Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ch09 Quiz
Uploaded by
catlovesfoodCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ch09 Quiz
Uploaded by
catlovesfoodCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 09 - Nucleic Acids: How Structure Conveys Informa?
on
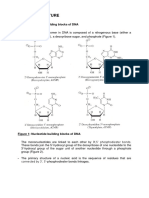
1. The nucleo?de sequence of DNA is which level of structure?
a. primary
b. secondary
c. ter?ary
d. quaternary
2. The double helix of DNA is which level of structure?
a. primary
b. secondary
c. ter?ary
d. quaternary
e. None of these
3. Which of the following is the most dis?nguishing difference between a purine and a
pyrymidine
a. purines are found in DNA while pyrimidines are found in RNA
b. purines have nitrogens in the rings while pyrimidines do not
c. pyrimidines have nitrogens in the rings while purines do not
d. purines are found in RNA while pyrimidines are found in DNA
e. purines are double ring structures while pyrimidines have a single ring
4. Deoxyadenylate (dA) is a:
a. purine base
b. pyrimidine base
c. purine based nucleoside
d. purine based nucleo?de
e. pyrimidine based nucleo?de
5. Which of the following nucleobases is a purine?
a. adenine
b. cytosine
c. thymine
d. uracil
6. The fundamental differences between RNA and DNA are
a. the organic bases only
b. bases, ribose units, and the phosphodiester linkage
c. bases, ribose units, and the glycosidic bond type
d. bases and the ribose units only
7. The backbone of nucleic acids consists of
a. a phosphodiester bond between the 2' and 5' hydroxyl groups of neighboring
sugars
b. a phosphodiester bond between the 3' and 5' hydroxyl groups of neighboring
sugars
c. a glycosidic bond between a pyrimidine and a sugar
d. a glycosidic bond between a purine and a sugar
8. The oligonucleo?de AGGUCCAUUGAAp, is best described as
a. an RNA oligonucleo?de with a 3'phosphate
b. an RNA oligonucleo?de with a 5'phosphate
c. a DNA oligonucleo?de with a 3'phosphate
d. a DNA oligonucleo?de with a 5'phosphate
9. Which of the following statements is true for double-stranded DNA?
a. The amount of A is the same as the amount of T, and the amount of G is the
same as the amount of C.
b. The amount of A is the same as the amount of G, and the amount of T is the
same as the amount of C.
c. The amount of A is the same as the amount of C, and the amount of G is the
same as the amount of T.
d. More than one of the above is true.
10. Which is the dominant form of DNA found in the cell?
a. A
b. B
c. Z
d. H
e. All forms of DNA are found in equal amounts
11. Which of the following characteris?cs is associated with the B form of DNA?
a. the sugars are located in the interior of the double helix
b. the distance between base pairs along the axis of the helix is 8 Å
c. the major and minor grooves are readily apparent
d. the planes of the bases make about a 20 degree angle with the helix axis
12. Propeller twists occur in B-DNA so that
a. Z-DNA can form
b. base pairing distances are op?mized
c. base stacking can beaer occur
d. none of these
13. Which of the following sequences of DNA is most likely to form Z-DNA?
14. In DNA structure, hydrophobic bonding via pi-clouds is referred to as
a. base stacking.
b. propeller twist.
c. hyperchromicity.
d. supercoiling.
e. denatura?on
15. The A and B forms of DNA
a. both have 10 base pairs per turn of the helix
b. both have 11 base pairs per turn of the helix
c. are both leb-handed helices
d. are both right-handed helices
16. The strands in the double helix
a. both run in the same 3' → 5' direc?on, i.e., they are parallel.
b. have their 3' → 5' direc?ons opposed, i.e., they are an?-parallel.
c. can be either parallel or an?-parallel.
d. are perpendicular to one another.
e. None of these
17. Base pairs with a propeller-twist
a. are found only in Z-DNA
b. have op?mum base stacking
c. bind water in the minor groove
d. have stronger hydrogen bonds than base pairs without a propeller twist
18. Supercoiling of DNA
a. is not observed in prokaryotes
b. requires the ac?on of topoisomerase enzymes
c. does not require ATP
d. is not observed in eukaryotes
19. The helix can be untwisted by the ac?on of which type of topoisomerase?
a. Type I only
b. Type II only
c. Both types I and II
d. Topoisomerases cannot untwist the helix.
20. In the DNA in chroma?n, subs?tu?on muta?ons:
a. are at a maximum in the linker regions
b. are at a maximum in the nucleosomes
c. occur maximally in the same places as dele?on muta?ons
d. are rarely seen, but dele?on muta?ons are common
21. The Tm for mel?ng the double helix is:
a. The temperature at which the helix starts to open.
b. The midpoint of the range over which the helix denatures.
c. The temperature at which the helix is completely open.
d. The energy needed to melt the DNA.
e. None of these is correct.
22. RNA is hydrolyzed in basic solu?on, but DNA is not. This occurs because
a. thymine is found in DNA, and uracil is not
b. DNA is double stranded, and RNA is single stranded
c. DNA contains 2'-deoxyribose, but RNA does not
d. RNA has modified bases, but DNA does not
23. In analy?cal ultracentrifuga?on the sedimenta?on coefficient, which is expressed in
Svedberg units (S), characterizes a sedimen?ng par?cle on the basis of
a. size only
b. shape only
c. both size and shape
d. neither size nor shape
24. Transfer RNA molecules are characterized by all the following, except:
a. They are one of the largest of the RNAs.
b. Cloverleaf shape.
c. Many modified bases.
d. Extensive secondary and ter?ary structure.
e. All of these characterize transfer RNA molecules.
25. The _____ structure in DNA refers to the supercoiling of the DNA molecule.
a. primary
b. secondary
c. ter?ary
d. quaternary
You might also like
- POSSIBLE Question (Highlighted in Red Niggawas Pag Lle)Document8 pagesPOSSIBLE Question (Highlighted in Red Niggawas Pag Lle)Valerie Amor SalabaoNo ratings yet
- Structural and Evolutionary Genomics: Natural Selection in Genome EvolutionFrom EverandStructural and Evolutionary Genomics: Natural Selection in Genome EvolutionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- DNA and RNA MCQDocument6 pagesDNA and RNA MCQKashim AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Expression of Biological InformationDocument3 pagesChapter 5 - Expression of Biological InformationNur HanisNo ratings yet
- AP Practice Test Chapter 16-20Document27 pagesAP Practice Test Chapter 16-20swagtothemax100% (1)
- PRETEST - 37 CopiesDocument2 pagesPRETEST - 37 CopiesMageeNo ratings yet
- LS3 Johnson W13 MT1 Form BDocument9 pagesLS3 Johnson W13 MT1 Form BMarissa ClarkNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure and ReplicationDocument3 pagesDNA Structure and ReplicationMeek Adan RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Pharm. Biochem. Ips 300 QuestionsDocument15 pagesPharm. Biochem. Ips 300 QuestionsMERVI CHRAINBERLY ZOLETANo ratings yet
- Post Assessment Module 3: Commonly Used Microbes in BiotechnologyDocument4 pagesPost Assessment Module 3: Commonly Used Microbes in BiotechnologyRyan CuisonNo ratings yet
- 2023 Biochemistry ReremovalsDocument7 pages2023 Biochemistry Reremovalsbradden louisNo ratings yet
- Test Nucleic Acids SLDocument2 pagesTest Nucleic Acids SLKatrīna SimanovskaNo ratings yet
- Mcqs ImbDocument23 pagesMcqs ImbMuvawala Belekia AbelNo ratings yet
- 2018 CHM136 Exam - Q&aDocument9 pages2018 CHM136 Exam - Q&afgb9qfb7x6No ratings yet
- Bio Ws PDFDocument3 pagesBio Ws PDFlina atyaniNo ratings yet
- Principles of Life 2Nd Edition Hillis Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument55 pagesPrinciples of Life 2Nd Edition Hillis Test Bank Full Chapter PDFmarthalouisaq6x100% (8)
- Biochemistry 8th Edition Campbell Test BankDocument17 pagesBiochemistry 8th Edition Campbell Test BankchristinecohenceyamrgpkjNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry 8Th Edition Campbell Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument38 pagesBiochemistry 8Th Edition Campbell Test Bank Full Chapter PDFciaramilcahbrpe100% (15)
- 6 BIO462 Chapter 6Document21 pages6 BIO462 Chapter 6Syafiqah SuhaimiNo ratings yet
- Quiz Nucleic Acids Answer KeyDocument2 pagesQuiz Nucleic Acids Answer KeyAdrian BrillantesNo ratings yet
- MULTIPLE CHOICE: Write The Letter of The Best Answer On The Space ProvidedDocument2 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE: Write The Letter of The Best Answer On The Space ProvidedAdrian BrillantesNo ratings yet
- Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidsDocument29 pagesNucleotides and Nucleic AcidsTavonga ShokoNo ratings yet
- Ch10 QuizDocument6 pagesCh10 QuizcatlovesfoodNo ratings yet
- Foundations in Microbiology 10th Edition Talaro Test BankDocument38 pagesFoundations in Microbiology 10th Edition Talaro Test Bankpalproedpm7t100% (18)
- Quizlet Chapter 16Document10 pagesQuizlet Chapter 16EUNAH LimNo ratings yet
- Principles of Life 2nd Edition Hillis Test BankDocument34 pagesPrinciples of Life 2nd Edition Hillis Test Banktamaramillerdpcqjategf100% (28)
- NCERT Exemplar For Class 12 Biology Chapter 6Document31 pagesNCERT Exemplar For Class 12 Biology Chapter 6Me RahaviNo ratings yet
- Foundations in Microbiology 10th Edition Talaro Test BankDocument37 pagesFoundations in Microbiology 10th Edition Talaro Test Bankbunkerlulleruc3s100% (25)
- Life The Science of Biology 11th Edition Sadava Test Bank 1Document92 pagesLife The Science of Biology 11th Edition Sadava Test Bank 1denise100% (49)
- EXERCISE 5. Molecular Basis of Heredity Structure of The Genetic MaterialDocument3 pagesEXERCISE 5. Molecular Basis of Heredity Structure of The Genetic MaterialMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- GGL DNA Replication PDF VersionDocument7 pagesGGL DNA Replication PDF VersionlloaanaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument9 pagesNucleic AcidsRex Blanco NuñezNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry 5Th Edition Garrett Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesBiochemistry 5Th Edition Garrett Test Bank Full Chapter PDFciaramilcahbrpe100% (15)
- Biochemistry 5th Edition Garrett Test BankDocument15 pagesBiochemistry 5th Edition Garrett Test Bankdorothydoij03k100% (33)
- Problem SetDocument5 pagesProblem SetCristhy CalagueNo ratings yet
- Microbiology A Systems Approach 5th Edition Cowan Test BankDocument39 pagesMicrobiology A Systems Approach 5th Edition Cowan Test Bankbachelen69bqi100% (35)
- As Biology Assessment2Document7 pagesAs Biology Assessment2aby251188No ratings yet
- Dna StructureDocument23 pagesDna StructureAnonymous mHS76aNo ratings yet
- DNA QuizDocument2 pagesDNA QuizDee YipNo ratings yet
- MLB 110 MLS M 1920 02 (1) Molecular ExamsDocument15 pagesMLB 110 MLS M 1920 02 (1) Molecular Examsmaxwell amponsahNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Textbook of Biochemistry With Clinical Correlations 7th Edition Devlin Test Bank PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Textbook of Biochemistry With Clinical Correlations 7th Edition Devlin Test Bank PDFanimismmildpkajkl100% (11)
- MBB 10 2nd Long Exam ReviewerDocument7 pagesMBB 10 2nd Long Exam ReviewerAnonymous YRORccnMNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Fall Semester ReviewDocument12 pagesAP Biology Fall Semester ReviewDivineGloryMalbuyoNo ratings yet
- DNA Review AnswersDocument2 pagesDNA Review AnswersSpencer ChanNo ratings yet
- CH 6Document31 pagesCH 6Lovely King PramothNo ratings yet
- BIO3170 - Practice Midterm 1 PDFDocument5 pagesBIO3170 - Practice Midterm 1 PDFJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- Worksheet # 1 DNA Structure - Malana, Jay-Ar D.Document6 pagesWorksheet # 1 DNA Structure - Malana, Jay-Ar D.Jay-Ar MalanaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Molecular Diagnostics Fundamentals Methods and Clinical Applications 1st Edition BuckinghamDocument5 pagesTest Bank For Molecular Diagnostics Fundamentals Methods and Clinical Applications 1st Edition BuckinghamglendavictoriabbkNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids.Q&A Part1Document102 pagesNucleic Acids.Q&A Part1dhainey80% (5)
- Grade 10 Science - 2Document5 pagesGrade 10 Science - 2Nenia Claire Mondarte CruzNo ratings yet
- NAT SCI 9 Nucleic AcidsDocument12 pagesNAT SCI 9 Nucleic Acidskjgbitoon00125No ratings yet
- Dna and Rna DLLDocument2 pagesDna and Rna DLLHeidie BalabboNo ratings yet
- 9 Csomes DNADocument6 pages9 Csomes DNAKenth Roger A. MaquilingNo ratings yet
- Biotech Outpu - 3rd GPDocument8 pagesBiotech Outpu - 3rd GPGlenn Valentin MendozaNo ratings yet
- Cuestionario MolecularDocument35 pagesCuestionario MolecularelambatertulianoNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Answer Key-PINK PACOPDocument29 pagesBiochemistry Answer Key-PINK PACOPMicah Lou Calamba100% (2)
- Microbiology A Human Perspective 7th Edition Nester Test BankDocument40 pagesMicrobiology A Human Perspective 7th Edition Nester Test Bankmagnusngah7aaz100% (30)
- 10Document15 pages10AmaniNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Multiple Choice Questions For GATEDocument3 pagesCell Biology Multiple Choice Questions For GATEShaik Sayeed0% (1)
- Ch06 QuizDocument5 pagesCh06 QuizcatlovesfoodNo ratings yet
- Ch08 QuizDocument5 pagesCh08 QuizcatlovesfoodNo ratings yet
- Ch10 QuizDocument6 pagesCh10 QuizcatlovesfoodNo ratings yet
- Ch11 QuizDocument6 pagesCh11 QuizcatlovesfoodNo ratings yet
- Ch04 QuizDocument6 pagesCh04 QuizcatlovesfoodNo ratings yet
- Rr322302 Analytical Techniques in BiotechnologyDocument4 pagesRr322302 Analytical Techniques in Biotechnologygeddam06108825No ratings yet
- IPL Final SubmitDocument21 pagesIPL Final SubmitHRISHIKESH PRAKASH JAISWALNo ratings yet
- Edited Activity 1 8 2Document2 pagesEdited Activity 1 8 2Karl Mathew PajarillagaNo ratings yet
- Stem Cell ReportsDocument24 pagesStem Cell ReportsNguyen Dac Hanh HieuNo ratings yet
- Paperclip Activity-Dna ReplicationDocument4 pagesPaperclip Activity-Dna Replicationapi-201291946No ratings yet
- Sequecing - Khan AcademyDocument16 pagesSequecing - Khan AcademyMaryem SafdarNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesCell Cycle Lesson PlanJustine Pama94% (17)
- 13 Therapeutic Cloning Pros and ConsDocument9 pages13 Therapeutic Cloning Pros and ConserinaNo ratings yet
- Gene Modification: Editor: Jia Yue College of Science BiochemistryDocument10 pagesGene Modification: Editor: Jia Yue College of Science Biochemistryapi-316182657No ratings yet
- HPV PCRDocument34 pagesHPV PCRGuneyden GuneydenNo ratings yet
- Ms Paper 4 Topic 16 Inheritance j16-n22Document32 pagesMs Paper 4 Topic 16 Inheritance j16-n22mp7mustafaziad2No ratings yet
- BIO130Chapter2Notes PDFDocument4 pagesBIO130Chapter2Notes PDFjrenceNo ratings yet
- Difusi OsmosisDocument53 pagesDifusi OsmosisSulis tyani08No ratings yet
- R. R. Dhutmal, Et AlDocument10 pagesR. R. Dhutmal, Et AlFernando Castro EchavezNo ratings yet
- BSC 1010C Unit 2 Test - The CellDocument4 pagesBSC 1010C Unit 2 Test - The CellAmalee CarrascoNo ratings yet
- KT202-2× HotStart Taq PCR Mix-210831Document1 pageKT202-2× HotStart Taq PCR Mix-210831Sylvia SanceNo ratings yet
- HRAC MOA Poster January 6 2022Document1 pageHRAC MOA Poster January 6 2022Francisco EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Systems Biology ProblemSet1Document5 pagesSystems Biology ProblemSet1Elegant UniverseNo ratings yet
- Major Histocompatibility Complex: Seminar Presented ONDocument19 pagesMajor Histocompatibility Complex: Seminar Presented ONAshikNo ratings yet
- Hypertonic Stress Response: Natalia I. Dmitrieva, Maurice B. BurgDocument10 pagesHypertonic Stress Response: Natalia I. Dmitrieva, Maurice B. BurgKarina Pineda PérezNo ratings yet
- Genetics Take Home TestDocument12 pagesGenetics Take Home TestEdgarTriff50% (2)
- 1.introduction To MetabolismDocument7 pages1.introduction To MetabolismProtusha RakshitNo ratings yet
- Extraction,: Ancient DNA: Characterization, Molecular Cloning, and Enzymatic AmplificationDocument5 pagesExtraction,: Ancient DNA: Characterization, Molecular Cloning, and Enzymatic AmplificationSara MagoNo ratings yet
- The Neutral Theory of Molecular Evolution - A Recent Review of EvidenceDocument2 pagesThe Neutral Theory of Molecular Evolution - A Recent Review of Evidencepauline.tiong15No ratings yet
- Basic and Applied Aspects of BiotechnologyDocument543 pagesBasic and Applied Aspects of BiotechnologyAngel Lopez100% (2)
- Biosynthesis of CarbohydratesDocument31 pagesBiosynthesis of CarbohydratesDaniella Pasilbas Sabac100% (2)
- Application Form For PHD and Masters Programs 2022 and 23Document13 pagesApplication Form For PHD and Masters Programs 2022 and 23amin demisho100% (2)
- Recombinant Gene ExpressionDocument643 pagesRecombinant Gene ExpressionmaurobiotecnologiaNo ratings yet
- Business Education Vaccine Info For Filling OutDocument61 pagesBusiness Education Vaccine Info For Filling OutReniljay abreoNo ratings yet
- Digital COVID Certificate Certificat Digital CovidDocument2 pagesDigital COVID Certificate Certificat Digital CovidSterenco RitaNo ratings yet
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (517)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseFrom EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (52)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (393)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (812)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainFrom EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (110)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomFrom EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (216)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindFrom EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)From EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (411)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- Darwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignFrom EverandDarwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (39)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldFrom EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (596)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemFrom EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (115)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueFrom EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperFrom EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (16)