Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PRETEST - 37 Copies
Uploaded by
Magee0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesPRETEST for CENTRAL DOGMA
Original Title
PRETEST_37 copies
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPRETEST for CENTRAL DOGMA
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesPRETEST - 37 Copies
Uploaded by
MageePRETEST for CENTRAL DOGMA
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
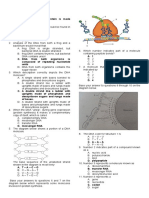
PRETEST
NAME: GRADE: SEX: M F
1. The DNA molecule is composed of three types of component molecule namely
a. phosphate group, the sugar deoxyribose, and the bases
b. thymine, cytosine, guanine
c. phosphate group, the sugar deoxyribose, and guanine
d. all of the above
2. All of the following are true of RNA except ?
a. RNA can leave the nucleus
b. RNA contain uracil in place of thiamine
c. RNA is a single strand
d. RNA and DNA has a 5 C sugar
3. The major type of RNA include:
a. messenger RNA (mRNA) c. transfer RNA (tRNA)
b. ribosomal RNA (rRNA) d. All of the above
4. What is the structural difference between DNA and RNA?
a. They are both have double helix structure
b. DNA is a double helix strand while RNA is a single strand
c. They have both a nitrogenous base
d. None of the above
5. Which one of these is not a valid comparison between DNA and RNA?
DNA RNA
a. Double Helix single strand
b. Replicate duplicate
c. Deoxyribose ribose
d. Thymine uracil
6. Is the most structurally varied molecule in which the human body contains atleast 10,000 different
kinds
a. Carbon c. Proteins
b. Nucleic Acid d. Carbohydrates
7. Is a large molecule composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus
a. Carbon c. Proteins
b. Nucleic Acid d. Carbohydrates
8. What do you call the three nitrogenous bases on a strand of DNA?
a. Codon c. Code
b. Anticodon d. Genes
9. The human body contains how many pair of chromosomes?
a. 22 pairs c. 23 pairs
b. 34 pairs d. 36 pairs
10. The molecule is a very large chain of repeating unit called polymer.
a. TRUE c. MAYBE
b. FALSE d. None of the above
11. It is a large, carbon based molecules formed by monomer
a. Nucleus c. Protein
b. Carbohydrates d. Polymer
12. The process in which the DNA is copied during the cell cycle
a. Transcription c. Replication
b. Translation d. Duplication
13. An enzyme called breaks the bond between nitrogenous bases.
a. Ligase c. Helicase
b. DNA polymerase d. None of the above
14. An enzyme that seal up the fragment into one long strand
a. Ligase c. Helicase
b. DNA polymerase d. None of the above
15. The sequence of bases in one DNA strand is A A C C C T G A G T C T. Identify the complementary sequence of
bases in the other strand of DNA.
16. Show how the DNA code translates into RNA code by placing the sequence of bases of the DNA and RNA side by
side. G C A A G T A C C T G A -
17. The following is the base sequence on one strand of a DNA molecule: A A T G C C A G T G G T
If this strand is replicated, which of the following is the complementary strand that is produced?
a. T C G T C C G T C T A G c. T T A C G G T C A C C A
b. A G C A G G C A G G G T d. U C G U C C U C U A G A
18. Referring to the given in the previous item, If transcribed into an mRNA, what would be the resulting strand?
a. U U A C G G U C A C C A c. A G C A G G C A G A U C
b. A G C A G G A G A T C d. T C G T C C G T C T A G
19. Referring to item no. 23. During translation, the tRNA sequence of nucleotides arranged linearly is _______.
a. T C G T C C G T C T A G c. A G C A G G C A G A U C
b. A A U G C C A G U G G U d. U C G U C C G U C U A G
20. – 24. Each combination of nitrogen bases on the mRNA molecule is a codon, which is a three letter code for a
specific amino acid. The table shows the mRNA codon for each amino acid. Use the Genetic Code Table to
answer the questions.
20. The codon for tryptophan is _______.
21. For leucine, there are _______ different codons.
22. The codon GAU is for __________.
23. -24 .In a stop codon, if the second base is G, the first and third bases are ____ and .
25– 30. Sequence the following steps in protein
synthesis from first to last (1-6)
___A. Transcription
___B. tRNA – amino acid units link to mRNA
___C. Amino acid separate from tRNA
___D. Polypeptide chain assembled
___E. mRNA links to ribosome
___F. Stop codon encountered in mRNA
You might also like
- The Molecular Biology of Plastids: Cell Culture and Somatic Cell Genetics of PlantsFrom EverandThe Molecular Biology of Plastids: Cell Culture and Somatic Cell Genetics of PlantsIndra VasilNo ratings yet
- DNA QuizDocument2 pagesDNA QuizDee YipNo ratings yet
- Post Assessment Module 3: Commonly Used Microbes in BiotechnologyDocument4 pagesPost Assessment Module 3: Commonly Used Microbes in BiotechnologyRyan CuisonNo ratings yet
- Quiz - No. - 6 Dna Rna MutationsDocument1 pageQuiz - No. - 6 Dna Rna MutationsJhamia Cruz EstradaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Expression of Biological InformationDocument3 pagesChapter 5 - Expression of Biological InformationNur HanisNo ratings yet
- Chapter Quiz General Biology 2Document7 pagesChapter Quiz General Biology 2Nikki San GabrielNo ratings yet
- 2023 Biochemistry ReremovalsDocument7 pages2023 Biochemistry Reremovalsbradden louisNo ratings yet
- Self Quizzes: Polymerase. Amylase Anhydrase. Helicase. Proofreading. Replication. Transformation. SubstitutionDocument2 pagesSelf Quizzes: Polymerase. Amylase Anhydrase. Helicase. Proofreading. Replication. Transformation. SubstitutionDr DolittleNo ratings yet
- Mcqs ImbDocument23 pagesMcqs ImbMuvawala Belekia AbelNo ratings yet
- Biotech Fourth QuarterDocument4 pagesBiotech Fourth QuarterRodge BuereNo ratings yet
- 10 Sat Revision 1st SemDocument14 pages10 Sat Revision 1st SemYousif ZidanNo ratings yet
- Long QuizDocument2 pagesLong QuizJhamia Cruz EstradaNo ratings yet
- Quizlet Chapter 16Document10 pagesQuizlet Chapter 16EUNAH LimNo ratings yet
- Chem 600 - Pre-ExamDocument2 pagesChem 600 - Pre-ExamSamuel CaoNo ratings yet
- Pharm. Biochem. Ips 300 QuestionsDocument15 pagesPharm. Biochem. Ips 300 QuestionsMERVI CHRAINBERLY ZOLETANo ratings yet
- LC 4Document2 pagesLC 4Jamalia Disimban MohammadNo ratings yet
- Posttest NewDocument3 pagesPosttest NewMageeNo ratings yet
- Microbiology A Systems Approach 5th Edition Cowan Test BankDocument39 pagesMicrobiology A Systems Approach 5th Edition Cowan Test Bankbachelen69bqi100% (35)
- Ch10 QuizDocument6 pagesCh10 QuizcatlovesfoodNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology Test Serie S 2Document7 pagesMolecular Biology Test Serie S 2ANIL KUMARSBMTNo ratings yet
- Foundations in Microbiology 10th Edition Talaro Test BankDocument38 pagesFoundations in Microbiology 10th Edition Talaro Test Bankpalproedpm7t100% (18)
- DNA Review AnswersDocument2 pagesDNA Review AnswersSpencer ChanNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Science - 2Document5 pagesGrade 10 Science - 2Nenia Claire Mondarte CruzNo ratings yet
- Replication, Transcription, Translation, Mutation QuestionsDocument2 pagesReplication, Transcription, Translation, Mutation QuestionskateNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNA QuizDocument2 pagesDNA and RNA QuizWen SilverNo ratings yet
- Foundations in Microbiology 10th Edition Talaro Test BankDocument37 pagesFoundations in Microbiology 10th Edition Talaro Test Bankbunkerlulleruc3s100% (24)
- Binder1 PDFDocument10 pagesBinder1 PDFSalih HassanNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry 8Th Edition Campbell Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument38 pagesBiochemistry 8Th Edition Campbell Test Bank Full Chapter PDFciaramilcahbrpe100% (15)
- Biochemistry 8th Edition Campbell Test BankDocument17 pagesBiochemistry 8th Edition Campbell Test BankchristinecohenceyamrgpkjNo ratings yet
- Biology Final ExamDocument7 pagesBiology Final ExamJillian FajardoNo ratings yet
- General Biology Ii: Engineering and Mathematics Science, TechnologyDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology Ii: Engineering and Mathematics Science, TechnologyKeirby CayanongNo ratings yet
- PMC Practice Test 05 2022Document11 pagesPMC Practice Test 05 2022Farhan GhanghroNo ratings yet
- Ch09 QuizDocument4 pagesCh09 QuizcatlovesfoodNo ratings yet
- Molecular BiologyDocument5 pagesMolecular BiologyRed AnthonyNo ratings yet
- PMC Mock Test 3Document18 pagesPMC Mock Test 3hmdNo ratings yet
- Pre Test SimDocument2 pagesPre Test SimDebbie Ann LaguindabNo ratings yet
- CH 10 Practice TestDocument3 pagesCH 10 Practice Testrylee graceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Biomolecules Test RevisitedDocument3 pagesChapter 3 Biomolecules Test RevisitedEps SabanganNo ratings yet
- MULTIPLE CHOICE: Write The Letter of The Best Answer On The Space ProvidedDocument2 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE: Write The Letter of The Best Answer On The Space ProvidedAdrian BrillantesNo ratings yet
- Quiz Nucleic Acids Answer KeyDocument2 pagesQuiz Nucleic Acids Answer KeyAdrian BrillantesNo ratings yet
- PMC Mock Test 3Document18 pagesPMC Mock Test 3Musharaf RehmanNo ratings yet
- Cuestionario MolecularDocument35 pagesCuestionario MolecularelambatertulianoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Biomolecules Test RevisitedDocument2 pagesChapter 3 Biomolecules Test Revisitedmuhammad khursheedNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNA QuizDocument3 pagesDNA and RNA QuizDavid GiraldoNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure and ReplicationDocument3 pagesDNA Structure and ReplicationMeek Adan RodriguezNo ratings yet
- MLB 110 MLS M 1920 02 (1) Molecular ExamsDocument15 pagesMLB 110 MLS M 1920 02 (1) Molecular Examsmaxwell amponsahNo ratings yet
- 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance - Entrance QuestionsDocument4 pages6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance - Entrance Questionsarjun1572003No ratings yet
- SEM VI Botany Paper 4 Question BankDocument28 pagesSEM VI Botany Paper 4 Question BankPreeti VermaNo ratings yet
- MQ C6 (Questions)Document8 pagesMQ C6 (Questions)Carin TanNo ratings yet
- CH Test BDocument4 pagesCH Test BTahfeel -- GamingNo ratings yet
- AP Practice Test Chapter 16-20Document27 pagesAP Practice Test Chapter 16-20swagtothemax100% (1)
- Long Test (Protein Synthesis)Document2 pagesLong Test (Protein Synthesis)ArdhieeNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance 01: Practice SheetDocument4 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritance 01: Practice SheetJasleen KaurNo ratings yet
- PMC Practice Test 03 2022Document11 pagesPMC Practice Test 03 2022Farhan GhanghroNo ratings yet
- Problem SetDocument5 pagesProblem SetCristhy CalagueNo ratings yet
- PMC Practice Test 04 2022Document11 pagesPMC Practice Test 04 2022Farhan GhanghroNo ratings yet
- Dr. Harvey Laranang MicrobiologyDocument9 pagesDr. Harvey Laranang MicrobiologyPatricia L.No ratings yet
- DNA Structure-Replication Quiz - Key 12-13Document4 pagesDNA Structure-Replication Quiz - Key 12-13Alvin Pabores100% (1)
- Exam 4 Study Guide Spring 2023Document5 pagesExam 4 Study Guide Spring 2023Masai PaceNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument9 pagesMCQNabd NabdNo ratings yet
- The Chemical Coordination SummaryDocument7 pagesThe Chemical Coordination SummaryTee Bio-ScienceNo ratings yet
- Gene FindingDocument31 pagesGene FindingAnmol MalikNo ratings yet
- Otto Warburg's Contributions To Cancer MetabolismDocument13 pagesOtto Warburg's Contributions To Cancer Metabolismsatya_chagantiNo ratings yet
- MetabolismeDocument31 pagesMetabolismeLalu Aldi PratamaNo ratings yet
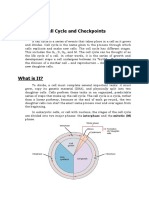
- Lesson 6 - Cell Cycle and CheckpointsDocument6 pagesLesson 6 - Cell Cycle and CheckpointsReuben Al'jaldi100% (1)
- Curtis Cecchi Biology 650 Dr. Ward Watt Essay #2Document7 pagesCurtis Cecchi Biology 650 Dr. Ward Watt Essay #2api-397479475No ratings yet
- B. Exon: C. Transcription, TranslationDocument5 pagesB. Exon: C. Transcription, TranslationRuhna BaigNo ratings yet
- Molecular Cell Biology 1 Basics of Molecular BiologyDocument80 pagesMolecular Cell Biology 1 Basics of Molecular BiologyIana Mira100% (2)
- Enzymes AS Biology Questions AQA OCR EdexcelDocument4 pagesEnzymes AS Biology Questions AQA OCR EdexceljanaNo ratings yet
- Revisi TerakhirDocument14 pagesRevisi TerakhirSyaiful RizalNo ratings yet
- CH 14Document40 pagesCH 14abdurNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Functions PPT 4Document22 pagesCell Structure and Functions PPT 4rajesh duaNo ratings yet
- 1 An Observation - The Krebs CycleDocument33 pages1 An Observation - The Krebs CycleOmbrog JustinNo ratings yet
- CH 29Document10 pagesCH 29VamNo ratings yet
- 1 Neoplasia Sample QuestionsDocument3 pages1 Neoplasia Sample QuestionsPAUL JASPER RONQUILLONo ratings yet
- MasteringBiology - The Endomembrane SystemDocument11 pagesMasteringBiology - The Endomembrane Systemshiyi33% (3)
- Nucleus PresentationDocument46 pagesNucleus PresentationArun Ravi100% (1)
- Glycogen MetabolismDocument21 pagesGlycogen MetabolismDiptadeep KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Light Independent Reaction - BiologyDocument3 pagesLight Independent Reaction - BiologyHidayah SakinahNo ratings yet
- Gene Regulation: Jssansebastian@dlsud - Edu.phDocument13 pagesGene Regulation: Jssansebastian@dlsud - Edu.phKate CamachoNo ratings yet
- WS1 - 11 Grade - The Genetic Code and DNA ReplicationDocument2 pagesWS1 - 11 Grade - The Genetic Code and DNA ReplicationMerey ZiyabekNo ratings yet
- BOCM 3714: T: +27 (0) 51 401 9111 - Info@ufs - Ac.za - WWW - Ufs.ac - ZaDocument30 pagesBOCM 3714: T: +27 (0) 51 401 9111 - Info@ufs - Ac.za - WWW - Ufs.ac - ZaNthabeleng NkaotaNo ratings yet
- SZL B206 Principles of GeneticsDocument28 pagesSZL B206 Principles of Geneticsawuors249No ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration FoldableDocument11 pagesCellular Respiration FoldableVivy LiuNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis QuestionarreDocument2 pagesProtein Synthesis QuestionarreRiza Sardido SimborioNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology Test Serie S 2Document7 pagesMolecular Biology Test Serie S 2ANIL KUMARSBMTNo ratings yet
- Lac OPERONDocument14 pagesLac OPERONAditya Wardana100% (2)
- IB Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument7 pagesIB Multiple Choice QuestionsJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- Genetics A Conceptual Approach 5th Edition Pierce Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesGenetics A Conceptual Approach 5th Edition Pierce Solutions ManualJackCoxmozj100% (48)
- Transcription Notes Class 12Document9 pagesTranscription Notes Class 12Meeta BiswasNo ratings yet
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (517)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)From EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (378)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (812)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperFrom EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouFrom EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (62)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainFrom EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (109)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueFrom EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldFrom EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (595)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindFrom EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemFrom EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (115)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Why We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsFrom EverandWhy We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2083)
- The Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineFrom EverandThe Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (17)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomFrom EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (216)