Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mineral Resources C.M.L. Aguilar
Uploaded by
Sako0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views4 pagesLab report in mineral resources
Original Title
Mineral Resources
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLab report in mineral resources
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views4 pagesMineral Resources C.M.L. Aguilar
Uploaded by
SakoLab report in mineral resources
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
MINERAL RESOURCES
C.M.L. Aguilar1
1Legazpi City Science High School
DATE PERFORMED: July 09, 2019
ABSTRACT
Minerals are inorganic abiotic solid crystalline compounds formed by natural
processes with definite composition and ordered internal structure which serves as the
building blocks of rocks. In this experiment, five physical properties of minerals are tested. It
includes the hardness, color, streak, luster, and cleavage. The experiment aims to know the
concept behind the different properties and to identify and classify minerals according to their
physical properties. Several procedures were done to test the different properties and various
materials and equipment required in the experiment were prepared. The experiment proved
that minerals vary in hardness, color, streak, luster, and cleavage. Some minerals are softer or
harder based on the Moh’s harness scale. Color is the least useful property for it might be
deceiving. Streak is the most helpful property because it shows the actual color of the minerals
in powdered form. Luster is the qualitative measurement of the amount of light reflected.
Cleavage proved that minerals do not appear to break the same way due to the arrangement
of their atoms.
then pulling 3 sturdy straws into the clay
in the bowl.
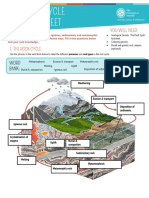
INTRODUCTION
In the second part of the
Mining is the process or business experiment, entitled “Mining Methods”,
of extracting ore or minerals from the sand, iron fillings, salt, elbow macaroni,
ground. Mining is needed to obtain any roasted peanuts, and raisins were mixed
material that cannot be grown through together in a bowl and were then
agricultural processes, or feasibly created sprinkled with saw dust all over the top. 5
by artificial means in a laboratory or mounds, 4 scoops each, were made with a
factory. Mining in a wider sense includes spoon and placed next to each other on a
extraction of any non-renewable resource piece of newspaper.
like crude oil, gas, or even water.
(https://www.wordnik.com/words/mining In the third part of the
) experiment, entitled “Milling Process,
Materials such as magnets, ice bags,
The significance of this study is to beakers, filter paper, tweezers, and water
find out and understand the processes were utilized in order to separate the
and methods involved in mining. different materials from each other.
METHODOLOGY RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Various materials and equipment 1. A. Are the mineral
were used in the experiment. It involved deposits (represented by the yellow clay
straws, clay, sand, iron fillings, a bowl, for gold and blue clay for copper) evenly
salt, elbow macaroni, roasted peanuts, distributed in the bowl? Explain its
saw dust, raisins, a spoon, newspaper, relevance on the actual mineral
plastic cups, plastic bags, filter paper, deposition.
tweezers, water, and soda.
No. The mineral deposits aren’t
In the first part of the experiment, evenly distributed in the bowl because just
entitled “Mineral Exploration”, pieces of like the actual mineral deposition, the
clay were molded into layers and were minerals aren’t spread out with even
then placed in a bowl. Samples of clay thickness and concentration. Some
were extracted by pushing, rotating, and geologic processes also contributed to the
uneven deposition of minerals such as Filling low solubl ic magnetic
temperatures, hydrothermal process, s densit e in and
eruptions, and such. y water metallic
becau propertie
b. Can the drill cores indicate how se of s
deep the mineral deposits are? Explain its
your answer. fine
partic
Yes. The drill cores indicate the les
depth of mineral deposits because with Macar Has Not Non- Curved
oni low solubl magne shape,
accurate measurements inclined with
densit e in tic with
drilling, the minerals in a drilling area can y and water narrow
be identified. floats hole
tubes in
c. How can additional drill holes short
affect geological interpretation? lengths
Salt Dense Solubl Non- Dissolves
Few drill holes provide a vague and e in magne in water
view of what’s underneath since increa water tic as the
correlation is not very accurate. It will be ses solvent
harder to create a clearer picture of the the
mineral deposits. Thus additional drill densit
holes positively affect the accuracy of the y of
geological interpretation. water
Sawd Less Not Non- Compose
2. a. What factors did you consider ust dense solubl magne d of
in selecting where to start mining? than e in tic particles
sand water of wood
The factors that were considered in and
selecting where to start mining are floats
locations of deposits, concentration of Roast Less Not Non- Low
ed dense solubl magne density,
mineral deposits, and depth of the mining
Peanu than e in tic oily
process, slope stability and closeness to ts raisin water composit
facility (place for stockpiling). s and ion
floats
b. How has mining change the on the
land? soda
Raisin Dense Not Non- Dark-
Mining had greatly changed the s r than solubl magne colored,
land. It caused destruction and the e in tic dried,
deformation of the landscape, disturbance roaste water natural
in the immediate area of mine site, sink d sugar
holes on the surface, and cleaning large peanu crystalliz
areas of land. ts ation
and
3. A. From personal experiences and sank
observations in the activity, describe the at the
properties of the different materials used botto
in the mixture. m
Densi Solubi Magnet Other
ty lity ism Propertie b. Based on the above properties,
s enumerate the steps that you did to
Sand Dense Not Non- Black, separate the mixture.
r than solubl magne grain-
the e in tic like size, Step Substance Separate
sawd water rough, 1. Tweezers was The substances that
ust compose used to manually were separated
and d of pluck out the were macaroni,
sank finely biggest mineral roasted peanuts,
at the divided
representations and raisins.
botto rock
m particles
from the mounds.
Iron Has Not Magnet High 2. A magnet was The substances
used to magnetize separated were the
all the iron fillings iron fillings. slurry where some Shaking the
from the remaining minerals and mixture helped the
mounds. metals based on sawdust get
3. Soda was used to Separated physical and concentrated above
separate peanuts substances were chemical properties the sand. The sand
(floated on the roasted peanuts may either sink to sunk to the bottom
soda) and raisins and raisins. the bottom or stick and the sawdust
(sunk at the to the bubbles and rose at the top,
bottom). rise to the top thus separating the two.
4. The remaining At this point, separating the Flotation is done
mounds were sawdust and sand minerals and before filtering the
submerged in the aren’t separated metals from the water with sawdust
water where the completely. waste.
sand sunk and the 4. Cyanide heap It represents the
sawdust floated. It leaching: This separation or
was stirred to method used for extraction of salt
dissolve the salt. low-grade gold ore from water since
5. The water from Sawdust was where the crushed dissolving is also
step 4 was poured separated from the rock is placed on a involved. The salt
to another sand. “leach pile” where was dissolved and
container with the cyanide solution is afterwards the
sawdust leaving the sprayed or dripped water was
sand using a filter on top of the pile. evaporated to
paper. As the leach separate the salt.
6. The filtered The separated solution percolates The salt represents
water was heated substance was salt. down the rocks, the a soluble precious
for evaporation and gold is dissolved metal like gold
left the salt behind. into the solution. which is dissolved
The solution is into the solution
processed further from crushed ore
c. Based from the steps that you to extract the gold. and placed on a
did to separate the mixture, which of it “leach pile”.
represents the following milling
processes?
4. A. What have you done to
Milling Process Representation rehabilitate the land after mining?
from the Activity
1. Heavy media It represents the The land was rehabilitated after
separation: The roasted peanuts mining by returning the land from the
crushed rocks are and raisins which stockpiles or mounds which were mined to
submerged in were separated. fill up the open pits.
liquid where the They were
heavier or denser submerged in soda b. Enumerate several ways to
minerals sink thus where the denser rehabilitate a mined-out area.
are separated from minerals (raisins) Some of the ways to rehabilitate a
the lighter sunk and the mined-out area are: a) know the
minerals. lighter minerals constraints and problem of the soil to be
(peanuts) floated. remediated; b) waste clumps are used to
2. Magnetic It represents the stabilize it from erosion; c) covering with
separation: If the separation of iron topsoil for vegetation; d) open big pits are
metal or mineral is fillings from the fenced to prevent access; e) tailing das are
magnetic, the mounds, Since iron left to evaporate; and f) fencing of dumps
crushed ore is fillings have to prevent livestock denuding them of the
separated from the metallic properties, plantation.
waste materials they are magnetic.
using a powerful A magnet was used
magnet. to separate these.
3. Flotation: The It represents the
powdered ore is separation of
placed into an sawdust and sand CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATION
agitated and frothy using water.
The experiment clearly explained
how minerals are found through
exploration, mined by drilling and
processed through milling for human use.
It also demonstrated the different types of
milling and recovery methods such as
heavy media separation, magnetic
separation, flotation, and cyanide heap
leaching. Different ways to prevent or
lessen the environmental impact that
result from the exploitation, extraction,
and use of mineral resources were cited.
REFERENCES
1. https://www.wordnik.com/word
s/mining
2. Agricola, Georg; Hoover, Herbert
(1950). De re metallica.
MBLWHOI Library. New York,
Dover Publications.
3. http://www.yourarticlelibrary.co
m/environment/minerals/minera
l-resources-definition-types-use-
and-exploitation-with-statistics-
and-diagram/28169
You might also like
- Identification Rocks PDFDocument11 pagesIdentification Rocks PDFjunaidNo ratings yet
- Rock Cycle Activity Sheet KS2 Answer SheetDocument2 pagesRock Cycle Activity Sheet KS2 Answer SheetHarold The GreatNo ratings yet
- 02 - Prospecting and Exploration 025-105Document41 pages02 - Prospecting and Exploration 025-105ramanaNo ratings yet
- Rock Cycle Activity Sheet KS2Document2 pagesRock Cycle Activity Sheet KS2dhivi89No ratings yet
- Dunham 1962 AAPG Classification of Carbonate RocksDocument14 pagesDunham 1962 AAPG Classification of Carbonate RocksDaniela MWNo ratings yet
- PMO Qualifying Round Version 4Document5 pagesPMO Qualifying Round Version 4Ryan QuimoNo ratings yet
- Specification For Sprinkler DesignDocument14 pagesSpecification For Sprinkler DesignFarhan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption of CarbohydratesDocument25 pagesDigestion and Absorption of CarbohydrateskhadijaNo ratings yet
- Research Title DefenseDocument19 pagesResearch Title DefenseSako100% (1)
- Catalogue Surfactants PDFDocument16 pagesCatalogue Surfactants PDFMukesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Influence of Electronic Gadgets ExcessiveDocument123 pagesInfluence of Electronic Gadgets Excessivenanana93No ratings yet
- Classification of Carbonate RocksDocument14 pagesClassification of Carbonate RocksAnderson100% (1)
- anapurna M: Operator ManualDocument62 pagesanapurna M: Operator ManualAnonymous gQcTl4bot867% (3)
- Barail Naga HillsDocument7 pagesBarail Naga HillsPradip BorgohainNo ratings yet
- Cliff - S Personal Report To TadiDocument12 pagesCliff - S Personal Report To TadiADJEI-YEBAOH SHALOMNo ratings yet
- National University of Moquegua: Professional School of Mining EngineeringDocument7 pagesNational University of Moquegua: Professional School of Mining EngineeringJeff Seid :3No ratings yet
- Archive of SID: Characterization of Reservoir Rock Types in A Heterogeneous Clastic and Carbonate ReservoirDocument10 pagesArchive of SID: Characterization of Reservoir Rock Types in A Heterogeneous Clastic and Carbonate ReservoirNajeeb Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Classifications of Rock PropertiesDocument5 pagesClassifications of Rock PropertiesAlwin AntonyNo ratings yet
- JFranckepaper GPRforNiLateriteDocument6 pagesJFranckepaper GPRforNiLateriteLUTHFAN ALIFI ANWARNo ratings yet
- @conferencepaperspwla 1999 NNDocument9 pages@conferencepaperspwla 1999 NNarispriyatmonoNo ratings yet
- Princess Xyra T. Mallari 11-HUMSS, ST - Anthony de Padua Ms - Krizia Mae Enriquez September 01,2021Document6 pagesPrincess Xyra T. Mallari 11-HUMSS, ST - Anthony de Padua Ms - Krizia Mae Enriquez September 01,2021Xyy MallariNo ratings yet
- Water Transport Studies in Stone Masonry With Soil Cement MortarDocument10 pagesWater Transport Studies in Stone Masonry With Soil Cement MortarTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Soil Science 22Document5 pagesSoil Science 22Aleah TyNo ratings yet
- F3 GR.5 3G Metallurgy, Soil, Dust&DirtDocument5 pagesF3 GR.5 3G Metallurgy, Soil, Dust&DirtJojoNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Week 2Document10 pagesEarth Science Week 2Rhea OraaNo ratings yet
- Acharya N.G.Ranga Agricultural University Rajendra Nagar, HyderabadDocument46 pagesAcharya N.G.Ranga Agricultural University Rajendra Nagar, HyderabadSanthosh Reddy DNo ratings yet
- Occurrence and Resources of China Clay in IndiaDocument7 pagesOccurrence and Resources of China Clay in IndiaSaeed AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Coal and Coal-Bearing Systems: Dr. Joan Esterle Earth Sciences University of QueenslandDocument33 pagesIntroduction To Coal and Coal-Bearing Systems: Dr. Joan Esterle Earth Sciences University of QueenslandGreen0789No ratings yet
- Rich PPL HahitDocument3 pagesRich PPL HahitRajiv JeetunNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Interplayofsedimentationanddiagenesisof Miocene Clastic Reserv PPtiesDocument16 pagesDynamic Interplayofsedimentationanddiagenesisof Miocene Clastic Reserv PPtiessatish kumarNo ratings yet
- 7 Indian Conf Mar Archaeol I.O Countries 2005 78Document4 pages7 Indian Conf Mar Archaeol I.O Countries 2005 78professorgamer795No ratings yet
- ACQ U8Document3 pagesACQ U8Naruto UzumakiNo ratings yet
- Groundwater in Geochemical ExplorationDocument20 pagesGroundwater in Geochemical Explorationjavicol70No ratings yet
- Khorat Part 2 JPGCanhametal 1996Document19 pagesKhorat Part 2 JPGCanhametal 1996ilham halikNo ratings yet
- Universidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos: Salida de Campo Pedregal-ChosicaDocument23 pagesUniversidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos: Salida de Campo Pedregal-ChosicaAnonymous GyEOgNGNo ratings yet
- 8G Rocks and WeatheringDocument12 pages8G Rocks and WeatheringRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Noo Blue Company - by SlidesgoDocument8 pagesNoo Blue Company - by SlidesgonaomiNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Properties of Siliceous Sediments From The Central Indian BasinDocument6 pagesGeotechnical Properties of Siliceous Sediments From The Central Indian BasinaminsuhadiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9: Mode of OccurrenceDocument15 pagesLesson 9: Mode of OccurrenceMarnoel MalapitanNo ratings yet
- Clay Mineral-Grain Size-Calcite Cement Relationships in The Upper Cretaceous Chalk, UK: A Preliminary InvestigationDocument27 pagesClay Mineral-Grain Size-Calcite Cement Relationships in The Upper Cretaceous Chalk, UK: A Preliminary InvestigationCarlos GalhanoNo ratings yet
- Diamong Drilling As An Aid in Ore Definition at Dome MineDocument7 pagesDiamong Drilling As An Aid in Ore Definition at Dome MineRenzo MisariNo ratings yet
- International Society For Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical EngineeringDocument9 pagesInternational Society For Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical EngineeringKingsley HayfordNo ratings yet
- Fluxes and The Heat Treatment of Ruby and Sapphire: Brush Prairie, WashingtonDocument3 pagesFluxes and The Heat Treatment of Ruby and Sapphire: Brush Prairie, Washingtonmakara5966No ratings yet
- Sedi Lecture 2Document44 pagesSedi Lecture 2Dennise ShughniNo ratings yet
- Freitas, M. H. de Dobereiner, L. (1986) - Geotechnical Properties of Weak SandstonesDocument16 pagesFreitas, M. H. de Dobereiner, L. (1986) - Geotechnical Properties of Weak SandstonesYonathan MolinaNo ratings yet
- Slickensides in Residual Soils and Their Engineering SignificanceDocument7 pagesSlickensides in Residual Soils and Their Engineering SignificanceJoko KlanthungNo ratings yet
- Types of RocksDocument29 pagesTypes of RocksHickory DickoryNo ratings yet
- Abbasi & Yasin 2017 Petrography of The Nagri Formation SandstonesDocument3 pagesAbbasi & Yasin 2017 Petrography of The Nagri Formation SandstonesMuhammad SaleemNo ratings yet
- A Further Examination of The Nature of Dispersive Soils in Natal, South Africa Bell 2000Document13 pagesA Further Examination of The Nature of Dispersive Soils in Natal, South Africa Bell 2000Suraj BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 - Answers To Courseboook QuestionsDocument1 pageUnit 8 - Answers To Courseboook QuestionsDeeyana Areef ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Pore Pressure Offshore Nile DeltaDocument5 pagesPore Pressure Offshore Nile Deltamohamed_booksNo ratings yet
- Activityno.2-Depositional Sedimentary Environment and StructuresDocument6 pagesActivityno.2-Depositional Sedimentary Environment and StructuresKevin RamiroNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Clay Mineralogy For A Calcrete-Hosted Uranium Deposit - Innovative Application of Existing Technology On An Unprecedented ScaleDocument8 pagesQuantitative Clay Mineralogy For A Calcrete-Hosted Uranium Deposit - Innovative Application of Existing Technology On An Unprecedented ScaleAldoNo ratings yet
- For Quiz RecipeDocument12 pagesFor Quiz RecipeChristian Rogel De TorresNo ratings yet
- Las4-Classificaton of RocksDocument5 pagesLas4-Classificaton of RocksMark joedel MendezNo ratings yet
- Las4-Classificaton of RocksDocument5 pagesLas4-Classificaton of RocksMark joedel MendezNo ratings yet
- Geology & Civil Engineering - Understanding The RelationshipDocument90 pagesGeology & Civil Engineering - Understanding The RelationshipMohammad Rafnie ArifNo ratings yet
- F3-GR.5 3F Metallurgy SoilDocument7 pagesF3-GR.5 3F Metallurgy SoilArkhio TraballoNo ratings yet
- SPE Estimating Fracture Gradient in Gulf of Mexico Deepwater, Shallow, Massive Salt SectionsDocument9 pagesSPE Estimating Fracture Gradient in Gulf of Mexico Deepwater, Shallow, Massive Salt SectionsTHiago LOpesNo ratings yet
- Quantification of Clay Mineral and Log Response Toward Reservoir Rock PropertiesDocument7 pagesQuantification of Clay Mineral and Log Response Toward Reservoir Rock PropertiesIhsan RaisNo ratings yet
- ClassificationDocument13 pagesClassificationalfred polejjoNo ratings yet
- Geology Report FormatDocument35 pagesGeology Report FormatalirezayusufyarNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science - Week2Document7 pagesEarth and Life Science - Week2Krisna Cortes Fernandez100% (1)
- Well Site Geology GTODocument43 pagesWell Site Geology GTOshubham panchalNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Quarter 1 - Week 2Document10 pagesEarth Science Quarter 1 - Week 2Leanne Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Report Sequence 222222Document32 pagesReport Sequence 222222Muhammad AwaisNo ratings yet
- EeewDocument5 pagesEeewSakoNo ratings yet
- Properties of A Mineral Lab. ReportDocument7 pagesProperties of A Mineral Lab. ReportSakoNo ratings yet
- Features and SP-WPS OfficeDocument1 pageFeatures and SP-WPS OfficeSakoNo ratings yet
- Research Scope MapDocument1 pageResearch Scope MapSakoNo ratings yet
- Souces ImfaDocument1 pageSouces ImfaSakoNo ratings yet
- Learning Act 3 Philosophy Module Region 5 - L.D GarciaDocument3 pagesLearning Act 3 Philosophy Module Region 5 - L.D GarciaSako100% (1)
- Z TableDocument1 pageZ TableSakoNo ratings yet
- If Proven effec-WPS OfficeDocument1 pageIf Proven effec-WPS OfficeSakoNo ratings yet
- New Stanford STDocument1 pageNew Stanford STSakoNo ratings yet
- Imfa Info LiquidsDocument33 pagesImfa Info LiquidsSakoNo ratings yet
- Commencement 20Document4 pagesCommencement 20SakoNo ratings yet
- Souces ImfaDocument1 pageSouces ImfaSakoNo ratings yet
- Natural Disaste-WPS OfficeDocument1 pageNatural Disaste-WPS OfficeSakoNo ratings yet
- If Proven effec-WPS OfficeDocument1 pageIf Proven effec-WPS OfficeSakoNo ratings yet
- Https WWW - UniDocument1 pageHttps WWW - UniSakoNo ratings yet
- 2013 World Risk ReportDocument73 pages2013 World Risk Reportveil clarizeNo ratings yet
- En-Biofuels From Coconuts-Krishna RaghavanDocument111 pagesEn-Biofuels From Coconuts-Krishna RaghavanSakoNo ratings yet
- Commencement 20Document4 pagesCommencement 20SakoNo ratings yet
- Welcome AddressDocument3 pagesWelcome AddressSakoNo ratings yet
- Live TVDocument17 pagesLive TVSakoNo ratings yet
- WorkplaceDocument2 pagesWorkplaceSakoNo ratings yet
- New Stanford STDocument1 pageNew Stanford STSakoNo ratings yet
- Disadvantages of EuthanasiaDocument4 pagesDisadvantages of EuthanasiaSakoNo ratings yet
- The Question ofDocument2 pagesThe Question ofSakoNo ratings yet
- Disaster DefinitionsDocument13 pagesDisaster DefinitionsSakoNo ratings yet
- Natural Disaste-WPS OfficeDocument1 pageNatural Disaste-WPS OfficeSakoNo ratings yet
- DebateDocument3 pagesDebateSakoNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0147651321012720 MainDocument17 pages1 s2.0 S0147651321012720 Mainardiani putriNo ratings yet
- 1H18B0 - Water Accessories Booklet Rev. 2A PDFDocument258 pages1H18B0 - Water Accessories Booklet Rev. 2A PDFcnl filesNo ratings yet
- User Manual - Hybaid - Omn E - UK Omn-E Thermal CyclerDocument48 pagesUser Manual - Hybaid - Omn E - UK Omn-E Thermal Cyclerluroguita0% (1)
- Lesson 3. The Mole Concept and The Molar Mass of ElementsDocument4 pagesLesson 3. The Mole Concept and The Molar Mass of ElementsJamelle SilvestreNo ratings yet
- HydraulicsDocument45 pagesHydraulicsredz00No ratings yet
- Acid StrengthDocument9 pagesAcid StrengthJesus Ponce GNo ratings yet
- BernsteinMedical Post-Op Instructions FUTDocument6 pagesBernsteinMedical Post-Op Instructions FUTOmer JunaidNo ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument6 pagesResearch PaperShivaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter IVDocument25 pagesChapter IVAlan P. MangalimanNo ratings yet
- Kimia Organik: Prof. Setiyo Gunawan, ST., Ph.D. Chemical Engineering Department Fti-ItsDocument7 pagesKimia Organik: Prof. Setiyo Gunawan, ST., Ph.D. Chemical Engineering Department Fti-ItsMohammad Farhan SNo ratings yet
- 303 - Gastrointestinal Physiology) Gastric Secretion - The Cephalic - Gastric PhaseDocument5 pages303 - Gastrointestinal Physiology) Gastric Secretion - The Cephalic - Gastric Phasekedas70No ratings yet
- TDS - 3765 - Texotile Spray-On - Euk - GB PDFDocument3 pagesTDS - 3765 - Texotile Spray-On - Euk - GB PDFSomanith KoumNo ratings yet
- ALERT - MCC CENTRALINA - BO0349675320 - SIDOC PLANTA 2 ACERIAS - VALVULA DESLIZANTE 3 - 1 - en - EsDocument2 pagesALERT - MCC CENTRALINA - BO0349675320 - SIDOC PLANTA 2 ACERIAS - VALVULA DESLIZANTE 3 - 1 - en - EsLuis CortesNo ratings yet
- StiochemistryDocument12 pagesStiochemistryutkarsh vaidNo ratings yet
- Vanders Human Physiology The Mechanisms of Body Function 14th Edition Widmaier Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesVanders Human Physiology The Mechanisms of Body Function 14th Edition Widmaier Solutions Manualconsignedurylic75hi100% (24)
- Crystals 10 00909 PDFDocument12 pagesCrystals 10 00909 PDFDimas Agung SetiajiNo ratings yet
- Biofertilizers Lecture No 10Document39 pagesBiofertilizers Lecture No 10jyothi katukuri100% (1)
- Report Final Kiran Sir InternDocument25 pagesReport Final Kiran Sir InternSandeep ReddyNo ratings yet
- Pedot:pss/go Nanocomposite For Indoor Co2 SensorDocument9 pagesPedot:pss/go Nanocomposite For Indoor Co2 SensorIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument4 pagesPeriodic TableFariz Arif KhanNo ratings yet
- HZL Chanderiya Pyro Training ReportDocument48 pagesHZL Chanderiya Pyro Training Reportkunalmech100% (5)
- AFW NewDocument4 pagesAFW NewJoão BaffiniNo ratings yet
- Emery Oleo ChemicalsDocument4 pagesEmery Oleo ChemicalseveslpNo ratings yet
- R&T 2004 - Underfloor Heating Design Considerations - DettmersDocument13 pagesR&T 2004 - Underfloor Heating Design Considerations - DettmersScott VitkoNo ratings yet
- Pipeclad Product Brochure Sherwin Williams EnglishDocument12 pagesPipeclad Product Brochure Sherwin Williams EnglishCésarNo ratings yet
- Applications of Kohlrausch LawDocument6 pagesApplications of Kohlrausch LawNadherdaman Alshamary100% (4)