views2 pagesReplication, Transcription, Translation, Mutation Questions
Uploaded by
kateDNA polymerase adds new nucleotides to the growing DNA strand during replication. Differences between DNA and RNA include that DNA is usually double stranded while RNA is usually single stranded, and they contain different sugars. The backbone of DNA is formed from sugar and phosphate groups. RNA polymerases require a DNA template for transcription. A nonsense mutation changes a codon into a stop codon, while a frameshift mutation is caused by insertion or deletion of nucleotides. The diagram shows a deletion mutation of the gene.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Replication, Transcription, Translation, Mutation Questions
1. DNA polymerase is the enzyme that
a. Unzips the DNA strands
b. Adds new nucleotides to the growing DNA strand
c. Edits the new DNA molecule
d. Ties together new pieces of DNA
2. Differences between DNA and RNA include:
a. DNA is usually double stranded, RNA is usually single stranded
b. The DNA sugar is ribose; the RNA sugar is deoxyribose
c. Thymine is found in the RNA nucleotides; Uracil takes the place of thymine in
DNA
d. All of the above
3. The backbone of the DNA chain is formed of
a. A cytoskeleton and a cell wall
b. The sugar and phosphate groups
c. The protein and nitrogen groups
d. A protein
4. RNA polymerases used for the transcription of genes require a ____ template
a. tRNA
b. DNA
c. RNA
d. mRNA
5. A mutation that changes a codon specifying an amino acid into a stop codon is called a
a. Missense mutation
b. Nonsense mutation
c. Frameshift mutation
d. Deletion mutation
6. Changing the codon ACG to ACA represents a ___ mutation
a. Missense
b. Nonsense
c. Frameshift
d. Deletion
7. Frameshift mutations are caused by
a. Insertion of nucleotides
b. Deletion of nucleotides
c. Substitution of one nucleotide to another
d. A and B
8. Which of the following is not used during translation
a. DNA
b. mRNA
c. tRNA
d. All of the above are used in translation
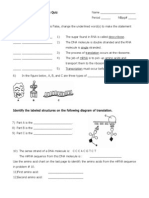
9. In the below molecule of RNA, the shaded regions are exons while the light regions are
introns. Knowing this, which of the following could NOT be a mature mRNA molecule
after transcription?
a. A molecule composed of A,C,E
b. A molecule composed of C,G
c. A molecule composed of A,B,E
d. All of the above are possible mature mRNA molecules
10. The following diagram shows the protein products that are made with a normal gene
and in an instance when that gene is mutated. What kind of mutation is shown in the
mutated gene?
a. Base substitution
b. Insertion
c. Deletion
d. A&C
You might also like
- Study Guide Protein Synthesis (KEY)Document2 pagesStudy Guide Protein Synthesis (KEY)owls_1102No ratings yet
- Cell Final ExamDocument8 pagesCell Final ExamJorge GomezNo ratings yet
- MLB 110 MLS M 1920 02 (1) Molecular ExamsDocument15 pagesMLB 110 MLS M 1920 02 (1) Molecular Examsmaxwell amponsahNo ratings yet
- RNA and Protein Synthesis QuizDocument6 pagesRNA and Protein Synthesis QuizJeremy Guggenheim100% (2)
- Topical Guidebook For GCE O Level Biology 3 Part 2From EverandTopical Guidebook For GCE O Level Biology 3 Part 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Multiple Choice Questions in Molecular BiologyDocument72 pagesMultiple Choice Questions in Molecular Biologydanishuddin_danish50% (2)
- Dr. Harvey Laranang MicrobiologyDocument9 pagesDr. Harvey Laranang MicrobiologyPatricia L.No ratings yet
- Biotech Fourth QuarterDocument4 pagesBiotech Fourth QuarterRodge BuereNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Science - 2Document5 pagesGrade 10 Science - 2Nenia Claire Mondarte CruzNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument20 pagesGeneticsNaji Mohamed Alfatih100% (1)
- Biology Final ExamDocument7 pagesBiology Final ExamJillian FajardoNo ratings yet
- Chapter Quiz General Biology 2Document7 pagesChapter Quiz General Biology 2Nikki San GabrielNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Summative Test 2 Quarter 3 With Answer KeyDocument3 pagesScience 10 Summative Test 2 Quarter 3 With Answer KeyRowena Nim100% (2)
- Protein Synthesis Transcription and Translation Distance LearningDocument10 pagesProtein Synthesis Transcription and Translation Distance LearningjaneyzhouNo ratings yet
- What Is The Main Function of DNA TranscriptionDocument8 pagesWhat Is The Main Function of DNA TranscriptionMega XtericsNo ratings yet
- Chem 600 - Pre-ExamDocument2 pagesChem 600 - Pre-ExamSamuel CaoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 12 Protein SynthesisDocument10 pagesCHAPTER 12 Protein SynthesisNadeem IqbalNo ratings yet
- PRETEST - 37 CopiesDocument2 pagesPRETEST - 37 CopiesMageeNo ratings yet
- Long Test (Protein Synthesis)Document2 pagesLong Test (Protein Synthesis)ArdhieeNo ratings yet
- DNA QuizDocument2 pagesDNA QuizDee YipNo ratings yet
- Pre Test SimDocument2 pagesPre Test SimDebbie Ann LaguindabNo ratings yet
- Long Test As Level Nucleic AcidDocument9 pagesLong Test As Level Nucleic AcidPrisky Jofan SimbarNo ratings yet
- Microbiology A Human Perspective 7th Edition Nester Test BankDocument40 pagesMicrobiology A Human Perspective 7th Edition Nester Test Bankmagnusngah7aaz100% (30)
- Bio Practice 7.2Document24 pagesBio Practice 7.2Xian Ni WooNo ratings yet
- Binder1 PDFDocument10 pagesBinder1 PDFSalih HassanNo ratings yet
- Foundations in Microbiology 10th Edition Talaro Test BankDocument38 pagesFoundations in Microbiology 10th Edition Talaro Test Bankpalproedpm7t100% (18)
- Foundations in Microbiology 10th Edition Talaro Test BankDocument37 pagesFoundations in Microbiology 10th Edition Talaro Test Bankbunkerlulleruc3s100% (25)
- HL Paper1Document13 pagesHL Paper1JennyNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication and Protein Synthesis Review Practice MC CPDocument5 pagesDNA Replication and Protein Synthesis Review Practice MC CPBernie Cabang PringaseNo ratings yet
- 12 Review WSDocument11 pages12 Review WSJASON WILLSNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Preview - DNA: Multiple ChoiceDocument5 pagesChapter 9 Preview - DNA: Multiple ChoiceyeateshwarriorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Expression of Biological InformationDocument3 pagesChapter 5 - Expression of Biological InformationNur HanisNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument9 pagesMCQNabd NabdNo ratings yet
- Transcription Q&ADocument7 pagesTranscription Q&AGabriel Delos Reyes100% (1)
- Bio Ws PDFDocument3 pagesBio Ws PDFlina atyaniNo ratings yet
- Mcqs ImbDocument23 pagesMcqs ImbMuvawala Belekia AbelNo ratings yet
- Exam 3 RetakeDocument8 pagesExam 3 RetakeMahima SikdarNo ratings yet
- Quiz - No. - 6 Dna Rna MutationsDocument1 pageQuiz - No. - 6 Dna Rna MutationsJhamia Cruz EstradaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology A Systems Approach 5th Edition Cowan Test BankDocument39 pagesMicrobiology A Systems Approach 5th Edition Cowan Test Bankbachelen69bqi100% (35)
- Lec 014 Gene To ProteinDocument6 pagesLec 014 Gene To ProteinQusizleNo ratings yet
- Posttest NewDocument3 pagesPosttest NewMageeNo ratings yet
- Full Download Genetics and Genomics in Nursing and Health Care 1st Edition Beery Test BankDocument35 pagesFull Download Genetics and Genomics in Nursing and Health Care 1st Edition Beery Test Bankbeliechopper05srz100% (39)
- DNA Vs RNA Notes BiologyDocument4 pagesDNA Vs RNA Notes Biologymarianna hutchisonNo ratings yet
- Module 4 KKKDocument32 pagesModule 4 KKKbhrayancachero100% (1)
- True or FalseDocument4 pagesTrue or Falsetaya guyNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Genetics and Genomics in Nursing and Health Care 1st Edition Beery Test Bank PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Genetics and Genomics in Nursing and Health Care 1st Edition Beery Test Bank PDFzaridyaneb100% (10)
- BioSc 231 Exam 3 2003Document9 pagesBioSc 231 Exam 3 2003Quốc ViệtNo ratings yet
- Microbiology A Systems Approach Cowan 3rd Edition Test Bank DownloadDocument42 pagesMicrobiology A Systems Approach Cowan 3rd Edition Test Bank Downloadjoelmalonentadsbkfic100% (23)
- Exam Questions Topic 1Document31 pagesExam Questions Topic 1Max ArmourNo ratings yet
- Mmoi BC SbaDocument15 pagesMmoi BC SbaYoon YoonNo ratings yet
- Cuestionario MolecularDocument35 pagesCuestionario MolecularelambatertulianoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 & 3: D. Structural Gene of The Prokaryotes Is Split GeneDocument3 pagesChapter 2 & 3: D. Structural Gene of The Prokaryotes Is Split Genenanang eko yuliantoNo ratings yet
- Self Quizzes: Polymerase. Amylase Anhydrase. Helicase. Proofreading. Replication. Transformation. SubstitutionDocument2 pagesSelf Quizzes: Polymerase. Amylase Anhydrase. Helicase. Proofreading. Replication. Transformation. SubstitutionDr DolittleNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis QuestionarreDocument2 pagesProtein Synthesis QuestionarreRiza Sardido SimborioNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiotechnologyDocument2 pagesIntroduction To BiotechnologyChemengNo ratings yet
- Genetics Chapter 8Document19 pagesGenetics Chapter 8Zahraa TermosNo ratings yet
- 6Document17 pages6AmaniNo ratings yet
- ExamDocument2 pagesExamglaiza abucayNo ratings yet
- DNA in Supramolecular Chemistry and NanotechnologyFrom EverandDNA in Supramolecular Chemistry and NanotechnologyEugen StulzNo ratings yet