Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Impulse of Force: Demonstration-Newton's Third Law of Motion
Uploaded by
SadguruOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Impulse of Force: Demonstration-Newton's Third Law of Motion
Uploaded by
SadguruCopyright:
Available Formats
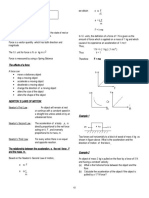
Demonstration- Newton’s third law of motion
F 20
then m2 = = = 40 kg
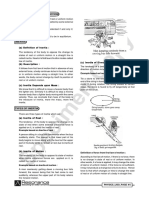
a 0 .5 The other end of the spring balance A is pulled out to
When m1 and m2 are tied together : the left. Both balances show the same reading (20 N)
for the force.
Total mass = m1 + m2 = 45 kg, F = 20N
The pulled balance A exerts a force of 20N on the
F 20 balance B. It acts as action, B pulls the balance A in
then a= = = 0.44 ms–2
(m1 m 2 ) 45 opposite direction with a force of 20 N. This force is
known as reaction.
We conclude that action-reaction forces are equal and
IMPULSE OF FORCE opposite and act on two different bodies.
A large force acting for a short time to produce a finite
change in momentum is called impulsive force. NO ACTION IS POSSIBLE WITHOUT REACTION
The product of force and time is called impulse of force.
Examples :
i.e., Impulse = Force × Time
(i) A nail cannot be fixed on a suspended wooden ball.
or I = Ft (ii) A paper cannot be cut by scissors of single blade.
The S.I. unit of impulse is Newton-second (N-s) and (iii) A hanging piece of paper cannot be cut by blade.
the C.G.S unit is dyne- second (dyne-s)
(iv) Writing on a hanging page is impossible.
Impulse and Momentum : (v) Hitting on a piece of sponge does not produce
reaction. You do not enjoy hitting.
From Newton’s second law of motion
p 2 p1 ACTION AND REACTION ARE NOT BALANCED
Force, F = or Ft = p2 – p1
t
Action and reaction, though equal and opposite are
i.e., Impulse = Change in momentum
not balanced because they act on two different bodies.
This relation is called impulse equation or momentum- In case when they act on two different bodies forming
impulse theorem. It has an important application in a single system, they become balanced.
our everyday life.
ANY PAIR OF EQUAL AND OPPOSITE FORCES IS
IMPULSE DURING AN IMPACT OR COLLISION NOT AN ACTION–REACTION PAIR
Consider a book kept on a table. We have seen that
The impulsive force acting on the body produces a
change in momentum of the body on which it acts. We the table pushes the book in the upward direction. Then
know, Ft = mv – mu, therefore the maximum force why does not the book fly up? It does not fly up because
needed to produce a given impulse depends upon there is another force on the book pulling it down. This
time. If time is short, the force required in a given is the force exerted by the earth on the book, which we
impulse or the change in momentum is large and vice- call the weight of the book. So, there are two forces on
versa. the book– the normal force, N acting upwards, applied
NEWTON’S THIRD LAW by the table and the force, W acting downwards,
applied by the earth. As the book does not accelerate,
(a) Statement : we conclude that these two forces are balanced. In
other words, they have equal magnitudes but opposite
The law states that “ To every action there is an equal directions.
and opposite reaction“. Moreover, action and reaction
act on different bodies.
(b) Demonstration : N
Two similar spring balances A and B joined by hook as N=W
V
shown in the figure. The other end of the spring V V
balance B is attached to a hook rigidly fixed in a rigid
wall.
Can we call N the action and W the reaction ? We
cannot. This is because, although they are equal and
PHYSICS_IJSO_PAGE #88
You might also like
- Force 8Document20 pagesForce 8Liana Belle0% (1)
- Third Law and GravitationDocument12 pagesThird Law and GravitationDebayan RoyNo ratings yet
- Work Energy PowerDocument40 pagesWork Energy PowerJames MaxwellNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion: Inertia. The Inertia of A Body Is Related To What We Can Think of As The Amount of Matter It ContainsDocument8 pagesLaws of Motion: Inertia. The Inertia of A Body Is Related To What We Can Think of As The Amount of Matter It ContainsEduard Benjamin LauronNo ratings yet
- Dynamics NotesDocument31 pagesDynamics NotessubashiniNo ratings yet
- ForcesDocument98 pagesForcesWee Chee LimNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Work, Energy and Power Revision Notes - Free PDF DownloadDocument5 pagesJEE Main Work, Energy and Power Revision Notes - Free PDF DownloadSancia SamNo ratings yet
- DynamicDocument41 pagesDynamicRohit rajNo ratings yet
- 05 PH Newtons LawsDocument22 pages05 PH Newtons Lawsapi-235269401No ratings yet
- Newtons LawsDocument15 pagesNewtons LawsTania MakaringeNo ratings yet
- Physics Lesson ReviewsDocument9 pagesPhysics Lesson ReviewsРубабе ХалиловаNo ratings yet
- Newton's: Motion F!:T Mi&fDocument6 pagesNewton's: Motion F!:T Mi&fMinh LụcNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of A ParticleDocument41 pagesDynamics of A ParticlePrantik SealNo ratings yet
- T-Effect of ForceDocument2 pagesT-Effect of ForceGan Hock KiamNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes Zahid I. B. Khan: EchanicsDocument6 pagesPhysics Notes Zahid I. B. Khan: EchanicsZahid IbkNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of Elements ListDocument7 pagesPeriodic Table of Elements ListMin YoongiNo ratings yet
- Module 2 DynamicsDocument47 pagesModule 2 DynamicsTaha Kafil-HussainNo ratings yet
- NEWTON's 1st, 2nd & 3rd LawsDocument20 pagesNEWTON's 1st, 2nd & 3rd LawsNorKamilahMakhtarNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion-01Document34 pagesLaws of Motion-01wixirepNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion MKDocument26 pagesLaws of Motion MKriddhiarunkarangaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Force Mass AccelerationDocument12 pagesChapter 5 Force Mass AccelerationAivan SaberonNo ratings yet
- Forces and Newton LawsDocument37 pagesForces and Newton LawsRavenSkullNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Newtons Laws PDFDocument5 pagesChapter-3 Newtons Laws PDFMohammad Fuad HasanNo ratings yet
- Newton'S Laws: Unit Is 4.45 NDocument2 pagesNewton'S Laws: Unit Is 4.45 NGabriel VirayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Force Mass Acceleration PDFDocument12 pagesChapter 5 Force Mass Acceleration PDFAivan SaberonNo ratings yet
- Newtons Law of MotionDocument14 pagesNewtons Law of MotionJohn Irvin M. AbatayNo ratings yet
- Forces 3 Newton's Third Law - 2Document10 pagesForces 3 Newton's Third Law - 2mallikammu12No ratings yet
- Newton's Laws & MomentumDocument5 pagesNewton's Laws & MomentumSky WhiteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Basic Physics SEDocument15 pagesChapter 7 Basic Physics SEtsoniffNo ratings yet
- Xi Physics - Work, Energy & PowerDocument16 pagesXi Physics - Work, Energy & PoweradarshdarasinghNo ratings yet
- Science 8: Q Uarter 1 - M Odule 1: ForcesDocument8 pagesScience 8: Q Uarter 1 - M Odule 1: ForcesCeelyn QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - 2Document25 pagesChapter 5 - 2Qassem MohaidatNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Physics Sample FounationDocument25 pagesClass 8 Physics Sample FounationPraveen MaramNo ratings yet
- Newtons Laws of MotionDocument23 pagesNewtons Laws of MotionAnsh MishraNo ratings yet
- Work Energy and Power PDFDocument16 pagesWork Energy and Power PDFjonelle27No ratings yet
- Physics Lab Report 6: ForcesDocument14 pagesPhysics Lab Report 6: ForcesJustin PedrozaNo ratings yet
- FSC I Short Que Chapter 3Document5 pagesFSC I Short Que Chapter 3Voice of People جمہور کی آوازNo ratings yet
- Unit 11Document3 pagesUnit 11LGG MATRICULATIONNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 Work, Energy and MomentumDocument8 pagesChapter-4 Work, Energy and Momentum2220678No ratings yet
- Work, Energy, and PowerDocument15 pagesWork, Energy, and PowerperwinsharmaNo ratings yet
- Linear Mechanics: Motion in A LineDocument19 pagesLinear Mechanics: Motion in A LineDilla DefayanaNo ratings yet
- Asp - WpeDocument44 pagesAsp - WpeKrishnashis DasNo ratings yet
- StaticsDocument6 pagesStaticsWednesday GuillermoNo ratings yet
- WEEK 4 Forces and Newton LawsDocument36 pagesWEEK 4 Forces and Newton LawsShare linkNo ratings yet
- Topic111Newtons Second and Third Lawswith Key 1Document16 pagesTopic111Newtons Second and Third Lawswith Key 1serenity xxNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Physics Revision Notes Law of MotionDocument17 pagesClass 11 Physics Revision Notes Law of MotionThulasinathNo ratings yet
- LP Week 1 2 Science 8Document4 pagesLP Week 1 2 Science 8rommel mukayNo ratings yet
- Newtons Law Force & Friction WA (English)Document19 pagesNewtons Law Force & Friction WA (English)Swarnlata MishraNo ratings yet
- Physics111 Lecture03Document22 pagesPhysics111 Lecture03Juliana MosqueraNo ratings yet
- gr-11 Physics 14 MarchDocument6 pagesgr-11 Physics 14 MarchDonald DubeNo ratings yet
- CH 6 Sec 2Document21 pagesCH 6 Sec 2FWGANo ratings yet
- Physgen Unit 5Document13 pagesPhysgen Unit 5emji miraNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Newtons LawsDocument11 pagesModule 5 - Newtons LawsKrizel CalasaraNo ratings yet
- CH Apter 4 Motion and ForceDocument18 pagesCH Apter 4 Motion and ForcePapa's AngleNo ratings yet
- Forces - Completed - V1Document2 pagesForces - Completed - V1Saad Hamoudi [Student]No ratings yet
- Study Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Document19 pagesStudy Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Shashwat MishraNo ratings yet
- AS LEVEL PHYSICS NOTES Newton's LawsDocument2 pagesAS LEVEL PHYSICS NOTES Newton's LawsKartika PrajogoNo ratings yet
- Phys 1011 - Dynamic NotesDocument10 pagesPhys 1011 - Dynamic Notesnigusayele06No ratings yet
- IJSO Part-17Document1 pageIJSO Part-17SadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-20Document1 pageIJSO Part-20SadguruNo ratings yet
- (B) The Working of A Rocke T:: N' and MG Are Not Action - Reaction Pair. Since PairDocument1 page(B) The Working of A Rocke T:: N' and MG Are Not Action - Reaction Pair. Since PairSadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-15Document1 pageIJSO Part-15SadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-14Document1 pageIJSO Part-14SadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-16Document1 pageIJSO Part-16SadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-19Document1 pageIJSO Part-19SadguruNo ratings yet
- Principle of Conservation of Linear Momentum: (A) Recoil of GunDocument1 pagePrinciple of Conservation of Linear Momentum: (A) Recoil of GunSadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-13Document1 pageIJSO Part-13SadguruNo ratings yet
- Translatory Equilibrium: F F F MaDocument1 pageTranslatory Equilibrium: F F F MaSadguruNo ratings yet
- (A) Conservative Force:: Galileo'S ExperimentsDocument1 page(A) Conservative Force:: Galileo'S ExperimentsSadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-8Document1 pageIJSO Part-8SadguruNo ratings yet
- Newton'S First Law of Motion: (A) de Finition of Ine RtiaDocument1 pageNewton'S First Law of Motion: (A) de Finition of Ine RtiaSadguruNo ratings yet
- (A) Normal Force (N) :: Detailed Analysis of Contact ForceDocument1 page(A) Normal Force (N) :: Detailed Analysis of Contact ForceSadguruNo ratings yet
- (B) Tension:: - KX K SpringDocument1 page(B) Tension:: - KX K SpringSadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-2Document1 pageIJSO Part-2SadguruNo ratings yet
- Nso Set-B Class-12 UpdatedDocument1 pageNso Set-B Class-12 UpdatedSadguruNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 CH 1 To 4Document4 pagesPaper 1 CH 1 To 4SadguruNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiment 1 Water and Its PropertiesDocument6 pagesLaboratory Experiment 1 Water and Its PropertiesRenee Dwi Permata Messakaraeng100% (1)
- ASTM A572 Steel - Grade 50Document1 pageASTM A572 Steel - Grade 50FWICIP100% (1)
- Numerical Simulation of Solidification and Melting Problems Using Ansys Fluent 16.2 PDFDocument40 pagesNumerical Simulation of Solidification and Melting Problems Using Ansys Fluent 16.2 PDFAntarim Dutta50% (2)
- DC Pandey Mechanics Volume 1 (Crackjee - Xyz) - RemovedDocument500 pagesDC Pandey Mechanics Volume 1 (Crackjee - Xyz) - Removedsaadvik1121No ratings yet
- Brochure Leaching 4824 01 23 en MNGDocument8 pagesBrochure Leaching 4824 01 23 en MNGOsamaNo ratings yet
- 1969 - Greenfield - Computed Circular Dichroism Spectra For The Evaluation of Protein ConformationDocument9 pages1969 - Greenfield - Computed Circular Dichroism Spectra For The Evaluation of Protein ConformationAngelico ObilleNo ratings yet
- App Note 002 Measuring The Conductivity of Pure Water Using USP 645Document8 pagesApp Note 002 Measuring The Conductivity of Pure Water Using USP 645fonsynickNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2: Quarter 4 - Week 1Document21 pagesGeneral Physics 2: Quarter 4 - Week 1Ralph QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- Challenges and A Possible Solution For The RecyclingDocument10 pagesChallenges and A Possible Solution For The RecyclingJuan TrianaNo ratings yet
- NC20B1NL 2 UsansiDocument7 pagesNC20B1NL 2 UsansiBERSE MAJU INDONESIANo ratings yet
- A ThesisDocument101 pagesA ThesisMurtaza SieamNo ratings yet
- Operating Manual For Ammonia - Rev 2Document379 pagesOperating Manual For Ammonia - Rev 2Mangihut Lumbantoruan100% (3)
- Prepreg 1080 vs. Prepreg 2116 How Do They DifferDocument14 pagesPrepreg 1080 vs. Prepreg 2116 How Do They DifferjackNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties and Chemical Reactions ofDocument9 pagesPhysical Properties and Chemical Reactions ofTUANA DURMAYÜKSELNo ratings yet
- Chemical Processing of Textiles - I - CompressedDocument118 pagesChemical Processing of Textiles - I - CompressedOmkar Jadhav100% (1)
- 32 Productivity Increase in A PeirceSmith Convert 153013Document14 pages32 Productivity Increase in A PeirceSmith Convert 153013amirlpNo ratings yet
- Spiritual Secrets From The Carbon AtomDocument3 pagesSpiritual Secrets From The Carbon Atomtanaha100% (2)
- Chapter 6: Imperfections in Solids: Issues To Address..Document50 pagesChapter 6: Imperfections in Solids: Issues To Address..ÖmerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - The Bernoulli Equation and Pressure VariationDocument20 pagesChapter 4 - The Bernoulli Equation and Pressure VariationErnesto LimNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Chemistry A-Level: Topic 19: Modern Analytical Techniques IIDocument8 pagesEdexcel Chemistry A-Level: Topic 19: Modern Analytical Techniques IILulwa KhaskiehNo ratings yet
- United States Patent (19) : Im, Naperville, Both of Ill. Attorney, Agent, or Firm-William C. Clarke Arthur GDocument9 pagesUnited States Patent (19) : Im, Naperville, Both of Ill. Attorney, Agent, or Firm-William C. Clarke Arthur GFebrian Dimas Adi NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Fire Fighthing InvestigationDocument32 pagesFire Fighthing InvestigationjmNo ratings yet
- 1501ENG Supplementary Material & Workbook For Statics 2019 (T3) - Pages-DeletedDocument14 pages1501ENG Supplementary Material & Workbook For Statics 2019 (T3) - Pages-DeletedMatthewNo ratings yet
- Tabla Comparativa de Adsorcion de SO2Document27 pagesTabla Comparativa de Adsorcion de SO2Juan NanoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Properties of SoilsDocument178 pagesEngineering Properties of SoilsAndrewNo ratings yet
- Rubber Properties Chart PDFDocument1 pageRubber Properties Chart PDFsefaNo ratings yet
- A Critical Review of Carbon Fiber and Related Products From An Industrial PerspectiveDocument17 pagesA Critical Review of Carbon Fiber and Related Products From An Industrial Perspectivechatgpt51023No ratings yet
- Hydrometallurgy Review PDFDocument13 pagesHydrometallurgy Review PDFBig100% (1)
- Lubrication &ignition SystemsDocument26 pagesLubrication &ignition SystemsKamaru ZamanNo ratings yet
- Vpci - 322 Oil Concentrate: FeaturesDocument2 pagesVpci - 322 Oil Concentrate: FeaturesazfarNo ratings yet