100% found this document useful (1 vote)
692 views3 pagesWell Trajectory Calculations
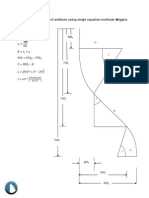
The document discusses methods for calculating well trajectories based on downhole survey measurements. It describes three key methods: the minimum curvature method, which models the wellbore as a smooth circular curve; the radius of curvature method, which also models the wellbore as circular segments; and the angle averaging method, which takes the average of measured inclination and azimuth angles. Equations are provided for calculating coordinate positions along the wellbore for each of these three methods from survey data.
Uploaded by
Lazuardhy Vozicha FuturCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
692 views3 pagesWell Trajectory Calculations
The document discusses methods for calculating well trajectories based on downhole survey measurements. It describes three key methods: the minimum curvature method, which models the wellbore as a smooth circular curve; the radius of curvature method, which also models the wellbore as circular segments; and the angle averaging method, which takes the average of measured inclination and azimuth angles. Equations are provided for calculating coordinate positions along the wellbore for each of these three methods from survey data.
Uploaded by
Lazuardhy Vozicha FuturCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Well Trajectory Calculations